Treatment tactics
Treatment of pulmonary artery diseases depends on the severity of the process. As for stenosis, in the absence of pronounced manifestations, there is no need for surgical intervention, but clinical observation and symptomatic therapy are required.
As the pathology progresses, the question of surgical treatment arises. When the pressure gradient increases above 50 mmHg, the question of surgery is not discussed - it must be performed immediately. Operation options are different. Valvuloplasty can be open, closed, endoscopic - balloon. Indications for a specific intervention are determined by a specialist.
The main directions in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension are the prevention of thrombosis, elimination of spasm of vascular smooth muscle fibers, stopping the proliferation of connective tissue structures of the vascular wall. In this case, the following application is indicated:
· drugs that normalize blood clotting;
· diuretics;
cardiac glycosides;
· vasodilators;
· oxygen therapy.
In case of hypertension, called secondary, complex measures should correct the underlying pathology - the root cause of the increase in pressure in the artery. The list often includes bronchodilators and corticosteroids.
Surgical treatment for hypertension: embolectomy, lung transplant, pulmonary-cardiac complex transplant.
Pulmonary embolism
Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism
Clinical manifestations of pulmonary emboli depend on the location of emboli, the degree of pulmonary blood flow impairment and concomitant diseases. Clinical signs, although not specific, give reason to suspect the disease and roughly judge the location of the lesion. With embolism of the distal branches of the pulmonary arteries, most patients develop symptoms of infarction pneumonia: sharp “pleural” chest pain associated with breathing, shortness of breath, cough with scanty sputum, fever. Hemoptysis is observed only in 1/3 of cases. An objective examination reveals moist rales and pleural friction noise. It should be taken into account, firstly, that in 60% of patients, infarction pneumonia does not develop (and then there are no symptoms), and secondly, it takes 2-3 days after the embolism for the formation of a heart attack. In the presence of concomitant pathology of the cardiovascular system, distal embolism can manifest itself as collapse and symptoms of right ventricular failure. With massive pulmonary emboli, emboli are localized in the pulmonary trunk or main pulmonary arteries. It usually manifests itself with symptoms of acute cardiopulmonary failure: collapse, severe shortness of breath, tachycardia, chest pain. If more than 60% of the arterial bed of the lungs is excluded from the blood circulation, an enlarged liver and swelling of the neck veins appear. If PE is suspected, the following studies are required: - electrocardiography - echocardiography - chest radiography - perfusion (perfusion-ventilation) lung scintigraphy or spiral computed tomography or angiopulmonography - ultrasound examination of the main veins of the legs.
On the ECG, the most typical signs are the appearance of Q in lead III, deep S in lead I and negative T in lead III (McGinn-White syndrome), as well as right bundle branch block. Negative symmetrical T waves may appear in leads V1-3(4); ST elevation in III, aVF, aVR and V1-3(4); displacement of the transition zone to the left chest leads. Only a third of patients show signs of right heart overload on the ECG. In 20% of patients with pulmonary embolism, there are no changes on the ECG.
An x-ray can reveal dilation of the superior vena cava, enlargement of the right heart, bulging of the conus of the pulmonary artery, high standing of the dome of the diaphragm on the affected side, disc-shaped atelectasis, pleural effusion - however, all these symptoms are not very specific. The only characteristic of PE is the Westermarck symptom: expansion of the root of the lung and depletion of the pulmonary pattern in the affected area, but it is observed only in 5% of cases. However, X-ray data are important for excluding pneumonia, pneumothorax, myocardial infarction, and pericarditis.
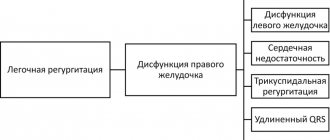
Echocardiography can confirm the diagnosis of PE and differentiate it from other acute heart diseases. An echocardiogram reveals hypokinesia and dilatation of the right ventricle; paradoxical movement of the interventricular septum; tricuspid regurgitation; absence or reduction of respiratory collapse of the inferior vena cava; pulmonary artery dilatation; signs of pulmonary hypertension.
Scintigraphy is informative in 87% of cases. It demonstrates perfusion defects of embolic origin - with a clear delineation, triangular shape and location corresponding to the blood supply zone of the affected vessel (lobe, segment). When small branches of the pulmonary artery are occluded, the diagnostic value decreases.
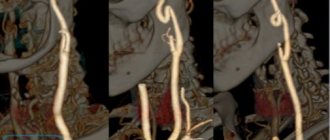
Multislice CT with vascular contrast allows visualization of blood clots in the pulmonary artery, as well as changes in the lungs caused by other diseases manifested by perfusion or filling defects. The sensitivity of this method is high when emboli are localized in large pulmonary arteries and is significantly reduced when subsegmental and smaller arteries are affected.
Pulmonary angiography is recognized as the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. Signs of embolism in this study are: amputation of a vessel or a filling defect in its lumen. A laboratory method for determining D-dimer is used to exclude PE. Its normal plasma level allows us to reject with 90% accuracy the assumption of the presence of pulmonary embolism in patients with low or moderate clinical probability. The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is established by analyzing the results of clinical, instrumental and laboratory studies. However, during life the diagnosis is correctly established only in 34% of patients. At the same time, in 9% of cases it is overdiagnosed.
Progress of CT angiography
The patient is placed on the moving part of the tomograph. During the examination, the table, together with the patient, passes through a hole in the round part of the apparatus - the aperture. The tomograph ring contains X-ray emitters, thanks to which three-dimensional images in the form of slices are displayed on the device screen. Next, the patient is given an intravenous injection of a contrast agent (Ultravist) and the specified area is re-scanned. The entire procedure takes about 30 minutes, after which the patient waits for the results of the examination.
Possibilities of 3D reconstruction of CT of the pulmonary artery and its branches
Our clinic uses the Siemens Somatom Emotion 16 2016 device; it allows scanning using the latest multispiral technology (MSCT). Thanks to MSCT, the time required for the procedure is significantly reduced, and the radiation dose is correspondingly reduced.
Conduction system of the heart
The heart, like any organ, has its own nervous system. The nervous system of the heart has several levels. The first and main pacemaker of the heart is the sinus node, located in the right atrium. It is subject to the atrioventricular node, which is located on the border between the atria and ventricles and quite often slows down the heart rate set by the sinus node. Then the nerve impulse goes to the ventricles of the heart along the branches of the Hiss bundle, which are divided into the smallest nerve endings - Purkinje fibers.
CT angiography of the pulmonary arteries with contrast
CT examination of pulmonary vessels is always carried out using contrast, since without it it will be very difficult to visualize their structure. The use of contrast enhancement allows for improved visualization of the vascular wall and traces the course of even the smallest arteries.
The non-ionic drug Ultravist is used as a contrast agent, which is well tolerated and rarely causes unwanted effects. Before administering the drug, our center requires a blood test for creatinine, an indicator of the functional activity of the kidneys.
What will a CT scan of the thoracic aorta and pulmonary artery show?
In the images obtained after a CT scan of the thoracic aorta and pulmonary artery, the anatomical structure of these formations is quite clearly visualized, their configuration, the diameter of the circumference of the vessels, and the structure of the walls are determined.
Blood supply to the lungs
CT scan of the thoracic aorta and pulmonary artery will also help detect:
- blood clots;
- tumors;
- developmental defects;
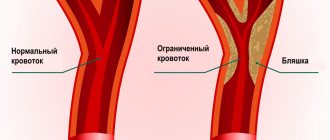
- atherosclerotic plaques;
- traumatic damage to the walls of blood vessels;
- tumors and the presence of metastases.
How to prepare for a CT scan of the pulmonary artery and its branches
No special preparation is required for this examination. It will be enough to exclude contraindications. You should tell your doctor in detail about your health status and report the possible presence of chronic ailments. It is also better to make sure that there is no pregnancy before the examination. If you are breastfeeding, provide this information to a specialist, he will give recommendations to prevent negative effects on the child.
It is recommended to refrain from bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol) before the examination.
One of the important conditions for undergoing a CT scan of the pulmonary artery and its branches in our clinic is the availability of a fresh creatinine test. If you wish, you can take it at our medical institution using the express method. These measures are used to exclude hidden kidney pathology and are necessary for your safety.
After the procedure, to speed up the removal of contrast from the body, drink more fluids.
Venous thromboembolic complications
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is part of a group of clinical problems collectively known as venous thromboembolic events (VTE).
Thrombosis is the blockage of a blood vessel by a blood clot (thrombus). Embolisms occur when part or all of a blood clot displaces from where it formed. The thrombotic masses then move with the bloodstream until they get stuck in narrower blood vessels in other parts of the body. In this case, the blood clot is called an embolus. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is the cause of venous thromboembolism, including pulmonary embolism (PE). Thrombosis most often occurs in the veins of the lower extremities.
Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism
The doctor's alertness, especially in situations in which the risk of the disease in question is significant, makes it possible to distinguish the symptoms of pulmonary embolism from other acute pathological conditions (myocardial infarction, acute pneumonia). Without exaggeration, we can say that a timely and accurate diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is at least half the success of treating this disease.
The decision on the choice and sequence of diagnostic methods depends on the clinical manifestations of the disease, and in each specific case it is necessary to decide whether the data obtained are sufficient to be confident in the diagnosis of PE. It is important to understand that a full examination and treatment, prevention of repeated episodes of pulmonary embolism is possible only in a hospital with modern equipment.
If the patient’s condition is serious, therapeutic methods should be used simultaneously with diagnostic methods. In the case of additional embolization, the patient's condition can instantly and radically change, which will require a reduction in diagnostic procedures and intensive care.
Results of CT scan of the pulmonary artery and its branches
After CT diagnostics, the doctor will need up to 2 hours to process the data received, after which you will be able to pick up the conclusion. When performing a CT scan in our clinic, you will receive a free detailed consultation after the examination, where you can ask all your questions. You will receive a disc with a recording of the study and a specialist’s conclusion.
Medical in St. Petersburg invites you to conduct an examination. It should be noted that our clinic employs only highly qualified specialists with at least 7 years of experience in radiation diagnostics. The center specializes in MSCT, MRI and ultrasound diagnostics. We have only the latest technologies and the latest equipment at our disposal. For any questions, please contact us by phone.