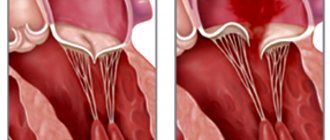
Among heart diseases, endocarditis is one of the most insidious. Under the influence of various infections (there are about 130 causative agents of this disease), the inner lining of the heart becomes inflamed. The danger is that the symptoms of infective endocarditis do not appear immediately, so patients do not always seek help in a timely manner. Also, the disease is not easy to diagnose, which is why treatment may be started later than expected. That is why cardiologists recommend regular examinations in medical centers equipped with modern equipment that has extensive research capabilities.
What is endocarditis
Symptoms of the disease occur in people of different ages, including children diagnosed with “congenital heart defects” (tetralogy of Fallot, single ventricle defects, etc.). It can be provoked by:
- mitral valve prolapse;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- surgery on heart valves;
- cardiac septal defects;
- coronary heart disease (especially after surgery).
The disease is primarily infectious. Inflammation caused by microorganisms affects not only the endocardium itself - the internal tissues of the heart muscle - but also the heart valves and nearby vessels. Often the infection penetrates the liver, kidneys, and spleen.
Most often, pathology becomes a consequence of other diseases. The prerequisites for the occurrence of infective endocarditis is bacteriological infection of the body under various conditions. The infection also affects the heart when its valves are injured due to the installation of prostheses and pacemakers, on the surface of which microorganisms can develop. There are atherosclerotic forms caused by dystrophic changes in cardiac tissue, and rheumatic forms - due to rheumatism of the heart valves.
INFECTIOUS ENDOCARDITIS: diagnosis, clinical course, treatment
Infective endocarditis (IE) is a serious disease with a high mortality rate. Without treatment, the mortality rate for IE is 100%. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number of patients with endocarditis in our country and abroad. According to various authors, today the incidence has increased in the elderly and senile, as well as among people under 30 years of age who use intravenous drugs [1, 2].
It is known that IE is a disease of an infectious nature with the primary localization of the pathogen on the heart valves and parietal endocardium, occurring with manifestations of systemic infection, vascular complications and an immune reaction [3, 4, 5].
Traditionally, the development of IE is associated with the presence of “intracardiac” risk factors, which include congenital and acquired heart defects, the presence of prosthetic valves, valve prolapse and other anomalies [6]. In recent years, patients with focal infection, as well as people who have had invasive research methods, including the installation of a subclavian catheter, have been classified as high-risk individuals [7]. A special risk group consists of drug addicts who practice intravenous drug administration, in whom IE occurs with damage to intact heart valves.
This paper summarizes the experience of diagnosing and managing patients with IE on the basis of the general therapeutic department of the Alexandrovskaya Hospital in St. Petersburg for the period 1998–2003. Diagnosis of the disease was carried out in accordance with Duke criteria [8]. The diagnosis of IE was assessed as reliable if two main criteria were present, namely:
- when a pathogen typical for IE is isolated from a patient’s blood culture;
- when determining echocardiographic signs of endocardial damage - mobile vegetations on the heart valves, abscesses in the area of the valve prosthesis; formation of intracardiac fistulas, etc., in combination with three and/or five auxiliary criteria, which included vascular complications (embolism of large arteries, septic pulmonary infarctions, intracranial hemorrhages, etc.), immunological phenomena (glomerulonephritis, Osler’s nodes, hemorrhagic vasculitis and etc.), as well as febrile fever, hepato-splenomegaly and other manifestations of systemic infection.
We examined 105 patients with IE, of which in 80 people aged 18 to 30 years (first group), the main risk factor for the disease was injection drug addiction.
In the second group of patients (25 people), the main predisposing factors for the development of IE were congenital and acquired heart defects, as well as prosthetic valves.
In people of the older age group, an additional risk factor was degenerative-dystrophic changes in the heart valves.
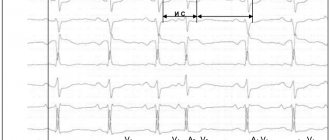
The relationship between the nature of heart valve damage and risk factors for IE is presented in Table 1.
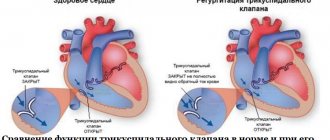
According to an echocardiographic study, 100% of patients in the first group had mobile vegetations on the leaflets of the tricuspid valve (TV), which was accompanied by the formation of its insufficiency of degrees I-III.
In the second group of patients with IE, there was damage to the left chambers of the heart with the formation of vegetations on the leaflets of the aortic and mitral valves. Isolated damage to the mitral valve was observed in two people with rheumatic heart disease (mitral stenosis), in one patient with a congenital ventricular septal defect, and in a single case of an obstructive form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Among elderly and senile people, nine people (36%) had isolated damage to the aortic valve in the absence of signs of aortic stenosis. Along with this, in five patients (20%) aged from 72 to 87 years, IE developed against the background of an aortic defect of atherosclerotic origin, and in all five, combined damage to the aortic and mitral valves was detected. Degenerative-dystrophic changes in other heart valves were detected in 100% of patients in the older age group.
The formation of vegetations on the aortic valve leaflets was observed in two patients with the tertiary form of syphilis against the background of an existing aortic defect associated with a specific process in the aorta.
In two cases, we observed the development of endocarditis of prosthetic valves.
When comparing the results of blood cultures in two groups of patients, significant differences were determined both in the frequency of microbial flora isolation and in the species composition of endocarditis pathogens. According to our data, the causative agent of IE in drug addicted patients in 71.3% of cases (57 people) was Staphylococcus aureus, while in the second group, along with coccal flora, gram-negative microorganisms were more often found (28%). Negative blood culture results were observed significantly less often in the first than in the second group of patients with IE: 18.7% and 56%, respectively. Data regarding the etiological structure of IE in the studied groups of patients are presented in Table 2.
Clinical characteristics and features of the course of IE
The clinical course and nature of complications of infective endocarditis largely depend on the localization of valve vegetations - in the right or left chambers of the heart, as well as the degree of virulence of the causative agent of the disease.
The course of IE in drug addicted patients was particularly severe and polysyndromic. The reason for hospitalization in most patients was acute complications of the underlying disease. A significant proportion of patients were admitted to the intensive care unit of the hospital with clinical symptoms of unilateral or bilateral multifocal pneumonia, the cause of which was septic thromboembolism of the branches of the pulmonary artery (72% of patients). The course of pneumonia was accompanied by severe respiratory failure, often with the development of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and foci of destruction in the lungs (12%). Manifestations of secondary nephropathy, which were found in 100% of patients in the first group, were sometimes mistakenly interpreted as an exacerbation of chronic glomerulo- or pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, which served as a reason for hospitalization of these patients in the urological and nephrological departments.
In the second group of patients, the main reason for hospitalization was prolonged febrile fever in combination with anemia and hepatolienal syndrome. Along with this, in five people (20%) the reason for hospitalization was progressive heart failure.
The main clinical syndromes observed in patients with IE of the first and second groups are presented in Table 3.
According to our observations, a characteristic feature of the clinical course of IE in drug addicted patients was a high incidence of septic pulmonary embolism with the formation of multiple foci of infiltration in the lungs. In many patients, pulmonary thromboembolism was recurrent (31.3% of patients) and was often complicated by the development of destructive foci in the lungs.
The formation of vegetations in 100% of patients of the first group was accompanied by tricuspid valve insufficiency of the I-III degree with the formation of regurgitant flows. At the same time, in most patients there were no severe disturbances of central hemodynamics associated with TC dysfunction. In this group of patients, a characteristic clinical feature was the reversible nature of hemodynamic disorders during therapy. Acute heart failure with dilatation of the heart cavities and a decrease in ejection fraction to 40% or lower was observed in 28 patients (35.3%) due to the addition of acute myocarditis or against the background of concomitant damage to the heart valves.
Secondary nephropathy was one of the most common syndromes in the first group of patients with IE. Acute renal failure was observed in 16 patients, and in 10 of them it was reversible and was associated with acute disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, as well as acute heart failure with edema. Infectious-toxic nephropathy was recorded in 73.8% of cases and was accompanied by urinary syndrome - hematuria, proteinuria, leukocyturia - with a sufficient level of glomerular filtration.
A characteristic feature of IE in the second group was the subacute course of the disease with a long period of fever at the prehospital stage, and in the elderly and senile age the fever was subfebrile in nature with rare rises in temperature to febrile levels.
Most patients with subacute infective endocarditis (PIE) were admitted to the hospital at the stage of a developed clinical picture of the disease with clinical signs of thromboembolism of vessels in the systemic circulation. In this group of patients, the most common complications should be recognized as cerebral embolism with the development of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, embolism of the renal vessels with pain and hematuria, as well as the formation of acute focal changes in the myocardium associated with embolism of the coronary vessels or covering the mouths of the coronary arteries with vegetations [9].
Septic thromboembolism of cerebral vessels was often accompanied by the development of purulent meningoencephalitis with a fatal outcome. At the same time, blood cultures of 56% of patients in the second group did not show growth of microbial flora. Noteworthy is the fact that septicemia in patients with positive blood culture results in 28% of cases was caused by gram-negative microflora. In this category of patients, the source of bacteremia was foci of chronic infection in the genitourinary system, and in two patients (according to autopsy) bilateral apostematous nephritis was detected.
A significant number of patients with PIE (62%) showed signs of acute circulatory failure with congestive wheezing in the lungs, pulmonary hypertension, enlarged cardiac cavities and peripheral edema.
In this group of patients, prerenal azotemia and acute renal failure associated with the development of acute circulatory failure were observed more often than in the first group.
Acute diffuse myocarditis, typical manifestations of which were various rhythm disturbances, was diagnosed in 27% of patients in the second group.
Anemia with a decrease in hemoglobin level to 80 g/l or less was detected in 100% of patients in the second group. A significant increase in ESR (more than 45 mm/h) was observed in 85.8% of patients with subacute IE.
Skin changes in the form of hemorrhagic rashes, Henoch-Schönlein purpura, as well as other manifestations of immune inflammation in both groups of patients were uncommon - 6.3 and 4% in the first and second groups, respectively.
Treatment of patients with IE
Conservative therapy of patients with IE was carried out using broad-spectrum antibiotics in combination with detoxification, anticoagulant and metabolic therapy. As part of antibacterial therapy, patients received cephalosporins of III-IV generations in combination with aminoglycosides and metronidazole. From the group of cephalosporins, the following were prescribed: ceftriaxone (Longacef) 2 g per day intravenously (IV), or cefotaxime (Talcef) 2 g per day IV, or cefepime (Maxipim) 2 g per day IV in combination with aminoglycosides ( amikacin in a daily dose of 1.5 g intravenously) and metronidazole 1.5-2 g per day intravenously. If such therapy was ineffective or there were contraindications to the above drugs, antibiotics of the lincosamine group were used: clindamycin 1.2 g per day IV or lincomycin 3 g per day IV in combination with fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin 400 mg per day i.v. /V). In the intensive care unit, therapy was carried out for five to seven days with imipinem (thienam) at a dose of 2-4 g per day intravenously or rifampicin at a daily dose of 0.45-0.6 g intravenously. The average duration of antibiotic therapy in the study group of patients was 28 + 3.5 days.
Detoxification therapy included intravenous infusions of rheopolyglucin, hemodez, polarizing mixtures in combination with loop diuretics. The volume of administered fluid averaged 2-2.5 liters per day. During the entire period of infusion therapy, the functional state of the kidneys, electrolyte composition of the blood, and daily diuresis were monitored. In the intensive care unit, CVP monitoring was carried out in all patients. Infusion therapy was carried out throughout the entire acute period of the disease until the manifestations of intoxication syndrome were relieved. The average course duration was 22 + 4.5 days.
The development of pulmonary embolism, especially in combination with signs of acute disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome in the hypercoagulable stage, served as the basis for prescribing anticoagulant therapy. The initial dose of heparin was 10 thousand units intravenously, in a stream, then - 1000 units per hour intravenously, drip with a transition to subcutaneous administration up to 30 thousand units per day. Heparin was administered under the control of coagulogram parameters and blood clotting time. At the same time, intravenous transfusions of fresh frozen plasma were carried out at a rate of 300 ml per day with the addition of 2500–5000 units of heparin. Severe anemia (Hb less than 80 g/l, Ht ≤25) was corrected by red blood cell transfusions (five to seven doses). In the presence of hypoproteinemia, the administration of solutions of amino acids, albumin or native plasma was used. Identification of clinical and radiological signs of pulmonary edema against the background of recurrent septic pulmonary embolism served as an indication for the prescription of corticosteroids (prednisolone from 120 to 200 mg per day intravenously). Therapy with direct-acting anticoagulants in combination with cryoplasma transfusions was carried out until there was a sustained improvement in hemostasis. The criteria for normocoagulation were the level of fibrinogen in plasma 3-4 g/l, the absence of thrombocytopenia, normalization of CVV, aPTT, thrombin time, as well as negative paracoagulation tests. According to our data, relief of the manifestations of acute DIC at the hypercoagulation stage in 75% of patients was observed on the seventh to tenth day from the start of complex therapy.
Some patients developed resistance to the ongoing antibacterial therapy, which was characterized by an increase in intoxication, febrile fever, progressive anemia, as well as blood cultures of the causative agent of IE - Staphylococcus aureus - in 65% of cases. During X-ray examination of this category of patients, foci of destruction of lung tissue were detected with a high frequency, and in three patients there was purulent effusion in the pleural cavity.
Long-term use of broad-spectrum antibiotics in 70.3% of patients (38 people) was accompanied by the development of side effects of antibacterial therapy. Candidiasis of the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, as well as intestinal dysbiosis of stage III-IV was detected in 36 patients (66.7%). The use of antibiotics with hepatotoxic properties (cephalosporins, lincosamines, metronidazole) in two patients (3.7%) with chronic hepatitis C and B led to the progression of liver failure, which was accompanied by high fermentemia (ALT 1500 IU, AST 1000 IU) and jaundice.
The development of congestive heart failure with the appearance of acrocyanosis, moist rales in the basal parts of the lungs, peripheral edema in combination with cardiomegaly and a drop in ejection fraction to 50-45% was observed in five patients (9.3%) against the background of massive infusion therapy.
Long-term anticoagulant therapy in 20.4% (11 people) of observations was accompanied by an increase in plasma tolerance to heparin, which was clinically expressed in the development of peripheral phlebothrombosis, while we did not observe heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in the examined group of patients.
Positive results of conservative therapy were obtained in 70.2% of patients (56 people) with TC lesions and only in 32% of patients (6 people) from the second group. The outcome of IE in both groups of patients was the formation of heart valve insufficiency.
Hospital mortality for IE in drug addicts was 29.4% (24 people), while in patients with damage to the left chambers of the heart (second group) the mortality rate was 68% (19 people).
According to autopsy data, the main causes of death in patients with IE were:
- septicopyemia with the formation of purulent foci in the liver, kidneys, spleen, brain with the development of multiple organ failure (46.2%);
- heart failure due to polyposis-ulcerative endocarditis with destruction of the heart valves, as well as acute myocarditis with dilatation of the heart cavities (39.4%);
- secondary nephropathy with the development of renal failure, pulmonary edema, cerebral edema (14.4%).
Thus, the characteristic features of IE in people with drug addiction are an acute course of the disease with damage to the right chambers of the heart and relapses of septic pulmonary embolism. The causative agent of IE in 71.3% of injection drug users is highly virulent Staphylococcus aureus. The formation of tricuspid valve insufficiency of degrees I-III has become the most common complication of IE in drug addicts. Moreover, most patients do not experience severe disturbances of central hemodynamics leading to the development of acute circulatory failure.
Subacute IE in patients with predisposing heart diseases, as well as in elderly and senile people, occurs with predominant damage to the left chambers of the heart, and monovalvular damage predominates in the older age group. The presence of concomitant pathology in people over 60 years of age masks the course of the underlying disease, which is responsible for late diagnosis and high mortality of patients. The protracted course of IE is characterized by low inoculability of the pathogen compared to acute forms of the disease. The development of thromboembolism of vessels in the systemic circulation is a characteristic clinical feature of subacute IE.
A positive effect from conservative therapy is observed in the majority of patients with IE with TC lesions, while in subacute endocarditis of the left chambers of the heart, conservative therapy is ineffective in most patients.
Hospital mortality in both groups of patients is due to dissemination of the pathogen with the formation of purulent foci and multiple organ failure, as well as the development of acute circulatory failure and secondary nephropathy.
Literature
- Butkevich O. M., Vinogradova T. L. Infective endocarditis. - M., 1997.
- Simonenko V. B., Kolesnikov S. A. Infective endocarditis: current course, diagnosis, principles of treatment and prevention. - Wedge. Med., 1999. - 3. - P. 44-49.
- Tazina S. Ya., Gurevich M. A. Modern infective endocarditis. - Wedge. med., 1999. - 12. - pp. 19-23.
- Bansal RC Infective endocarditis. Med Clin North America 1995; 79 (5): 1205-1239.
- Bayer AS, Bolger AF, Taubert KA et al. Diagnosis and management of infective endocarditis and its complications. Circulation 1998; 98: 2936-2948.
- McKinsey DS, Ratts TE, Bisno AI Underlying cardiac lesions in adults with infective endocarditis. The changing spectrum. Amer J Med 1987; 82: 681-688.
- Lamas CC Eykyn SJ Suggested modifications to the Duke criteria for the clinical diagnosis of native valve and prosthetic valve endocarditis: analysis of 118 pathologically proven cases. Clin Infect Dis 1997; 25: 713-719.
- Durack DT, Lukes AS, Bright DK et al. New criteria for diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis Utilization of Specific Echocardiographic Finding. Amer J Med 1994; 96: 200-209.
- Tyurin V.P., Dubinina S.V. Infectious endocarditis in elderly and senile people. - Wedge. Med., 2000. - 4. - P. 53-56.
V. I. Ulanova V. I. Mazurov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, St. Petersburg
Classification and causes of endocarditis
In accordance with the causes and clinical manifestations, the disease is classified as follows.
Infectious (bacterial) endocarditis most often manifests itself in an acute form. Ulcers and polyps form on the heart valves or in the heart tissues, which lead to functional disorders.
The chronic or subacute form is usually caused by streptococci. The disease is manifested by ulceration and changes in the shape of the heart valves, the formation of blood clots in the vessels, followed by blockage. The consequences may be inflammation of the kidneys and heart attacks of other organs.
A non-infectious disease occurs against the background of a general weakening of the body, with various intoxications, and in older people with the development of marasmus. Among the forms are degenerative warty, abacterial, etc. Most often it manifests itself in the form of thrombotic deposits on valve tissue.
Rheumatic endocarditis , as the name suggests, occurs due to rheumatism. In this case, inflammation spreads to the heart valves and causes heart defects. There are 4 forms: diffuse, acute warty, recurrent warty, fibroplastic.
Loeffler's endocarditis is characterized by an increase in blood eosinophils and a decrease in the volume of the heart chambers due to fibrous changes in the endocardium and then the myocardium. There are three stages: acute (cell death within 5-6 weeks), thrombotic (formation of blood clots and atrophy of some tissues), fibrosis (sclerosis and thickening of the endocardium).
Preventive actions
Endocarditis is one of the few heart diseases whose development can be prevented. Doctors give the following recommendations:
- Treat any infection in a timely manner, even if it is a simple sore throat. Under no circumstances should you “carry it on your feet.” Bed rest, taking medications and traditional medicine will reduce the load on the heart.
- If you experience even slight discomfort in the chest area and shortness of breath during physical activity, you should visit a cardiologist and undergo an examination. When endocarditis is detected at an early stage, recovery occurs in 98% of cases.
- If there is a history of any heart disease, including congenital defects, mandatory medical examinations with a special examination are recommended. Prevent pathogenic bacteria and infectious agents from entering the body. Be sure to strengthen your immune system.
More information about how you can avoid the development of inflammation of the inner lining of the heart and how rheumatic endocarditis is prevented can be found on our website.
Related services: Cardiological Check-up Complex cardiac surgery (simple)
Infectious (bacterial) endocarditis
In the acute form, the symptoms of bacterial endocarditis develop quite quickly. Typically, the infection affects the lining of the heart valves, 2-10 mm ulcers appear on the tissues of the valves, and the valves themselves swell - platelets and fibrin accumulate, and aneurysms form. As a result, one of the large vessels may become blocked by a blood clot, and valve particles may come off. In some cases, septic infarction cannot be excluded.
If you do not seek qualified help in time and do not start treatment:
- heart failure develops;
- the structure of valves and leaflets is deformed;
- arrhythmic phenomena appear;
- hemodynamics are impaired.
Patients with subacute septic endocarditis are characterized by the same manifestations of pathology, but in this case, most often the tissues are affected by thrombotic formations, which sooner or later clog one of the most important vessels.
Treatment
Most cases of endocarditis can be treated with antibiotics. In severe cases, they are injected into a vein. A blood culture test helps select the right antibiotic or combination of antibiotics. Treatment usually lasts from two to six weeks.
Surgical treatment of endocarditis
In 15-25% of cases, endocarditis leads to structural changes in the heart, which requires surgical treatment.
Surgery may be required if:
- heart failure, when the heart does not pump blood efficiently enough
- ineffectiveness of treatment with antibacterial or antifungal agents
- detection of blood clots in the cavities of the heart
- presence of an artificial valve
- suspected abscess or fistula (abnormal communication between cavities) in the heart area.
Three main types of operations are used for treatment:
- correction of valves with restoration of their normal shape
- replacement of damaged valves with artificial ones - prosthetics
- excision of an abscess or removal of fistulas.
Endocarditis in children
In children, the most common bacterial type of this disease occurs. The pathology is expressed by damage to the mitral and aortic valves, and then spreads to the internal cardiac tissues:
- the child experiences acute toxicosis;
- endocardial tissue becomes inflamed;
- myocardial damage occurs;
- blood vessels may become clogged;
- blood flow is disrupted.
Infectious endocarditis in children usually develops at a faster rate; inflammation can spread to other internal organs and lead to liver and kidney failure. Therefore, in this case, it is necessary to seek professional cardiac help as soon as possible.
Complications of endocarditis
Stroke is considered one of the most serious complications. If there is at least one of the following signs, you should immediately call an ambulance:
- facial asymmetry, in which the patient cannot smile, there is sagging of half the mouth
- weakness or numbness in the arms, inability to raise the arms up and hold them
- slurred speech.
Another serious complication is abscesses in the brain, kidneys, spleen, and liver.
If endocarditis is not treated, heart failure occurs, i.e. decreased pumping function of the heart.
Symptoms of endocarditis
The disease is characterized by an asymptomatic course at an early stage, as well as a sudden exacerbation against the background of a relatively healthy state. Symptoms of endocarditis in adult patients usually appear 10-14 days after infection:
- fever with chills, profuse sweating;
- the temperature may rise for several days;
- signs of intoxication appear: headache, weakness, exhaustion;
- the skin may acquire a pale, yellowish tint;
- rashes may be observed on the mucous membranes, feet, and palms.
These signs indicate the presence of an infection in the body, so you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
They are complemented by more characteristic symptoms of infective endocarditis in adults, which indicate the development of this particular disease:
- arthritic changes in joints;
- damage to the heart valves;
- thrombosis and blockage of large arteries;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- kidney infarction and other lesions;
- rapidly developing heart failure;
- pericarditis.
These symptoms of endocarditis are identified during diagnostic procedures.
Clinical manifestations
The clinical and anatomical picture of septic endocarditis depends on many factors: stage, prevalence of damage to certain organs, differentiation by infectious agents. The disease is usually preceded by tooth extraction, tonsillectomy, surgery or examination on the urethra, and abortion. The disease develops unnoticed, usually within two weeks from the moment of injury, but quickly gains momentum.
Main clinical manifestations:
fast fatiguability;- fever;
- weight loss;
- prostration;
- hematuria;
- night sweats;
- arthralgia.
Other manifestations of the disease are also possible. Emboli cause paralysis, chest pain due to myocarditis or pulmonary infarction. Vascular disorders provoke pain in the extremities, abdominal area, and hematuria.
Severe disorders also manifest themselves in the brain in the form of ischemia, abscesses, toxic encephalopathies, subarachnoid hemorrhages as a result of rupture of mycotic aneurysm, and meningitis.
Remitting fever with chills also causes problems for the patient. The pulse is often high, and it accelerates even more with the development of heart failure.
The appearance of the sick person will tell you a lot. The patient may exhibit pallor and mucocutaneous manifestations. As a rule, these are small ruby petechiae, similar to hemorrhages, that do not lighten when pressed. The main localization of the rash is the oral cavity, conjunctiva, and upper chest. On the mucous membranes they are distinguished by pallor in the middle of the formation. Subungual linear hemorrhages also attract attention. It is important to differentiate them from traumatic injuries.
Arterial emboli cause gangrene of the arms or legs. The fingers of the upper extremities may change like “drum sticks”, and nodules may appear on the surface of the palms. Sometimes patients experience slight jaundice.
It is very important to listen to the heart if septic endocarditis is suspected.
Signs noted during auscultation:
- dullness of blows;
- arrhythmia;
- cardiopalmus;
- gallopic rhythm.
Symptoms of malformation:
- weakening (disappearance) of the second tone over the aorta;
- systolic murmur at the top;
- diastolic over the aorta and Botkin point;
- Flint noise.
Splenomegaly is common in infective endocarditis. With necrotic lesions of the spleen, a typical friction noise occurs. The liver remains of normal size until heart failure develops.
Diagnosis of endocarditis
Qualified diagnosis of infective endocarditis is a whole complex of examinations. The patient is prescribed a cardiac screening program, which includes:
- various types of electrocardiogram (24-hour monitoring, stress echocardiography);
- Ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels;
- computer sphygmomanometry.
Modern diagnostic methods are also applicable: cardiac rhythmography, Dopplerography. Blood tests and cultures for sterility are required - one of the most important examinations for infective endocarditis.
Modern diagnostic methods
World clinical practice has summarized and derived criteria that are used for the diagnosis of septic endocarditis. They are divided into large and small. Larger ones include blood tests, during which a culture of microbes responsible for infecting the body is sown.
Big signs:
- two positive blood cultures taken at least twelve hours apart;
- three positive cultures out of three;
- out of four blood cultures or more, the maximum is positive;
- proven endocardial damage;
- characteristic symptoms of acute septic endocarditis on ultrasound of the cardiovascular system.
Minor signs:
- predisposition;
- fever;
- vascular changes;
- change in laboratory blood standards. The presence of anemia, a shift in the leukocyte formula, an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the presence of C-reactive protein, a decrease in platelets, etc.
The final diagnosis is made if the so-called pathological criteria are present:
- presence of positive blood culture;
- presence of intravascular substrate;
- myocardial abscesses.
All of the above positions must be confirmed histologically or by adding the criteria: two large, or one large, plus three small or five small.
The diagnosis of septic endocarditis is called into question, provided that there were not enough criteria for a certain infectious lesion of the myocardium, but it was not possible to completely refute it.
Suspicion of pathology is removed if, after taking antibiotics for four days, there is a disappearance of symptoms or signs of infection are absent in blood samples for the same duration of therapy.
Treatment of endocarditis
At an early stage, treatment of infective endocarditis consists of antibiotic therapy and cardiac support with medications. If septic endocarditis has already manifested itself as significant changes in the tissues of the heart (damage to the valves, aorta, myocardium), surgical intervention is possible.
- Antibacterial treatment for symptoms of endocarditis involves the use of modern antibiotics (benzylpenicillin, penicillins, amphotericin, etc.) administered intravenously.
- Passive immunization is carried out to neutralize bacteria in the body. For this purpose, special antitoxic serums (immunoglobulin, hyperimmune plasma) are most often used intravenously.
- Surgical intervention is performed in cases where it is necessary to remove foci of infection in the tissues of the heart and restore cardiac structures altered by the disease. The services of a cardiac surgeon are necessary if the patient has progressive heart failure, vascular thromboembolism, etc.
Treatment and observation of the patient
This disease is always treated in a hospital setting with adherence to medication and diet. The patient's physical activity is minimal.
For certain septic endocarditis, massive antibiotic treatment is used. The drug is selected taking into account the sensitivity of the suspected infectious agent to it. Usually, the prescription of a broad-spectrum drug from a number of penicillins and cephalosporins is indicated. They are often combined with aminoglycosides. Antifungals and NSAIDs may be prescribed.
For endocarditis with an unknown pathogen, combined antibiotics are used, for example, tetracycline, terramycin, erythromycin. It is preferable to change drugs every two to four weeks due to the development of resistance of microorganisms to them.
The effectiveness of treatment can be assessed by the following criteria:
48–72 hours after the start of therapy, health and appetite improve, chills disappear;- at the end of the first week, body temperature drops to normal levels, petechiae and embolism disappear, hemoglobin increases, ESR decreases, sterility of crops is recorded;
- at the end of the third week – the leukemia formula, ESR, and spleen condition return to normal;
- at the end of treatment - normal ESR, proteinogram, hemoglobin. New vasculitis and thromboembolism do not occur.
Sometimes surgery cannot be avoided. As a rule, this occurs in cases where conservative therapy has not been successful.
In terms of further observation, the patient is indicated for heart valve replacement. It is important to know that a recurrence of an infectious disease is always possible.
Sanatorium treatment in an institution with a cardiological focus may be recommended. Clinical observation of a patient who has had infective endocarditis is mandatory.
In terms of prognosis, it is worth noting that patients without treatment do not often recover. With early antibiotic therapy, approximately 70 percent of patients with infection of their own valve structure and 50 percent with damage to prosthetic structures overcome the disease.
Causes
There are many causes of endocarditis:
- infections;
- injuries;
- allergic diseases;
- intoxication;
- connective tissue damage.
Often endocarditis develops not as an independent disease, but as a consequence of other pathologies in the body. Both men and women are equally susceptible to the disease. It can occur at any age. Currently, about 130 types of microorganisms are known that can provoke endocarditis.
Prevention of endocarditis
If you are at increased risk of endocarditis or have had this disease in your life, it is important to protect yourself from possible infection. To do this you need:
- Monitor the condition of your teeth and gums - regularly brush your teeth and use dental floss. You should visit your dentist regularly to minimize the risk of bacteria entering your bloodstream through your mouth.
- Proper skin care: wash regularly with soap. It is very important to treat any cuts and abrasions. It is advisable to avoid any cosmetic procedures that violate the integrity of the skin, such as piercings and tattoos.
- Use antibiotics correctly. These medications should only be used when absolutely necessary. If used incorrectly, microbial resistance occurs (resistance), which complicates the treatment of endocarditis. Prophylactic use of antibiotics is indicated only in a few cases: before surgical interventions in the gum area or in the area of the tops of teeth and before invasive manipulations in the respiratory tract or infected skin. Prophylactic antibiotic treatment is not carried out before dental procedures, before procedures in the gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract.