Causes of the disease
The etiology of the disease continues to remain unclear to this day.
The constant search for the causes of gestosis is dictated by the sad statistics of maternal mortality: gestosis is one of the top three leading causes of death for women performing reproductive functions.
The most severe form of gestosis - eclampsia - was described back in the 4th century BC. Hippocrates, as a convulsive syndrome similar to epilepsy. Until the beginning of the 18th century, eclampsia was considered a special form of epilepsy. In 1843, the English physician Lever showed that eclampsia is preceded by edema, proteinuria and headache.
The existing understanding of the etiology of the development of gestosis includes more than 20 theories: infectious, intoxication, renal, hemodynamic, endothelial damage, endocrinological (impaired hormone production), placental (morphological changes in the placenta).
According to modern concepts, gestosis is considered as a genetically determined insufficiency of the processes of adaptation of the mother's body to new conditions of existence that arise with the development of pregnancy.
In the second half of pregnancy, a number of physiological changes occur in the body of pregnant women, predisposing to the development of gestosis. After 20 weeks of pregnancy, there is a significant increase in circulating blood volume (up to 150% of the initial level), a moderate increase in peripheral resistance, the formation of uteroplacental blood flow, and an increase in pulmonary blood flow with a tendency to hypertension.
Stages of pathology
Preeclampsia is classified as follows:
- Dropsy
- swelling in the arms and legs. But this is not only a sign of this pathology, so it is necessary to undergo tests to confirm. - Nephropathy
- high blood pressure is added to swelling. Already at this stage there is a danger to the woman’s life and she needs to urgently consult a doctor. The complication can quickly develop into another lethal form. - Preeclampsia
- the blood flow of the central nervous system is disrupted, at the same time nausea, high blood pressure, insomnia, migraine, protein in urine are observed. It is quite possible that there is a mental disorder due to pathology. - Eclampsia
requires urgent medical intervention. Convulsions are added to the previous symptoms, stroke, coma and death are possible. The placenta rapidly ages, and the baby may die.
Any form of gestosis poses a danger to the baby: it provokes hypoxia, lack of nutrition, and disrupts blood flow.
Unfortunately, gestosis begins unnoticed, but develops rapidly and moves from one stage to another, so doctors prescribe additional tests at the first sign.
Classification of the disease
Preeclampsia has four clinical forms, which is reflected in the classification of this disease according to clinical signs.
Preeclampsia is divided into: dropsy, nephropathy of pregnancy (mild, moderate, severe), preeclampsia and eclampsia. Various forms of gestosis are considered as stages of a single pathological process, however, each of them requires certain diagnostic and therapeutic measures.
In modern conditions, “erased” and monosymptomatic forms of gestosis are distinguished.
Dropsy of pregnancy
characterized by one symptom - the appearance of edema.
Nephropathy
characterized by a triad of symptoms: edema, proteinuria and hypertension. The clinical picture of gestosis and its diagnosis are based on identifying any of the symptoms.
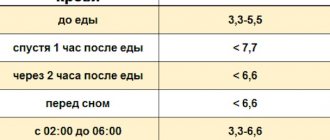
Normally, average blood pressure should be no more than 100 mm Hg. Art., an increase of 15 mm Hg. indicates the onset of the disease.
In order to diagnose gestosis, pregnant women should be weighed (physiological weight gain of 300-350 g per week), blood pressure measured in both arms, urine tests (determining proteinuria) weekly in the third trimester of pregnancy, a thorough obstetric examination be carried out, and if necessary, involve other specialists ( ophthalmologist, therapist, neurologist, etc.).
The traditional meaning is to assess the “ring” symptom and measure water balance. The diagnosis of renal dysfunction deserves special attention. For this purpose, the level of proteinuria and cylindruria in single and daily urine samples, the relative density of urine and daily diuresis in a urine sample according to Zimnitsky are determined (isosthenuria and nocturia are characteristic of gestosis). Indicators of biochemical blood tests are also of diagnostic importance: hypoproteinemia, a decrease in the albumin-globulin ratio below one, an increase in urea and creatinine levels, etc. An important role is played by the study of the blood coagulation system, in which thrombocytopenia (a decrease in the number of platelets to 150 thousand and below) and an increase in fibrin degradation products are possible. Ophthalmoscopy is an informative method for assessing the condition of the fundus vessels, which reveals angiopathy, hemorrhages, edema and retinal detachment.
It is known that gestosis is a prognostically unfavorable complication of pregnancy not only for the mother, but also for the fetus: against the background of gestosis, placental insufficiency develops, leading to fetal malnutrition, and sometimes to its antenatal or intrapartum death. Thus, in order to assess the condition of the fetus during pregnancy, a dynamic ultrasound study with Doppler measurements of the vessels of the utero-fetoplacental system and cardiac monitoring of the fetus are performed.
Dropsy and nephropathy are differentiated from kidney diseases (glomerulo- and pyelonephritis), hypertension.
The next stage of development of gestosis is preeclampsia
. In addition to the signs characteristic of nephropathy, symptoms of cerebrovascular accident, increased intracranial pressure and cerebral edema appear: headache, blurred vision, pain in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, decreased response to external stimuli or, conversely, excitement and euphoria. The duration of preeclampsia can range from several minutes to several hours.
The most severe form of gestosis is eclampsia
– the main manifestation of which is convulsions with loss of consciousness against the background of vascular spasm, hemorrhages and cerebral edema. Seizures can occur suddenly, but more often develop against the background of symptoms of preeclampsia.
Complications of eclampsia: heart failure, pulmonary edema, cerebral coma, hemorrhages in the brain, in the retina, liver and kidney failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, premature abruption of a normally located placenta, hypoxia and fetal death.
Treatment
Treatment of mild gestosis is carried out on an outpatient basis, at home. For more severe forms, treatment is carried out in a hospital. First of all, non-drug treatment methods are used - physiotherapy, acupuncture, psychotherapy, electrosleep, hypnosis. Drug treatment of gestosis should be comprehensive. Drugs that normalize the function of the central nervous system and suppress the gag reflex are used. Intravenous infusions of saline solutions, glucose, and vitamins are performed. Usually up to 2-2.5 liters of solutions are administered per day. In some cases, medications are prescribed to replace regular meals. When treating pregnant women suffering from early gestosis, it is necessary to monitor biochemical blood parameters and urine tests. In rare cases, with excessive (so-called indomitable) vomiting, which is accompanied by general exhaustion, it is necessary to raise the question of terminating the pregnancy.
Recommendations from experts
Some advice for women who have symptoms of early gestosis:
- Listen to your taste desires, eat only what you want. Food should be easily digestible and contain enough vitamins;
- Eat small meals every 3-4 hours. For nausea, relief comes from chewing (dried fruits, nuts, crackers, salty crackers, lemon, etc.);
- If nausea begins in the morning, after getting up, then you can organize breakfast in bed. In any case, it is recommended to eat something - a piece of white bread or a roll, a cracker, sweet tea. Don’t rush to brush your teeth first thing after getting up!;
- It is recommended to eat dry: food separately, drinks by themselves. In some cases, mixtures and purees for baby food, protein mixtures for pregnant women (femilak, berlamin-modular, enipit) help. Be sure to include alkaline mineral water in your diet. The total amount of liquid drunk can be increased to 2-2.5 liters.
- If you are drooling, it is good to rinse your mouth with an infusion of mint, sage, and chamomile.
Diagnosis of gestosis
To develop methods for early diagnosis and prevention, groups of women with a high risk of developing preeclampsia should be identified. Early manifestations of gestosis include: pathological weight gain (in the absence of visible swelling), swelling of the fingers (“morning stiffness of the fingers,” the “ring” symptom), an increase in the circumference of the ankle joint (by more than 1 cm within a week). Particularly noteworthy is the increase in diastolic pressure compared to the initial data, but not exceeding the normal range, a decrease in pulse pressure to 30 mm Hg. Art. or less, asymmetry of blood pressure in both arms exceeding 10 mm Hg. Art., transient proteinuria.
The danger of gestosis when carrying a child
Preeclampsia is considered one of the serious complications of pregnancy, but it all depends on the stage. Naturally, at the onset of pathology, it is possible to stop the symptoms and normalize the condition, safely carrying the child to term. But, at an advanced stage, late toxicosis can be fatal for mother and baby.
Swelling spreads to the woman’s internal organs and can even affect the brain. It negatively affects the placenta, causes hypoxia and, in severe cases, the death of the child. In the event of such a threat, the woman in labor undergoes an emergency caesarean section.
Diagnosis of hepatosis and its signs
Hepatosis in pregnant women is a disease that is sometimes very difficult to diagnose. By this time, the uterus already occupies the entire abdominal cavity, which makes palpation of the liver impossible. This disease is often confused with gallstone disease, because their symptoms are very similar. The most common signs of hepatosis include:
- skin itching;
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, the appearance of vascular networks on the face and hands, redness of the palms (they seem to be covered with red spots from the inside);
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, bitterness in the mouth, stool disorders, loss of appetite;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- lightening of stool and darkening of urine (from orange to dark brown);
When the bile duct is disrupted, a large amount of bile accumulates in the liver. Unable to escape, bile begins to break through into the lymphatic system, and from there into the general bloodstream. If you conduct a blood test, it will show an increase in the level of transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin and cholesterol, a decrease in hemoglobin, as well as red blood cells and platelets. A urine test will reveal the presence of bile acids and increased secretion of urobilin.
When bile enters the bloodstream, it causes itching, which intensifies in the evening and at night. Most often, pregnant women with this disease consult a doctor with complaints of an acute and irresistible desire to scratch. It drives you crazy, disrupts sleep, leads to fatigue and irritation. As a rule, the arms, legs and stomach itch the most. Filling the liver with bile causes overstretching of its capsule, the surface of which has a large number of pain receptors. This causes constant dull pain in the right side.
If hepatosis is suspected, the doctor at the antenatal clinic should carefully examine the patient, try to palpate the liver area, prescribe extensive blood and urine tests, as well as an ultrasound examination of the liver, gall bladder and neighboring organs.
Some signs of high blood pressure during pregnancy
If the consultation reveals problems with pressure surges in a pregnant woman, then it is worth buying a tonometer to measure pressure. High blood pressure during pregnancy is accompanied by the following sensations: tinnitus, deterioration in health, nausea or even vomiting, the appearance of dark spots before the eyes, redness of the skin on the face and chest, weakness and dizziness, headache. However, it also happens that the increase in pressure is asymptomatic and this can only be determined by measuring blood pressure.
How and why gestosis develops
Pathology has been studied for a long time, but medical science has so far put forward only theories about the mechanism of development and causes of gestosis.
One of the hypotheses is corticovisceral; it explains gestosis by disturbances in the physiological connection between the cortical and subcortical structures of the brain, which leads to pathological changes in the system of vascular reflexes and blood circulation in general. A hormonal theory has also been put forward, according to which gestosis is associated with disorders of the endocrine regulation of organs. The immunological hypothesis says that the pathological condition is caused by a conflict between the fetus (a foreign body) and the mother’s body. There are suggestions that gestosis is associated with a certain heredity. But most gynecologists argue that gestosis occurs due to a combination of various unfavorable factors.
The impetus for the appearance of gestosis is a spasm of blood vessels throughout the body, which disrupts blood flow. Blood pressure increases, the amount of blood in the vessels decreases. As a result, cells, tissues and organs experience a deficiency of oxygen and nutrition. The endothelium of blood vessels (the inner lining) is damaged during gestosis, which increases their permeability, fluid penetrates into the intercellular space, and edema occurs. The blood clotting function also changes, and the risk of intravascular thrombus formation increases. The cells of the brain, kidneys, adrenal glands, liver and placental system suffer most from a lack of oxygen and nutrition.
Gestosis in pregnant women leads to organic and functional changes in the brain - microcirculation is disrupted, blood clots form, degeneration of nerve cells develops, pinpoint or small focal hemorrhages occur, and pressure inside the skull increases.
Preeclampsia also causes a number of functional disorders in the kidneys. Protein is detected in the urine, renal filtration decreases, until failure of these excretory organs develops. When blood flow in the liver is impaired, associated with gestosis, necrosis and foci with hemorrhages form. If gestosis leads to impaired blood flow in the placenta, the formation of blood clots, the nutrition of the fetus is disrupted, which leads to developmental delays, sometimes to its death and termination of pregnancy.
Possible causes of high blood pressure during pregnancy
- Stress. The loads are so great that the body does not have time to readjust and reacts with an increase or surges in pressure.
- Lack of compensatory forces in the body - the heart, forced to pump blood for two, cannot cope with the increased volume of blood required for this.
- Hereditary factors. If blood relatives have problems with high blood pressure, there is a possibility of a similar problem occurring.
- Diabetes mellitus does not increase blood pressure, but serves as an additional unfavorable factor for its occurrence in the presence of other causes.
- Low physical activity, because a trained heart can cope with stress better.
- Smoking. Nicotine constricts blood vessels and, as a result, blood pressure increases.
- Excess weight and rapid weight gain. Therefore, doctors strictly monitor its increase weekly during pregnancy.
- Kidney pathologies. Pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis cause high blood pressure not only during pregnancy.
- Hormonal disorders - malfunctions of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal glands.
Causes of hepatosis in pregnant women
Doctors turned their attention to this disease relatively recently, so experts are still arguing about what causes its appearance. Most medical minds agree that hepatosis in pregnant women is caused by certain genetic characteristics or disorders and can be transmitted through the female line. These genetic abnormalities may not manifest themselves in any way throughout life. But sometimes pregnancy, which brings with it an increase in body weight, hormonal imbalances and an increased load on the body in general and on the liver in particular, gives impetus to the development of hepatosis. The liver is also very susceptible to the influence of pregnancy hormones. For example, estrogen.
The main factors that increase the risk of this disease include:
- Incorrect intake of vitamins. Vitamins are always an additional burden on the liver. Many vitamin complexes contain increased amounts of various components, which cause liver dysfunction, so they need to be taken correctly, taking into account age, body weight, dosage and stage of pregnancy.
- Dietary disorder. Overeating and eating salty, fried, smoked, fatty foods, as well as foods rich in chemical additives, overload the liver and impair its functioning.
- Insufficient physical activity. If the expectant mother moves little, then little energy obtained from food is consumed, and the metabolism, which is already slowed down by pregnancy, slows down.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Prevention
For prevention, you need to follow basic recommendations, but unfortunately, even this will not guarantee that preeclampsia will not occur. Therefore, timely observation by a gynecologist is one of the keys to a successful pregnancy.
Recommendations:
- absence of stress and neuroses;
- quality sleep, rest;
- proper nutrition;
- acceptable physical activity;
- walks in the open air;
- weight gain control;
- strengthening the immune system.
Being in an interesting position, a woman should carefully monitor her well-being. Preeclampsia can lead to tragic consequences, so at the first signs you need to consult a doctor for help.