Blood pressure is an integral indicator of human health and the fitness of the entire cardiovascular system.
By pressure in the general sense we mean its arterial variety, since it plays the greatest role.
Blood pressure is the force with which hematological fluid exerts pressure on the walls of blood vessels. The blood pressure value is determined by the difference between the barometer readings (atmospheric pressure level) and the tonometer readings.
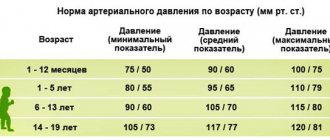
There are two main variants of pathological deviation of blood pressure values from the norm: hypertension (values above 140 to 90 mmHg) and hypotension (a decrease in the device’s readings below the permissible values of 100 to 70). The lower the blood pressure level, the more serious the reasons that brought about this phenomenon.
Blood pressure 110/50 mm Hg. Art. cannot be considered a variant of the norm for the very reason that the difference between systolic and diastolic indicators is 60 mm Hg (normally this value is no more than 50 mm).
This situation is called isolated hypotension and is considered a dangerous disease requiring medical correction. For what reasons does blood pressure decrease, and how to cope with this scourge?
When is a blood pressure of 110 over 50 normal?
{banner_banstat0}
It would not be an exaggeration to say never. In extremely rare cases, such blood pressure may be a working option, but this is casuistry.
Because there is a serious difference between systolic and diastolic indicators. Diagnosis and appropriate treatment for this condition are required. It's dangerous.
Diagnostics and specialists
If hypotension is regular and associated symptoms are present, it’s time to consult a specialist. In this case, you should go to a therapist.
To make a diagnosis, the therapist will need to study the life and family history, listen to the patient’s complaints, and also pay attention to the reasons and circumstances in which the symptoms accompanying hypotension arose. In case of ambiguous indications, the therapist may prescribe the following series of diagnostic procedures:
- blood and/or urine test;
- Ultrasound examinations (ultrasound) of the chest and abdominal organs;
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- radiography;
- electrocardiography;
- echocardiography, etc.
Serial tonometry results are the main diagnostic indicator, demonstrating fluctuations in blood pressure at different times of the day and in different situations.
In what cases do we talk about pathology?
{banner_banstat1}
This condition is considered pathological in 99% of cases. In 1% of situations, physiological factors for the development of isolated diastolic hypotension are possible. The latter should be considered in more detail.
Age
During early and late puberty, and possibly throughout puberty, surges in blood pressure occur.
This is a normal process, and the reason is the influence of a hormonal factor: the nature of the production of androgens and estrogens, as well as cortisol, catecholamines and adrenal hormones in general, changes.
Interesting:
More often, adverse events from the cardiovascular system are observed in male adolescents; girls are considered more resilient due to their physiology.
The second peak of changes in blood pressure regulation occurs at 50-60 years of age, the period of the so-called premenopause, menopause and postmenopause.
It would be a misconception to believe that menopause is a purely female phenomenon. It also exists in men and is caused by a similar process by a decrease in the concentration of androgens: testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, androstenedione and other substances.
In women, we are talking about disturbances in the production of estrogen and progesterone. Hence pressure surges, constant hypertension or hypotension. Clinical variants of the conditions are different.
Body type
{banner_banstat2}
Pressure of 110 over 50 can occur in people with a special body constitution. For example, in slender representatives of both sexes with an asthenic physique.
This is not the norm, as has already been said. Most likely we are talking about a concomitant pathological process.
Hypotension is rare in thin, large, or obese patients. In this case we are talking about a clear pathology.
Peak hormonal states
In addition to menopause and the already mentioned puberty, representatives of the fairer sex have two more conditions: menstruation in any phase and pregnancy.
Both are associated with disturbances in the regulation of vascular tone. Most often, severe hypotension occurs. Clinical variations of this process also vary.
Other factors
Features of professional activity, place of residence. In this case we have to talk about adaptive mechanisms.
Metallurgists and residents of the southern regions “suffer” from physiological hypotension. This is how the cardiovascular system protects itself from overload.
The influence of diet and bad habits is possible, but these factors are not so significant and rather provoke hypertension.
Indicators 90/50 during pregnancy
A pregnant woman experiences constant changes in hormonal levels, which provokes changes in blood pressure. If during pregnancy the indicators drop to 90 to 50 or 90 to 55, then this indicates the formation of the following conditions:
Blood pressure 80 over 60 - what does this mean?
- high susceptibility to stress;
- excessive nervous and mental stress;
- a sign of toxicosis;
- vascular and heart diseases;
- disruption of the vegetative-vascular center.
A decrease in parameters can be observed if the pregnant woman is in an incorrect position during night sleep (on her back), which leads to circulatory disorders, so experts recommend that women lie on their sides.
Causes of low blood pressure
The most common factors causing the problem should be considered.
For women, this is pregnancy or gestation. Low blood pressure is a normal physiological phenomenon. It is associated with a change in the balance of estrogen and progesterone, which are partly responsible for regulating blood pressure levels.
On the other hand, a redistribution of blood circulation occurs. Tissue nutrition is disrupted. The cardiovascular system is being rebuilt into a different working mode. Things may not be so simple. It is possible to develop pituitary tumors of both secreting and non-secreting types.
In the first case, the neoplasm is capable of producing hormones, including TSH, prolactin, disrupting the functioning of the endocrine system; in the other, it can compress the hypothalamus and disrupt the secretion of hormones (hypopituitarism and other “charms”).
In all controversial cases, it is recommended to undergo an MRI; it is safe and informative. In the presence of a space-occupying formation, the pressure can be 110 over 55, 110 over 40, which is even more dangerous.
In medical science and practice, etiological (root cause) factors in the development of isolated hypotension are divided into several groups.
Endocrine factor
{banner_banstat3}
This is the most significant group of reasons in terms of volume. Among the main elements are:
- Violation of the synthesis of adrenal hormones. Primarily ACTH, adrenaline, norepinephrine. The lack of hormones has a hypertensive (increasing blood pressure) effect.
- Changes in the nature of production by the cells of the anterior pituitary gland (adenohypophysis). First of all, we are talking about dopamine and catecholamines. Secondly, about vasopressin. With their deficiency, the pressure decreases significantly, and the correlation is determined by the degree of synthesis disruption.
- Lack of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream. The so-called hypothyroidism. It is caused by decreased activity of the thyroid gland. Here, slight deviations from the considered indicators of blood pressure 112-113 to 50-55 are likely.
This type of condition is possible in the presence of tumors, injuries, and toxic lesions. You need to understand each specific case.
Disorders of the autonomic nervous system
{banner_banstat4}
Excessive production of acetylcholine (a special substance that ensures nerve conduction) and insufficient synthesis of catecholamines affect it.
As a result, the sensitivity of the receptors of the heart and blood vessels decreases, the tone of the blood structures, arteries, veins, and capillaries is disrupted.
The process is of generalized origin, that is, it affects the entire body at once.
Cerebrovascular accident
As a result of insufficient nutrition of special centers of cerebral structures, a disruption of the normal regulation of vascular tone occurs. This is also a generalized process.
It is observed in several diseases and pathological conditions at once: osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, heart attacks, strokes and the rehabilitation period after them. Vertebrobasilar insufficiency plays an important role.
Other diseases
{banner_banstat5}
- Imbalance of special substances: kinins, prostaglandins. The result of such changes is the inhibition of the effects of vasopressin on the body. This hormone is responsible for normal diuresis and also has a hypertensive effect (increases blood pressure levels).
- Post-traumatic conditions. Including periods of rehabilitation after a stroke, heart attack, or severe injuries. In this case, a change in the nature of hemodynamics is observed. A temporary redistribution of blood circulation occurs.
- Anemic processes. Almost always associated with bleeding and loss of hematological fluid. This results in a violation of the volume of circulating blood and general changes in blood circulation and tissue nutrition, including the heart muscle.
Humoral causes are also possible, which are explained by an imbalance of hypertensive (lowering blood pressure) and hypotensive (increasing blood pressure) substances. As a result, for example, long-term fasting, intoxications of various etiologies.
A pressure of 110 over 50 in adults means that something is wrong in the body, 70% of cases are hormonal. You need to sort it out with your doctor.
What does the tonometer reading 105 to 65 mean?
The vascular walls are constantly exposed to pressure from the blood passing through the blood vessels. The pumping function of the heart and the elasticity of blood vessels have a direct impact on the strength of this pressure.
The highest pressure, systolic, is recorded at the moments when cardiac contraction occurs, and the stage of the cardiac cycle itself, when pressure increases (heart contraction), is called systole.
In the intervals between heart contractions, the heart muscles relax and blood pressure decreases. This value (second digit) is called diastolic, and the corresponding stage of the cardiac cycle, when the muscles are relaxed, is called diastole.
An electronic blood pressure monitor typically displays pressure readings from top to bottom: systolic pressure will be located at the top of the display, and diastolic pressure will be at the bottom. That is, the upper number 105 is the person’s systolic pressure, and the lower 65 is the diastolic pressure.
This is an alarm bell and a reason for a person to pay more attention to their health, because a pressure of 105 over 65 is slightly lower than the reference readings of 120/80. In some cases, it indicates the beginning of some pathological processes in the body.
Consequences of low pressure
Low blood pressure poses a tremendous danger to the health and even life of the patient.
The following pathological consequences are possible:
- Collaptoid and syncope states. In other words, fainting. As a result of loss of consciousness, injuries of varying severity may occur. Because an attack of low blood pressure can catch a person in the most inappropriate place (on the road, on the stairs).
- Stroke as a result of a sharp jump in blood pressure. Hemorrhagic type with the formation of a hematoma in most cases.
- A heart attack, in other words, is a malnutrition of the heart muscle.
- Early dementia as a result of weak cerebral circulation. Causes phenomena similar to symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
- Early death as a result of “wear and tear” of the heart.
In patients with hypotension, the quality of life decreases significantly. To avoid becoming a victim of this insidious condition, you need to undergo treatment on time.
A sharp decrease in blood pressure from 100 to 60 - first aid
A person's blood pressure is 100 over 60 and is dangerous if it has dropped quickly from normal levels. This happens in the following cases:
- blood loss after injury,
- a consequence of prolonged lying position of the patient,
- severe infections
- diarrhea,
- taking diuretics and antihypertensive drugs,
- internal bleeding from the stomach or intestines,
- physical exhaustion,
- lowering blood glucose in diabetics,
- allergic conditions,
- paroxysmal tachycardia,
- atrial fibrillation,
- myocardial infarction,
- taking drugs.
In such cases, emergency assistance is required. A sharp decrease in blood pressure is dangerous due to disruption of the blood supply to vital organs - the brain, heart.
What to do if your blood pressure drops quickly:
- without wasting time, call an ambulance,
- put the person on his back with his head down, while raising his legs,
- In the hospital, during infections, doctors restore the volume of circulating blood with intravenous drips of saline. At the same time, antibiotics are used
- in case of blood loss after injury, plasma and rehydrants are administered.
Important! Do not try to diagnose on the Internet and treat using traditional methods. Losing time can cost a person his life.
Symptoms that require you to see a doctor
{banner_banstat7}
As a rule, physiological hypotension does not make itself known by specific symptoms. The maximum that the patient feels is slight weakness and drowsiness. In all other cases, a clinical picture of varying completeness develops.
You can define a list of manifestations as follows:
- Low-grade fever or increased body temperature (this also happens, the exact etiology of the process is not clear).
- Headache (or cephalgia). It is explained by insufficient nutrition of brain structures.
- Dizziness. The vestibular apparatus, centered in the cerebellum, is affected.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting that does not bring relief.
- Intolerance to travel by transport, including water (motion sickness).
- Palpitations (tachycardia) or the reverse process of baracardia.
- Weakness, mental impairment, decreased cognitive function up to dementia, if the process has been going on for a long time.
- Orthostatic fainting with sudden movements and changes in body position.
- Shortness of breath even at rest. Increases with physical activity.
Any of the symptoms presented is a reason to be wary and call an ambulance.
Characteristic signs of reduced values
Of course, the main signs of low pressure are the tonometer readings - ninety to fifty. However, hypotension can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- causeless weakness, fatigue;
- pale skin;
- headaches in the temples, forehead;
- dizziness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- fainting;
- pain in the heart area;
- frequent urge to yawn.
In cases where hypotension develops against the background of other pathologies, the symptoms are supplemented by other signs characteristic of them.
No ads 2
What treatment will be required?
You can improve your well-being only by undergoing a course of treatment of the primary pathology that causes hypotension. Therapeutic measures are prescribed by a doctor: a cardiologist, endocrinologist or neurologist.
Typically, pharmaceutical drugs are used:
- Tonic blood vessels (aspirin, Citramon).
- Substitutes for natural hormonal substances (preparations based on thyroid hormones, etc.).
- Sedatives of natural origin (Corvalol, Valerian, Motherwort).
But this is not enough. It is necessary to adjust your lifestyle: stop smoking, alcohol, adhere to a strict regime of physical activity and rest.
It is important to normalize the diet: eat as many fortified foods as possible, as little fatty, fried, smoked foods as possible. It is necessary to optimize the consumption of table salt. It has hypertensive properties (increases blood pressure).
Prevention measures
For good health and normal blood pressure, you should adhere to the following preventive rules:
- Get enough sleep. Experts strongly do not recommend sleeping less than 6 hours a day, and the optimal duration of daily sleep is 8 hours. It is also recommended to spend some time in bed after the signal to get up: stretch, warm up, do a short warm-up while lying down.
- Proper and regular nutrition. Avoid diets, but stick to a proper diet with optimal protein, fat and carbohydrate content. It's better to eat more often, but less.
- Vitamins. It is important not only to eat a variety of foods and do it on time, but also to ensure that the menu contains a sufficient amount of vitamins. If difficulties arise with this, it is recommended to take multivitamins in courses according to the recommendations of the therapist or the instructions of each specific manufacturer.
- Daily walks. Walking in the fresh air not only saturates the human body with oxygen and vitamin D, but also provides healthy physical activity.
- Hardening. Hardening not only improves immunity, but also strengthens blood vessels, which is extremely important when the pressure is 105/65, which is not normal for a particular person.
- Exercise stress. Preference should be given to short, but moderately intense exercise, after which a person will not feel like after a marathon. For example, active morning exercise for twenty minutes is an excellent choice.
- Correct mode of operation. For people with a blood pressure of 105 over 65, it makes sense to choose jobs with a schedule that does not involve staying at work in the evening and on night shifts. It's best to work early in the morning. This is important due to the fact that the strength of hypotensive people runs out quite quickly, and after the lunch break they may notice their decline.
- Rest. You shouldn’t get too involved in physical exercise and the work process: rest is no less important. A hot bath, aromatherapy, relaxing massage are great helpers with this.
Pulse
Pulse indicators with hypotension are very variable.
And also read on our website: What do blood pressure readings of 150 to 100 mean, how to reduce them, what pills to take, causes and treatment
A pulse of 60 to 90 beats per minute is considered normal if it is combined with chronic hypotension, then in this case low blood pressure is not considered an indication for hospitalization, however, in some cases additional examinations are required to exclude certain pathologies.
A slight increase in pulse readings with arterial hypotonicity is also normal, as this is a compensatory reaction of the body to a decrease in blood pressure. This is how the body provides vital organs with oxygen and nutrients, since without them existence is impossible.
The combination of low blood pressure and a drop in heart rate may result from:
- high-grade blood loss;
- septic condition;
- anaphylaxis;
- states of shock;
- heat stroke;
- hemorrhages in brain tissue.
A slow heart rate with hypotension can be caused by:
- congenital characteristics;
- hypothermia;
- atherosclerosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- pericarditis;
- myocarditis;
- endocarditis;
- oncopathology;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- intoxication of the body.