Thrombocrit in general blood test
The most accessible method of laboratory diagnosis of thrombocrit and other blood parameters is a general analysis. CCA (general clinical analysis) of blood allows us to identify disturbances in microprocesses in the body, indicating certain possible diseases. Blood, as a biological fluid, consists of plasma and a cellular part containing groups of formed elements: platelets, leukocytes, erythrocytes, etc.
Each group of blood cells is responsible for certain biochemical processes and has its own content norm in quantitative equivalent and percentage of the total blood volume. Basic parameters are assessed according to the reference values accepted in clinical hematology.
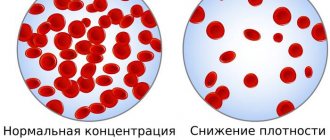
All indicators are correlated, so a comparative interpretation (an increase in some values against the background of a decrease or increase in others) gives the doctor an idea of which system of the body the failure occurred. Platelets are plate-shaped cells without a nucleus or color that are formed in the bone marrow.
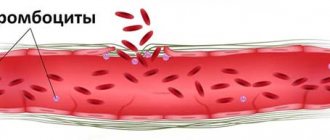
The functional responsibility of platelets is to protect blood vessels from damage and ensure normal blood clotting. If a vessel is damaged (serious rupture or microtrauma), flat shaped elements move to the site of the “accident”, form a clot and stop pathological bleeding.
The complexity of the analysis lies in the organic property of blood platelets to stick together (aggregation). To prevent cells from sticking together, the laboratory uses a special automatic analyzer that continuously rotates the blood placed in it. Thrombocrit (platelet mass as a percentage) is studied in combination with other platelet indices:
- platelet count (PLT);
- distribution range (PDW);
- average volume (MPV).
Such a comprehensive study makes it possible to obtain more complete results about the behavior of platelets in the blood composition. As cells increase in size, their distribution range increases, and an increased average value may be associated with hematological diseases, intestinal inflammation, and other pathological processes. An altered platelet count indicates problems with blood clotting and a risk of blood clots. The percentage is calculated using the formula PCT = MPV* PLT.
The PCT blood test deserves increased attention in case of suspected disorders:
- infections of bacterial etiology (origin);
- secondary infectious blood disease (sepsis);
- postoperative pathological processes;
- complicated pregnancy;
- hematological pathologies.
Formed blood elements to be assessed (briefly)
In relation to other indicators of general analysis, thrombocrit is assessed when monitoring the treatment of meningitis, pneumonia and other diseases of inflammatory origin.
Additionally
To determine platelet indices, venous blood is taken. To obtain objective results, clinical analysis is performed on an empty stomach. Three days before the procedure, the patient is recommended to eliminate heavy fatty foods and alcoholic beverages from the diet. On the eve of the analysis, you should avoid sports training and limit general physical activity. Avoid taking medications that affect blood clotting (antiplatelet agents, coagulants and anticoagulants).
Causes of thrombocrit
When measuring thrombocrit, we must not forget that each person has his own upper and lower limits. It is calculated based on diseases, age, gender. For this reason, it is quite difficult to understand, after finding out that the thrombocrit is below normal, and what this means in women, men or children.
If we put aside possible individual reasons for deviation, the following options remain:
- bacterial infection;
- viral infections of the body;
- sepsis and other vascular lesions;
- side effect after tissue transplantation.
Mandatory measurement of the number of corpuscles is carried out when connected to a ventilator, when trying to understand the cause of an acute febrile state. Each of the possible ailments that may be hidden behind a decrease in the number of blood cells must be dealt with only under the supervision of a doctor. The therapist will determine the exact cause of the symptoms, after which the patient will be referred to a surgeon, immunologist, inflammation expert, etc.
In particularly acute situations, a blood transfusion or artificial stimulation of platelet production is prescribed. This is done to prevent dangerous hemorrhages that cannot be stopped.
PCT reference values
Standard thrombocrit values are not differentiated by the patient’s gender (the indicators are identical for women and men). They also do not have a gradation by age (for adults and children). For all age categories, the norm is from 0.22 to 0.24%.
Reference! Interval values may fluctuate. In the absence of deviations from other analysis indicators, the lower limit is allowed in the range of 0.11% - 0.15%, the upper - 0.28% - 0.4%.
A distinctive feature of platelet indices is the influence of physiological factors on their values, which is not abnormal. In women, in the first seven days of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle (the period of bleeding), PCT may fall by half. A similar deviation is observed in the perinatal period. In this way, the body tries to reduce the risk of blood clots in the expectant mother.
After intense sports or other physical activity, PLT and PCT levels double. Due to the peculiarities of the body’s biological processes, thrombocrit is usually lower in the spring and at night. The difference between the indicators and the reference values is 10%.
The reason for the low level of indices is the patient’s depressive state and distress (constant neuropsychological tension). All components of the platelet unit (volume, quantity, percentage, range) are interconnected, their values change proportionally to each other.
Conditions under which PLT reduction is acceptable
If a thrombocrit was detected below normal, what does this mean during pregnancy? Is the deviation associated with altered hormonal levels? Yes, pregnant women may experience a halving of the rate, since some of the substances produced are redirected to the child. This condition does not require treatment, but the health of the expectant mother must be carefully monitored.
Another question concerns mothers who have already given birth: when a thrombocrit is diagnostically determined to be below normal, what does this mean for the child? In children from birth to adulthood (15 years), thrombocrit has its own limits. In the period from 0 months to 1 year, the lower limit is 180 PLT. But upon reaching one year of age, its content may drop to 160, and this will still be within the normal range.
Before the end of the period of active growth, the child’s body is constantly being rebuilt, and platelets do not have time to be produced in increased quantities. After 16 years, the lower limit again reaches 180. If a child notices a decrease in platelets even to a value below 160, do not immediately panic: this may be a seasonal effect. In late autumn and early spring, people, especially children, lose some of the clogging bodies due to natural life processes.
For any serious deviation it is necessary to undergo additional examination. Timely diagnosis is especially important for pregnant women and children.
Thrombocrit is an important indicator of a person’s condition. Its deviation may indicate illnesses and hemorrhages, therefore, if deviations are detected, further therapy should not be neglected.
Symptomatic manifestations of deviations from the norm
An increase or decrease in the percentage in the analysis results are clinical signs of disorders that may be accompanied by the following somatic symptoms:
- CFS (chronic fatigue syndrome);
- pallor (often blueness) of the skin of the fingers;
- bleeding from the nasal cavity (more often observed in children and the elderly).
- tingling sensations, itching in the extremities;
- cephalgic syndrome (headache);
- formation of hematomas on the body of non-traumatic origin;
- decreased visual perception.
Small amounts of blood may be found in urine and feces. You should not self-diagnose. Only a doctor can correctly assess the patient’s condition by comparing test results, medical history and symptoms.
Blood test form with results
Increased level
A high platelet count means increased platelet production, hence thickening of the blood. With this condition of the blood, the risk of heart attack, blood clot formation and vascular blockage (thromboembolism) increases. Elevated levels of all platelet indices accompany the following chronic diseases and acute conditions:
- chronic myeloproliferative diseases CMPD (transformation of bone marrow cells)
- hematological diseases, including oncological ones (polycythemia, leukemia, Werlhof’s disease, etc.);
- iron deficiency anemia (anemia);
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism);
- diabetes mellitus and related disease complications - angiopathy;
- infection of the body with bacteria, viruses, fungi;
- atherosclerosis of blood vessels of the lower extremities and brain;
- acute or chronic inflammation of the pancreas;
- infection of the pulmonary system with Koch's bacillus (tuberculosis);
- protein metabolism disorder (amyloidosis);
- pre-stroke and pre-infarction condition;
- systemic inflammation of the connective tissue of the heart and musculoskeletal system (rheumatism).
In women, thrombocrit may be increased due to incorrectly selected hormonal contraception. In children, an increase in PCT levels is often associated with previous viral and colds, or improper nutrition and drinking habits.
As a risk factor for heart attack, high platelet levels are more indicative of men aged 60+. An increase in platelet indices is recorded after surgical interventions, in particular splenectomy (removal of the spleen), as well as after bone fractures. Deviations of PCT results from the norm are provoked by nicotine addiction.
Reduced thrombocrit values
The main reasons for a low thrombocrit level are thrombocytopenia (active destruction of platelets and their accelerated removal from the body) and the inability of the bone marrow to synthesize blood cells in the quantity required by the body. Thrombocytopenia provokes anemia of various types:
- Hemolytic. Most often occurs due to incorrect blood transfusion or heavy metal poisoning;
- Pernicious, otherwise Addison-Birmer's disease. Associated with a deficiency of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) in the body.
Aplastic anemia is caused by dysfunction of the bone marrow. Low platelet indices are characteristic of:
- a group of diseases with characteristic damage to connective tissue (collagenosis);
- oncohematological diseases;
- state of chronic intoxication of the body;
- cirrhosis;
- renal failure in the decompensated stage;
- pathologies of an autoimmune nature;
- infection with viruses.
A decrease in thrombocrit is a clinical sign of weight deficiency in a newborn baby. In such cases, the baby is prescribed special anti-anemic therapy. An external sign of thrombocrit deficiency is bruising. If hematomas of non-traumatic origin and subcutaneous hemorrhages (hemorrhages) appear on the body, it means that the capillaries in this area are damaged.
To fix the problem, platelets need to block the damaged area. The frequent occurrence of such bruises indicates that blood cells are not coping with the task due to their small number.
Chemotherapy and a course of antibacterial medications can lower PCT levels
Violation of the reference values of platelet indices does not diagnose a specific disease. In case of deviations from the norm, it is necessary to compare the data of all blood test parameters. In case of pronounced changes, the patient needs additional examination, including laboratory microscopy and hardware diagnostic procedures (ultrasound, MRI, CT, etc.).
Additional Research
If a person has an increased or decreased thrombocrit in the blood, additional tests will be prescribed. Which ones? The time it takes for the blood to clot is recorded. Additional tests will “tell” about the presence of protein and sugar in the blood and indicate the exact amount of iron. An examination for the presence of fibrinogen will also be carried out; often the patient will be prescribed a urine test, and we are talking about an expanded type of analysis, and if necessary, a referral may be issued for a test for the content of hormones in the body and tumor markers.
Doctors often write out a referral for an echogram, as well as an x-ray of the kidneys, liver and spleen. To understand how well the blood vessels function, it is necessary to do a Doppler ultrasound. If there is a suspicion that there is a blood disorder in the body, a bone marrow biopsy will be taken. Tissues are also often examined for the content of certain types of cells.
Results
The PCT indicator in the blood test form indicates thrombocrit - the percentage of platelets in the total mass of biological fluid (blood). Platelets are plate-shaped blood cells produced by the bone marrow. Their main function is to prevent bleeding when blood vessels are damaged. In addition to the percentage index, laboratory blood microscopy evaluates the platelet count (PLT), platelet distribution range (PDW) and mean volume (MPV).
The thrombocrit rate for adults and children ranges from 0.15 to 0.4%. A non-pathological decrease in values is the perinatal period and menstruation in women, as well as at night and in the spring season. An increase in the percentage, first of all, characterizes the danger of developing thrombosis, strokes and heart attacks. High PCT values accompany a number of chronic diseases.
A low platelet index indicates thrombocytopenia and insufficient platelet production, which is a clinical sign of anemia, blood cancer, autoimmune and other chronic pathologies. If the study results deviate from the norm, determining the cause of the violation and prescribing appropriate therapy is the responsibility of the attending physician.
The effect of a decrease in platelet count on the body
Thrombocrit is the amount of blood cells called platelets in the blood. These are non-nucleated cellular formations that circulate through the blood and help plug holes that form in blood vessels or veins. Their functions:
- stopping bleeding due to external wounds;
- preventing internal bleeding.
Without the proper content of blood elements, the patient will experience problems with blood clotting. The norm for these cells is from 0.1% to 0.4%. It varies depending on the age and hormonal state of the patient.
A decrease in the required level (measured in PLT) will lead to increased weakness of the body. The patient, even with minor cuts, will lose a lot of blood and will take a long time to recover. Simple bruises with the formation of hematomas, that is, weak subcutaneous hemorrhages, will take almost all your strength. Symptoms at a low level are similar to the manifestations of hemophilia - blood incoagulability, which was the main problem of the royal houses until the 20th century.
If you notice symptoms of weakness and incoagulability, you should consult a doctor. If the study reveals a deviation from the norm, then therapy adequate to the cause will be prescribed.