The main reasons for the development of CNS HIP:
- anemia in the mother (a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin, which reduces the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the tissues of the baby’s body) - any chronic diseases and defects: congenital heart defects, lungs of other organs, kidney disease, the presence of diabetes mellitus, which contribute to poor circulation - complications pregnancy and childbirth (gestosis, threat of premature birth, pathology of the placenta and umbilical cord, prematurity and post-term pregnancy, multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios, various anomalies of labor) - fetal diseases (hemolytic disease of the newborn, intrauterine infection, bleeding) Tangible signs of fetal hypoxia mainly are expressed in changes in its motor activity (sudden increase, increased heart rate and movements (movements) of the fetus during acute hypoxia, or a decrease and weakening of them during chronic hypoxia). When a diagnosis of intrauterine fetal hypoxia is made, the expectant mother needs to carry out procedures to identify the causes, followed by comprehensive treatment of their source, with possible hospitalization in a hospital, adherence to bed or home rest and daily routine.
Prognosis and consequences of cerebral ischemia
It is much more effective to eliminate ischemia itself after the birth of a baby than to treat its complications. Among the consequences of cerebral ischemia of the 2nd degree:
- sleep disorders;
- headache;
- irritability;
- isolation;
- physical inactivity.
- Stage 3 disease has severe consequences:
- cerebral palsy;
- attention deficit disorder;
- mental retardation;
- Graefe's symptom, etc.
If all actions to eliminate ischemia were carried out by doctors in a timely manner, then the symptoms disappear during the rehabilitation period, which usually lasts 6-12 months.
Hypoxia results
A lack of oxygen to the brain can have the following results:
- Severe cerebral ischemia
This condition is fatal in a quarter to half of cases. The babies do not survive even a few days. Another scenario is pneumonia or another infection that kills the child a little later. Most of those who do not die are diagnosed with autism, cerebral palsy or dementia. And only 10% of survivors experience no consequences.
- Moderate ischemia
According to statistics, severe long-term consequences occur in 30 to 50% of children.
- Mild ischemia
The outcome in most cases is favorable, no disability is noted.
Cerebral ischemia grade 2
A dangerous form of the disease. It is characterized by:
- severe apnea (stopping breathing during sleep);
- decreased grasping and sucking reflexes;
- weak muscle tone;
- increase in head shape due to fluid accumulation;
- lack of coordination;
- loss of consciousness;
- changes in skin color.
Most often, grade 2 ischemia manifests itself in the first day of a newborn’s life, and symptoms can be observed for 2-4 weeks. At this time, the child is carefully monitored by doctors, and he undergoes a course of therapy. If necessary, surgery is performed to remove the blood clot.
Diagnostics:
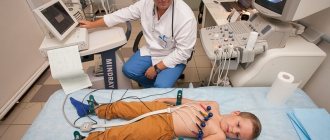
It is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the fetus, use cardiotocography (recording of the fetal cardiac activity) and Dopplerometry (study of the blood flow of the vessels of the uterus and umbilical cord of the fetus) with the frequency prescribed by the attending physician. Auscultation (listening) of the fetal heartbeat with a stethoscope is also used. It should be noted that not every pregnancy occurs against the background of the above diseases, complicating intrauterine fetal hypoxia. To prevent the possible occurrence of hypoxia, special attention is paid to its prevention: long walks in the fresh air, mandatory dosed physical activity (gymnastics, exercises, exercises for pregnant women and breathing exercises, swimming, yoga). It is possible to use hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO) as prescribed by the attending physician. It must be remembered that treatment must be prescribed by a gynecologist, be comprehensive and take into account an individual approach to each expectant mother.
Early symptoms that should be addressed to a pediatric neurologist
- sluggish breastfeeding, choking during feeding, leakage of milk through the baby's nose - weak cry of the child, nasal or hoarse voice - frequent regurgitation and insufficient weight gain - decreased motor activity of the child, drowsiness, lethargy or severe anxiety - trembling of the chin, upper and/or or lower extremities, frequent startlings - difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during sleep - throwing back the head - slowing or rapid increase in head circumference - low (flabby muscles) or high tone of the muscles of the limbs and torso - decreased activity of movements of the arm or leg on any side , limited hip separation or the presence of a “frog” position with pronounced hip separation, unusual position of the child - strabismus, torticollis - birth of a child by caesarean section, in breech presentation, with an anomaly of labor or with the use of obstetric forceps, extrusion, with the umbilical cord entwined around the neck - prematurity of the child - presence of convulsions during childbirth or in the postpartum period
Cerebral ischemia grade 3
The most severe form, in which:
- the baby has no reflexes;
- the child falls into a coma;
- heart rhythm is disrupted;
- blood pressure rises sharply;
- there are problems with independent breathing;
- strabismus is observed.
An experienced doctor can already determine the presence of signs and symptoms of grade 3 cerebral ischemia in the first 5 minutes of a newborn’s life. In this case, the child is sent to intensive care and, if necessary, connected to a ventilator.
Treatment of cerebral ischemia in newborns
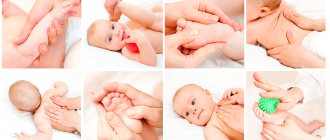
The goal of treatment is to restore normal blood circulation in the brain tissue, prevent pathological changes and eliminate the consequences of ischemia. For stage 1 disease, treatment usually involves prescribing massage to improve blood circulation.
For diseases of the 2nd and 3rd degrees, drug therapy and surgery are used to remove a blood clot in the vessel and restore the structure of the vascular bed. In difficult cases, the baby undergoes a rehabilitation course of intensive therapy.
Signs and symptoms of cerebral ischemia in newborns
The disease manifests itself with obvious symptoms that attract attention.
- The child is easily excitable, cries for no reason, sleeps poorly, shudders, and has tremors.
- Muscle tone is reduced, the baby moves little, has difficulty sucking and swallowing.
- The fontanel is enlarged, intracranial pressure is increased due to the fact that fluid accumulates in the brain.
- Convulsions, twitching of the limbs and head, as well as comatose states with loss of coordination of movements and consciousness occur.
- The newborn's skin takes on a marbled hue.
- The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted - bloating, constipation, and diarrhea are observed.