A high pulse with high blood pressure is observed quite often, but the relationship between both indicators in hypertension is not natural. A simultaneous increase in indicators occurs with excessive load on the myocardium, which may indicate the development of complications from the cardiac and vascular systems. The combination of both disorders provokes the occurrence of stroke and heart attack - dangerous pathologies that cause death. To prevent the progression of the disorder and reduce the risk of negative consequences, it is necessary to consult a specialist in a timely manner. What are the causes of rapid heartbeat with elevated blood pressure and how to stabilize the indicators?
The relationship between high heart rate and hypertension
High pulse with high blood pressure is a fairly common phenomenon that often occurs simultaneously. Constantly elevated levels of blood pressure contribute to pumping a large volume of circulating blood, as a result of which the heart muscle is subjected to excessive stress. As a result, myocardial contractile activity increases, provoking the formation of tachycardia. An increased number of heart contractions is characterized by a strong and intense pulse wave with an indicator higher than 90 beats per minute, which indicates a possible disorder if the patient is at rest.
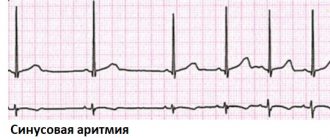
Why is heart rhythm disorder most often recorded in hypertension? Arterial hypertension reflexively provokes the development of tachycardia. Thus, in most hypertensive patients, the first sign of the negative impact of increased blood pressure on the body is a heart rhythm disorder. With hypertension, paroxysmal tachycardia is most often recorded, manifested by a sharp attack of rapid heartbeat up to 120 beats/min, while the rhythm is maintained, since electrical impulses come from one area. Frequent attacks of this form of tachycardia lead to the formation of acute vascular and heart failure. An unfavorable course of hypertension can cause the formation of arrhythmia, which is provoked by a hypertensive attack of the cardiac form, when an increase in blood pressure is combined with acute cardiac left ventricular failure.
Important! The appearance of a rapid pulse in hypertension is a poor diagnostic sign, indicating the transition of the disease to the third stage, when irreversible changes form in the organs.
Clinical case
I would like to present an interesting incident that happened quite recently. A 36-year-old man approached me. For several months he was bothered by general weakness, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, pale skin, and slight shortness of breath. I took a clinical blood test on my own in a private laboratory. The results showed a decrease in the level of hemoglobin, red blood cells, and a high content of reticulocytes. On the advice of relatives, I began taking iron supplements. No particular therapeutic effect was observed, which forced me to consult a doctor. Of the concomitant diseases, the patient noted only osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Denies the presence of hemorrhoidal disease and gastrointestinal pathologies. During the examination, an increase in heart rate to 115 per minute and a decrease in blood pressure to 100/60 mm Hg were revealed. When palpating the upper abdomen, I was able to detect pain.
I issued a referral for fibrogastroduodenoscopy. During the study, a weakly bleeding ulcer was discovered on the lesser curvature of the stomach, 0.5 cm in diameter. The bleeding was stopped by laser coagulation (cauterization). A urease breath test was performed to diagnose Helicobacter pylori infection. The result is positive. A diet (1st table according to Pevzner) and drug therapy were prescribed: drugs that suppress the production of hydrochloric acid (Omeprazole), antacids (Almagel), antibiotics (Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin). It is also recommended to continue taking iron supplements. After some time, the patient noted a significant improvement in his condition: dizziness and weakness disappeared, and the skin acquired a healthy shade. A repeat blood test showed normalization of hemoglobin and red blood cell levels.
Rapid pulse and hypotension
Short-term tachycardia and low blood pressure may be physiological. The most striking example is dizziness, darkening of the eyes, mild nausea when suddenly getting up from the sofa or bed after lying for a long time. Perhaps almost every person has encountered this phenomenon. It is called "orthostatic tachycardia, or hypotension." However, you should not be afraid of this, since it is absolutely normal and physiologically justified.
A short-term decrease in blood pressure and increased heart rate are caused by the redistribution of blood flow under gravity to the lower parts of the body at the moment of transition from a horizontal to a vertical position.
The most dangerous conditions in which hypotension and rapid pulse are observed are the so-called paroxysmal arrhythmias. These include supraventricular, ventricular tachyarrhythmias, atrial fibrillation and flutter. Without emergency help, these heart rhythm disturbances can end very badly. Therefore, a person with a rapid pulse, regardless of blood pressure, must have an electrocardiogram.
Other pathological causes of tachycardia at low pressure:
- anemia (anemia);
- bleeding. Chronic blood loss can occur in the presence of hemorrhoids, gastric or duodenal ulcers;
- dehydration, for example, in patients with diabetes, or with prolonged diarrhea;
- hormone deficiency - Addison's disease (adrenal insufficiency), hypothyroidism (low thyroid function);
- neurocirculatory (vegetative-vascular) dystonia;
- overdose of drugs for the treatment of hypertension, prostate adenoma or impotence (“Viagra”).
I am often asked about how to treat tachycardia with low blood pressure. I always emphasize that you first need to find out the cause of hypotension.
Tachycardia at normal pressure
It may also be that the blood pressure is normal and the pulse is high. This usually occurs due to increased cellular oxygen demand, a short-term release of hormones into the blood that stimulate heart contraction, or exposure to various toxins. The reasons may be as follows:
- exercise stress;
- emotional stress or neurotic disorder;
- any infectious diseases accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- smoking;
- excessive consumption of coffee and energy drinks;
- heart defects (tachycardia is especially often observed with mitral valve prolapse);
- pregnancy - due to hormonal changes in the third trimester, an increase in heart rate may be observed with normal blood pressure readings.
Hypertension and heart palpitations
Tachycardia and high blood pressure are most common in people who have hypertension in combination with other cardiac pathologies (chronic heart failure, cardiomyopathies, myocarditis).
In my practice, I often see patients in whom an increase in heart rate and blood pressure may be a sign of various endocrinopathies, such as:
- diffuse toxic goiter (hyperfunction of the thyroid gland) - the patient becomes irritable, he loses weight, his temperature rises slightly, he is bothered by excessive sweating (perspiration, hyperhidrosis);
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease/syndrome (a formation in the adrenal glands or in the brain that produces a large amount of glucocorticoids) - obesity occurs, purple or purple stretch marks appear on the skin of the abdomen, thighs, the concentration of glucose in the blood increases, bone strength decreases;
- pheochromocytoma (a tumor of the adrenal glands that excessively produces adrenaline and norepinephrine) - there are paroxysmal significant increases in blood pressure and heart rate, often leading to stroke and heart attack.
It also happens that hypertension and tachycardia are the result of an overdose of medications - antidepressants, psychostimulants, adrenomimetics (vasoconstrictor nasal drops).
Physiological causes of the disorder
Against the background of hypertension, high pulse pressure of a physiological nature can be observed, which affects patients with an unstable nervous system. As a rule, the disorder is short-lived, about 20–25 minutes. Heart rate reaches 100/140 beats/min, after which it stabilizes.
A physiological number of factors that provoke an attack of tachycardia:
- increase in body temperature;
- overdose or individual intolerance to medications;
- long stay in a stuffy room;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages, nicotine;
- excessive mental stress;
- eating large amounts of fatty foods;
- excessive consumption of caffeinated drinks.
Stress causes a sharp increase in the concentration of catecholamines, an increase in heart rate and pressure, the stabilization of which occurs over a long period of time.
Physical activity can also increase the number of heart contractions, but the level of blood pressure should remain within the original limits.
No ads 1
Why can heart rate change at rest?
The main factors influencing changes in heart rate:
- when the temperature and/or humidity increases, the heart rate increases by 5 – 10 beats per minute;
- when moving from a lying position to a vertical one, heart rate increases in the first 15–20 seconds, then returns to its original value;
- heartbeat increases with tension, anxiety, expressed emotions;
- in people with large weight, the heart rate is usually higher than in people of the same age and gender, but with normal body weight;
- with fever, an increase in temperature of 1 degree is accompanied by an increase in heart rate by 10 beats per minute; There are exceptions to this rule, when the heart rate does not increase so much - these are typhoid fever, sepsis and some variants of viral hepatitis.
Reasons for the slowdown
First of all, you need to make sure that the pulse measurement is carried out technically correctly. A heart rate less than 60 per minute is not always associated with health problems. It can be caused by medications such as beta blockers.
Rare heartbeat (up to 40 per minute) is often observed in physically active people or professional athletes. This is due to the fact that their heart muscle contracts very well and is able to maintain normal blood flow without additional effort. Below we provide tables that allow you to roughly determine a person’s physical fitness by his resting heart rate.
Reasons for the increase
The most common cause of accelerated heart rate is inadequate rest before measurement. It is best to measure this indicator in the morning after waking up, without getting out of bed. You should also make sure that your heart rate is counted correctly.
Children and adolescents have a higher heart rate than adults. Other factors that increase heart rate:
- use of caffeine or other stimulants;
- recent smoking or drinking alcohol;
- stress;
- high blood pressure.
Pathological causes of the disorder
The development of the pathological form of the disease is associated with functional changes in the functioning of the heart, kidneys, thyroid gland or the presence of infectious agents in the body. The attacks are longer and are not caused by physiological factors.
The group of main pathologies that cause increased heart rate and increased blood pressure includes:
Can there be a fever with high blood pressure?
- Hypertensive crisis of the first type (sympatho-adrenal crisis). When the regulation of the autonomic system is disrupted, the body's normal reaction to stimuli is disrupted, which is associated with diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Arterial hypertension of various etiologies. It is observed in cases of hormone imbalance, renal failure, and vascular regulation disorders.
- Hyperthyroidism. An increase in sympathetic activity occurs when the metabolism of thyroid hormones is disrupted. The pathology is characterized by sinus tachycardia, provided that foci of ectopic activity remain in the myocardium.
- Hypercorticism. The pathological condition is caused by hormonal imbalance due to excessive activity of adrenal hormones. The disease is characterized by a mechanism of increased automatism of the sinus node.
- Diseases of neurogenic and psychogenic nature. Minor positive or negative emotions provoke tension in the nervous system. Cardiovascular neurosis causes increased heart rate as a result of dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system with increased sympathetic nerve activity.
In cases where an increased pulse is diagnosed with increased pressure, the risk of developing vascular complications increases, which can cause rupture of blood vessels in the brain or heart. This pattern affects people aged 45 to 55 years, so the higher the pulse and blood pressure, the higher the risk of negative consequences.
Concomitant pathologies
In addition to age, a systematic increase in pressure is provoked by metabolic disorders, kidney disease, bad habits, etc. Smoking provokes a narrowing of small blood vessels, which in the long term causes a decrease in the lumen of large arteries and, as a result, hypertension. When kidney function is impaired, the hormone aldosterone is produced, which also leads to an increase in blood pressure. There is a risk of hypertension in diabetics, whose blood vessels are especially prone to deposits on the inner walls. Timely detection and prevention of major diseases will allow you to maintain normal blood pressure and live an active life.
By what signs can a deviation be identified?
Every hypertensive person has the concept of “working” pressure, which means pressure indicators at which the general condition is within normal limits. This indicator is individual for each person, since it can be either normal or elevated (135/100). However, a slight excess of the norm can cause a number of uncomfortable sensations. A short-term and slight acceleration of the heart rate does not provoke pronounced symptoms, but is accompanied only by the occurrence of tinnitus and uncomfortable feelings.
A prolonged attack of high blood pressure and high pulse is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Throbbing headache localized in the temporal and occipital region.
- Dizziness with concomitant loss of coordination of movements.
- Visual impairment (darkening, flickering “flies” before the eyes).
- Cardiac dysfunction (irregular rhythm, feeling of rapid heartbeat).
- Increasing shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air.
- Unreasonable muscle weakness, a feeling of trembling throughout the body.
- Nausea followed by vomiting.
The severity of symptoms depends on the state and sensitivity threshold of the autonomic nervous system, as well as on the stage of hypertension. Thus, an increase in cardiac activity can lead to the development of heart failure and angina.
Cardiac bradycardia - what is it?
Unlike tachycardia, bradycardia is characterized by low pulse rates compared to normal. The genesis is due to functional and pathological disorders. Functional genesis is due to the manifestation of a decrease in pulsation during night sleep and during professional sports.
For professional athletes, it can be reduced to 35 beats/min. In some cases, after taking certain medications, a medicinal form of bradycardia develops.
With pathological genesis, the disease manifests itself due to:
- pathologies of blood vessels and heart;
- age-related pathologies;
- inflammatory processes in the muscle tissue of the heart.
With such bradycardia, disturbances are associated with pathological processes associated with sinus block - failure of the conduction of an electrical impulse between the sinus node and the atrium. In this case, tissue hypoxia develops due to poor blood supply.
Among the pathologies that provoke bradycardia are:
- hypothyroidism and hypothyroid coma (myxedema);
- ulcerative defects in the stomach;
- intracranial hypertension.
In most cases, with a significant decrease in heart rate (less than 40 beats), bradycardia can cause the development of heart failure syndrome. Associated symptoms include weakness, dizziness, fainting, cold sweat and unstable blood pressure.
It should be remembered that with age our body does not get younger, but becomes significantly weaker. Many patients who have crossed the forty-five-year mark are diagnosed with serious changes in the body.
A person's normal blood pressure differs by age. Hypertension or hypotension leads to deterioration of health and complications. A frequent cause of significant changes in the results obtained from the norm are diseases of the internal systems of the body. Changes in the minimum and maximum permissible pressure limits depend on many unfavorable factors.
Possible consequences and complications
Dissonance between pulse and blood pressure is dangerous for the functional state of the body, since with a rapid heartbeat, hypoxia of tissues and organs occurs, which entails the development of irreversible changes in them.
With a simultaneous increase in diagnostic indicators, the following very dangerous conditions may occur:
- disorder of the digestive tract;
- ischemic brain damage;
- necrosis of the cardiomyocyte area;
- arrhythmic shock.
A prolonged and constant increase in heart rate can significantly reduce the performance of a hypertensive patient. The patient experiences a feeling of irritability and complains of causeless weakness and malaise.
Under conditions of excessive load, the myocardium requires more oxygen, which leads to its increased waste. In vessels of small diameter, a deficiency of nutrients occurs, provoking the formation of cardiomyopathy.
Results
As a rule, the human body undergoes changes with age. Even normal blood pressure after 60 years of age is higher than at a younger age.
However, it must be remembered that a person accumulates most diseases throughout his life.
Neglect of health in youth can have a detrimental effect on the condition of the body after a certain number of years.
A healthy lifestyle without stress and anxiety, with moderate physical activity and spending time in the fresh air, should be the main habit in order to visit hospitals as little as possible after 60 years of age, and enjoy life as often as possible.
Providing self-help
What to do if there is a sharp increase in heart rate against the background of high blood pressure? In this situation, you should contact a specialist to clarify the diagnosis and identify the root cause of the disorder. However, functional etiological factors can also cause tachycardia, for which first aid can be provided independently.
First you need to determine the source causing the violation. The patient is recommended to rest, have a good night's sleep, and also have a fasting day that excludes fatty, spicy, and sweet foods. To prevent worsening of the pathology, caffeine drinks, smoking and alcohol should be avoided.
Algorithm for providing assistance:
- Remove constrictive clothing and provide fresh air.
- Take a horizontal position or half-sitting with support under your spine.
- Take sedatives (Persen, Validol, Fitosed, motherwort tincture).
- To lower your blood pressure, take the prescribed antihypertensive pills (Captopril, Captopress, Enap).
- Use a breathing technique with deep inhalation and slow exhalation.
- Massage the area of your eyeballs and temples if you have a headache.
Important! Monitor indicators every 30 minutes. If the use of therapeutic measures does not have the desired effect, then a medical team should be called.
How to normalize indicators
You can normalize your child’s blood pressure and heart rate by following the following recommendations:
- give the body regular physical activity;
- stabilize sleep and strictly adhere to the daily routine;
- adjust your diet by enriching the menu with light and at the same time high-calorie foods, vegetables and fruits;
- take daily walks in the fresh air;
- protect the child from stress or reduce its impact on the psycho-emotional background (the help of a psychotherapist may be needed);
- reduce mental load - for example, it is better for schoolchildren to refuse extracurricular activities.
Swimming and a massage course, which is carried out 2 times a year, help bring blood pressure and heart rate back to normal.
Drugs
Drug therapy is prescribed to children only by a doctor and after identifying the true cause of problems with pulse and blood pressure, since the underlying disease needs to be treated. But as symptomatic therapy they use:
- Seduxen, Valerian and other drugs with a sedative effect;
- Inderal, Obzidan - a group of adrenergic blockers that are used for hypertension.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy often helps solve the problem of rapid pulse and uneven blood pressure, so parents should do morning exercises with the child, give him mint tea (no more than 150 ml per day), carry out hardening procedures, and actively play with him in the fresh air.
The pulse rate and blood pressure level in a child must be regularly monitored, because their increase/increase or, conversely, decrease/decrease can be the primary signs of the development of serious pathologies of cardiovascular diseases and kidney pathologies. To understand the true clinical picture, measurements are taken every morning for 7 days, and the results are given to the doctor for analysis.
Dangerous symptoms requiring immediate medical attention
Unfortunately, the symptoms are not always obvious. Some people, especially those who are accustomed to their condition, do not feel their heartbeat. Such conditions are detected only on a cardiogram.
The warning signs are:
- Palpitations. Feeling like your heart is going to jump out of your chest. Often the process is accompanied by visual impairment, including transient blindness, darkening, and the formation of scotomas (areas of loss of visual fields).
- Headache of a stabbing nature.
- Dizziness.
- Chest pressure, pain. They are given to the arms, back, epigastric region (where the stomach is located).
- Heaviness in the legs, weakness, drowsiness, disturbances in general condition.
- Fainting and syncope. Loss of consciousness. Repeated processes of this kind are especially dangerous.
- Shortness of breath, inability to breathe normally. Feeling of lack of air.
- Numbness of the limbs and fingers.
If there is at least one manifestation, you should urgently seek medical help. It is not known what process we are talking about. Need diagnostics.
Treatment
A difficult and complex task. Sometimes pills alone are not enough. Therapy is aimed at restoring heart function and eliminating the root cause of the condition.
Among the methods:
- Administration of special medications. Calcium channel blockers and beta blockers. They should be taken systematically at high heart rates. There are emergency medications, but they cannot be used without the knowledge of a doctor.
- Surgical techniques: endovascular ablation, installation of a pacemaker (pacemaker), etc. All surgical techniques are carried out as planned, excluding emergency cases. You need to discuss the pros and cons with your doctor and clarify any unclear points.
All methods are determined by the doctor based on their initial parameters and the data obtained.
It is important to change your lifestyle: minimal physical activity, only therapeutic exercises, lack of stress, normalization of the diet, vitamin supplementation, quitting smoking cigarettes and electronic devices, drinking alcohol (full), normalizing the drinking regime (up to 2 liters a day or a little less).
Therapeutic measures are varied and will require efforts not only on the part of the specialist, but also on the part of the patient himself.