If you are involved in medicine or sports, then you already know that this procedure is associated with changes in pulse and pressure in the circulatory system under the influence of changes in the position of the body in space. But how and why does our heart rate change, and how can athletes benefit from an orthostatic test?
This question remains open for many. So let's figure out what is really happening to our body, causing such a sharp change in heart rate, and how, by making daily observations, any athlete can determine even hidden indicators of overtraining and overload of the autonomic nervous system.
When our body is in a horizontal position, the forces of gravity act approximately equally on all its parts, and with a sharp change in position to a vertical one, blood outflows from the upper parts of the body and deposits (stagnation) of that same blood in its lower parts. The degree of severity of the body's reaction, expressed in changes in heart rate and pressure, indicates its current condition.
Reasons for measuring heart rate
If the blood stagnates in the veins of the legs that are large enough in volume, it returns to the heart far from being in its full composition. And our main circulatory organ needs to compensate for the lack of blood return in order not to disrupt the normal trophism (nutrition) of various tissues and organs of our body.
Since the flow of venous blood is not enough, an increase in heart rate becomes a compensatory mechanism, that is, the heart begins to work faster, hence the increase in pulse.
In sports, the orthostatic test is an extremely important indicator of the stability of the cardiovascular system under load, and if minor instability is acceptable for young athletes, then in the case of adult athletes there are no such concessions.
A sharp rise is stressful for our body, so the centers of the sympathetic department of the autonomic nervous system are overexcited. This is the department that monitors the state of our internal organs in stressful situations. Due to its excitement, the neurotransmitter norepinephrine is released into the blood, which also helps to increase heart rate.
Depending on the fitness of the athlete’s body and the general state of the autonomic nervous system, the orthotest indicators will deviate significantly or within normal limits. Thus, with minimal time and effort, it is possible to quickly diagnose the condition of athletes by analyzing pulse rate and pressure. More accurate data on sympathetic arousal is shown by studying heart rate variability (HRV or HRV) using specialized applications.
Benefits of diagnostics at the Kutuzovsky Children's Center
There are many advantages to undergoing diagnostics in a diagnostic and treatment center:
- Experienced and highly qualified doctors.
- A full range of services for the whole family in one building - we can quickly get all the necessary diagnostic services at a convenient time: laboratory tests, ultrasound, MRI and other hardware diagnostic methods, and get consultations with doctors of the required specialization.
- Affordable pricing policy.
You can sign up for this and other examinations and find out the cost by phone.
Test methods
There are the following methods for conducting an orthostatic test:
Active orthostatic test
The first, and most common among athletes, is an active orthostatic test. The idea is that they first take measurements in the person’s normal state, then measure the indicators while the person is in a horizontal position, after which the subject changes the position to a vertical one and the pulse is measured in a vertical position of the body over the next 3-5 minutes. Usually, the test is carried out in the morning, immediately after waking up.
Controlled test
The second, and most common among medical workers. It is used if there is a risk of fainting due to a sudden change in position.
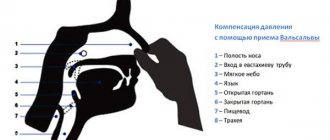
This type of orthostatic test is also carried out first in a standard position, then in a horizontal position, but measurements of the vertical position are carried out much more interesting than in the first method. If, as mentioned above, a person has a risk of fainting, then the risks should be minimized, so the subject is tightly attached to the bed and, instead of actively rising, the position of the bed is changed, measuring the pulse immediately and 3 to 5 minutes after rising. The violation of the accuracy and meaning of the study is minimal, because the change in gravitational forces remains the same, only the action of the muscles changes. An example in the picture for clarity.
Modified orthostatic test
And the third, modified orthostatic test, is suitable for weakened people. The technique is almost identical to the active orthostatic test, but the distinguishing factor is that the subject stands one foot away from the wall on which he rests his back. With this research method, in order for the patient to achieve a state of significant relaxation, a roller with a diameter of 12-14 cm is placed under the sacrum, due to this the angle of inclination becomes approximately 75-80 degrees, as a result of which the required body position is achieved
Taking measurements
Measurements in the orthostatic test can be carried out both by classical heart rate measurement (on the wrist, on the carotid or femoral arteries), and using heart rate monitors, the functions of which, today, are found in smart watches, smart bracelets and applications.
In practice, working with an orthostatic test does not end with getting your heart rate (HR) three or four times in a week; you must be able to correctly evaluate the results obtained. To do this, you need to rely on normal pulse and blood pressure values.
How the study is performed
Electrocardiogram
carried out using a stationary or portable electrocardiograph.
The patient is in a supine position. To increase the electrical activity of the skin, the area of the sternum and limbs is wiped with a damp sponge. Branch electrodes are installed in the heart
, on the ankles, and on the wrists. Then the diagnostician turns on the device and begins reading information about electrical potentials.
Graphs of cardiac muscle activity are displayed on the screen in the form of an oscillation graph and recorded on a special tape. The standard duration of ECG recording does not exceed 15 minutes. The results obtained are assessed by general practitioners, cardiologists, and general practitioners. The description (decoding) of the electrocardiogram is performed by cardiologists and functional diagnostics doctors.
Norm and results of pulse measurement
Normal heart rate is 60-80 beats/min. Changes in heart rate when changing position can be assessed at the following levels:
- from 0 to +10 can be considered an excellent result
- from +11 to +16 – good
- from +17 to +22 – normal
- more than +22 – already unsatisfactory
Deviations in the negative direction (i.e., slowing of the pulse during an orthostatic test) are also considered an unsatisfactory result.
Research results
The resulting cardiogram
transferred to a cardiologist for functional diagnostics to
decipher
the information. The results are sent to the attending physician, who recommends additional research or selects effective treatment tactics.
ECG parameters are considered normal:
:
- Heart rate (number of contractions within 1 minute) - 60–80 beats/min.
- Type of heart rhythm (where the nerve impulse that causes the contraction occurs) hearts
) - sinus. In case of disturbances, the rhythm can be ventricular, atrial, or atrioventricular.
- The electrical axis of the heart (the direction characterizing the propagation of impulses) is 30–70 degrees. During pregnancy, EOS up to 90 degrees is considered normal.
Norm and results of pressure changes
| For men | For women | |
| Up to 20 years | 123/76 | 116/72 |
| From 20 to 30 years | 126/79 | 120/75 |
| From 30 to 40 years | 129/81 | 127/80 |
| From 40 to 50 | 135/83 | 137/84 |
| From 50 to 60 | 142/85 | 144/85 |
| 60 and older | 142/80 | 159/85 |
The normal deviation of systolic pressure (first indicator) is a deviation from 0 to +20
The normal deviation of diastolic pressure (the second indicator) is also a deviation from 0 to +20
For clarity, let's look at an example:
During the active test, the heart rate increased by 19 beats per minute, which corresponds to normal values
Further, the heart rate increased by 17 beats per minute, which again corresponds to the norm.
In addition to measuring heart rate, the minimum and maximum blood pressure was measured in both tests. Deviations above the norm are not observed; the subject has close to normal fitness of the cardiovascular system.
To save time, it is recommended to take blood pressure measurements once a week. Orthotest measurements of heart rate - at least 3-4 times a week in the active phase of the training cycle.
Who is recommended for an orthostatic test?
The study of orthostatic stability is quite simple and requires minimal costs, both energy and material.
- An orthostatic test is strongly recommended for athletes, especially for those whose sport is associated with changes in body position in space (artistic gymnastics, rhythmic gymnastics, acrobatics, trampolining, diving, high jumping, pole vaulting, etc.)
- Also, an orthostatic test is often performed by those people who are trying to maintain the condition of varicose veins in good shape, thereby monitoring the effectiveness of training and other procedures.
- Everyone else who cares about their own health is recommended to regularly carry out an orthostatic test, and the mechanism of its implementation is so simple that everyone has the opportunity to conduct an orthostatic test at home,
If we take into account the number of devices that facilitate an already fairly easy study, take for example various kinds of “smart” watches like the Polar smart watch, then this study becomes tantamount to prevention.
How to take measurements
When starting data collection, six baseline measurements must be completed over a period of no more than two weeks. Take the average. This is your baseline. It should be understood that basic orthostatic tests should be performed during normal training weeks. It is advisable to avoid ultra-intense workouts to which your body is not yet accustomed.
Once baseline data has been obtained and a baseline has been established, it is recommended to continue testing at least two to three times per week. This way, if there is a sudden change in training volume or intensity, you can compare the new orthotest values with the normal level and determine the level of your overtraining. A heart rate deviation of more than +25 points (while maintaining all initial conditions) is a clear signal of under-recovery of the body.
An orthostatic test is performed in the morning, on an empty stomach, immediately after waking up. It is advisable to take key measurements after a recovery day (deviation should be minimal) and after a training day (higher deviation is expected). You can also do research before and after your workout. Tests in the absence of training or with irregular training may not be reliable enough. After a break of two or more weeks, it is recommended to re-establish the initial (basic) indicators
During the test itself, you must lie or sit quietly. Remember, for subsequent trials, you should have the same starting position as the previous times.
The advantage of such watches is that they allow you to test them at home, in the gym, at work and in other places convenient for you. The only important thing is that nothing should disturb you at the time of the study; you should exclude any distracting factors, such as sounds, smells, flashes of light and even people.
2-3 hours before the procedure, stop smoking, food and alcohol. It is recommended to carry out the test regularly and at the same time, then you can achieve more accurate results.
Methods of taking measurements using modern means
In modern conditions, an orthostatic test can be carried out using a watch with a built-in heart rate monitor, specialized applications on a smartphone, and other available cardio sensors.
Preparing for the study
No special preparation is required. If there is thick hair in the chest area, it is recommended to remove hair. The day before, you can stick to your usual drinking and eating regimen. To obtain reliable results, it is not recommended to undergo diagnostics immediately after eating food, coffee, energy drinks, alcohol, or after intense physical activity. ECG accuracy
may be affected by the time of the study, extraneous electromagnetic background, location of the branch electrodes, elevated temperature in the patient, stress and other factors.
Using a smart watch
Let's look at the step-by-step instructions using a Polar watch as an example. Sample collection is similar in other models.
Select Tests > Orthostatic test > Relax and start measuring
The display shows the following message: Heart rate determination. After determining your heart rate, a message will appear on the display: Take a lying position and relax.
- As your heart rate begins to graph on the screen, relax and try to remain still for three minutes.
- Then, 3 minutes after the start of the orthostatic test, the watch will emit a sound signal and the message “Stand up” will appear on the display.
- You must remain upright for the next three minutes.
- After the end of the second stage, the watch will again signal with a sound signal that the orthostatic test has been completed.
If the test has to be interrupted, you can take the test again. Click the “back” button to cancel this procedure.
How to choose a watch
- Choose a watch with a heart rate monitor.
- Assess the requirements you place on the device. If you are new to sports, do not overpay for the brand and extra functionality, take the basic model.
- Please note additional features. Such as GPS, altimeter or maps. For some this will be a necessity, but for others it will be a pleasant addition at the right time. Consider the brands Garmin, Polar, Suunto, Sigma.
We recommend two models with advanced features that can help you at different stages of sports training and include the ability to take an orthostatic test.
Smart watch Polar V800 H1
This model is perfect for serious sports. A nice addition will be the protection of the watch from shocks, scratches, water, snow and other damage. They hold a charge for up to 30 days. Suitable for both cyclic and strength training and endurance training.
As for the medical stuff, Polar V800 allows you to take orthostatic tests, determine the maximum oxygen capacity (VO2max), calculate the RR intervals of the cardiac cycle (HRV) and much more.
Polar 430 sports watch
The device uses the most accurate optical heart rate monitor in its class, which allows continuous heart rate monitoring. The watch weighs only 51 grams and holds a charge for up to 10 days. The Polar Flow system contains training programs for races of 5, 10 km, half marathon or marathon, which are scheduled for every day for 2-3 months. The system also makes it possible to create a personal training plan with the ability to further track progress.
Just like the previous model, it allows you to track aerobic running efficiency and maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max). Analytics of sleep duration and quality is also available. A nice addition is the built-in GPS system.
Using mobile applications
If you still haven’t decided on the need to buy a sports watch, but want to control your health indicators now, you can use alternative methods. Namely, applications that will always be at your fingertips.
Today, there are already many applications that can quite accurately read a person’s pulse using a camera directly from the tip of the finger. Here are some of them:
Runtastic Heart Rate Pulse and Heart Rate
This application will allow you to find out your heart rate in any place convenient for you. The application also has a statistics function, thanks to which you can track your data
Unique Heart Rate Monitor
The application allows you to read your pulse and immediately enters the result into statistics, asking you what state you were in, taking measurements, be it rest, training or time after training. A nice addition will be the ability to leave a comment for each result.
Azumio Heart Rate Monitor
The application is entirely in English. Compared to the previous ones, it takes a little longer to read the pulse. It also allows you to leave notes for each result.
Blood Pressure History
There are applications that have the function of reading pulse and pressure at the same time, for example Blood Pressure History
Like the previous one, this application is entirely in English, but the functionality can be understood even with complete ignorance of the language. Calculates systolic, diastolic pressure and heart rate by touching the phone screen with your finger. Keeps a history log of your past measurements.
Well, the last application that we would recommend to those who want to get more serious sports indicators on the screen of their smartphone
HRV4Training
The application is paid, but by downloading it, you will receive not only more accurate indicators, but also the possibility of both classical and orthostatic data collection. Plus, the program has the ability to synchronize with the training log in other applications. But you must understand that you can only get the full range of functions if you have an HR heart rate monitor
With this set of knowledge about the orthostatic test and how to take its measurements, you are fully prepared for self-diagnosis and better training.
Contraindications
Carrying out an ECG
may be difficult in the following cases:
- the patient is overweight;
- there are injuries in the sternum area;
- Excessive hair growth in the area being examined.
Electrocardiogram
with a load is not carried out in the presence of the following pathological conditions:
- chronic cardiac dysfunction;
- acute coronary circulatory disorder (ischemia hearts
);
- myocardial infarction during the acute stage;
- viral and other infectious diseases in the acute phase;
- persistent arterial hypertension with deterioration;
- increased risk of aortic dissection or rupture.