Co-author, editor and medical expert - Dmitry Dmitrievich Volosov.
Number of views: 150 240
Last updated date: 08/26/2021
Average reading time: 3 minutes
Headache with blood pressure disorders Treatment of headaches with blood pressure disorders Motrin® in the treatment of headaches
Headache with high blood pressure is one of the most common symptoms. It indicates a number of health problems that require seeing a doctor and receiving appropriate treatment. Depending on what exactly causes the headache, its characteristics may vary.
Headache and hypertension
Why, if the pressure is relieved, does my head continue to hurt? First, you need to understand the following thing: it matters how exactly the pressure was reduced. Let's take a closer look at what happens in various cases.
If you have lowered your blood pressure with medication, the mechanism may be as follows. With high blood pressure, intracranial pressure rises accordingly. The heart works hard, and first of all it is necessary to “calm it down.” Tablets that lower blood pressure affect the heart rate, making it more regular, therefore, the pressure drops, blood does not flow as much to the brain, and the headache should disappear.
You can get more information about this and many other aspects of health related to blood pressure, osteochondrosis, atherosclerosis, ask your questions to Dr. Shishonin and just chat by joining our community - the Club of
Former Hypertensive Patients
.
Symptoms of intracranial pressure in adults
In many cases, a slight increase in ICP may not manifest itself for a long time. If the pressure rises sharply or high enough, the following symptoms may occur:
- headache - it can be pressing or bursting, usually occurs in the morning, this pain has no clear localization, it can be felt in different parts of the skull;
- nausea and vomiting - they usually occur at the peak of the headache;
- drowsiness, malaise, general poor health;
- memory impairment (forgetfulness), attention disorders, problems with thinking;
- changes in the autonomic nervous system – surges in blood pressure, slow pulse, increased sweating;
- visual impairment up to complete blindness.
Symptoms may come on suddenly or develop gradually over weeks or months.
Why does my head hurt?
If the venous outflow is disrupted, that is, the veins are pinched, you take pills, the heart stops pumping blood in large quantities, but it cannot descend back from the brain in full, which means the headache does not disappear. In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor and check the condition of the blood vessels, since excessive accumulation of blood in the brain is very dangerous.
Important:
If the venous outflow is impaired, the pressure in the body system drops, but the intracranial pressure remains high, which provokes a headache.
This is the main reason why, when taking medications, the headache may not go away, but remain the same, and it does not matter how sharply the pressure drops. In this case, do not panic and take other pills that have pain-relieving properties. After some time, the pain will go away, and neck exercises will help speed up this process. They normalize blood flow and help veins cope better with their function.
Causes of intracranial pressure in adults
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is not an independent disease, but a syndrome.
Doctors sometimes call it intracranial hypertension. Pressure inside the brain (similar to arterial pressure) fluctuates when the head is tilted back and forth or to the sides, during physical activity or sneezing. But it can increase to serious numbers in case of pathologies, and there are many of them. “ICP (intracranial pressure) occurs as a result of an increase in the volume of intracranial contents (cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid), tissue fluid, or the appearance of foreign tissue (tumors, cysts, brain abscess), says neurologist Polina Petrosyan.
In addition, the causes of increased ICP may be:
- traumatic brain injury;
- tumor;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- neuroinfections (encephalitis, meningitis).
“The cause may also be long-term use of drugs from the group of hormonal contraceptives, corticosteroids or antibiotics,” adds Dr. Polina Petrosyan.
Pressure increases because fluid is either produced in excess (for example, due to an infection that has spread to the brain or its membranes), or because fluid flows out of the skull through special pathways less easily. If volumetric processes develop in the cranial cavity (for example, a tumor grows or hemorrhage occurs), there will be less space for fluid, and its pressure will also increase.
What to do?
At Dr. Shishonin’s clinic, specialists very often encounter cases where the patient complains of a headache that does not disappear after the pressure is reduced. Then an ultrasound examination is required to find out the condition of the vessels of the skull.
The doctor says:
Dr. Shishonin draws the attention of patients to the fact that almost every second case of headache with which they come to him is associated with a violation of the venous outflow.
If you relieve pressure through correction, that is, without medications, normalizing venous outflow and arterial inflow naturally, as happens in Dr. Shishonin’s clinic, then this problem does not arise. With a natural decrease in pressure, when blood circulates freely, the head will not hurt, which means the blood vessels will be in order.
Advice:
Gymnastics for the neck, which Alexander Yuryevich recommends to all his patients, will help reduce blood pressure naturally and normalize the outflow and inflow of blood without the use of drugs that poison the liver.
This problem can only happen if you reduce your blood pressure with medication. The pills affect the heart, causing it to work less forcefully, and intracranial pressure remains at the same level. As a result, the tonometer will show that your blood pressure is normal, but your head will hurt. What to do in this case? This situation means that the neck and its vessels are affected, and the neck needs to be treated. Check out other videos on the “Club of Former Hypertensive Patients” channel and find out how you can use gymnastics to get rid of vascular problems, improve the health of the cervical spine and get rid of pain forever. Be healthy!
Diagnostics
It is extremely difficult to suspect an increase in ICP based on external signs.
The doctor must know all the complaints and those facts from life that preceded the symptoms. This could be a hypertensive crisis, head injury, severe infection, kidney or liver problems. In order to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a number of studies to the patient: CT or MRI of the brain to evaluate the structure of all tissues of the skull, note the condition of the ventricles of the brain where cerebrospinal fluid accumulates;
- echoencephaloscopy to determine brain function;
- Ultrasound of the brain (mainly in children through the fontanelle);
- examination of the condition of the fundus by an ophthalmologist;
- spinal cord puncture with measurement of the pressure of the escaping cerebrospinal fluid (the cerebrospinal fluid itself is taken for analysis).
What to do with fluctuating pressure?
It often happens, especially in older people, that the pressure is either high or low. As soon as you take a pill for the high, it goes down, and you feel completely out of control again. What to do in such cases?
First, you need to remember that low blood pressure is not as dangerous as high blood pressure. With high blood pressure, a complication can be a stroke, and low blood pressure, as a rule, does not threaten anything other than poor health. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce high blood pressure, even if there is a danger of lowering it too much.
Secondly, you should not try too hard to increase low blood pressure, otherwise this may lead to a crisis. The simple home measures listed above are sufficient. If your head hurts very badly, the same Paracetamol will help, which does not affect blood pressure, but perfectly relieves unpleasant symptoms.
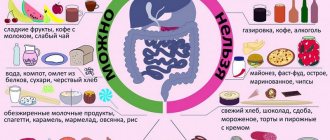
To keep your blood pressure stable, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle regardless of age, walk as much as possible and be in the fresh air. As the latest research shows, the best way to prevent blood pressure disorders is moderate physical activity.
And if walking or exercise causes discomfort, treatment by an osteopath can help. Often the reasons why a person is unable to move can be treated with osteopathic methods. Instead of sitting in your apartment drinking handfuls of pills, you can use osteopathy to put your body in order and begin active prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Symptom treatment
If you have a headache in the temples, back of the head, crown or forehead, the cause should be treated first, otherwise the discomfort will recur regularly. Therefore, if you do not need to call an ambulance, you need to visit the Pain Treatment Center at JSC Medicine (clinic of Academician Roitberg).
JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) employs the best specialists of the capital and region. The center has a convenient location: it is located in the center of Moscow, near the Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Chekhovskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya metro stations.
However, its main advantage over other clinics is the wide range of medical services provided at a high level for the diagnosis and treatment of headaches.
To understand what to do if you have a headache, you need to identify the cause. JSC "Medicine" (academician Roitberg's clinic) has the most modern equipment that allows for the most accurate diagnosis. These include methods such as:
- MRI;
- CT;
- PET/CT;
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- ECG;
- dopplerography;
- bone densitometry;
- echocephalography;
- 24-hour blood pressure test;
- multislice computed tomography.
There is also a large-scale clinical diagnostic laboratory, which allows performing analyzes as quickly as possible and with high accuracy.
Depending on the cause of the symptom, the therapist can begin treatment on his own or refer the patient to a more specialized specialist. In most cases, the following methods are used:
- drug therapy;
- psychotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapeutic methods.
In more serious situations, surgery may be used after a thorough examination.
Hypotension of training
Another form of hypotension that occurs in athletes and simply trained people is training hypotension. But reduced vascular tone does not play a role here, it’s just that the body of such people is constantly under increased stress and therefore is accustomed to working in an “economical” mode.
The main complaints with hypotension are decreased performance, irritability, bad mood, memory may deteriorate, the person becomes distracted, and finds it difficult to concentrate. Emotional instability, increased sensitivity to bright light or loud speech predominates. Headaches and dizziness are common manifestations.
Headache is often associated with fluctuations in atmospheric pressure, large meals, and prolonged standing. The pain is usually localized in the occipital region or frontal region, feels like heaviness, and as the pain increases, the patient feels as if there is “pressure from the inside” on the skull. Sometimes you may experience a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, bitterness in the mouth, loss of appetite, nausea, belching, heartburn, flatulence, constipation - that is, almost all gastrointestinal disorders. In addition, hypotensive men may have reduced sexual potency, and women often experience menstrual irregularities. However, menstruation is often painful.
Hypotonic people often feel tired even after just waking up. They have difficulty waking up in the morning, even after a long sleep, feeling sleepy. Activity and performance return to normal only after 2-3 hours, weakening again during the day. The peak activity of hypotensive patients usually occurs in the late afternoon. With increased physical activity, people with hypotension may experience an increase in pulse and heart rate, and sometimes there are unpleasant sensations in the heart area and shortness of breath, which sometimes make a person suspect that they have angina pectoris or other serious illnesses.
Many hypotensive people constantly yawn, but not because they are tired, but because they “don’t have enough air,” which sometimes causes fainting or darkening of vision when suddenly moving from a horizontal to a vertical position. Sensitivity to weather changes is also a hallmark of people with low blood pressure. Most often, they do not tolerate heat very well, and even worse is the autumn or spring off-season with cloudy weather and low atmospheric pressure. Such people feel best on sunny and frosty winter days with high atmospheric pressure or on warm sunny days in late spring or early autumn. In addition, hypotensive patients are sensitive to weather changes and changes in climatic conditions.