Why does coughing cause pain in the heart area?
Causes of heart pain when coughing:
- Coronary heart disease - the characteristic pain of an attack of coronary artery disease, called angina, occurs when blood flow to part of the heart muscle stops. The lumen of the coronary vessel is blocked by an atherosclerotic plaque or spasm, the myocardium does not receive enough oxygen and glucose, resulting in ischemia - the cause of pain.
This phenomenon is reversible and goes away on its own or after rest and taking Nitroglycerin, but is sometimes complicated by a heart attack;
- myocardial infarction - cough becomes a trigger factor for the disease, especially in patients suffering from unstable angina, aggravated by atherosclerosis. During an attack, intense pain occurs that radiates to the left arm, shoulder blade, neck, and lower jaw. This condition requires emergency medical attention and restoration of blood flow, thrombolysis or revascularization;
- myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle, which is caused by both infectious agents and one’s own immune cells during an autoimmune process. In addition to chest pain when coughing, myocarditis is sometimes accompanied by cardiac arrhythmias, fever, weakness and shortness of breath;
- pericarditis - any sudden movement of air through the respiratory tract is accompanied by a feeling of acute aching pain in the front of the chest. Normally, there is a small amount of fluid between the epicardium and pericardium, which allows the organ to glide during contraction. Inflammation makes the inner surface of the heart sac dry and rough, and this causes pain in the patient. The condition forces a person to assume specific positions in which the pressure in the chest cavity is minimal in order to obtain relief;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a genetic disease in which the heart muscle abnormally increases in size. Characteristic symptoms are weakness, attacks of tachycardia and frequent fainting. The cough in such patients causes discomfort due to its persistence and dryness. The cause is pulmonary hypertension syndrome (increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation, in particular in the pulmonary arteries). Such a patient exhibits signs of congestion in the lower parts of the lungs;
- Mitral valve prolapse is a malfunction of the valve between the left ventricle and the left atrium, in which one of the leaflets does not close during systole. As a result, part of the oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium. In people with this anomaly, physical activity, including coughing, causes pain in the heart area, palpitations, dizziness and fainting;
- dissecting aortic aneurysm - a life-threatening condition that occurs when there is a defect in the vascular wall, which results in the formation of a “bruise” inside. The aorta is the largest vessel in the human body with the highest blood pressure, as a result of which a small tear quickly increases in size, leading to massive blood loss and death.
Risk factors are high uncontrolled arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis. Other causes include chest injuries, genetic diseases, and involvement of the esophagus in the cancer process.
- heart failure - coughing with pain in the heart is a sign of worsening heart failure. Depending on the degree of the disease, it can be either dry or wet with foamy pink sputum. Obvious signs of decompensation are generalized edema and accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
What hurts when you cough?
The pain syndrome caused by coughing attacks can be defined by different levels of intensity and the nature of the pain: sharp or dull, localized or widespread, severe or moderate.
The location where the pain is detected may indicate the affected organ: in the throat, sternum, inside the chest, under the ribs or in the back, stomach, head. Very often, patients describe their sensations as pain in the lungs, but it is worth clarifying that there are no pain nerve endings in the lungs themselves. Cough, accompanied by pain, is a consequence of diseases of a very different nature.
What to do
Pain in the heart area when coughing should attract the attention of both patients with already diagnosed diseases and healthy people.
If your heart suddenly hurts when you cough, take a semi-sitting position and provide access to fresh air. Take a Nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue. If the pain does not improve, repeat the dose after five minutes and call emergency medical help. The faster you respond to the alarm bell given by your body, the higher the chance of a favorable outcome for life and health.
When you notice pain for a while (this is not an acute process), consult a general practitioner. With the help of simple and accessible studies: electrocardiogram, chest x-ray, physical examination (listening to heart and respiratory sounds, percussion of the heart and lungs) many pathologies are diagnosed in the early stages.
If you smoke and notice a cough that is aggravated by chest pain, consult a doctor and try to get rid of the bad habit. To learn how smoking affects your heart function and blood pressure, watch the video at the link below.
Treatment of painful cough
We remind you that in order to prepare competent treatment, you need to contact a general practitioner, who will refer you to a specialist (otolaryngologist, phthisiatrician, cardiologist, neurologist, etc.) for a full examination. Selecting your own medications and abusing painkillers can be dangerous to your health and lead to complications.
- If the pain is of an infectious-inflammatory nature, antibacterial, antiviral therapy, or treatment with other drugs may be prescribed, depending on the causative agent of the infection and the location.
- For the symptomatic treatment of cough, drugs are first prescribed that promote sputum separation and convert a dry cough into a productive one.
- In rare cases, medications may be prescribed to suppress coughing attacks, but this may slow down the healing process.
- If the cause of pain is identified as pleurisy or pericarditis, then a puncture of the pulmonary or cardiac membrane is prescribed to relieve the corresponding organs.
- For GERD, antacids and medications that help reduce the acidity of gastric juice may be prescribed.
- Pinched nerve endings localized in the sternum area can be relieved with painkillers and sedatives.
Cardiac cough: how to recognize pathology
Cough as a symptom accompanies not only colds, but also a number of others. Moreover, in each case it will have its own specifics. A cardiologist explained to us what a cardiac cough is and how it differs from the others.
Nino Revazovna Malania, cardiologist, answered the questions
1st category FSBI “National Medical Research Center named after. acad. E.N. Meshalkin" of the Ministry of Health of Russia, Member of the ESC (European Society of Cardiology) and RKO (Russian Society of Cardiology).
– What is a cardiac cough?
– To begin with, I would like to say what the cough itself is. This is a protective-adaptive reaction that occurs as a result of irritation of receptors that are located in the respiratory tract, and therefore it is traditionally associated with pathologies of the respiratory system.
However, cough is often a serious symptom of a disease of the cardiovascular system, progressive heart failure. The reason is the occurrence of congestion in the lungs, which occurs when the heart is not able to pump blood normally. Most often, the essence lies in the improper functioning of the left ventricle.
Pathological processes occurring in the left ventricle cause a decrease in its contractility, and it cannot effectively pump blood coming from the pulmonary arteries to the aorta. Such changes in the functioning of the heart lead to an increase in pressure in the lungs and a slowdown in blood microcirculation. Slow blood flow causes increased venous pressure and oxygen starvation of tissues. Due to hypoxia, collagen fibers are deposited on the interalveolar septa and walls of small vessels, which cause the development of pneumosclerosis. The small vessels of the lungs gradually become sclerotic and completely obliterated (overgrown with connective tissue). Such pathological processes lead to a decrease in blood flow in the lungs and an even greater increase in pressure in the pulmonary vessels.
Increased pressure in the pulmonary artery leads to increased load on the left ventricle, and it hypertrophies. Then dilatation (expansion of the boundaries) of the right half of the heart occurs, which causes stagnation of the systemic circulation. The liquid part of the blood seeps into the lung tissue and irritates the bronchial receptors.
The patient develops a cardiac cough, which is chronic, appears when trying to take a horizontal position and worsens in the evening or at night.
– What diseases cause cardiac cough?
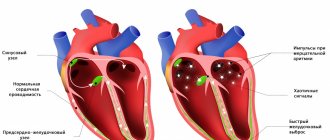
– A cardiac cough may indicate that the patient has heart failure, which is formed as a result of certain diseases, such as: coronary heart disease, heart defects, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, arterial hypertension, arrhythmias, etc.
– How to distinguish a cardiac cough from another, allergic or infectious nature?
– Cardiac cough in heart failure occurs occasionally, under certain conditions, for example, at a height of physical activity (the greater the physical activity, the stronger the cough) or when the patient’s body position changes (the cough intensifies when the patient is lying down and therefore often appears at night).
There are other characteristic symptoms: dry cough (no sputum when coughing); in the initial stages there is shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air, in the future coughing can be provoked even by prolonged communication (during a conversation by the patient); in decompensated patients, the cough forces them to sleep while sitting, as it intensifies when the patient is lying down, orthopnea; cyanosis - manifests itself as blue discoloration in the area of the nasolabial triangle, earlobes, fingertips - drumsticks; presence of heart pain and rapid heartbeat; dizziness, fainting or lightheadedness; When coughing, swelling of the veins in the neck is observed.
A cough of an allergic nature can often be associated with the action of an allergen (during the flowering period of certain plants, after sleeping on a pillow with fluff, or after interacting with a pet). Characteristic accompanying symptoms of an allergic cough: runny nose and sneezing; redness of the eyes and watery eyes; sore and itchy throat and others. The use of anti-allergy drugs to relieve an attack is effective.
An infectious cough is often associated with infectious diseases of the respiratory tract, which are caused by viruses or pathogenic bacteria.
Characteristic symptoms: severe paroxysmal cough (productive); discomfort and pain in the chest, increasing at the height of the respiratory movement of the chest; shortness of breath during physical exertion, and sometimes at rest; weakness, lethargy, apathy, increased fatigue; increased body temperature and others.
If the primary patient, at the height of physical activity, begins to notice the appearance or intensification of shortness of breath and dry cough, or a “night” cough appears, then you need to contact a general practitioner to undergo a complex examination.
If a patient with a cardiac history develops a dry cough mainly at night, exercise tolerance has decreased, as shortness of breath and coughing have increased, coughing has begun to appear during a conversation - you need to consult a cardiologist as soon as possible to assess the degree of heart failure and correction planned therapy.
– Are there any risk groups for this type of pathology?
– Cough can develop as a result of various pathological conditions and diseases of the heart and blood vessels, if the therapy of the underlying disease is not adjusted in a timely manner and the increase in heart failure is not controlled, for example, in diseases such as coronary heart disease, heart defects, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, arterial hypertension, arrhythmias, etc.
– Why is a cardiac cough dangerous?
– Cough of cardiac origin is a severe and dangerous symptom of heart failure, but proper treatment by a specialist and adherence to a healthy lifestyle will help control the manifestations of heart failure – and the prognosis will be quite favorable.
In most cases, cardiac cough caused by heart failure can be corrected with drug therapy and lifestyle modifications; more radical measures, including surgery if indicated, are possible.
A cardiac cough can progress rapidly and lead to severe pulmonary congestion, so it should not be ignored and should be contacted by a medical professional when it first appears.
– Is it possible to get rid of a cardiac cough, and how?
– When the first episodes of cardiac cough appear, the patient must consult a cardiologist and undergo examinations, based on the results of which a course of treatment for the underlying disease that caused it is prescribed. Timely treatment of the detected disease will quickly get rid of the cough and slow down the progression of the underlying disease. Drug therapy and lifestyle modification are the main guarantors of the patient’s quality of life in the future. If necessary, surgical correction methods are possible if they are indicated for the patient.
Bromhexine for pain
Bromhexine is prescribed for the rapid removal of mucus from the respiratory tract in various diseases of the respiratory system: bronchitis, pneumonia, ARVI and influenza, asthma, pneumoconiosis. Bromhexine does not have an analgesic effect, it alleviates respiratory symptoms and helps get rid of an unproductive painful cough that can cause pain.
For other causes of cough (cardiac, gastric, neurological), the use of bromhexine and other mucolytics is ineffective.