Why does the hand stop moving after a stroke?
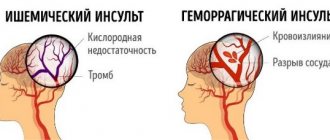
A stroke occurs due to an acute circulatory disorder in the brain, in which a portion of it dies. Depending on which part of the brain is affected, a person’s brain function is impaired. Because of this, various organs may stop functioning, including limbs - for example, a hand. Because the nerve pathways cross, the left arm will be affected if the stroke occurs in the right hemisphere, and vice versa.
At the same time, there is another dependence: the closer to the right hemisphere the stroke occurred, the more painful the damage to the limbs is felt. This happens because it is in the right hemisphere of the brain that the nerve centers responsible for the motor activity of the body are located. Therefore, a stroke, after which the left arm fails, usually requires longer rehabilitation.
Both types of stroke - ischemic and hemorrhagic - can cause such lesions and impair the motor activity of the hand. Disturbances can be different: pain, loss of sensitivity and coordination, complete paralysis of a limb.
Treatment by positioning on the back and on the healthy side
The paretic limbs are positioned with the patient in a supine position so that the muscles in which tone usually increases after a stroke (shoulder adductors, arm flexors, hip adductors, leg extensors and dorsal flexors of the foot) are stretched. To do this, place a chair with a pillow at the patient’s bedside, on the side of the paralyzed limbs, on which the sore hand is placed, palm up.
The arm is straightened at the elbow and moved to the side at an angle of 90 degrees. A cotton swab covered with oilcloth is placed under the patient's armpit. The fingers are extended. The hand and forearm are bandaged to a splint, which can be cut out of some hard material (for example, plywood) and covered with gauze.
To fix the position of the hand, place a bag of sand or salt (weighing 0.5 kg) on it. The paralyzed leg is bent 15-20 degrees at the knee, under which a bolster is placed. The foot rests against a wooden box (“boot”) covered with soft material. It is recommended to put a small pillow in the boot to better support the foot.
The patient can remain in the supine position for 1.5 to 2 hours. Then it should be turned onto its healthy side.
When laying the patient on his healthy side, as opposed to laying him on his back, the paralyzed limbs are given a flexion position. The sore arm is bent at the shoulder and elbow joints and a pillow is placed under it, and the paralyzed leg is bent at the knee and hip joints and also placed on a pillow. Just as in the supine position, it is very important to ensure the correct position of the hand and foot. The fingers of the hand should be straightened, the hand should be tied to the splint and lie on the pillow, palm down. The foot should rest against the box. The patient can remain in a lying position on the healthy side for 30 to 50 minutes.
During the first days after the disease, they regularly alternate between placing the paretic limbs in the position of the patient on the back and the healthy side. Treatment by position is not performed during meals, sleep at night, or other therapeutic measures.
Styling paretic limbs prevents the development of muscle contractures, helps reduce muscle tone and prevents the development of pain in the joints (especially in the shoulder). In addition, changing the patient's position in bed every 1-2 hours prevents the development of bedsores.
A set of measures to restore the hand after a stroke
Restoration of hand motor skills after a stroke occurs under the supervision of physiotherapists. The list of measures includes procedures in different areas:
- physical rehabilitation therapy;
- drug treatment;
- psychological counseling.
Physical rehabilitation therapy
Physical rehabilitation is a critical part of restoring arm movement after a stroke. It involves doctors of various specializations, but primarily physiotherapists, neurologists and rehabilitation specialists. Treatment is aimed at developing and strengthening everyday motor abilities.
The process uses:
- physical therapy and gymnastics
: physical exercises on the arm - from the simplest gradually to more complex, developing fine motor skills; - action and observation therapy
- during these procedures, the patient watches another person performing some actions with his hand (in person or on video), and then repeats after him. The method triggers the work of similar areas of the brain, and this helps restore motor skills of the hand; - mirror therapy method
- within the framework of this rehabilitation technique, a mirror is placed between the patient’s hands in such a way that the image of the movement of the healthy limb creates the illusion of the same normal movement of the affected arm; - tekar therapy
- radio wave exposure to the body to produce endogenous heat. This helps reduce pain and speed up the tissue healing process; - massage techniques
; - acupuncture, modeling
from dough, plasticine or clay; - hydrotherapy methods
: hydromassage baths, contrast and circular showers.
The rehabilitation department has an occupational therapy department and a neuromotor department for the upper limbs. Robotic technologies are used here, including virtual reality. Neuromotor rehabilitation using such high-tech systems is a modern method of restoring hand motor abilities.
The greatest effect is achieved when the doctor competently combines all these methods. In this case, the specialist must first assess the extent to which the patient’s condition allows him to undergo these measures.
Drug treatment
In most cases, rehabilitation of the hand after a stroke requires drug treatment. However, it must be strictly under the supervision of the attending physician.
There are no universal dosages and regimens; each patient needs his own therapy. To make a decision about which drugs and in what doses the patient needs, the specialist studies all available information about him. In particular, medical history, anamnesis, data on clinical manifestations, results of previous examinations and tests.
The doctor may also change your medication regimen during treatment if he has reason to believe that the current dosage is ineffective or insufficient. The basis is new biometric data, information from the patient’s daily records (“diary of a stroke patient”). First of all, we are talking about the dynamics of blood pressure, heart rate, as well as side effects from medications.
Types of drug therapy that are used to restore limb activity after a stroke:
- intramuscular and intravenous injections
, which are aimed at increasing vascular activity and strengthening neurons. These include Botox injections, which significantly reduce muscle spasticity; - lymphotropic drugs
, which are injected directly into the lymphatic system so that the active substance gets into the arm faster; - analgesics
(to reduce pain in the arm),
muscle relaxants
(to relax the muscles of the limb),
anticoagulants
(to prevent the formation of blood clots),
antidepressants
(to treat depression that has developed due to illness) and other drugs, including antibiotics, vitamins and potent drugs - of necessity.
Psychological counseling
The patient’s internal state greatly influences the process and result of restoring the activity of the arms and legs.
Rehabilitation in a specialized center forces a person to change his usual way of life: he distances himself from society, loses independence and independence even in everyday worries. This cannot but affect the psychological state and leads, at a minimum, to discomfort, and at most to the development of depression.
The patient needs understanding, respect and care, but may also experience anger and powerlessness due to loss of control over his own body. To deal with this, a psychotherapist is needed. He will develop the correct technique for working with the emotional state and select a communication method for the family. The doctor will also prescribe pharmaceutical treatment to the patient if it is necessary and fits into the overall drug treatment plan.
Rehabilitation at the Yusupov Hospital
At the rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, the patient will be provided with all the necessary assistance. The hospital's psychologists work not only with patients - they also provide assistance to the patient's family members. The rehabilitation process of restoring motor activity of the limbs requires patience from the patient and a lot of work - this will allow you to return to a full life after a stroke. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone. The rehabilitation doctor will develop individual exercises for the patient, the patient will be under constant medical supervision and receive qualified assistance from specialists.
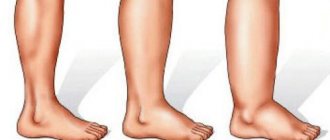
Causes of swelling
Swelling of the hands that develops after a stroke is a violation of trophism, that is, the movement of blood and lymph in the affected area of the body.
This condition is caused by several reasons:
- Disorders of blood circulation and lymph movement develop in situations where the paralyzed limb is immobile. This provokes stagnation, causing the formation of edema of varying intensity.
- Edema caused by problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system. They develop as complications of a stroke. They are characterized by the fact that when pressure is applied to the site of edema, a fairly noticeable mark remains there.
- Swelling caused by problems with kidney function . They stand out for their loose structure.
IMPORTANT! But still, the main cause of swelling is the immobility of the hand.
Passive movements and massage
Simultaneously with positional treatment, they begin to engage in passive gymnastics (movements in the joints of paretic limbs, which are carried out by a physical therapy methodologist or a person replacing him). Passive movements are carried out without active muscular assistance from the patient. They are performed carefully, at a slow pace.
Passive movements are carried out as fully as possible, isolated in each joint. To do this, the person working with the patient clasps the paretic limb above the joint being worked on with one hand, and with the other below this joint. And the development is carried out in the following sequence: shoulder, elbow, wrist joints and fingers, hip, knee, ankle joints and toes. The volume and tempo of movements gradually increase, their number for each joint can be from 5 to 10. Passive movements in the first days after a stroke are recommended to be carried out 2-3 times a day for all joints of the limbs.
When performing movements, the initial position of individual parts of the limbs is of great importance.
For example, during passive movements in the shoulder joint, the patient is placed on his healthy side, and the affected arm is bent at the elbow. With one hand they fix the shoulder joint of the sore arm, with the other they clasp the arm bent at the elbow joint and make circular movements, pressing towards the shoulder joint, as if screwing the head of the humerus into the glenoid cavity. Abduction of the hip is more complete when the leg is bent (at the hip and knee joints), since this reduces muscle tension in the adductor muscles of the thigh, and the resistance of these muscles decreases.
On these same days, you should begin to do a light massage of both healthy and paretic limbs. If you can use a variety of massage techniques when massaging healthy limbs, then when massaging paretic limbs you need to be very careful. The fact is that excessive massage can lead to a sharp increase in the tone of certain muscle groups, which is undesirable. Therefore, when massaging paralyzed limbs, it is recommended to use the following rules.
Massage on the arm should begin from the shoulder, and on the leg - from the buttocks and thigh (the patient's position is lying on his back or on his healthy side). Then they move on to massage other parts of the limbs.
When massaging muscles in which the tone is usually increased (pectoralis major muscle, biceps brachii, flexors of the hand and fingers, quadriceps femoris, triceps surae), only light stroking should be used. In this case, the pace of massage movements should be slow. When massaging their antagonists, in which the tone is usually also increased (extensors of the forearm, hand and fingers, posterior femoral group, tibialis anterior and peroneus longus muscles), you can still use other massage techniques: rubbing and shallow kneading. These muscles can be massaged comparatively more energetically and at a faster pace.
Caring for patients after a stroke: what is worth knowing?
While a person who has suffered a stroke is in hospital, he is looked after by qualified medical personnel. But sooner or later the patient is discharged, and then his relatives have to look after him. To help your loved one recover and to maintain the strength to perform the necessary procedures, it is worth learning the basics of correct and high-quality general nursing care.
From a medical point of view, there are two types of paralysis: right-sided and left-sided. The behavior of patients with different types of paralysis differs significantly. This is worth considering when developing an exit strategy. With right-sided paralysis, damage to the left side of the body, the patient’s motor function on the left side of the body is impaired. As a result, he:
- does not feel the left lower and upper limbs;
- does not understand where they are located;
- does not perceive the surrounding space (while walking he bumps into doors, cannot calculate the distance to the nearest object);
- loses place of reading.
Tips that will make life easier for such a patient:
- the bed must be placed so that the patient can see with his right eye the center of the room and whoever enters the room;
- Place household items on the side of your right hand;
- encourage your ward to talk more, as speech helps to quickly restore spatial perception.
With left-sided paralysis, damage to the right side of the body, the patient’s emotional background is disturbed. He is in a lethargic depressed state and does not experience any emotional experiences. Patients with left-sided stroke:
- have problems with speech, it is difficult for them to pronounce words and form sentences;
- have difficulties with perception, do not understand what is being said to them;
- they forget words and names of objects.
Tips on how to make the life of such a patient more comfortable:
- at first, replace words with gestures, facial expressions, and gentle touches;
- speak slowly, clearly, avoid complex sentences;
- try using written language instead of spoken language;
- perform smooth, unhurried movements;
- ask the doctor to develop a speech therapy complex, help the patient perform the developed speech therapy exercises.