Symptoms of varicose veins of the labia
More often, symptoms of varicose veins of the female genital organs appear during pregnancy at 18-24 weeks. In multiparous women, signs of the disease may become apparent as early as 12-14 weeks. A natural clinical manifestation of the pathology is deformation of the vascular walls. The veins dilate, look flabby, with nodular formations, and the labia enlarges. Along with external symptoms, there are also painful sensations:
- burning in the perineum;
- nagging pain radiating to the leg during physical activity;
- feeling of heaviness, swelling in the intimate area;
- dysmenorrhea (heavy bleeding accompanied by pain, changes in the menstrual cycle);
- dyspareunia (pain during intimate contact);
- discoloration and dry skin.
Symptoms increase gradually. As the disease progresses, painful urination and chronic pelvic pain may occur. In pregnant women, varicose veins cause miscarriage or premature birth.
Vaginal reconstruction after childbirth
The vagina after childbirth, as a rule, undergoes many changes, and this applies to both the mucous membrane and the muscular frame. The mucous membrane and muscles, due to changes in hormonal levels, ruptures during childbirth, become thinner, drier, with many scars, in addition, the vagina “stretches” after childbirth. These phenomena can cause vaginal dryness after childbirth, pain during sexual intercourse, a feeling of air being trapped, decreased sensations during lovemaking, vaginal enlargement, urinary incontinence, and prolapse of the vaginal walls. Due to this, sex after childbirth becomes a difficult, unpleasant necessity, rather than a pleasure, and in some cases, sex life after childbirth becomes simply impossible.
Currently, most of these problems can be solved with the help of modern laser and injection technologies, which can become a complete replacement for surgical plastic surgery after childbirth.
Non-surgical methods of postpartum vaginal restoration include laser vaginal rejuvenation, plasma lifting of the mucous membrane, and vaginal muscle training. Treatment of the vaginal mucosa using a fractional laser can make the vaginal mucosa thicker, more elastic (due to the “twisting” of existing collagen fibers and the growth of new ones), and improve blood supply to this area. Plasmolifting has a pronounced healing, anti-inflammatory, moisturizing effect. Vaginal muscle training improves the condition of the muscular frame. Due to these effects, the vagina after childbirth becomes narrower, elastic, moisturized, libido and the regenerative abilities of the mucosa are enhanced. Problems such as vaginal dryness after childbirth, pain during sexual intercourse, decreased sensations during sexual intercourse are solved, symptoms of a “wide” vagina, urinary incontinence, initial forms of prolapse of the vaginal walls are eliminated, and the frequency of recurrences of inflammatory diseases is reduced.
Why does it appear
The main prerequisite for the development of varicose veins of the labia is the insufficient strength of the connective tissue that forms the vascular walls. Under the influence of a number of factors, the number of collagen fibers decreases and muscle tone decreases. An increase in blood pressure and the filling of blood vessels leads to their stretching and expansion to such an extent that the lumen is no longer blocked by the valve. Blood overflows into the subcutaneous veins of the genital organs, contributing to the development of the disease.
Triggering factors for varicose veins of the genital organs in women:
- Hormonal changes. During pregnancy, the production of progesterone and relaxin increases, which relax the smooth muscles of the venous walls. Due to the abundant blood flow, the valves do not completely block the lumen of the vessel, resulting in venous stagnation.
- Fetal growth during pregnancy. Increasing in size, the uterus puts pressure on the vessels, which affects the volume of venous blood and the elasticity of the venous walls.
- Increased blood flow. During pregnancy, the amount of fluid circulating in the vascular bed constantly increases, which causes increased blood pressure and dilation of the veins.
- Sedentary lifestyle. Prolonged sitting or standing leads to stagnation, which provokes vasodilation.
- Excess weight. Excess body weight creates a load on the entire body, the cardiovascular system, which causes deformation of the vascular walls.
- Genetic predisposition. If someone in your family has suffered from varicose veins, the likelihood of developing pathology increases.
- Chronic constipation. Digestive disorders lead to stagnant processes in the pelvic organs and, as a result, varicose veins.
Pathological expansion of the vascular walls may persist in women after childbirth. Normal blood flow in tissues is also hampered by inflammatory processes, tumors of the genital organs, and the use of hormonal contraceptives.
Disease prognosis
Varicose veins of the uterus and perineum are not a life-threatening disease. But it is important to note that the quality of life of patients is significantly reduced. In addition to aesthetic discomfort, large perineal phleboectasis can cause painful symptoms during menstruation and complicate sexual life. Sometimes varicose veins become inflamed, causing a lot of physical suffering to patients. You should not count on the therapeutic effect of ointments and tablets - such therapy is not effective, but only eliminating the causes of varicose veins and the venous nodes themselves using sclerotherapy or miniphlebectomy allows one to achieve excellent therapeutic and aesthetic results in all patients. At the Innovative Vascular Center, complete treatment of this disease is possible. We successfully perform endovascular correction of deep vein pathology, eliminate varicose veins of the small pelvis and venous vessels on the genitals.
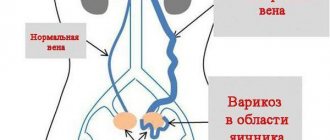
Vaginal varicose veins in pregnant women
This type of pathology is characterized by dilation of blood vessels located in the vagina. The disease often develops against the background of existing varicose veins. The vascular walls lose elasticity, become fragile and vulnerable. In pathological veins, blood circulation is impaired and the risk of blood clots increases.
Vaginal varicose veins are accompanied by pain in the perineum, flatulence, indigestion, constipation, and frequent urination. A prolonged illness is characterized by cramps and a feeling of heaviness in the legs.
During pregnancy, if the presence of varicose veins of the labia at a late stage is confirmed, a cesarean section is performed, since natural childbirth can be dangerous to the health of the mother and child.
Tears after childbirth
Another problem of the perineum after childbirth is its rupture. Tears after childbirth or incisions often lead to the formation of rough scars, which in turn can cause pain during sexual intercourse, as well as grossly deform the perineum.
Non-surgical methods for treating tears after childbirth include laser scar resurfacing and intimate contouring. The effect of an erbium laser can soften and reduce the size of the scar. Due to this, pain is relieved and the quality of sexual life improves. Intimate contour plastic surgery (injection of hyaluronic acid preparations) can eliminate the perineal defect in the area of scars and tears. In addition to the aesthetic effect, by narrowing the entrance to the vagina, intimate contour plastic surgery solves the problem of “squelching”, the entry of air during sexual intercourse. Both methods are absolutely safe, practically painless (carried out under anesthesia with a cream), performed on an outpatient basis, and do not affect the ability to work or drive a car. Restrictions after the procedures - sexual rest for 1-2 days.
Varicose veins of the vulva
Vulva is a term used to describe the female genitourinary organs at the entrance to the birth canal. With the development of this type of pathology, patients complain about unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen; spider veins and nodes are noticeable on the skin of the labia. If left untreated during pregnancy, the risk of rupture of the uterine vessels, death of the child and heavy loss of blood in the mother increases.
Popular questions
I suspect inflammation and cysts.
The doctor prescribed IV thiosulfate, IM ceftriaxone, and Diclovit suppositories. I just didn’t explain, is it necessary to apply everything at the same time or what? Hello! Most often, this complex of treatment is carried out simultaneously, but it is better to check with your doctor.
Hello. My labia and clitoris are swollen, there is a burning sensation and a cheesy discharge with something in it, the color is unclear. What could it be and how to treat it? Before that I had inflammation and treatment, and after that it all started. Hello! This is how vulvovaginitis manifests itself. I recommend that you contact an obstetrician-gynecologist and conduct an examination to find out the cause of the inflammation. This will allow you to correctly prescribe therapy. At this stage, you can use Gynocomfort gel with tea tree oil, 1 dose once a day, which will limit the spread of inflammation and improve your well-being.
Hello! Severe itching on the labia, irritation. There is nothing to worry about in the vagina itself. What could it be?
Hello! This may result in an allergic reaction or inflammation. I recommend using Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract, applying it once a day to the discomfort zone for 7 days. If you do not notice relief, consult a doctor.
Good morning, I have vulvitis on my labia minora, I don’t know what to do or how to treat it.
Hello!
If inflammation occurs in the labia minora area, you can use Gynocomfort gel with tea tree oil. The gel is applied in a thin layer once a day for 1 week. If complaints persist, you should consult a specialist. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
Diagnostics
Standard diagnosis involves examination on a gynecological chair to identify dilated, nodular vessels, cyanosis and smoothness of the vaults of the vaginal wall. Selective variography helps determine in which zone the blood is discharged into the veins.
To assess the vascular system of the pelvic area, instrumental studies are prescribed:
- ultrasonography;
- Doppler ultrasound;
- laparoscopy;
- CT scan of the pelvic organs.
In the classical course of the pathology, diagnosing the disease is not difficult. Based on the results, the gynecologist prescribes treatment.
Treatment of vulvitis
If you notice any alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist can diagnose the cause and prescribe correct and quick treatment, including a set of measures: relieving inflammation, eliminating factors that are catalysts for the process.
The basis of treatment for vulvitis is the elimination of the causes of the inflammatory process and treatment of concomitant diseases, which may include diabetes mellitus (Diabetes mellītus), gonorrhea (Gonorrhoea), diphtheria (Diphtheria), helminthiasis. After receiving smear test data and checking the sensitivity of the infectious agent, the doctor can prescribe medication, most often antibacterial drugs. Vulvitis responds well to treatment with local remedies, which include all kinds of ointments, gels and suppositories.
In parallel, in the course of treatment of vaginitis, vitamin complexes can be prescribed, including vitamin A to effectively protect the epithelial layer, as well as vitamins E and C, known for their antioxidant properties.
To combat severe symptoms, other drugs may be prescribed:
- Antihistamines that help relieve itching.
- Hormonal, occurring in atrophic vulvitis in the postmenopausal period.
- Anesthetics that relieve pain.
In addition to the medications prescribed by your doctor, you can use Gynocomfort Restoring Gel. This product was created by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX and underwent clinical trials at the Department of Dermatovenerology with the clinic of the St. Petersburg State Medical University. During testing of the gel, it was proven that it is a very effective additional agent as part of the complex therapy of inflammatory processes of the female genital tract.
As additional therapeutic measures that can be used at home, it is worth mentioning warm baths with herbal infusion.
Chamomile, calendula, string, and comfrey have excellent anti-inflammatory properties.
Baths will help not only reduce inflammation, but also relieve symptoms such as itching, burning and pain.
Treatment of varicose veins of the labia
Treatment tactics are determined by the severity of the pathology, the risk of complications and differ in the postpartum period and during pregnancy. For uncomplicated vulvar varicose veins, medications are prescribed:
- venotonics (increase the contractility of vascular smooth muscles, strengthen valves);
- antiplatelet agents (reduce the risk of thrombosis);
- angioprotectors (prevent damage to the walls of blood vessels).
Women are prescribed to wear compression garments, which reduce pressure and stress on the venous valves, normalizing blood circulation. It is recommended to limit physical activity and introduce more vegetables and fruits into the diet to avoid constipation.
If conservative therapy does not lead to positive results, surgical treatment is resorted to. But this is possible only after delivery. Minimally invasive surgical methods for treating varicose veins of the genital organs include:
- Sclerotherapy. A surgical operation in which a drug is injected into the lumen of a vein using a very thin needle, causing it to close due to the proliferation of connective tissue. After the operation, varicose nodes disappear.
- Laser coagulation. Micro-instruments are inserted through a skin puncture. Under the influence of the beam, the walls of the vessel are sealed, after which it dissolves.
- Miniphlebectomy. Surgical intervention to remove varicose veins through a skin puncture.
Drug treatment helps reduce the severity of symptoms. Modern surgical techniques are assessed as minimally invasive and safe. If you seek medical help in a timely manner, it is possible to achieve the disappearance of signs of pathology.
Still have questions about vulvar varicose veins?
Free consultation with AngioClinic specialists
Author
Salmina Daria Vladimirovna
Geneticist. Graduated from the Chelyabinsk State Medical Academy. She completed an internship at the Northwestern State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov.
Benefits of foam sclerotherapy
- Simplicity - treatment takes place on an outpatient basis.
- Availability.
- Good cosmetic effect.
- Speed of implementation - the procedure lasts approximately an hour.
- The ability to combine with your usual lifestyle and busy work schedule.
- The effect is noticeable immediately after treatment - the affected vein disappears.
- No contraindications (except for one – allergy to the drug).
- Getting rid of the disease in a short time.
- The treatment takes place without incisions, anesthesia and pain.
- Almost complete absence of relapses.
Join the number of patients who have already gotten rid of varicose veins using foam sclerotherapy! Sign up for a consultation with a surgeon or phlebologist and take the first step towards recovery.
Symptoms of vulvovaginitis
Vulvovaginitis (see photo) can occur in acute or chronic form, and the symptoms of the disease will differ.
Symptoms of acute vulvovaginitis:
- redness, swelling of the vulva;
- pain in the lower abdomen, which can sometimes radiate to the sacrum;
- itching and burning in the genital area, which intensifies during urination;
- pain in the external genital area;
- difficulty urinating, which is sometimes accompanied by difficulty defecating;
- general weakness;
- vaginal discharge, most often purulent;
- painful intercourse;
- if vulvovaginitis is caused by E. coli, then liquid discharge from the vagina is yellow-green in color and has an unpleasant odor.
Symptoms of specific types of vulvovaginitis:
Gonorrhea:
- purulent discharge;
- itching, burning, pain;
- frequent painful urination;
- Symptoms of gonorrhea in women disappear relatively quickly.
Trichomoniasis:
- after infection with the disease, there is an incubation period of 3–5 days;
- foamy vaginal discharge of a gray-yellow color with an unpleasant odor;
- itching and burning, redness of the external genitalia;
- in the granulosa form of the disease, the vaginal mucosa has a granular surface and a bright red color.
Syphilis:
- the disease has an incubation period of 3–4 weeks;
- at the site of pathogen penetration, a hard chancre appears: an erosion or ulcer of a round or oval shape, in the area of which there is a thickening of the skin;
- during the illness, the woman is not bothered by pain;
- lymph nodes in the groin area enlarge;
- after some time, general malaise is noted, the woman’s body temperature rises - secondary syphilis develops;
- Many nodules appear on the mucous membrane of the vulva, which are painless, but contain a large number of pathogens inside, and therefore are very contagious.
Candidiasis:
- against the background of redness, swelling, itching, burning, and pain, white, curd-like discharge from the vagina occurs.
- Bubbles appear in the vulva area, which burst open, leaving behind erosions. In the future, crusts remain at the site of erosion.
Herpes:
- the disease lasts 2–4 weeks;
- general symptoms are noted: increased body temperature, weakness, lethargy;
- Bubbles with a diameter of 2–8 mm appear on the skin and mucous membrane of the vulva, which burst and leave ulcers.
Human papillomavirus infection:
- A characteristic manifestation of human papillomavirus vulvovaginitis is genital warts, which appear on the skin and mucous membranes in the area of the external genitalia and anus. Gradually they grow, merge with each other, and sometimes reach such large sizes that they resemble tumors. At the same time, sexual intercourse is greatly difficult.
Allergic conditions and autoimmune diseases:
- Vulvovaginitis is accompanied by severe itching, burning, and redness. The discharge is usually liquid and transparent. Symptoms occur during contact with the allergen. Later, infection and corresponding symptoms appear.