Useful articles
Publication date:
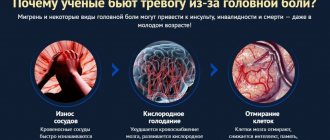
Very often, the cause of headaches (cephalalgia) is lability of blood pressure, which is why such pains are also called “vascular.” Treatment of vascular headache should always begin with eliminating the cause, that is, normalizing the pressure if it provokes the appearance of this symptom. A typical picture of the pathology will look like throbbing or tingling pain, sometimes even a burning sensation.
In a number of cephalgia, headaches with normal pressure are also often encountered, the treatment of which can be very different from vascular headaches. Often such pain occurs against the background of other pathologies and is only a sign, not a disease. The pain mechanism is triggered by the direct impact of various processes on the sensitive receptors of the dura mater and cranial tissue. When cephalalgia appears, it is always worth determining its cause.
The following factors can cause headaches against the background of normal blood pressure:
- traumatic brain injury;
- inflammatory processes both in the head and in other parts of the body (sinusitis, otitis, mastoiditis, etc.);
- neuralgia of the facial trigeminal nerve (usually only part of the head hurts, paroxysmal, tingling);
- brain abscess (temples, frontal part hurt);
- pregnancy;
- flu, colds, adenoviral infection;
- pituitary adenoma;
- frequent stress;
- allergy;
- fistula;
- PMS in women;
- vertebral artery syndrome;
- excessive mental stress (tension cephalgia);
- general fatigue.
All these reasons require a different medical approach, so treatment of headaches with normal blood pressure consists of identifying the factor that caused it and selecting adequate therapy. Sometimes a Paracetamol or Ibuprofen tablet is enough, sometimes normal sleep and rest, in other cases the mandatory help of specialists is required.
Headache and hypertension
Why, if the pressure is relieved, does my head continue to hurt? First, you need to understand the following thing: it matters how exactly the pressure was reduced. Let's take a closer look at what happens in various cases.
If you have lowered your blood pressure with medication, the mechanism may be as follows. With high blood pressure, intracranial pressure rises accordingly. The heart works hard, and first of all it is necessary to “calm it down.” Tablets that lower blood pressure affect the heart rate, making it more regular, therefore, the pressure drops, blood does not flow as much to the brain, and the headache should disappear.
You can get more information about this and many other aspects of health related to blood pressure, osteochondrosis, atherosclerosis, ask your questions to Dr. Shishonin and just chat by joining our community - the Club of
Former Hypertensive Patients
.
Dosage
The dosage of Nurofen for adults and children over 12 years of age is 1 capsule or tablet (200 mg) up to 3-4 times a day. The interval between doses should be about six hours. The maximum permissible daily dosage is 1200 mg.
The dosage of Nurofen for children depends on age and body weight. It should not exceed more than 30 mg/kg:
- 3-6 months (5-7.6 kg) - 2.5 ml three times a day;
- 6-12 months (7.7-9 kg) - 2.5 ml up to 4 times a day;
- from one to three years (10-16 kg) - 5 ml 3 times;
- from 4 to 6 years (17-20 kg) - 7.5 ml three times a day;
- from 7 to 9 years (21-30 kg) - 10 ml in the morning, lunch and evening;
- from 10 to 12 years (31-40 kg) - 15 ml three times.
Treatment of a child with Nurofen should last no more than three days.
The dosages of children's suppositories are as follows:
- age from 3 to 9 months - 1 piece three times a day;
- from 9 months to 2 years - 1 piece 4 times.
The gel is intended for patients over 14 years of age. You need to squeeze out a strip 4 to 10 cm long from the tube and gently rub it into the painful area. Reuse is possible after 4 hours.
Why does my head hurt?
If the venous outflow is disrupted, that is, the veins are pinched, you take pills, the heart stops pumping blood in large quantities, but it cannot descend back from the brain in full, which means the headache does not disappear. In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor and check the condition of the blood vessels, since excessive accumulation of blood in the brain is very dangerous.
Important:
If the venous outflow is impaired, the pressure in the body system drops, but the intracranial pressure remains high, which provokes a headache.
This is the main reason why, when taking medications, the headache may not go away, but remain the same, and it does not matter how sharply the pressure drops. In this case, do not panic and take other pills that have pain-relieving properties. After some time, the pain will go away, and neck exercises will help speed up this process. They normalize blood flow and help veins cope better with their function.
pharmachologic effect
NSAIDs. Has analgesic properties. Relieves fever. Blocks the spread of inflammatory processes.
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of the drug is explained by the properties of a propionic acid derivative and is caused by inhibition of the synthesis of PG - mediators of pain, inflammation and hyperthermic reaction. Indiscriminately stops the work of COX of the first and second types. Slows down the production of prostaglandins.
Reversibly inhibits platelet aggregation. The analgesic effect lasts for up to eight hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Has high absorption. Almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration in blood plasma when taken orally on an empty stomach is recorded after 45 minutes. If you take the tablets with food, the Cmax time approximately doubles.
90% bound to blood proteins. Gradually penetrates into the joint cavities. Retains in synovial fluid. Lower concentrations of ibuprofen are found in cerebrospinal fluid than in plasma. Passes into breast milk in small quantities.
Metabolized in the liver. It is excreted from the body by the urinary system, a small part - with bile. The half-life is two hours.
What to do?
At Dr. Shishonin’s clinic, specialists very often encounter cases where the patient complains of a headache that does not disappear after the pressure is reduced. Then an ultrasound examination is required to find out the condition of the vessels of the skull.
The doctor says:
Dr. Shishonin draws the attention of patients to the fact that almost every second case of headache with which they come to him is associated with a violation of the venous outflow.
If you relieve pressure through correction, that is, without medications, normalizing venous outflow and arterial inflow naturally, as happens in Dr. Shishonin’s clinic, then this problem does not arise. With a natural decrease in pressure, when blood circulates freely, the head will not hurt, which means the blood vessels will be in order.
Advice:
Gymnastics for the neck, which Alexander Yuryevich recommends to all his patients, will help reduce blood pressure naturally and normalize the outflow and inflow of blood without the use of drugs that poison the liver.
This problem can only happen if you reduce your blood pressure with medication. The pills affect the heart, causing it to work less forcefully, and intracranial pressure remains at the same level. As a result, the tonometer will show that your blood pressure is normal, but your head will hurt. What to do in this case? This situation means that the neck and its vessels are affected, and the neck needs to be treated. Check out other videos on the “Club of Former Hypertensive Patients” channel and find out how you can use gymnastics to get rid of vascular problems, improve the health of the cervical spine and get rid of pain forever. Be healthy!
Hypoglycemia: causes and prevention
Hypoglycemia is a rather narrow topic related to diabetes mellitus. However, it is still unrealistic to fully cover diabetes mellitus in one article. Therefore, today I will talk about one of its serious consequences, which occurs due to a lack of glucose in the body. The hypoglycemic state develops rapidly, leads to severe disturbances in brain function and is potentially fatal.
Physiology of the phenomenon
At first, a boring and dry definition. Hypoglycemia is an metabolic-endocrine syndrome that occurs when plasma glucose levels decrease by at least 0.5 mmol/l from the lower limit of normal and is accompanied by symptoms of dysfunction of the central nervous system. Let me remind you that the norm is 3.5–5.5 mmol/l.
The fact is that the brain is a highly energy-consuming organ (especially its gray matter), one might say - a spender. Yes, yes, compared to other organs, it consumes an enormous amount of energy and at the same time lives in isolation (the cranium).
This means that any starvation, be it oxygen or glucose, can lead to organ death within a few minutes. And the fact that the brain lives in the cranium, which is unable to expand even with cell swelling, further aggravates the problem.
Here I must explain that any tissue damage leads to swelling: bite your finger and it will swell, but after a couple of days (or even hours) the swelling will go away and the finger will return to its previous appearance and functionality, but the swollen brains will increase in size, will rest against the walls of the prison (skull) and begin to flow away to where there is free space. The blood vessels will contract, nutrition will stop, damage to nerve cells will increase, the brain will swell even more and proceed into the foramen magnum. The first to suffer will be the neurons of the medulla oblongata, which contains the oldest centers of respiration and control of the cardiovascular system, and this will completely finish off the body.
And I ask you not to think that the brain swells only from hitting a wall - it swells from any damaging factor, including a lack of oxygen, glucose and other substrates that lead to cell damage.
Causes of hypoglycemia
Undoubtedly, patients suffering from diabetes mellitus are most susceptible to this condition, for example, due to an overdose of insulin, errors in the method of its administration (administration of insulin without preliminary shaking in the bottle, administration of the drug to places where rapid absorption of the drug can occur). Some manage (apparently, thinking that for some reason it didn’t work) to inject insulin into a vein along with subcutaneous injection.
Nurofen's analogs
Among the most popular analogues of Nurofen are: Ibuprofen, MIG 400, Faspik, Maximcold.
The gel form can be replaced with Ibuprofen ointment, Dolgit gel and Dolgit cream.
Which is better Nurofen or Ibuprofen?
Both drugs contain the same active ingredient, therefore they have the same indications and contraindications. But, according to patient reviews, Ibuprofen more often causes unwanted side reactions.
Which is better Nurofen or Paracetamol?
Paracetamol begins to act more slowly, which is why the patient is forced to endure the pain longer. It also lowers body temperature worse and for a shorter period of time in viral and infectious diseases.
Paracetamol does not have anti-inflammatory properties like Nurofen. But it is safer for pregnant women.
At the same time, during treatment with Ibuprofen, adverse reactions occur more often, and there is a possibility of bleeding. It should not be used for a long time, as the risk of damage to the mucous membranes of the stomach increases.
Which is better Nurofen or Panadol?
Panadol is based on paracetamol, Nurofen is based on ibuprofen. Both drugs relieve pain and reduce body temperature. They qualitatively eliminate the signs of acute respiratory viral infections, headaches, toothache and muscle pain. They do not accumulate in the human body and do not form toxic compounds.
Panadol lowers body temperature more slowly. It is safer for children and pregnant women. If necessary, drugs can be combined or alternated.
Which is better Nurofen or Cefekon?
Cefekon is a medicine based on paracetamol. Its effect lasts for up to 4 hours. Nurofen acts longer (up to 6-8 hours) and much faster. This is its significant advantage. It also relieves toothache better.
Which is better Nurofen or Ibuklin?
Ibuklin is a combination drug. It contains both ibuprofen and paracetamol. Very quickly lowers body temperature to normal levels. It is stronger than Nurofen. At the same time, it is characterized by a stronger load on the liver and irritates the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract. It can only be purchased with a doctor's prescription.
The use of Ibuklin is relevant if the body temperature exceeds 39 ° C. It is advisable to use it once.
Which is better Nurofen or Nise?
Nise is recognized as a more progressive anti-inflammatory. It is based on nimesulide. This substance quickly relieves muscle pain, has antipyretic properties, and does not cause stomach ulcers. But it is contraindicated in patients under 16 years of age. Long-term use may cause toxic liver damage.
Nise has more pronounced toxic properties than Nurofen. But with short-term use, they most often do not appear.
How to find the reason?
Depending on the description of the main manifestations, the therapist may involve other specialists in the work: an endocrinologist, a neurologist, a dentist, an oncologist. After making the first assumption about the disease, laboratory procedures are carried out designed to give a comprehensive picture of the person’s condition. The most common research methods are:
- Laboratory analysis of urine/blood.
- CT scan.
- Angiography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
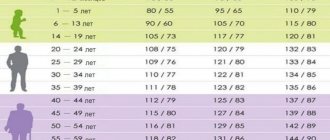
- Blood pressure measurement.
Through tests, an inflammatory process can be detected in the body, but it does not always occur with headaches and nausea. Tomographic technologies are considered the best ways to detect even microscopic changes in the body. Only through MRI and CT can one find hidden, complex diseases, find out the causes of previously diagnosed disorders, plan treatment and safely monitor the course of the pathology.
Treatment
As first aid, it is necessary to exclude all possible external irritants, including unpleasant odors, loud sounds, and bright lights.
Take your usual painkiller, lie down and massage your head. You need to try to relax, before that open the window to freshen the air, drink a cup of weak tea. You cannot prescribe medications for yourself; this can only be done by a specialist. After consultation with him, a specialized examination and diagnosis, further treatment is planned.
The doctor can prescribe analgesics and adsorbents only for frequently recurring or unbearable attacks. The basis of therapy is the fight against the root cause; special drugs are prescribed, depending on the source of the disease. In particularly difficult cases, the issue of surgical intervention is decided. During the rehabilitation period, medications are also continued and physiotherapy is prescribed: massages, magnetic effects, gymnastics, cool compresses.