Causes
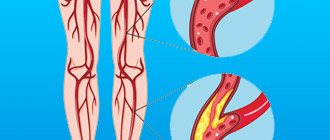
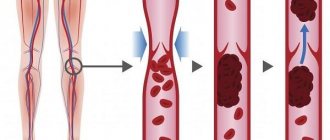
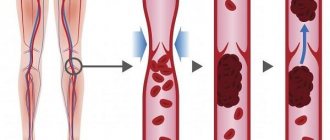
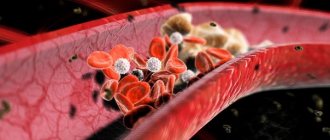
The main cause of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities is a violation of lipid metabolism - an increase in the level of cholesterol in the blood, and especially its “dangerous” fraction of low-density lipoproteins (LDL). However, an increase in high-density lipoproteins (HDL) does not cause atherosclerosis.
Elevated cholesterol levels alone are not enough to cause the disease. There must also be risk factors that affect the vulnerability of the artery wall, its protective properties, etc. These include:
- Smoking is the most dangerous risk factor and needs to be discussed separately. Even smoking several cigarettes a day leads to damage to the vascular endothelium; with high cholesterol, this gives a high risk of cholesterol deposition at the site of the lesion and the beginning of plaque formation. When smoking a large number of cigarettes per day, this risk increases significantly.
- Hypertonic disease
- Overweight
- Diabetes
- Alcohol abuse
Gymnastics for capillaries
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels. They deliver oxygen and nutrients to each cell and free them from decay products. If the vessels are narrowed, harmful substances will begin to accumulate, increasing the risk of developing chronic diseases of the internal organs.
The simplest and most effective way to strengthen blood vessels and capillaries is vibration according to the Katsuzo Nishi method. Perform in the morning, immediately after waking up, while lying in bed:
- Raise your legs and arms up, shake finely and frequently for about a minute.
- Place your hands behind your head, under the fourth cervical vertebra. Pull your socks towards you, strongly strain your whole body. Next, make small vibrating movements with your whole body, like a fish.
It turns out a kind of vibration massage of capillaries, arteries, veins. Blood circulation and lymph outflow improves, vascular tone is normalized.
Symptoms, diagnosis
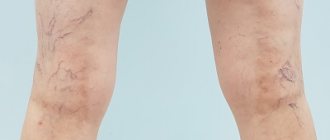
The main and earliest symptom of obliterating atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities is intermittent claudication. When walking a certain distance, the patient begins to feel fatigue, heaviness in one or both legs, and then pain, forcing him to stop and continue moving after a short rest.
The stage of the disease is even determined by the length of the pain-free walking distance. From 500 m to 1 km – stage 1, from 200 to 500 m – stage 2A, less than 200 m – stage 2B, less than 50 m and pain at rest – stage 3. Stage 4 of atherosclerosis of the extremities is gangrene.
When examining the patient, attention is drawn to a decrease in the calf muscles, dystrophy of the nail plates, and a decrease in the amount of hair on the legs. A characteristic symptom is the absence of pulse in the feet, popliteal, and femoral arteries (depending on the level of the lesion).
Important methods for diagnosing atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities are ultrasound (ultrasound ultrasound, doppler ultrasound, duplex angioscanning), angiography.
Breathing exercises
Breathing exercise therapy dilates blood vessels, enriches the blood with oxygen, and speeds up metabolism. It is very useful to conduct training in the fresh air, which enhances the healing effect. The basic rule: inhale through your nose, exhale through your mouth through pursed lips.
Effective practices for atherosclerosis:
- Stand straight, feet shoulder-width apart. Place the palm of one hand on your chest, the other on your stomach. Take 4-6 short breaths, engaging your chest first, then your stomach.
- Bring your feet together, stretch your arms up. Inhale - rise on your toes, exhale - lower.
- Legs wider than shoulders. Inhale – lean forward, arch your back. Exhale - slowly return to the starting position.
- While standing or sitting, take 4 short breaths alternately. Hold your breath for up to 10 seconds and exhale as well.
It is recommended to do each exercise 10-15 times in one session.
Treatment of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities
Lifestyle changes, non-drug treatment
Patients with atherosclerosis of the arteries of the extremities, as a rule, need to change their lifestyle.
First of all, you need a COMPLETE cessation of smoking. Reducing the number of cigarettes smoked, of course, has a positive effect on the course of the disease, but the risk of damage to the vascular wall still remains.
Overweight patients need to lose weight.
An important factor in reducing blood cholesterol levels (especially its dangerous fractions - LDL) is following a diet low in animal fats.
Patients suffering from hypertension and diabetes mellitus need to be monitored by an appropriate specialist (therapist, endocrinologist) to correct these diseases.
Against the background of drug correction, training for the development of collateral circulation is desirable. The fact is that with obliterating atherosclerosis, the main vessels are affected. In this case, blood circulation begins to occur through small bypass (collateral) vessels. With good development of collateral circulation, limb ischemia can be minimized even with complete closure of the lumen of the main artery. Along with medications that help improve collateral circulation (they will be discussed below), training walking is used using special techniques on a treadmill and just on foot.
Recommendations for training walking: patients are recommended to walk 2-3 hours a day, not at a fast pace, so that there is no pain in the legs. At the same time they exercise on a treadmill. They start by selecting a walking speed along the path that does not cause fatigue in the legs for at least 10 minutes of continuous walking. Then increase the speed by 0.5 km/h. They begin walking at this speed, when fatigue and pain in the lower leg appear, they rest until the discomfort completely disappears, then they resume walking again until discomfort appears. The average walking time on the path is 30-40 minutes per day. The goal is to increase the distance of pain-free walking to 1.5 km, after which the walking speed is increased by another 0.5 km/h, etc. Training should be done under the supervision of a doctor.
Exercises
The exercises can be done many times a day, for a few minutes each time. Do not self-medicate. Therapeutic gymnastics exercises are effective, but only in combination with treatment prescribed by a doctor. You also need to consult a specialist in exercise therapy (physical therapy), who, based on the doctor’s prescriptions and the characteristics of your body, will select the movements that will bring you the maximum effect. We do gymnastics exercises ten times each.
Lying on your stomach
There is only one exercise while lying on your stomach - try to touch your buttocks with your heels ten times without raising your hips.
Lying on your back
- Slowly bend your knees without lifting your feet off the floor. Then we pull the knee towards the body with our hands, the back should lie firmly on the floor. Slowly, with some effort, straighten the leg and repeat with the other.
- We imitate working with pedals, the “bicycle” exercise.
- Raise your straight leg at a distance of your foot from the floor and hold for fifteen seconds.
- We keep one leg bent at the knee, raise the other leg up to a distance of two feet from the floor, turn the toes inward so that the foot is parallel to the floor and hold for ten seconds.
- Keep your legs straight and press them tightly together for ten seconds, then press them firmly to the floor for five seconds.
- Raise your legs in the air, place your palms on the floor and bend both legs at the knees at the same time.
- Wave your arms and legs at the same time, like an insect turned onto its back.
- Place your palms between your tailbone and the floor, raise your legs and cross them in the air, working like scissors.
- Pull the toe of the raised outstretched leg toward you, first in turn, then both legs at the same time.
- With your arms spread out to the sides, lift your two legs and pull your toes away from you and towards you.
In a sitting position
- Bend your knees, rest your palms on your knee joints and move your knees to the sides, and your hands should counteract the movement.
- Bend your chest towards your straight legs, trying to touch your knees with your chest, then clasp your feet with your palms by the soles and touch your shins with your head. It won’t work out the first time, but you need to stretch a little, because the flexibility of the spine will help the whole body stay in shape.
- Pull the foot of the leg bent at the knee towards you, clasp it with your hands and straighten it, continuing to hold on with your hand.
Standing
- Holding the back of the chair, slowly squat while rising on your toes. Do partial squats at first, but over time you need to make them deeper and finally full.
- You can hold onto a chair with your hands, alternately place your feet on your toes, transferring your body weight, you can do it while listening to music, or spring your feet.
- March with your knees high.
- Make circular movements with your leg bent at the knee, keeping your hands on your belt.
- Standing on your knees, bend over, trying to touch your head to the floor.
- Standing straight, alternately raise straight legs.
- Grasp your knee with your hand and twist your foot.
- Walk on your heels.
- Squat on one leg, keeping the other straight.
Drug treatment
There are many medications that are used for obliterating atherosclerosis of the lower extremities.
They can be divided into several groups:
- Antiplatelet agents - thrombo ACC, cardiomagnyl, trental, plavix, reopoliglucin.
- Drugs that reduce blood viscosity - vesel due f (sulodexide), phlogenzyme, wobenzym.
- Agents that improve peripheral blood circulation and microcirculation - alprostan (vasoprostan), nicotinic acid, xanthinol nicotinate.
- Agents that promote the development of collateral circulation - Actovegin, solcoseryl.
- Drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels - Torvacard, Crestor, etc.
- Other medicines – chimes, analgesics (for pain), antibiotics (for purulent-necrotic ulcers), etc.
Typically, patients are permanently prescribed one of the acetylsalicylic acid drugs for life - thrombo-ass or cardiomagnyl. Other drugs are prescribed in courses, depending on the stage of the disease and clinical manifestations.
It is believed that twice a year patients require hospitalization in the vascular surgery department for courses of conservative therapy - intravenous infusions, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, physical therapy.
Surgery
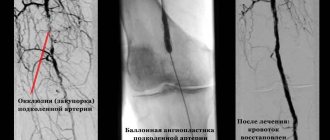
Surgical treatment is possible in the presence of narrowings (stenoses) of large vessels, mainly in the popliteal-femoral segment or above. Reconstructive operations for damage to the arteries of the leg are practically not used.
For small stenoses, stenting is possible - installing a stent in the area of stenosis in a minimally invasive way (through a puncture in the femoral artery), which restores the patency of the artery.
In case of significant narrowings, reconstructive operations on blood vessels are used - bypass surgery, prosthetics.
With timely and correct treatment of obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, it is most often possible to stabilize the process and avoid late complications - trophic ulcers, gangrene.
Breathing exercises by Strelnikova
Initially, a set of exercises was used to improve vocal singing skills. Over time, breathing training has been found effective in treating cardiovascular problems.
Exercises are combined with tension in the peritoneum, thoracic and lumbar regions, and neck. Thanks to this, the coronary, carotid arteries, and muscle corset are being worked on.
For cerebral atherosclerosis, the following exercises are most effective:
- Bend over so that your body is parallel to the floor. Inhale - touch the floor with your fingers, exhale - stand up straight.
- Perform standing or sitting. The head is tilted to the right, touching the shoulder. Exhale - straighten. Inhale – tilt to the left, also touching the shoulder. Exhale - straighten.
- Do it while standing. Inhale – clasp your left shoulder with your right hand, and your right shoulder with your left. Exhale - lower.
Training is carried out 2 times a day, total duration is 1 hour.