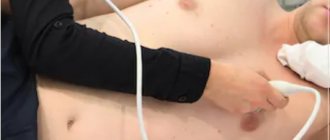
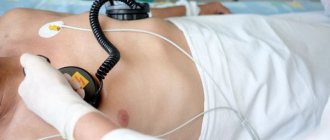
Echocardiography (Echo CG) is an ultrasound examination of the heart necessary to assess its functional activity. The ultrasound machine's sensors record reflected ultrasonic waves, resulting in an image being formed on the screen. Decoding the results of a cardiac ultrasound is carried out by a cardiologist and takes 5-7 minutes. After viewing the echocardiography results, the doctor can immediately decide whether treatment or hospitalization is necessary.
What does Echo KG show?
The procedure is carried out by an ultrasound diagnostic specialist, and the duration of the examination is 15-30 minutes. Echocardiography is prescribed for frequent or recurrent pain in the heart, irregular heartbeat, severe shortness of breath, high or low blood pressure, suspected heart disease, or a previous heart attack. The main indicators of cardiac echocardiography are presented below:
- ventricular myocardium mass (right and left);
- condition and contractility of the valve apparatus;
- the speed of blood flow through the heart valves and chambers;
- the thickness of the partitions between the chambers of the heart.
There is no cause for concern if your cardiac ultrasound results are normal. However, the decoding results may differ from the standard ones - the data obtained will tell about anomalies in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Based on what the Echocardiogram of the heart shows in adults or children, the doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis:
- pericarditis, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy;
- pre-infarction condition/myocardial infarction;
- heart failure (left-sided, right-sided);
- coronary heart disease (myocardial damage).
A comprehensive ultrasound of the heart with Doppler sonography also displays indicators that allow you to assess the condition of the blood vessels. The procedure makes it possible to determine the speed of blood flow, as well as identify pathological changes in the walls of blood vessels. Thanks to the study, the doctor can timely detect atherosclerotic processes, aortic aneurysm and heart defects.
Ultrasound of the heart: when is it prescribed and what will it show?
To clarify a cardiac diagnosis, one of the most frequently prescribed studies is an ECG. However, often the doctor refers the patient to an ultrasound of the heart. What does this diagnosis show and is it worth doing it at all?
Today we are having an unusual conversation, as our consultants will be two doctors.
Olga Nikolaevna Vitkova, and her colleague, an ultrasound diagnostics doctor in pediatric practice, Inna Vyacheslavovna Popova, tell us about heart ultrasound and its capabilities.
— Olga Nikolaevna, Inna Vyacheslavovna, please tell us what ultrasound of the heart is and when is it prescribed?
This is a research method based on the use of ultrasound with certain characteristics for diagnostic purposes. Ultrasound is beyond the audibility of the human ear. During the examination, the ultrasound machine generates a stream of ultrasonic waves. The doctor directs them using a sensor to one or another part of the body. Ultrasound, having reached anatomical formations, is reflected from them and returns. These signals are recorded by an ultrasound machine, which, based on their characteristics, “constructs” an image of the organ being examined on the monitor screen.
Ultrasound examination allows us to judge the size of the heart, its layers, valves, and the characteristics of blood circulation.
It is prescribed for pain in the heart, high blood pressure, edema, shortness of breath, wheezing in the lungs; for dizziness, loss of consciousness, general weakness, prolonged increase in body temperature of unknown origin, patients with diabetes mellitus, and those with a history of myocardial infarction; people whose relatives suffered from certain diseases.
It's off scale! We are looking for the causes of high blood pressure. Read here
In children, ultrasound is performed on the direction of a cardiologist or pediatrician - most often if a heart defect is suspected. More than half of young patients come for examination precisely for this reason.
Ultrasound is prescribed for children with serious infections, in particular bacterial ones. Occasionally - if a heart tumor is suspected, it is extremely rare, but still a common diagnosis in children.
Preventive examinations are also performed for babies up to one year old.
— Are cardiac ultrasound and echocardiography the same study or are there differences between them? And if so, what is the difference?
Ultrasound of the heart and echocardiography are the same thing.
— Can ultrasound of the heart replace an ECG? What is the difference between these studies?
No, these studies are not interchangeable. It is correct to say that they complement each other. These methods characterize different aspects of the heart’s work. An ECG indicates the function of the conduction system of the heart and its possible disorders. With its help, you can indirectly judge the size of the cavities of the heart.
However, the ECG is not informative regarding the structural features of the organ - for example, the valve apparatus, the presence of defects, blood clots or inflammatory changes in the heart. In these cases, compared with ECG, ultrasound is the method of choice. It will allow you to directly evaluate the chambers of the heart, its layers, valves and their defects, aneurysms after a heart attack, the amount of blood ejected by the chambers of the heart, etc.
Specific example. The patient's ultrasound revealed tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), but we cannot say anything about its origin or type. This is the power of an ECG.
What causes tachycardia? Elena Viktorovna Novikova, a cardiologist at the Expert Kursk Clinic, says:
— What diseases can ultrasound of the heart diagnose?
Taking into account what has already been listed above, ultrasound also reveals signs of congestive heart failure (for example, fluid in the pericardial cavity), neoplasms and aneurysms of the heart, dilation of the heart chambers and blood clots in them, dissecting aortic aneurysm.
— In order to identify heart pathology, is it enough for a patient to undergo only an ultrasound scan or should the diagnosis be comprehensive?
No, ultrasound alone is definitely not enough. The examination must be comprehensive and must include a survey and examination of a doctor, an ECG and/or - as indicated - Holter monitoring (24-hour ECG), laboratory tests (depending on the intended diagnosis), ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck, gastrointestinal tract, as indicated - coronary angiography (x-ray examination of the heart vessels using a contrast agent).
Why are x-rays dangerous? Yulia Aleksandrovna Rutskaya, head of the radiation diagnostics department at Clinic Expert Kursk, says:
— Is there an alternative to cardiac ultrasound?
It depends on what you mean by alternative. If the method is safe, non-invasive and accessible, then there is no alternative. If it refers to diagnostic capabilities, to a certain extent, transesophageal echocardiography, as well as spiral computed tomography with a contrast agent, can be an alternative. These methods can be used in cases where traditional echocardiography is difficult for some reason or does not answer some of the doctor’s questions.
— How safe is heart ultrasound and how often can this study be done?
Completely safe. It can be performed as often as required.
— How is heart ultrasound performed for adults and children?
There are no fundamental differences between adults and children. It is performed with the patient lying down, more often on the left side. Using a sensor, the doctor examines all heart formations and evaluates a number of functional parameters.
The peculiarity of children is that it is often difficult to convince them to lie on their left side, and therefore studies are often performed on their back. Another point is the location of the sensor. In childhood, research is often carried out through the so-called subcostal access (when the sensor is located in the epigastrium). In adults, this approach is rarely used due to their anatomical features.
— Is preparation necessary for an ultrasound examination of the heart?
There is no special preparation for adults.
It is important to calm children before the test. Due to their inherent mobility and restlessness, they may not lie as they should. Therefore, in this regard, parents play a big role, who must explain to the child what is happening and calm him down. Before the planned examination, you can play ultrasound with your child at home.
It is recommended that before the study the child is well-rested and well-fed (but preferably not immediately after eating, i.e. not with a full stomach). Or, if conditions permit, a small child can first be euthanized and only then examined.
Occasionally, examinations are performed under anesthesia - usually in a hospital setting and for certain indications.
— Can ultrasound examination of the heart be recommended as a preventive method?
Yes. In addition, in children under 1 year of age, echocardiography for preventive purposes is mandatory, not to mention examination after infectious diseases.
— In order to undergo a heart ultrasound at the Expert Clinic, do you need a doctor’s referral?
You can undergo the examination with or without a referral. The advantage of a referral is that the doctor can provide some additional information about the patient (for example, about a heart murmur detected during an examination). Algori makes more sense.
You can sign up for a cardiac ultrasound here
Please note: diagnostics are not available in all cities
For reference:
Vitkova Olga Nikolaevna
Graduate of the Faculty of Medicine of the Smolensk State Medical Academy in 2012.
From 2012 to 2014 she completed clinical residency in the specialty “Therapy”.
In 2014, she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “Cardiology”, in 2015 - in the specialty “Ultrasound Diagnostics”.
Since 2021, he has been working at Clinic Expert Smolensk LLC as an Ultrasound Doctor.
Popova Inna Vyacheslavovna
Graduate of the pediatric faculty of the Smolensk State Medical Academy in 2007.
In 2008 she completed an internship in the specialty “Pediatrics”
In 2009, she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “Functional Diagnostics”, and in 2010 - in the specialty “Ultrasound Diagnostics”.
Since 2021, he has been working at Clinic Expert Smolensk LLC as an Ultrasound Doctor.
Normal echocardiogram findings
After completing the procedure, the doctor draws up a cardiac ultrasound protocol, which specifies the size and volume of the chambers, local contractility and blood pumping speed. The table shows the permissible values of cardiac echocardiography in men, women and children, which do not require special attention or treatment.
| Index | Men | Women | Children |
| Thickness of the interventricular septum | 6-10 mm | 6-9 mm | 2-3 mm |
| Thickness of the posterior wall of the ventricle | 6-10 mm | 6-9 mm | 2-3 mm |
| Left ventricular myocardial mass (LVMM) | 65-150 g | 65-150 g | 34-85 g |
| LVM index (takes into account the patient’s height) | 49-115 g/m2 | 43-95 g/m2 | 58-74 g/m2 |
| Ejection fraction | 55-70% | 50-55% | |
| Contractility | not violated | ||
If echocardiography readings deviate slightly from normal, it should be understood that the result may be affected by the person's age and health status. In older people, borderline values are acceptable; they are not always associated with heart disease. In childhood and adolescence, indicators can differ significantly, which is explained by the rapid growth of the child’s body.
Only a qualified doctor can decipher the results of an echocardiogram of the heart with normal or altered indicators, who will explain the situation and prescribe the optimal treatment. To confirm the diagnosis, electrocardiography (ECG), chest x-ray, laboratory blood diagnostics, etc. are additionally performed.
Diseases detected by echocardiography:
Echocardiography allows you to obtain important diagnostic information and identify many diseases in the early stages:
- acquired heart defects (rheumatism, infective endocarditis, degenerative aortic valve stenosis);
- Congenital heart defects (bicuspid aortic valve, patent foramen ovale, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Falo, Ebstein's anomaly, etc.);
- Left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy (with arterial hypertension, cardiomyopathies, valvular defects, etc.);
- Coronary heart disease and its complications (scar changes in the myocardium, aneurysm and thrombosis of the left ventricle, rupture of the interventricular septum, etc.);
- Cardiomyopathies (dilated, hypertrophic, restrictive, etc.);
- Chronic heart failure (systolic and diastolic forms);
- Infective endocarditis (damage to the heart valves due to infections);
- Dissecting aneurysm of the ascending aorta (life-threatening with a hereditary predisposition, traumatic or atherosclerotic lesion);
- Diseases of the pericardial sac (pericarditis, tumors, hydropericardium, etc.);
- Heart tumors (benign – myxoma, fibroma; malignant – sarcoma, mesothelioma and metastases in the heart);
- Heart damage due to extracardiac diseases (hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, amyloidosis, HIV, sarcoidosis, etc.).
The results obtained from echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) are superior to routine electrocardiography (ECG) in both diagnostic and prognostic criteria.
Ejection fraction
Along with other important parameters, an echocardiogram provides data on ejection fraction (EF), which measures the heart's activity during each beat. To understand the danger of deviations in such values, it is necessary to understand what EF is during cardiac ultrasound and why these indicators should not exceed the established norm.
Ejection fraction measures the volume of blood pushed from the ventricle into the blood vessels during one heartbeat. When conducting EchoCG, the ejection fraction of the left ventricle is taken into account, because it is the one that sends blood into the systemic circulation.
Even in a calm state, the heart of a healthy person releases most of the blood from the ventricle into the vessels - the normal EF according to cardiac ultrasound in adults is considered to be 55-70%. A significant decrease in the indicator (less than 40%) indicates the onset of heart failure. With this condition, blue skin, shortness of breath and periodic dizziness are observed.
How is an ultrasound of the heart performed?
First of all, we should consider the classic diagnostic method through the surface of the skin in the chest area (transthoracic). The procedure can be carried out in a hospital or at home - the person undresses to the waist and lies down on a flat surface. After applying the gel to the patient’s chest, the specialist begins the examination, which lasts 15-20 minutes. To decipher an ultrasound of the heart in an adult and draw up a conclusion, it will take an additional 10-15 minutes.
A much less common and more complex method of cardiac ultrasound, which is performed only in a hospital setting, is transesophageal cardiography: the sensor is inserted into the oropharynx and lowered down the esophagus to the required depth. The main advantage of this method is high detail. It is possible to obtain more accurate data than with transthoracic ultrasound of the heart. Transesophageal echocardiography is indicated before surgery to repair heart valves, ruptured aortas, repair heart defects, treat bacterial infections of the heart or valves, or endocarditis.
Ultrasound of the heart in Moscow
The most competent interpretation of a heart ultrasound may not bring results if a poor-quality diagnosis was carried out: this can happen if you were examined using outdated equipment, and the protocol was drawn up by an inexperienced, unqualified doctor.
Don't risk your health! Contact a trusted clinic! The Elena Malysheva Diagnostic Center is your confidence in the quality of diagnostics! Experienced doctors with many years of experience, an expert-class ultrasound scanner and affordable prices are at your service!
Sign up for an interpretation of cardiac ultrasound at the Elena Malysheva Diagnostic Center near the Baumanskaya metro station (see map) by phone: 8 (495) 127-03-71 or leave a request on the website.
Baumanskaya metro station (see map) 8
leave a request on the website
Preparation for cardiac ultrasound
To conduct a classic ultrasound procedure, no additional preparation is needed - just limit the amount of food and liquid consumed. To obtain undistorted results of Echo CG, the doctor will ask the patient not to drink alcohol the day before the examination and temporarily give up strong tea and coffee. As for the transesophageal examination using a probe, you will have to thoroughly prepare:
- the last meal should be 20 hours before the start of the procedure;
- You cannot drink liquid immediately before an echocardiography;
- if the examination is scheduled for the evening, you are allowed to drink water in the morning;
- the day before the test, you should limit strong physical activity.
The Ultrasound+ clinic invites you to have an ultrasound of the heart at home with a decoding of the indicators and an explanation of whether they are normal. We work in Moscow and the Moscow region, visiting patients’ homes within 1-2 days. It is possible to conduct an urgent ultrasound - then departure is carried out 2-3 hours after the application. The examination is carried out by cardiologists: they immediately interpret the results and, if necessary, draw up a list of further examinations and prescribe treatment.