Stenting of the lower extremities is a treatment method based on strengthening the vascular wall with a special metal structure - a stent. Critical ischemia and gangrene of the lower extremities have long been treated only with open bypass surgery. Despite all the positive qualities, bypass surgery has one drawback - it is a large open operation with incisions to access the vessels. This creates risks of complications associated with major interventions in patients with gangrene. Endovascular methods have made it possible to effectively treat critical ischemia in patients with concomitant lesions of the coronary, renal and carotid arteries of the brain.
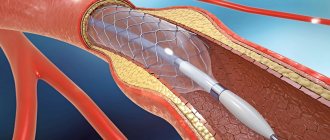
The development of medical technologies has made it possible to minimize surgical trauma using endovascular interventions through skin puncture and without incisions. The main endovascular operations are angioplasty of the lower extremities and installation of stents in the vessel. The purpose of vascular angioplasty is to inflate a narrowed or blocked segment using a special balloon passed through a thin guide. After angioplasty, a special metal mesh, a stent, can be installed into the lumen of the restored vessel to support the wall. Historically, laser angioplasty was used to destroy plaque in blood vessels, but this has given way to new, advanced endovascular instruments.
Endovascular technologies at the Innovative Vascular Center
The main mission of our clinic is the treatment of critical ischemia and gangrene of the extremities. We are committed to using the latest approaches to solve this problem. Since 2011, endovascular surgery methods for critical ischemia have been introduced into the practice of our vascular surgeons. Noting the advantages of the endovascular approach, every year we expand the capabilities of our clinic in the use of these methods.
The role of minimally invasive technologies is growing - now more than 50% of patients with critical ischemia and gangrene are operated on endovascularly, and even more than 40% use a hybrid approach. This is bypass surgery with angioplasty and stenting of the arteries of the lower extremities. The Innovative Vascular Center is a clinic where more than 500 angioplasty and stenting operations of lower extremity arteries are performed per year.
The capabilities of endovascular surgery are developing synchronously with the creation of innovative treatment tools, so in our practice, puncture operations are increasingly replacing open interventions.
Preparing for stenting
Before performing stenting surgery, the patient must be properly examined for vascular lesions and risks of complications. A set of laboratory tests and a coagulogram must be performed before surgery. Considering the patient's load on antithrombotic drugs, it is necessary to exclude possible sources of bleeding (stomach ulcer, bleeding hemorrhoids).
On the eve of the intervention, a light sedative is administered, allowing the patient to sleep well and not be nervous. Before the operation, the patient will shave the site of the intended access. In the preoperative room, the nurse will place a urinary catheter and an intravenous needle for infusions. In the operating room, a pressure cuff is placed on the shoulder and sensors for continuous ECG recording are fixed on the chest.
Anesthesia for stenting
Most endovascular angioplasty procedures and lower extremity vascular stenting can be performed with mild intravenous sedation and local anesthesia at the access puncture site. Monitoring of blood pressure, electrocardiogram and blood oxygen saturation level (pulse oximetry) is mandatory. In case of unforeseen complications, the operating room is equipped with a breathing apparatus and a defibrillator. If the operation is performed for critical ischemia, then to make the patient comfortable, epidural anesthesia is performed (injection of an anesthetic drug through a catheter into the spinal area).
Principles of physical therapy
Moderate physical activity after stenting leads to several effects:
- Improves current circulation in blood vessels
. This has a positive effect not only on the functioning of the heart, but also on the entire body as a whole. - Improve nitric oxide absorption
. Under its influence, blood vessels dilate and, accordingly, blood flow improves. - Strengthen regeneration processes
. Exercise speeds up cell repair, which in turn promotes rapid healing of damaged arteries.
After stenting, only intense physical activity and training, which require good endurance of the heart muscle, are prohibited. Therefore, patients can do:
Advertising:
- fast walking - up to 6-7 km per hour;
- easy jogging;
- cycling;
- swimming;
- water aerobics.
The intensity of the load should be increased gradually, carefully noting all changes in well-being. After installing stents in vessels, many doctors recommend spending time on a health path every day. This activity involves walking with a gradual increase in time and angle of inclination. In the first days you need to walk only on flat terrain, then the route needs to be designed so that along its length there are hills with an inclination angle of 5 to 30 degrees. Gradually the duration of the path increases.
Rules for performing exercises
When performing physical therapy, you must adhere to the following rules:
- the training time should take from 30 to 45 minutes;
- classes are carried out either on an empty stomach, or no earlier than an hour and a half after eating;
- the intensity of the exercises is increased gradually;
- before training you need to “warm up” - move around, swing your arms and legs;
- If shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat and other uncomfortable changes in well-being appear, classes are stopped.
You should not perform exercises that lead to pain and discomfort. The goal of exercise therapy is to improve, not worsen, well-being.
Therapeutic exercise strengthens the immune system, helps lose weight, strengthens the nervous system, and stabilizes blood pressure. It is better to select classes with your attending physician, since only a specialist can know the maximum level of permissible load.
Types of angioplasty
- Subintimal balloon angioplasty of vessels - the conductor is passed under the modified inner wall (intima) of the vessel and then extends into the free lumen.
- Intraluminar angioplasty is a type of intervention where the conductor passes through the natural lumen of the artery, sliding through narrowed and blocked areas.
- With laser angioplasty, the atherosclerotic plaque is burned out with a special laser catheter.
Balloon angioplasty of lower extremity arteries without stenting is recommended for the treatment of lower leg lesions. It is imperative to stent the iliac arteries, since the frequency of repeated narrowings (restenosis) without a stent is very high.
After angioplasty and stenting, control angiography is required to evaluate the result.
Possible complications
Complications after balloon angioplasty of the vessels of the lower extremities usually develop during the intervention and should be immediately eliminated. Methods for eliminating these complications are available to vascular surgeons. The most commonly observed complications are:
- Bleeding from the access site (hematoma or pseudoaneurysm) most often occurs when the patient violates bed rest. Sometimes requires open access to eliminate the source of bleeding.
- Puncture site infection is a very rare complication. It can develop with severe purulent-destructive processes on the lower limb. It is necessary to treat with antibiotics. If necessary, open the purulent focus.
- Contrast kidney injury is a rare complication from contrast media.
- Dissection (dissection) of the artery - sometimes observed with complex lesions and attempts at subintimal passage. Most often it can be eliminated by installing a stent.
- Blockage of the arterial bed with pieces of plaque can be determined during control angiography.
- Fracture of the stent in the places where it bends is a late complication associated with mechanical stress on the metal.
- Repeated narrowing at the site of stent installation (restenosis) is the process of overgrowth of the lumen of the stented segment.
- Arterial rupture is a complication that develops due to excessive balloon inflation in a severely calcified vessel. Detected during control angiography. It is often possible to stabilize the situation with prolonged exposure of the balloon; installation of a stent graft or open surgery may be required.
- Arterial spasm is a reaction to inflating a vessel with a balloon. Occurs in 10% of procedures. To eliminate spasms, medications (papaverine, nitroglycerin) can be administered.
The frequency of all complications is no more than 5% of all procedures performed and they are usually eliminated in a timely manner during the intervention.
Duration of recovery period
Each person’s body is individual and the time frame for full recovery of health after vascular bypass surgery depends on many factors. Doctors recommend starting to gradually return to normal life after 2-2.5 weeks. However, stenting is an operation whose further outcome is largely determined by how willing the person operated is to follow the doctor’s recommendations.
First of all, you need to completely reconsider your lifestyle. That is, choose the right diet, quit smoking and alcohol abuse, avoid stress, choose dosed physical activity.
This will help reduce the risk of further progression of atherosclerosis and significantly reduce the likelihood of developing early and late complications after stent installation.
Observation after angioplasty and stenting
Our clinic has adopted a patient management scheme after surgery to avoid complications of angioplasty and stenting of peripheral arteries of the lower extremities:
- For better results, dual antiplatelet therapy is indicated, including taking Plavix and aspirin. Drug prevention plays an important role in the long-term results of the intervention and the life expectancy of patients.
- The first examination is carried out in the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period with mandatory ultrasound of peripheral vessels.
- Further examinations are carried out after a few months.
- One year after surgical treatment, MSCT angiography of the legs is mandatory.
Balloon angioplasty and stenting of the arteries of the lower extremities is an effective method of restoring blood flow in most occlusive lesions except the popliteal artery. In terms of its immediate results, this method is not inferior to open bypass surgery if performed according to strict indications. The advantage of endovascular surgery is low trauma, lack of pain, the possibility of repeated interventions, and a lower risk to life.
With the improvement of instruments for angioplasty and stenting, minimally invasive interventions are occupying an increasing place in the management of patients with critical ischemia and gangrene.
Life expectancy of patients with a stent
Before surgery, many patients are interested in how long they can live with a stent and whether they give them disability. Life expectancy largely depends on the patient’s age, concomitant diseases, and complications after the intervention.
On average, patients can live more than 10-15 years with a stent.
But of greater importance for many is the significant difference in well-being before and after the operation - the patient is less bothered by other uncomfortable sensations, their physical activity expands and they have the opportunity to do what they love.
[media=
https://youtu.be/7RIATl7INOM
]
How long such a life will last depends on following a diet, performing physical therapy, and timely treatment of all acute and chronic diseases.
Advertising:
Disability after stenting is not given, since such an operation improves, and does not worsen, the patient’s well-being and does not require significant restrictions after it is performed. However, there are a few exceptions. Law enforcement officers may become disabled after the installation of a stent, since excessive physical activity is prohibited after such a surgical procedure. Disability is often given to persons with concomitant severe diseases. The decision to recognize a patient as disabled is made by an expert commission consisting of several doctors.