The Latin name for persimmon translates as “food of the gods,” and lovers of this fruit agree: its taste is truly divine.
Persimmon is considered to be the national fruit of Japan, although in fact its homeland is China. Today it is also grown in Korea, Burma, India, Pakistan, Europe, Australia and the southern United States. That is, persimmon is an “inhabitant” of warm countries with a dry climate. Cold winters scare her and drought kills her.
general characteristics
Content:
- general characteristics
- The nutritional value
- Beneficial features
- Role in the body
- Side effects
- Medicinal properties
- How to choose the right persimmon
- Interesting recipes with persimmons
- Interesting facts about persimmons
Young foliage on a persimmon tree is usually light green in color, and as it becomes more mature, it acquires a rich dark shade. By the way, in the homeland of persimmon, the leaves of this tree (fresh or dried) are used to brew healing tea. The flowers of this culture are divided into female and male. Women's - single, cream color. Male ones are pink, in inflorescences.
More often, only one type of flower is found on one tree, although some varieties can be bisexual. Ripe fruits range from bright orange to red-brown in color and are juicy and sweet. Unripe fruits tend to be tart and very sour. The diameter of a ripe fruit, depending on the variety, can range from 1.5 to 9 centimeters [1].
There are many types of persimmons in the world. Different varieties may differ significantly in appearance and taste, but they have the same basic beneficial properties.
Where does the astringent taste of persimmon come from?
This berry has an astringent taste. Tannins are to blame for everything. But, as soon as the persimmon ripens, these substances disappear and the berry becomes sweet. Conclusion: you should only eat ripe fruits, especially since eating unripe fruits is dangerous to your health.
But what to do if you bought a persimmon, but it knits? Do not rush to throw it in the trash - under the right storage conditions, the fruit can ripen.
“Persimmon lovers run the risk of growing a “fibrous stone” in the stomach - the so-called phytobezoar,” doctor Marina Antipova told the Doctor Peter portal. — It is formed due to eating the peels of berries and fruits with a high content of the astringent substance tannin. For example, persimmons, cherries, figs. The cause is usually stomach disease. For example, insufficient production of hydrochloric acid, the so-called “lazy” stomach - slow evacuation of the food bolus, secretory insufficiency, impaired gastric motility after surgery, gastroparesis (decreased activity of the stomach muscles).
Another risk factor is the amount of astringent fruits and berries, especially eaten on an empty stomach - the same persimmon with skin, poor chewing of food, swallowing seeds.
Elderly people should be especially careful with fruits and berries high in tannins. Due to age-related changes, their stomach acidity, as a rule, decreases, the condition of the gastrointestinal mucosa and peristalsis worsens. This means there is a risk of bezoar formation.”
© healthy-food.rf persimmon health benefits and harms
The nutritional value
One average persimmon contains approximately 120 kilocalories and consists of almost 20 percent carbohydrates.
This Chinese delicacy can provide about a fifth of the daily fiber requirement, and it contains approximately 110% of the daily minimum vitamin C.
In addition, persimmons contain minerals and plant compounds that are beneficial to humans, such as zeaxanthin, lutein, lycopene and tannins. The latter give the unripe fruit a tart and bitter taste. Other important components include catechins (strengthen capillaries), betulinic acid (an antitumor substance), and carotenoids. Nutritional value (per 100 g) [2][3]
| Calorie content | 70 kcal |
| Squirrels | 0.6 g |
| Fats | 0.2 g |
| Carbohydrates | 18.5 g |
| Cellulose | 3.5 g |
| Vitamin A (retinol) | 80 mcg |
| Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) | 7.4 mg |
| Vitamin E (tocopherol) | 0.74 mg |
| Vitamin K | 2.5 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (thiamine) | 0.05 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 0.04 mg |
| Vitamin B3/PP (niacin) | 0.3 mg |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 0.1 mg |
| Vitamin B9 (folic acid) | 8 mcg |
| Vitamin B4 (choline) | 7.4 mg |
| Calcium | 7 mg |
| Iron | 0.16 mg |
| Magnesium | 9 mg |
| Phosphorus | 16 mg |
| Potassium | 160 mg |
| Sodium | 0.9 mg |
| Zinc | 0.13 mg |
| Copper | 0.11 mg |
| Manganese | 0.3 mg |
| Selenium | 0.5 mcg |
Benefits and harms for hypotension
As was said, persimmon helps with hypertension, but people with low blood pressure should not completely give it up. In small quantities it:
- strengthens the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- will reduce cholesterol levels;
- will facilitate the work of the kidneys;
- cleanses the liver.
There is no need to eat berries too often; one persimmon fruit in the afternoon is enough , when the body releases excess fluid as much as possible.
If adverse symptoms appear after eating the fruit, then you should stop taking the fruit. Even if you feel well, you need to treat yourself at least every other day.
Beneficial features
The nutritional components that make up persimmon have a beneficial effect on the entire human body:
- support the health of the nervous system, bones, teeth, skin, eyes;
- promote the production of red blood cells;
- strengthen the immune system;
- regulate glucose in the bloodstream;
- protect cell membranes from damage;
- slow down signs of aging;
- prevent various types of cancer;
- improve metabolism;
- reduce blood pressure;
- increase cognitive functions of the brain;
- improve digestion;
- contribute to the effective recovery of the body after illness.
Chemical composition
Persimmon contains a whole vitamin and mineral complex. It contains:
- potassium;
- magnesium;
- sodium;
- calcium;
- phosphorus;
- iron.
Persimmon also includes minerals:
- copper;
- nickel;
- manganese;
- iodine;
- citric and malic acid.
The vitamin composition of persimmons is also very rich:
- vitamin A is responsible for the condition of the skin, improves vision, helps maintain immunity, and rejuvenates the body;
- B-carotene is a powerful antioxidant and is responsible for the regeneration of cellular composition;
- vitamin B5 lowers cholesterol levels, increases hemoglobin, promotes better absorption of amino acids;
- Vitamin P strengthens the walls of blood vessels and protects against infectious diseases.
By considering the chemical composition of persimmons, you can understand whether the fruit increases or decreases blood pressure, and also why it does not increase blood pressure.
Important!
Due to the high content of potassium, magnesium and minerals, persimmon is a diuretic (has a diuretic effect). When fluid is removed, the load on the heart becomes less, and the functioning of the cardiovascular system improves, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure.
If this effect is beneficial for hypertensive patients, then in case of hypotension you should know when to stop eating persimmons .
Role in the body
This exotic fruit is more than just a delicious dessert. Persimmon has many beneficial properties for human health.
Cholesterol control
Laboratory studies have shown that persimmon can affect blood cholesterol levels. The results of a nine-week experiment confirmed that daily consumption of fruit reduces not only “bad” cholesterol in the bloodstream, but also other types of lipids. Biologists say that the reason for this effect is the tannins (tannins) that make up the berries. At the same time, less ripe fruits contain more of these substances [4].
Cardiologists, citing the results of their own experiments, added persimmon to the list of products that reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases [5].
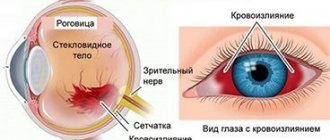
Visual acuity
Persimmon is an important food for eye health.
Vitamin A, zeaxanthin, lutein, lycopene, which are part of the fruit, significantly improve vision. These ingredients help prevent macular degeneration and cataracts, disorders that lead to blindness. Research shows that lutein and zeaxanthin can completely cure some eye diseases.
Antiviral agent
The antiviral effect of persimmon is achieved through tannins, which block viruses and prevent the spread of infection. Researchers say this fruit can destroy intestinal viruses. The results of scientific experiments allowed biologists to conclude that persimmon is effective as a natural antiviral agent.
Antitumor effect
These exotic fruits contain a huge amount of anti-cancer substances. They protect the body from free radicals, which are a byproduct of cellular metabolism and cause mutation of healthy cells. As a result, a malignant tumor grows in the damaged area of tissue. Antioxidants contained in persimmon prevent and stop these dangerous processes. Phenolic compounds, vitamins A and C, found in large quantities in persimmons, are extremely important for effective protection against cancer. Considering all this, it becomes clear why persimmon is called a cure for cancer [6].
Immunity
This orange fruit is one of the leaders in ascorbic acid content. Only 1 fruit contains a daily dose of vitamin C [7]. And it is known to stimulate the immune system and activate the production of white blood cells (leukocytes), which are the body’s “line of defense” against germs, viruses, fungi, toxins and foreign bodies.
Digestion
Persimmons, like most fruits, are an excellent source of fiber.
Dietary fiber enhances intestinal motility, improves the secretion of gastric juice, and also relieves diarrhea or constipation. It is believed that foods rich in these fibers serve as a preventive measure against colorectal cancer and other colon diseases. For overweight people, fiber from persimmon pulp will help them lose weight faster.
Potion for old age
This “food of the gods” is rich in various beneficial substances, especially beta-carotene, lutein and lycopene. All of them function as antioxidants in the body, which means they can prevent signs of premature aging. Frequent consumption of fresh persimmons will protect against early wrinkles, age spots, Alzheimer's disease, chronic fatigue, vision loss and other unpleasant symptoms.
Normalization of blood pressure
Potassium was also found in persimmons, and in considerable quantities. It would be worth recalling that this mineral has vasodilating abilities, which means it significantly reduces blood pressure [8]. Thus, persimmon is an extremely healthy fruit for hypertensive patients. In addition, the chemical composition of the exotic is not devoid of copper, and it is an important element for the production of red blood cells. This property of persimmon is no longer useful only for people with high blood pressure.
Metabolic processes
B vitamins, such as pyridoxine, vitamin B9 and thiamine, are an important component of most enzymatic processes in the body. The normal level of these substances is the key to ensuring that the food processing process proceeds correctly. And proper digestion means a healthy metabolism. In addition, B-group vitamins, present in the delicate pulp of persimmons, are important for maintaining muscle tone, strengthening the immune system and supplying the body with the necessary energy [9].
Supports immunity
Due to the high content of vitamin C, B vitamins, rutin and others, persimmon has a powerful stimulating effect on the immune system and the body’s resistance to various adverse factors. A large amount of minerals, in particular manganese, zinc, copper, also helps strengthen the immune system.
This fruit also has the ability to stimulate antitumor immunity, improves peripheral blood flow, reduces the risk of thrombosis, and protects the walls of blood vessels from the formation of cholesterol plaques. In general, heart patients, as well as those at risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and high blood pressure, should include persimmons in their diet more often.
Knits - doesn't knit. How to choose delicious persimmons Read more
Side effects
Allergies to persimmons are extremely rare - and this is good news. However, there is also not very good news. This fruit contains a lot of fiber, but unripe fruits contain specific dietary fibers, which clump into indigestible lumps in the stomach. Doctors call these formations bezoar stones. They inhibit the process of normal digestion of food and also block it in the upper part of the digestive tract.
Large portions of ripe fruit can also cause flatulence, so people prone to bloating are not recommended to indulge in this sunny fruit too much. A similar warning applies to hypotensive people, as this fruit lowers blood pressure.
In addition, it is not advisable to consume a lot of persimmons for people with diabetes (as it is a very sweet fruit), for people with chronic intestinal diseases, or on an empty stomach (it can cause diarrhea).
With low blood pressure
Persimmon can reduce blood pressure by 10-12 mmHg. Art. Such a decrease in indicators can be dangerous for hypotensive patients, so this fruit is contraindicated for them. A decrease in pressure of even 10 units can lead to:
- hypotensive crisis;
- coma;
- lethal outcome.
Eating the fruit is allowed with minor deviations in blood pressure from the norm and only with the permission of a doctor. After use, be sure to rinse your mouth to remove any remaining acids from the tooth enamel and drink a glass of water. You should also not eat the skin of the fruit. It contains tannins, which cause intestinal obstruction and the formation of rocky deposits.
Medicinal properties
In traditional Chinese medicine, persimmon is used as a remedy for hiccups. To get rid of unwanted contraction of the diaphragm, Eastern healers use 9 g of persimmon and 3 g of ginger. The products are crushed, a little water is added to this slurry and brought to a boil. Then the tasty medicine should be eaten quickly.
And the same oriental doctors used dried fruits to get rid of asthma, respiratory tract infections and diarrhea. To do this, still green fruits (as soon as they begin to turn slightly yellow) are picked from the trees, peeled and dried under the sun until a white glaze appears. After this, the fruit turns into medicine.
But Japanese researchers suggested that cosmetologists use only the peel of the fruit. In their opinion, the fruit shell contains the maximum amount of proanthocyanidins - essential substances for fighting aging. And European cosmetologists advise using a paste of persimmon and egg yolk as a mask for acne and enlarged pores.
Source of iodine and iron
Another pleasant bonus in persimmon is its fairly high content of iron and iodine. This combination is rarely found in other vegetables and fruits. Moreover, iron is absorbed quite well from persimmon. And iodine, which is needed for the thyroid gland to work well, is found in plant products, as a rule, mainly in seaweed.
The peculiarity of persimmon is the astringent properties that tannin gives it. The younger the fruit, the more tannin. As the wine matures, there is less insoluble tannin and the astringent taste is no longer as pronounced. If you don't like the strong astringent taste, there is a way to get rid of it - freeze the fruit. Tannins will become insoluble, but most of the beneficial properties will remain.
However, there are lovers who like this feature of persimmon. It is worth remembering here that tannins have a fixing effect. Therefore, the astringent fruit is not advisable for people who suffer from constipation. With diarrhea, on the contrary, it can help get rid of the unpleasant symptom. Although the benefits of persimmon itself practically do not depend on the concentration of tannin.
From salad to dessert. What dishes to prepare from persimmons Read more
How to choose the right persimmon
The fruits of these trees can be consumed raw, dried or in the form of jams. Ripe fruits are always fleshy and sweet in taste. Fruit that is too soft is a sign of rotting. Such fruits are no longer suitable for food. You should not eat unripe fruits: they are tasteless, tart and can be harmful to health.
Here are some tips on how to choose the most delicious persimmon:
- All attention to form! Fruits with a flat base, reminiscent of tomatoes, are usually always sweet. Elongated, like an acorn - tart.
- Almost all small persimmon fruits are tart.
- Fruits with cracks are a sign of rotting.
- A properly ripened fruit should be orange or reddish and dense in consistency. Excessively soft fruit is always overripe.
Helps you not gain weight
In addition, tanning substances like tannin slightly slow down the absorption of nutrients. Therefore, if you are watching your weight and want calories to be absorbed more slowly, tannins will also come to the rescue.
I would like to point out that persimmon is a sweet fruit. And the content of mono- and disaccharides in it is quite high. This gives reason to recommend persimmon to diabetics with caution. A large amount of it can lead to a jump in blood glucose levels, a sharp release of the hormone insulin and various associated adverse effects. In particular, many scientists associate the appearance of excess body weight with an increase in insulin levels in the blood. But it is the less ripe fruit, which contains a lot of tannins, slows down the absorption of sugars and does not lead to a sharp increase in blood glucose levels, that is suitable for such patients. Therefore, if a person suffers from diabetes, one should give preference to those varieties of persimmon that are more astringent. In addition, unripe fruits contain less sugar and more dietary fiber, which is also beneficial for people with excess body weight and diabetes.
Of course, to get the maximum benefit from persimmons, you shouldn’t eat kilograms of them. Otherwise, side effects in the form of constipation, allergies, exacerbation of chronic diseases of the digestive system, etc. cannot be avoided. 2-3 medium or one large fruit per day is enough. It is also not recommended to give persimmon to children under 3 years of age.
Popular types of persimmons. Infographics Read more
Interesting recipes with persimmons
The most common way to consume persimmons is raw as a dessert.
Some may be surprised, but this fruit goes well with meat and fish, and is added to salads and cookies. Here are some tasty examples.
Duck with persimmon
Take:
- duck (1.5 kg);
- persimmon (300 g);
- onions (2 pcs.);
- butter (50 g);
- white wine (100 ml);
- olive oil (1 tbsp);
- vinegar (1 tsp);
- ginger (2 slices);
- cloves (2 cloves);
- thyme (0.5 tsp);
- cinnamon;
- red pepper;
- salt.
How to cook:
Marinate the cleaned and cut into pieces duck carcass for 4 hours. Prepare the marinade from onions, ginger, cloves, thyme, red pepper, vegetable oil and wine. Then place the pieces of meat on a baking sheet and bake until golden brown.
During this time, heat the butter and put the persimmons cut into slices into it, add cinnamon and red pepper. Fry for about 3 minutes. After this, remove the persimmon slices and add the remaining marinade to the mixture. Simmer until the liquid is reduced by half. Place the finished duck with persimmons in the sauce and simmer for another 5 minutes.
Royal snack
Place a few slices of salmon on a plate. Near the fish on a piece of lettuce is a boiled egg, cut lengthwise. Place a teaspoon of red caviar on each half of the white. Mix soft processed cheese with ginger and salt. Place the finished mixture on salmon slices (you can use a culinary syringe), and on top - a peeled slice of ripe persimmon.
Homemade cookies
Take:
- flour (2 cups);
- chopped walnuts (1 cup);
- sugar (1 cup);
- chicken egg (1 pc.);
- butter (100 g);
- baking powder (1.5 tsp);
- nutmeg;
- persimmon (2 pcs.).
How to cook:
Grind the eggs with sugar and butter, pour into flour with baking powder, add persimmon puree. Stir thoroughly. Add nutmeg, cinnamon and finely chopped walnuts. Mix. Place onto a baking sheet with a tablespoon or using a pastry bag. Bake for about 15 minutes.
Varieties
There are about 500 varieties of persimmon. About a dozen of them gained the love and respect of Russians.
- Chocolate king. Round, dark orange, sometimes with brownish tints, with chocolate pulp - a juicy, delicious fruit. Moreover, the darker the flesh and the more seeds, the sweeter the king. And what is characteristic is that even the unripe fruit does not have a hint of an astringent taste. It remains sweet under any circumstances.
- Tangerine persimmon (or honey). The shape resembles a tangerine and the taste resembles honey, which is why it got its name. Seedless. The pulp is always bright orange, and in a ripe fruit it is soft, with a consistency close to jelly.
- Chinese persimmon. It is also called eastern or Japanese. The most common variety. This variety is easy to recognize: there is a shallow groove along the entire length of the fruit. The taste is very specific: astringency is present regardless of the degree of ripeness of the fruit, so Chinese persimmon is necessarily tart and astringent in taste, it lacks sweetness. But if you keep it in the freezer for a short time, the viscosity and astringency will go away. True, it still won’t get any sweeter.
- Sharon. This is not even a variety, but a hybrid - the result of crossing a persimmon and an apple. The fiery orange fruit tastes simultaneously like quince, persimmon, apricot and apple. The hybrid was bred in Israel in the Sarona Valley, where it got its name. The fruits have no seeds or seeds. Both ripe and unripe fruits are sweet. In addition to the Israelis, Azerbaijan and Spain are engaged in breeding Sharon. Azerbaijani fruits are pointed at the end; Spanish ones have grooves in the same place in the form of a small cross.
- Russian. The yellow-orange fruits weigh no more than 100 g and ripen at the end of November. But they are removed from the tree much earlier, so they reach the desired condition as they are stored. The fruits are sweet, can be with or without seeds, the pulp is light.
- Chamomile (fig persimmon). Another name for this variety is fuyu. In appearance it resembles figs - these are flat brownish fruits with or without seeds, quite sweet, without being cloying. Seedless fruits have a viscous taste; those with seeds are tastier; the taste largely depends on the climate of the producing country: the further south you go, the sweeter it is. So don't hesitate to ask where persimmons come from.
© gresei/Getty Images/iStockphoto persimmon health benefits and harms
Contraindications
Before consuming persimmon, it is important for hypotensive and hypertensive patients to consult with their doctor. This fruit is strictly prohibited from being included in the diet for gastrointestinal pathologies. It is known that persimmon is indicated for gastritis, but if the acidity in the stomach is very high, there is a high risk of exacerbation of the disease or the occurrence of ulcers. In this case, the fetus can harm its health and worsen its overall well-being.
Before using persimmon, you should consult your doctor.
Another serious contraindication is stomach and intestinal problems. In this case, it is recommended to give preference to slightly overripe berries that have low viscosity. If a patient has been diagnosed with gastritis and high acidity, excessive consumption of this fruit will lead to an exacerbation of the disease and deterioration of health. The patient begins to complain of cutting pain in the stomach.
The berry is strictly prohibited for consumption during the progression of Crohn's disease, as well as intestinal obstruction. This is a serious disease characterized by a long course. Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease.
Intestinal obstruction: the main contraindication to therapy
The inner mucous membrane, submucosa, and muscle layer are affected. Patients experience periods of exacerbation and incomplete remission. The berry can harm your health and worsen your condition. The fruit can be consumed to prevent frequent constipation.
Before starting treatment, it is recommended to check for an allergic reaction. Only then can blood pressure treatment begin. In other situations, persimmon has no contraindications. It is important not to overuse the berry. It is recommended to eat one medium fruit at a time. As hypotension progresses, persimmon is consumed 3-4 times a week, but not every day.