Basic functions of platelets
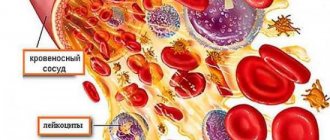
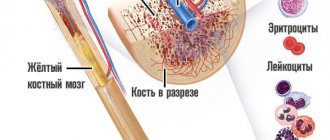
In appearance, platelets are round or oval red plates with a smooth surface. They are formed in the bone marrow. They mature in approximately 8 days. These components constantly circulate in the bloodstream.
The main function of platelets is to ensure blood clotting. In addition, the ability of these blood components to stop bleeding is important. This is ensured by the fact that individual platelets can stick together and stick to sites of vascular damage. The process is automatically started by the human body when there is a risk of bleeding.
An important question is how long platelets live. Their viability time lasts approximately 10 days. Depending on the age of the red plates, their size changes: from 2 to 5 microns in diameter.
The process of platelet renewal in the blood occurs constantly. Therefore, an important factor to ensure the maintenance of blood condition is the balance between the formation of red plates and their death. Otherwise, there may be a tendency to blood clots or increased bleeding.
Platelets are...
A thrombus is a blood clot (translated from Greek), the basis of which is platelets.
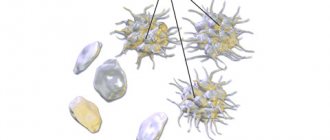
A platelet is a small, colorless, spherical platelet of blood (Bizzocero plaque). Plates are formed from the plasma structure (megakaryocytes - plasma cells) of the bone marrow. Platelets do not have a nucleus, but are equipped with an abundant number of granules (more than 200).
The value of granulations is due to the high content of special components of platelet growth (thromboxane, thrombin, adenosine diphosphorate and other factors), which ensure the formation of amino acids and enzymes (what are they?) that destroy the membranes of bacterial cells, of pathogens into the blood
The size of platelet plates varies within their age (young, middle, mature), from 2 to 5 microns.
However, when a platelet comes into contact with a surface that does not correspond to the internal vascular endothelium or the cavity of the cardiac pericardium, the plates are activated, releasing up to 10 pseudopods (processes) tens of times larger than the size of the plate itself.
This feature allows platelets to serve as a kind of “patch” that, if necessary, covers the wound surfaces of blood vessels, preventing bleeding.
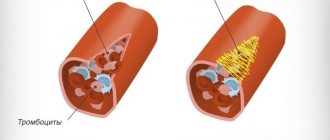
It is the pseudopods that ensure the movement of the plates through the circulatory system. Platelets have the ability to adhere to foreign agents , capture them and destroy them, form a blood clot by aggregation (gluing the plates together) to prevent hemorrhagic processes (bleeding).
The main role of platelets is to actively participate in the process of blood clotting (hemostasis).
They provide a transport function, delivering nutritional components to the tissues (endothelium) lining the internal cavity of the vascular walls. They remain viable for up to 10 days , after which they are destroyed in various organs (spleen, lungs, or liver).
Recent developments by Japanese scientists have proven that megakaryocytes are not the only sources of formation of Bitsocerro plaques (platelets). They were able to obtain platelets from the patient's own stem cells.
These studies increase the success of transplantation, since the presence of such platelets does not cause the body to reject donor organs.
How platelets participate in the process of hemostasis can be seen in the diagram:
Having appreciated the basic functions of platelets, you can understand what their imbalance in the body entails and what the negative consequences may be.
Any imbalance in platelet activity and number is medically called thrombocytopathy.
- A decrease in the concentration of platelet platelets is called thrombocytopenia.
- And an increased concentration is thrombocytosis.
- A dysfunction of their activity is diagnosed as thrombosthenia.
Blood test for platelets
A complete blood test can determine the platelet count. The main indications for its implementation are the following:
- Increased bleeding of gums.
- Heavy menstruation.
- The appearance of bruises from minor impacts.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- Difficulty stopping bleeding from minor injuries.
The number of platelets in the blood is measured in thousands per 1 microliter of blood. Counting is carried out in specialized laboratories in various ways that guarantee high accuracy.
The normal platelet count in the blood depends on gender and age and is:
- For men, 200–400 thousand.
- In women, 180–320 thousand, during menstruation the amount can decrease to 75–220 thousand, and during pregnancy to 100–310 thousand.
- In children, indicators depend on age, and the corresponding values are given in special tables.
To conduct a general blood test, blood is taken from a finger. No special preliminary preparation is required before this. To ensure accurate results, it is better to donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. At the same time, 12 hours before the procedure it is not recommended to consume fatty spicy foods, carbonated drinks, and alcohol.
Additionally, to determine blood clotting indicators, Sukharev and Lee-White tests are performed. They are informative and allow you to obtain the necessary additional data about the pathological condition. This will allow you to carry out correct treatment measures and avoid dangerous consequences.
Blood tests
In the category of qualitative transformations of platelets, there is a deficiency or blockade of membrane receptors or the absence of compact granules. Symptoms of hemorrhagic diathesis arise due to a shift in the release of spherosomes, when the production of thromboxane and prostaglandins is impaired. An anomaly and deficiency of von Willebrand factor, as well as a violation of the interchange of nucleotides and calcium movement, are important.
In modern medicine, the following types of blood tests are used:
- general clinical;
- biochemical research;
- determination of the degree of coagulation;
- Sukharev's test.
Blood testing is recommended as the first step in making a diagnosis. As a result of laboratory tests, pathology is revealed and the true state of the human body is reflected.
General clinical
Based on the results of the study, the level of hemoglobin, the number of leukocytes, lymphocytes are checked, the color coefficient, the degree of erythrocyte sedimentation (ESR) are determined, and the volume of platelets present is shown in the overall picture. Based on the research, the degree of functioning of the body is determined and deviations from the norm are identified.
A general analysis is prescribed by a doctor to confirm or refute:
- the appearance of inflammation;
- development of diseases of hematopoietic organs and systems;
- the occurrence of immune failures;
- allergic reactions.
The analysis is recommended for pregnant women, patients with varicose veins, heart and vascular diseases. The study is necessary for organ pathologies and autoimmune diseases. The analysis does not require complex preparation; the morning time before breakfast is more suitable for taking blood.
Biochemical research
The analysis informs the doctor and provides a detailed table of indicators, so a large volume of blood is required, which is taken from a vein. Biochemical indicators reflect the functioning of most organs and the degree of development of the disease.
Check shows:
- inflammatory processes;
- indicators of the state of the blood system;
- position of water-salt exchange;
- volumes of microelements important for life.
As a result, the indicator of proteins and carbohydrates is determined, the level of blood enzymes, and the concentration of bilirubin are checked. An advanced biochemical analysis shows whether the content of trace elements is normal or not. As a result, nitrogen metabolism is examined, the presence of urea and creatinine is established.
Determination of clotting
The study reveals the rate of blood clot formation and platelet aggregation. Extension of the indicator leads to excess blood loss, and low activity of flat bodies causes blockages of blood vessels. Pregnant women are tested twice, since timely clotting is very important during childbirth. The occurrence of traffic jams is dangerous with varicose veins because it causes the appearance of blood clots. A coagulogram is prescribed before surgical treatment or extensive blood transfusion.
The analysis is carried out before the morning meal or 8 hours after a meal; alcohol intake is not recommended. 1 ml of blood is taken from a vein and divided into two tubes. The samples are kept at a temperature of +37˚C, and the time from blood collection to the start of the clotting stage is determined.
Diagnostics according to Sukharev
In the process, the time of blood thickening to the time of its complete immobility is studied. The development of the procedure should be limited to a period of 35-120 seconds, and the end of the process is extended to 3.5-5.0 minutes.
Decreased indicators indicate changes:
- anemia of various origins;
- pregnancy;
- improper functioning of platelets;
- excessive use of blood thinning medications.
Accelerated clotting indicates hormonal imbalances, the development of atherosclerosis, and infectious lesions in the body. For analysis, a Panchenkov tube is used, blood is taken from a finger, the first drop is removed with cotton wool. The capillary is filled to the control level and placed horizontally. After 30 seconds, the laboratory technician turns the tube over, changing sides, and uses a stopwatch while working.
Increased platelet levels
Elevated platelets are a pathological condition. It is called thrombocytosis. The main danger of the pathology is the increased risk of blood clots.
The cause of an increase in the level of platelets in the blood can be various diseases. Most often thrombocytosis occurs against the background of:
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Infectious diseases.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Surgical operations.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Kidney failure.
High levels of platelets in the blood are observed in older people. Temporarily, indicators may increase after heavy physical exertion, for example, after playing sports.
The symptoms of thrombocytosis are characteristic, but mild. It is imperative to conduct a general blood test if the following symptoms are noted:
- Pain in the fingers and toes.
- Itching of skin surfaces.
- Unreasonable weakness, which leads to decreased performance.
- Lack of appetite.
What do elevated platelets mean?
An increase in the concentration of Bizzocero plaques can warn of the presence of various pathological processes - the development of tuberculosis infection, blood cancer (leukemia), cancer of various organs, Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Thrombocytosis (increased platelets) is a constant companion :
- erythrocytosis;
- inflammatory intestinal and joint pathologies;
- chronic form of myeloid leukemia;
- acute course of infectious diseases;
- intravascular hemolysis and anemia.
lead to an increase in the number of platelets , which can ultimately lead to the development of thrombocytemia and failure of the functions of stem cells in the bone marrow.
Oddly enough, significant blood loss does not reduce the concentration of platelet platelets, but, on the contrary, increases it. This is due to the presence of compensated properties of the body that can replenish platelet losses.
It doesn’t matter for what reasons platelets go beyond the normative values. In such a situation, a medical assessment with appropriate therapy is necessary.
Decreased platelet levels
Low platelet levels, the norm of which differs between men and women, provoke the development of a condition known as thrombocytopenia. Very often it occurs against the background of uncontrolled use of medications: antidepressants and antibiotics.
The reasons for a decrease in the level of platelets in the blood can be various infectious diseases: ARVI, hepatitis, herpes, etc. Thrombocytopenia can be observed when a large number of blood thinning products are included in the diet. These are ginger, cherries, garlic, onions, etc.
Non-infectious factors that reduce the level of platelets in the blood include pregnancy, vitamin deficiency, alcohol or heavy metal poisoning.
Thrombocytopenia can be suspected based on the following signs:
- Heavy menstruation.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- The appearance of hematomas.
With a constant pathological decrease in the level of platelets in the blood, the risks of developing severe bleeding and stroke conditions, which are life-threatening, increase.
Restoring platelet levels in the blood
You can normalize the level of platelets in the blood with a balanced diet. It is important to saturate your diet with foods high in materials and microelements. You need to give up spicy food, alcohol, fast food and sweet carbonated drinks, lead a healthy lifestyle and maintain a drinking regime.
If it is not possible to normalize the indicators using natural methods, then you need to undergo a full examination by a hematologist. If platelet levels are elevated, special medications may be prescribed - anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents. They thin the blood and minimize the risk of blood clots. But at the same time, they should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. It should be understood that stabilization of the condition is possible only after eliminating the underlying causes that provoke deviations from the norm.