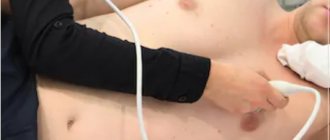
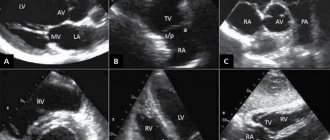
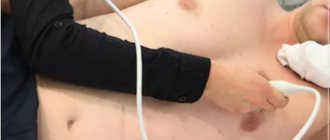
What is a cardiac echo?
Echocardiography is the leading method for diagnosing pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
High information content, safety for humans and relatively low price of cardiac ultrasound (compared to other types of diagnostics) are the three main parameters due to which the method has become widespread. Cardiac echocardiography is a non-invasive ultrasound diagnostic method. During the examination, the doctor, in real time, evaluates the activity, size and structure of all structures of the heart:
- heart muscles,
- chambers (atria and ventricles),
- valve apparatus,
- walls,
- main vessels.
Using an ultrasound examination of the heart, a doctor can confirm or exclude many pathologies of the heart and large vessels in both children and adults:
- acquired congenital heart defects,
- post-infarction cardiosclerosis,
- atrial fibrillation,
- heart tumors,
- intracavitary thrombi,
- hypertension,
- ischemic disease,
- valve damage, etc.
Where to get an echocardiogram
Standard echocardiography is carried out both in public medical institutions (clinics and hospitals) and in private medical centers. To register for an examination, you must provide a referral from your attending physician or cardiologist.
More specific types of echocardiography - transesophageal examination or stress echocardiography - can only be performed in specialized medical institutions, since they require special equipment and personnel who have undergone special training.
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis
In our center, in addition to standard echoCG (one-dimensional and two-dimensional), with which the doctor can identify heart pathologies, echocardiography with Doppler analysis is performed. Our equipment allows us to perform an advanced assessment of the functioning of the heart and great vessels using the following techniques:
- pulsed wave dopplerography
. Serves to assess the pumping function of the heart. Allows you to record the clicks of opening and closing valves. Registers the speed of blood flow in the valves and great vessels;
- continuous wave Dopplerography.
Allows you to measure high blood flow velocities. Also serves to calculate pressure in large vessels and cavities of the heart in different phases of the cardiac cycle;
- color dopplerography
. Allows you to evaluate not only the speed, but also the direction of blood movement through the main vessels. Used to assess pathological blood flow through the heart valves.
What does an ultrasound show?
Sonography is used in medicine both for diagnosing various diseases and for visual monitoring of complex surgical interventions.
The scope of application of ultrasound includes the study of:
- abdominal organs;
- thyroid gland;
- heart (echocardiography);
- vessels (carotid arteries or veins of the legs);
- mammary glands;
- uterus, ovaries (including during pregnancy);
- joints, such as the hip.
There are two types of ultrasound: diagnostic and therapeutic. Diagnostic ultrasound creates images using high-frequency sound waves generated by a transducer (probe). But for better visualization, the ultrasound head can also be inserted into the body through the gastrointestinal tract, vagina or blood vessels.
Therapeutic ultrasound also works with sound waves, but does not generate images. It is used to move and apply pressure to tissue, heat it, dissolve blood clots, or administer medications. Standard ultrasound has no harmful effects.
Abdomen
It is used both for diagnosing diseases and for monitoring the course of pathological processes in the body. Used to evaluate the condition of various organs, such as the liver, kidneys and spleen. The doctor determines the structure, size and location of the bladder, gallbladder and pancreas.
Limited assessment of bowel health is possible. It is also possible to detect free fluid in the abdominal cavity, such as inflammatory effusion or blood.
Thyroid
It is possible to determine the structure, size and focal formations. Scanning allows you to identify problems at the initial stages of progression, which makes it possible to begin treatment in a timely manner - before complications develop. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is the most accessible and informative research method that can be performed as many times as necessary without harm to the patient’s health.
Echocardiography
Typically, an echo examination of the heart is performed like any other ultrasound, that is, using a sensor that the doctor moves over the surface of the patient’s body. When diagnosing the heart, transesophageal (TEE - transesophageal) echocardiography can be performed. The doctor pushes a special probe through the esophagus to the entrance to the stomach. The heart is in close proximity and can therefore be examined better.
Doppler ultrasound
A comprehensive study aimed at determining the anatomical structure, nature, speed of blood flow and condition of the vascular walls (tension, elasticity). Allows you to identify damage to vascular structures, congenital anomalies and pathological tortuosity. Visualizes atherosclerotic changes, blood flow disorders, aneurysms and occlusions, as well as inflammatory processes and thrombophlebitis.
Ultrasound of female breast
A painless examination is the “gold standard” for the prevention of breast diseases. Allows you to examine all areas of glandular tissue, much more informative than with radiography and mammography. Using breast sonography, it is possible to identify various pathological changes: cysts and tumors, as well as assess the condition of the lymph nodes.
Gynecological ultrasound
Sonography of the pelvic organs is prescribed to evaluate ongoing therapy in gynecology or to identify pathological changes in the uterus, appendages, etc. Gynecological ultrasound reveals the fact of pregnancy, fetal development abnormalities and pathological disorders in the reproductive health of a woman.
Sonography of joints
Aimed at studying the condition of soft tissues and bone structures to identify pathological foci and prescribe effective therapy. Ultrasound of joints is performed for congenital anomalies, after injuries and to diagnose degenerative or inflammatory diseases. The diagnostic procedure does not replace radiography of the joint, since it does not allow assessing the displacement, the presence of fragments and the nature of the fracture.
Indications for echocardiography (echocardiography)
Diseases of the cardiovascular system in both children and adults can often develop without symptoms. In order to notice in time and prevent the development of a minor pathology into a serious disease, it is recommended to undergo echocardiography once a year. If the following symptoms occur, a study is required:
- acute pain in the heart and chest;
- feeling of lack of air and shortness of breath;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- swelling of the legs;
- frequent bluishness of the skin: ears, hands and fingers, around the lips;
- fast fatiguability;
- heart rhythm disturbances and detection of noise during listening;
- frequent headaches;
- hypertonic disease;
- atherosclerosis.
An ultrasound of the heart of a child under one year of age is most often performed on the direction of a cardiologist or therapist. It is given when noise is detected during listening or if one of the immediate family suffers from severe cardiac diseases. In addition, it is recommended to perform an ultrasound of the child’s heart in the following cases:
- the baby weakly sucks the breast;
- there is blueness around the mouth and nose when crying and sucking;
- with stunted growth and weight gain;
- with increased sweating.
For older children, echocardiography (echoCG) is prescribed if the child:
- often suffers from pneumonia,
- loses consciousness
- complains of pain in the heart area,
- gets tired quickly.
The price of echocardiography for adults and children is the same.
Indications and contraindications
The need for a heart ultrasound is determined by a cardiologist. At the same time, he relies on the patient’s words about the occurrence of symptoms indicating specific pathologies.
- frequently increasing blood pressure;
- pain in the chest;
- shortness of breath with active exertion;
- swelling of the arms and legs;
- pale or bluish skin;
- presence of extraneous non-functional noise;
- an electrocardiogram or Holter ECG monitoring showed irregular heartbeats.
Patients diagnosed with chronic cardiovascular diseases are recommended to undergo mandatory regular echocardiography – once every six months.
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- defect of the interventricular, interatrial septum;
- angina pectoris;
- myocarditis, pericarditis;
- diagnosed aneurysms;
- ischemia;
- previous myocardial infarction;
- myocardial neoplasms;
- atherosclerosis;
- arterial hypertension.
Heart ultrasound is a non-invasive and safe examination, suitable even for newborn children. The reasons for carrying them out are a weak sucking reflex, low temperature of the arms and legs, increased sweating, and a lag in weight gain.
Professional athletes regularly undergo echocardiography to monitor their health and access to competition. This mainly applies to sports such as weightlifting and long-distance running.
This examination is also prescribed to women during pregnancy if they suspect they have a pathology. Echocardiography of the fetal heart is rarely prescribed, since a woman at different stages of pregnancy undergoes a mandatory set of screening ultrasounds, during which the condition of the organs of the unborn child is studied in great detail.
For preventive purposes, a heart check using ultrasound can be performed annually by any person who cares about their health. It will be more effective to conduct a comprehensive examination in conjunction with an ECG, since these two methods complement each other. A cardiogram will reveal deviations in heart rhythm (if any), and an ultrasound will determine the causes of these deviations.
There are no absolute contraindications for standard echocardiography, since the procedure is carried out without intervention inside the body. The only relative prohibition on diagnostics is skin irritation in the chest area.
How is cardiac echocardiography performed?
In our clinic or directly at the patient’s home, tests are carried out only by certified diagnosticians specializing in cardiovascular diseases. Thanks to their extensive experience and special training, they are well aware of how the structures of the heart are displayed on an echocardiogram, normally and in the presence of pathologies.
The procedure for echocardiography and ultrasound of the heart vessels (Dopplerography), performed at home or in the clinic, is simple and does not require special training. During the examination, the patient is placed on the couch on his back or left side. The doctor, using a special sensor, scans the heart in various positions to obtain images of all its parts and surrounding vessels.
After the procedure, a conclusion is issued. Depending on what the ultrasound of the heart shows, the doctor may prescribe additional studies and tests.
Preparing for the study
Although most ultrasound examinations do not require preparation, there are a few exceptions:
- before an ultrasound of the gallbladder, the patient is asked not to eat or drink anything 6 hours before the procedure;
- a full bladder may be required during pelvic ultrasound;
- to improve image clarity, a harmless substance called contrast agent is injected before the examination;
- If necessary, intravenous tranquilizers are used.
Young children may require additional preparation for an ultrasound. We are talking about the use of sedatives to prevent the child from being overly active during the procedure.
How is the stress echo CG procedure performed?
At the CBCP clinic, stress echocardiography is performed in two ways:
- using horizontal and vertical bicycle ergometers;
- using special stimulant drugs.
The study is carried out under the supervision of certified and experienced specialists:
- a cardiologist with special training in performing stress tests;
- diagnostician working in the field of stress echocardiography and cardiac ultrasound.
First, the patient, who is at rest, undergoes echocardiography and records the indicators. After which the body is exposed to strictly calculated physical activity or medicinal stimulants. Doctors monitor changes in the well-being and functional state of the patient’s heart, processing the results using a computer.
Stress echo CG makes it possible to obtain images of the heart at various stages of the examination. The indicators recorded under load are analyzed and compared with the indicators at rest.
Possible types of procedure
In cardiology, there are several types of echocardiography depending on the technique used:
- Transthoracic. This is the most standard type of study, in which a hardware sensor is located on the surface of the skin within the chest. It is used most often due to its safety and availability. However, in rare situations this technique is not informative, for example, if the patient has too much fat or the chest is deformed. Then the standard technique will not allow you to obtain a clear image.
- Transesophageal. The difference between this type is that the sensor is inserted into the body through the esophagus. Studying the structure of the heart in this way provides more information than with the standard method. After all, the esophagus is located near the heart, and this allows the use of high-frequency sensors and obtain images of its segments with high resolution. Examination through the esophagus is prescribed to diagnose pathological changes in natural and prosthetic valves, diseases of the aorta, atrial septal defects, pathological condition of the pericardium, thrombosis and atherosclerosis, infections in the myocardium. The disadvantages of this type of examination include the patient’s discomfort when the sensor moves along the esophagus: increased gag reflex. Unpleasant sensations are relieved by taking specially selected sedatives and analgesics for the pharynx. If necessary, general anesthesia is given.
- Stress echocardiography. The method is an ultrasound examination of the heart with a simultaneous stress test. In other words, the patient receives a certain load, and the doctor monitors the heart’s reaction on the screen of the device. Running on a treadmill, simulating cycling on a simulator, electrical stimulation through the esophagus, and medications are used as test loads. The load is selected individually for each patient. The main purpose of such an echocardiography is to find out whether the coronary vessels are narrowing before and after exercise or stimulation, and to assess the condition of the myocardium. This method will also confirm or deny the presence of ischemia or angina.
Echocardiography is also classified according to the format of the resulting image:
- One-dimensional echocardiography (or M-mode). It will show a top view of the heart on the device screen.
- Two-dimensional. The sensor transmits two-plane visualization to the monitor.
- Doppler. An improved method that allows you to additionally see the direction and speed of blood flow in the vessels. Doppler sonography is of great diagnostic importance in cardiology, as it reveals hidden heart defects and the filling of the left ventricle. Doppler is usually combined with two-dimensional echocardiography.
- Contrasting. It involves the introduction of an echo contrast agent into the patient’s circulatory system, as in a CT scan (computed tomography). This allows you to clearly visualize the inner surface of the heart and see abnormalities.
Benefits of stress echocardiography
Stress echo CG is a safe study that can be repeated as many times as necessary. Highly sensitive equipment is highly informative and detects even asymptomatic abnormalities in the heart.
This method also makes it possible to:
- diagnose silent myocardial ischemia and angina pectoris;
- assess heart rate;
- determine the viability of the myocardium after a heart attack;
- identify blood flow disorders;
- record changes in blood pressure at rest and after exercise.
What is functional diagnostics
Functional diagnostics is a branch of medicine that evaluates, detects abnormalities, and establishes the degree of disturbances in the functioning of various organs and systems by objectively measuring their performance using instrumental studies.
The specific purpose of functional diagnostics depends on the clinical task. So in some cases it is necessary to identify deviations in a specific organ function. For example, analyze the secretion of hydrochloric acid by the stomach. In other cases, it is necessary to evaluate the functioning of several important organs that constitute a physiological system. For example, evaluate blood pressure indicators over time. Studies are also carried out to assess the functioning of the system - blood circulation, breathing.
Interpretation of cardiac ultrasound results
The results of the study are interpreted using an echocardiograph. Diagnostics provides information on more than 100 indicators of heart condition.
After the procedure, you will receive a transcript of the study results. Do not attempt to independently analyze the data obtained, much less draw conclusions about the use of any medications. This is especially true for ultrasound data of a child. Only a cardiologist can accurately and correctly interpret the obtained indicators.
Doctors at the CBCP clinic will explain to you in detail the meaning of the parameters indicated in the report and make an objective diagnosis. You will receive further recommendations regarding treatment and a prognosis of your health situation.
Research methodology
For transthoracic echocardiography, the patient is placed in the left lateral position. When a person lies in this position, the apex of the heart and the left side of the chest are brought closer together. This makes it possible to provide the most accurate visualization of the heart - as a result, all four of its chambers are visible on the monitor at once.
The doctor applies a gel to the sensor, which improves contact between the electrode and the body. After this, the sensor is alternately installed first in the jugular fossa, then in the area of the fifth intercostal space, where the apex beat of the heart can be monitored as clearly as possible, and then under the xiphoid process.
Of course, every doctor strives to ensure that the results of the study are as accurate as possible. It should be noted that how informative the procedure will be depends on three main factors.
First of all, the anatomical features of the patient should be taken into account. Serious obstacles to ultrasound are obesity, chest deformation and other similar factors. As a result, the resulting image may not be clear and cannot be interpreted properly. In order to clarify the diagnosis, doctors in such cases offer a transesophageal examination or MRI.
The quality of the equipment should also be taken into account. Of course, more modern equipment will provide the doctor with more opportunities to obtain sufficient information about the patient's heart.
Finally, the competence of the person conducting the examination should be taken into account. In this case, not only his technical skills are important (the ability to position the patient in the correct position and place the sensor at the right point), but also the ability to analyze the data obtained.
When performing stress echocardiography, the patient first undergoes a regular echocardiography, and then special sensors are applied that record parameters during physical activity. For this purpose, bicycle ergometers, treadmill test, transesophageal electrical stimulation or medications are used. In this case, the initial load is minimal, and then it is gradually increased, monitoring blood pressure and pulse indicators. If the patient's health worsens, the examination is stopped.
All this time, an electrocardiogram is continuously performed, which makes it possible to quickly respond if any extreme situations arise. During exercise, the patient may feel dizziness, increased heart rate, and discomfort in the heart area. After stopping the exercise, the heart rate slows down. Sometimes, in order for the heart to function completely back to normal, it is necessary to administer other medications. In this case, the patient's condition is carefully monitored until complete recovery.
Typically, the entire procedure lasts about an hour.
Transesophageal echocardiography begins with irrigating the patient's mouth and pharynx with lidocaine solution. This is intended to reduce the gag reflex during insertion of the endoscope. After this, the patient is asked to lie on his left side, a mouthpiece is inserted into his mouth and an endoscope is inserted through which ultrasound will be received and delivered.
Benefits of echocardiography (echoCG) at the CBCP clinic
Cardiac ultrasound, both directly at the CBCP clinic and at the patient’s home, is performed using modern equipment by highly qualified specialists. Our doctors have extensive experience in conducting functional studies, as well as certificates confirming successful training in ultrasound diagnostics in the field of cardiology. The clinic uses additional research methods to make the most accurate diagnosis.
You can get detailed information on heart ultrasound for adults and children (including at home), as well as echocardiography with Doppler analysis in Moscow, the price of the procedure and the possibility of making an appointment by calling, or by leaving a request on the website.
Functional diagnostic methods
Functional diagnostics is based on the use of modern precision equipment with high sensitivity. There are various methods for diagnosing diseases of the heart, cerebral vessels, central nervous system, pulmonary system, muscular system, etc. All of them have one feature - they do not provide an unambiguous interpretation of the results in all cases. Each person’s body is unique and the norms for the functioning of its organs and systems are different. Therefore, in functional diagnostics, a comprehensive comparative study takes place under different loads, which makes it possible to evaluate the functioning of an organ or system in dynamics.
On-site diagnostics at home
The basic package includes the following services:
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Basic complex | |
| Preliminary consultation with a cardiologist | |
| ECG 12 leads with interpretation | |
| EchoCG (ultrasound of the heart) | |
| Final consultation with a cardiologist with selection of therapy and recommendations | |
| Within the Moscow Ring Road cost | 10 000 |
| Outside the Moscow Ring Road (cost of one kilometer) | 150 |
Re-departure of the team*:
- consultation with a cardiologist - 5,000 rubles
- consultation + ECG with interpretation - 6000 rubles
- consultation + echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) - 8000 rubles
* outside the Moscow Ring Road the cost of one kilometer is 150 rubles.