Myocardial infarction occurs when the artery supplying the heart is completely or partially blocked. In this case, necrosis develops and cardiac muscle cells die.
In men, the disease occurs 5 times more often than in women. In addition, according to statistics, women encounter this pathology on average 10 years later. Experts attribute this to the late onset of atherosclerosis in women, which is one of the causes of heart attacks. Atherosclerosis, in turn, develops more slowly due to the presence of estrogens - female hormones, as well as due to less addiction to smoking and drinking alcohol. However, as both men and women age, the risk of having a heart attack increases.
Risk factors
They are divided into two groups:
- Modifiable (they can be changed or reduced impact): smoking, arterial hypertension, physical inactivity, high cholesterol, consumption of foods high in animal fats and high calorie content, diabetes mellitus, stress, excess weight, menopause and postmenopause, increased homocysteine.
- Unchangeable: age, genetic predisposition, gender.
Etiological factors are also identified:
- Atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries and the appearance of blood clots in them.
- Non-atherosclerotic lesions of the coronary vessels. It occurs when the walls of the arteries become inflamed due to vascular injuries, congenital anomalies, blood clotting disorders, and vasospasm. As a result, blood flow decreases.
How long do they stay in the hospital?
Myocardial infarction is a serious condition.
It is a form of ischemic pathology and is characterized by the development of necrosis of an area of the heart. About 50% of people die before being admitted to hospital. A third of patients die in the hospital due to the development of irreversible complications incompatible with life. A cerebral infarction is an acute circulatory disorder in which nerve cells die.
The patient has severe neurological symptoms. Every year, 360,000 Russians have a cerebral infarction. About 15% of patients die on the first day of the disease. Hospitalization for a heart attack is mandatory.
The medical institution carries out a number of resuscitation measures aimed at stopping the attack and preventing the development of complications of the disease. It is difficult to say exactly how many people with heart attacks are kept in hospital.
The following factors influence the length of hospital stay:
- patient's age;
- general health;
- type of heart attack;
- the presence of complications, the risk of their occurrence;
- the likelihood of a recurrent attack;
- the effectiveness of the therapy;
- the treatment method used.
To preserve life and prevent extensive cell death, the following procedures are performed in a hospital setting:
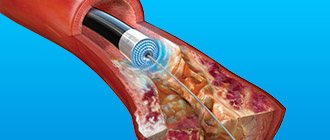
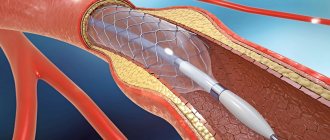
- stenting;
- angioplasty;
- coronary artery bypass grafting;
- catheterization
Measures are being taken to dissolve blood clots in the arteries. The first 5-7 days after a heart attack are considered the most life-threatening. Therefore, the patient is in the intensive care unit during this period.
If a person has a heart attack for the first time, he is kept in the hospital for about 28 days. If an attack occurs in a young patient, the acute condition is quickly relieved, and he can be discharged from the hospital after a couple of weeks.
People with post-infarction complications take the longest to undergo treatment. They may require not only drug therapy, but also surgical treatment. In this case, inpatient treatment may last more than a month.
Symptoms of a heart attack
Depends on the stage of development of the pathology.
Pre-infarction period
- Cardiac symptoms of a heart attack: shortness of breath, pain, cardiac arrhythmia, palpitations.
- Non-cardiac symptoms: dizziness, sweating and weakness, lips and tissues under the nail plates turn blue.
The most acute period
- The main symptom is pain.
- The sensations are intense and pressing. Localized behind the sternum. They can spread throughout the chest or only on the left or right.
- Some feel burning pain - younger patients experience more severe pain, older patients experience it weaker. Smoothed sensations appear in those who suffer from diabetes.
- The skin is pale. Sweating, shortness of breath, increased heart rate, and arrhythmia may occur.
- The pain often radiates to the shoulder, shoulder blade, jaw, wrist, and ear on the left side.
- The pain syndrome can manifest itself in waves: increase, reach a peak, and decrease.
Acute period
At this stage, the final formation of a necrosis focus occurs. The pain disappears. If it is still felt, then the heart attack zone is still expanding. Other symptoms include low blood pressure and rapid pulse.
Atypical forms of myocardial infarction
There are also atypical forms of myocardial infarction. Their symptoms are often similar to those of other diseases, which makes it difficult to diagnose the pathology.
- Asthmatic. Pronounced symptoms include suffocation, coughing, cold sweat, and wheezing in the lungs. There is either no pain at all or it is mild.
- Abdominal. Signs: epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, stool upset, a tense and painful abdomen. With this form, acute appendicitis is often suspected.
- Arrhythmic. Signs: heart rhythm and conduction disturbances, low blood pressure. Symptoms similar to those of cerebral ischemia also appear: dizziness, vision becomes dark, and the patient loses consciousness.
- Cerebrovascular. There are also symptoms similar to a condition when the brain does not receive enough oxygen: dizziness, fainting, weakness, blurred vision. There is almost no pain felt.
- Asymptomatic. It is usually discovered in older people during examinations associated with other diseases: diabetes mellitus and others. If signs of a heart attack occur, patients ignore them because the symptoms quickly pass. A heart attack is noticed accidentally during electrocardiography.
- Heart attack with atypical pain syndrome . Unpleasant sensations are felt in areas far from the heart: hand, shoulder blade, jaw. A false picture emerges; doctors suspect osteochondrosis or other diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
How many days does a paid ballot last?
Let's consider how long they keep on a certificate of incapacity for work in case of myocardial infarction. The approximate periods of temporary disability for this disease are established in the Recommendations of the Ministry of Health of Russia No. 2510/9362-34 of August 20, 2000 (hereinafter referred to as the Recommendations) and are:
- 70-90 calendars. days – in case of acute transmural infarction of the anterior or lower myocardial wall, as well as other specified localizations without significant complications with mild anginal syndrome and 90-130 calendar days. days if complications of the acute period occur.
- 60-70 calendars. days – in acute subendocardial (non-transmural) myocardial infarction without complications and longer periods in cases of heart failure, depending on its degree:
- I FC, i.e. not causing discomfort during physical activity (60-80 calendar days);
- FC II, when physical activity causes moderate, minor discomfort (80-110 calendar days);
- III-IV FC, in which poor health can manifest itself even at rest (90-120 calendar days).
- 90-120 calendars. days – repeated myocardial infarction.
Important! It should be noted that for all types of heart attack, accompanied by complications in the acute period, as well as for repeated heart attack, in accordance with the Recommendations, it is possible to be referred for a medical and social examination to obtain disability.
How long does the period of disability last after cardiac stenting and bypass surgery?
The need for surgical intervention for myocardial infarction occurs quite often. There are two types of operations that radically solve the problem of acute coronary circulatory disorders:
- bypass surgery is a cavity operation to install a shunt, the purpose of which is to create an artificial path for blood movement;
- Stenting is an endovascular intervention in which an implant is inserted through a puncture in the artery through a catheter, expanding the vessel in the place where it is needed.
The duration of sick leave directly depends on which of these operations the doctor will resort to.
Bypass surgery is a full-fledged surgery and is performed on a stopped heart during artificial ventilation with the patient being placed under anesthesia.
Accordingly, the recovery period after such an operation will last as long as the doctor decides , guided by Part 4 of Art. 59 of the Federal Law “On the Fundamentals of Protecting the Health of Citizens in the Russian Federation”, according to which, if the prognosis is favorable, after 10 months from the date of opening the sick leave, the patient must either be discharged to work or referred to the ITU to resolve the issue of assigning disability.
The average period of sick leave after coronary artery bypass surgery is 90 calendar days. As a result of stenting, which does not require putting the patient under anesthesia and is not associated with a chest incision, the recovery period will be shorter, however, in this case, the doctor will focus on the general condition of the patient and many other factors.
Regarding the duration of sick leave, the medical worker, as in the case discussed above, will be limited to a ten-month period.
Attention! On average, after stenting, the need for which arose as a result of myocardial infarction, the patient is on sick leave for about 60 calendar days.
The further duration of sick leave depends on the characteristics of the postoperative period.
Diagnosis of heart attack
ECG plays a major role in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction. Electrocardiography is repeated several times, since in the first hours and even days the ECG manifestations of a heart attack are often not clearly expressed and appear later.
In addition to this study, the doctor prescribes:
- UAC. 5-6 hours after a heart attack, the number of leukocytes increases, and on the second day - ESR. Leukocytosis decreases after 7 days. If elevated levels persist, this indicates complications.
- Biochemical analysis of blood serum. A change in certain indicators will indicate the death of heart muscle cells.
- If the methods listed above are not informative (for example, due to the presence of concomitant diseases), selective coronary angiography is performed.
What kind of care is provided to a patient in intensive care?
A patient diagnosed by an ambulance with acute coronary syndrome is immediately taken to the intensive care unit.
Often, large cardiology clinics have separate specialized infarction intensive care units. Resuscitation during a heart attack primarily consists of providing the damaged heart muscle with oxygen, stopping the developed life-threatening arrhythmias, and correcting hemodynamic disorders and thrombus formation.
To do this, the following procedures are used:
- oxygen therapy - the patient is connected to a ventilator to combat hypoxia;
- infusion therapy - indicated to restore normal blood supply to tissues, water and electrolyte balance, and is used to provide parenteral (intravenous) nutrition;
- sedation – during a heart attack it is very important to calm the patient’s nervous system, for which appropriate medications are used;
- pain relief – ischemia of the heart muscle is accompanied by intense pain, which can lead to the development of shock, so it is relieved with the help of narcotic analgesics;
- prevention of thrombus formation or dissolution of a formed thrombus - it is very important to prevent a recurrent attack or to ensure access of oxygen to the ischemic area, for which anticoagulants such as heparin or warfarin are prescribed;
- strict bed rest is necessary to minimize physical activity and restore the body.
While in intensive care, the patient can be treated surgically:
stenting of coronary arteries;- coronary artery bypass grafting;
- laser angioplasty;
- balloon dilatation of coronary vessels.
Patients are in intensive care after a heart attack under constant supervision of medical personnel. They are connected to equipment around the clock, which automatically takes an ECG, monitors blood pressure, respiration, heartbeat and other indicators. If the patient develops clinical death, he is urgently given cardiopulmonary resuscitation, which consists of the following actions:
- indirect cardiac massage;
- artificial ventilation;
- defibrillation;
- drug support for the patient.
Recovery after a heart attack
Rehabilitation after a heart attack is a whole complex of measures. Moreover, for each patient they are developed individually, taking into account the characteristics of his health, as well as the speed and quality of medical care provided during a heart attack. Patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction need to be regularly monitored by a cardiologist, at least once a year, and strictly monitor blood pressure levels and cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
Physical rehabilitation
Increasing physical activity after a heart attack is one of the important points of rehabilitation. Unnecessarily prolonged bed rest can have a negative impact on health - lead to muscle weakness, the development of congestive pneumonia and increase the risk of thromboembolic complications. And this, in turn, affects the recovery time. In the hospital, after acute pain has been relieved, the severity of the heart attack is assessed and a rehabilitation program is offered. In the future, they judge by the dynamics and transfer the patient to the next stage of activity.
Long-term physical rehabilitation will help prevent recurrent myocardial infarction. At the same time, psychological support from family and friends, their care and the mood of the patient himself are also important. Therefore, during rehabilitation, psychological work is also carried out, which helps reduce stress and speed up recovery.
FIND OUT PRICES
Grounds for issuing a certificate of incapacity for work
Myocardial infarction is an acute condition that threatens not only the health of the patient, but also his life, therefore, any person who applies to a licensed medical institution for medical care has the right to issue a sick leave certificate and receive temporary disability benefits if he is insured in system of compulsory health insurance and is an employee in the sense provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In this case, the basis for issuing sick leave is a combination of the following factors :
- the occurrence of an insured event in the form of a myocardial infarction, certified by a doctor at a licensed medical institution;
- insurance of a person in the compulsory medical insurance system;
- the sick person is a person who is in an employment relationship with the employer in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (this fact is not subject to any verification and the patient’s oral statement is sufficient for the health worker).
Myocardial infarction is a serious disease in itself, in which the doctor opens a certificate of incapacity for work absolutely , and if surgical intervention is necessary to treat it (which happens in the vast majority of cases), it is all the more impossible to do without a certificate.
Grounds for extending sick leave
The main reason for extending sick leave is unrestored ability to work. If a person feels unwell or has post-infarction complications, then his release from work is extended.
Often, people who have suffered an attack are recommended to undergo rehabilitation in a sanatorium. Patients with grade 1-3 severity of the condition are usually referred to such institutions. In sanatorium conditions, physiotherapy, massage, and physical therapy are carried out.
All these procedures are aimed at restoring working capacity and maintaining health. Sanatorium treatment is also the basis for extending sick leave.
Exemption from work is given for the entire period of stay in such an institution. If a person who has had a heart attack requires invasive procedures, they cannot perform their job duties. In this case, the sick leave is extended. When extending a certificate of incapacity for work, the type of activity of a person also plays a big role.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilyeva
Civil law expert
People of certain professions (pilots, installers, cooks, security guards, tour guides, teachers, crane operators, stewards) with a history of heart attack are not allowed to perform job duties. They receive a disability group.
Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
— contact the on-duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call:
+7
— Moscow and region.
+7
— St. Petersburg and region.
8
- Other regions of the Russian Federation
You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will take care of solving all your problems!
Estimated duration of disability
People who have had an attack have a question about how long sick leave lasts after a heart attack. When inpatient therapy ends, a person needs to undergo outpatient treatment and recovery. To do this, he is given a certificate of incapacity for work.
How many days of sick leave after a heart attack lasts depends on the following factors:
- type of pathology;
- general health, well-being;
- severity of the disease;
- presence of complications;
- type of human activity;
- the patient's working conditions;
- compliance by the patient with the treatment regimen selected by the doctor;
- following a correct lifestyle;
- the need for rehabilitation in a sanatorium.
The local doctor has the right to issue sick leave for up to 15 days. Further release from work can be extended. The decision on the need to continue, terminate outpatient treatment or send the patient to a hospital is made by the medical commission.
As a rule, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued for a period of two to four months. In some cases, a person who has had a heart attack is assigned a disability group. Then the sick leave is closed. In most cases, it is possible to maintain the ability to work.
Therefore, after recovery, a person begins to work. Before this, he goes through a commission, which makes, if necessary, a decision to change working conditions, reduce workloads, and shorten the working day.
Sometimes a person is recommended to be transferred to an easier position. If the patient previously worked on night shifts, then daytime work is indicated for him.