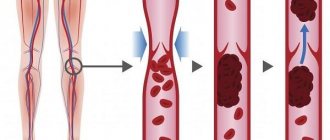
Thrombectomy is a procedure to remove a blood clot from a diseased blood vessel. Therapy involves, first of all, the use of medications aimed at thinning the blood and breaking up the blood clot. However, if a health threat occurs, for example, pulmonary embolism, the blood clot must be removed surgically. Modern technology allows us to minimize the consequences of surgical intervention, excluding the excision of blood vessels. A thrombus is a blood clot in the lumen of a blood vessel. The reason for its formation is an imbalance between the coagulation and anticoagulation systems of blood regulation. Platelets tend to clump together in response to bleeding and thus help stop it. But sometimes platelets clump together for no reason and form clots that block blood flow. At the site of the blockage, soluble blood protein is converted to insoluble protein. It is he who attaches the blood clot to the walls of blood vessels. Red blood cells, platelets and leukocytes continue to adhere to this structure.
Typically, blood clots simply restrict blood flow without blocking it. But the main danger of thrombosis lies in the fact that a blood clot detached from the vessel wall can enter the heart and cause a heart attack.
Briefly about the main thing
Thrombectomy is a minimally invasive (low-traumatic) operation that is performed to eliminate a blood clot formed in hemorrhoids.
This intervention is performed for acute hemorrhoids. Thrombectomy is performed under local anesthesia and takes no more than 10 minutes . The procedure has the shortest list of contraindications and does not require hospitalization of the patient. You can go home immediately after surgery .
The recovery period passes quickly and is not associated with serious restrictions. It will be necessary to follow basic hygiene rules: wash the anal area with warm water after each bowel movement. You should also follow all the doctor’s recommendations: ___• follow a diet, ___• limit physical and nervous stress, ___• avoid excluding thermal procedures, ___• take prescribed medications, ___• carry out local treatment of the postoperative wound.
Causes of thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins
Thrombosis can develop as a consequence of an acute, first-time attack of hemorrhoids, as well as as a complication of chronic hemorrhoids. The likelihood of developing thrombosis in chronic pathology increases with increasing “length” of the disease and the size of the nodes.
An attack can be triggered by: ___• chronic stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea, constipation alternating with diarrhea), ___• increased physical activity, ___• labor, ___• consumption of spicy food and/or alcohol, ___• hypothermia, overheating.
The development of acute hemorrhoids is promoted by all conditions accompanied by an increase in intra-abdominal pressure - from pregnancy to chronic cough and obesity.
Another factor in the occurrence of hemorrhoids is stagnation of blood in the veins of the pelvis, which often occurs as a result of a sedentary lifestyle and “sedentary” work.
Mechanism of blood clot formation
Thrombosis of external hemorrhoids occurs more often. It is extremely rare that the process spreads from external to internal nodes. Even less commonly, it occurs isolated in internal nodes.
Thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid occurs in both acute and chronic processes. In both cases, the pathology develops as a result of a combination of three factors: ___• slowing blood flow in the node, ___• blood thickening, ___• damage to the vascular network of the hemorrhoid.
Signs of thrombosis
___• The main symptom of thrombosis is acute, excruciating pain that prevents normal bowel movements. The pain syndrome intensifies many times over with straining, movement, and also in a sitting position. In severe cases, the pain takes on a pulsating character and, depending on the location of the node, can radiate to the leg, inside the rectum or to the external genitalia. ___• Bleeding often occurs, which varies in intensity - from individual drops on the surface of the stool to a trickle of blood during bowel movements. ___• Thrombosis of the internal node causes the sensation of a foreign body inside the rectum. Since the bleeding injured node comes into contact with feces, a secondary infection may occur. In such cases, mucous or purulent discharge appears and body temperature rises.
What complications may arise
Most often, the operation and healing are quick and painless. Possible complications:
- wound infection;
- pain syndrome;
- bleeding.
For severe pain in the anus, the doctor prescribes suppositories and ointments with an analgesic effect. After 5-7 days, the need for medications disappears. Infection and bleeding occur if hygiene is not observed. It is worth noting that the cost of hemorrhoidal thrombectomy is quite affordable for patients. The surgical procedure takes no more than 15 minutes. With proper preparation for surgery and following the doctor’s recommendations, complications are practically excluded. The patient recovers quickly and returns to his normal lifestyle.
If any complications occur, contact the proctology center immediately.
When is thrombectomy necessary?
Indications for surgery
Most cases of acute thrombosis of hemorrhoids (uncomplicated thrombosis, small size of the node) respond well to treatment with conservative methods. The main thing is to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Surgical procedures are performed if the period from the onset of the disease is 48-72 hours. If more time has passed since the onset of thrombosis, the doctor prescribes conservative treatment followed by surgical treatment. Surgical removal of a thrombosed node is carried out at a later stage from the onset of the disease in the following cases : ___• conservative therapy was unsuccessful, ___• acute pain syndrome, poorly controlled by standard painkillers, ___• symptoms of intoxication (general weakness, fever, headache), ___ • contraindications to the use of thrombolytic agents (pregnancy, lactation), ___• large size of the hemorrhoid.
The decision on surgical intervention is made by the doctor after an examination, which will reveal contraindications to surgery. Another goal of diagnostic manipulations is the choice of surgical intervention method.
Thrombectomy procedure
Local anesthesia is a prerequisite for thrombectomy. The surgeon makes a small incision on the thrombosed node - about 0.5 cm. Through it, a special instrument - a catheter - is inserted into the vessel. The specialist uses a syringe to remove the blood clot. In cases where the size of the blood clot is too large, the doctor takes additional measures. To avoid complications, a saline solution is injected into the body of the clot, due to which the clot softens and is divided into smaller parts. This technique reduces the likelihood of injury to the walls of blood vessels, inflammation and other complications. After the procedure, the doctor prescribes a course of drug treatment designed to prevent the recurrence of a blood clot.
Types of operations
Removal of a blood clot for external hemorrhoids
Removing a blood clot for external hemorrhoids is a simple operation that lasts only a few minutes. The doctor makes a small incision over the blood clot. Then the blood clot is removed with tweezers or a clamp; the wound is not sutured. The inflammatory edema subsides almost immediately, the pain subsides, and the patient’s general condition improves.
According to indications, a more complex operation can be performed - excision of an external hemorrhoid with blood clots , which is also performed under local anesthesia and does not require the patient to be hospitalized. During excision, the pathological element is removed, which reduces the risk of recurrent thrombosis.
Removal of a blood clot for internal hemorrhoids
Thrombosis of internal hemorrhoids is much less common and, as a rule, develops in the later stages of the development of the process (III-IV stages of hemorrhoids).
Treatment in this case is conservative. After stopping the acute process, treatment is carried out aimed at removing internal hemorrhoids (hemorrhoidectomy).
The essence of thrombectomy of hemorrhoids
Most often, thrombosis is observed in the later stages of hemorrhoids: it causes physical suffering to the patient and knocks him out of the usual rhythm of life. Complications of the disease can develop inside the rectum, on the outside of the anus, and sometimes in combination. This disease is accompanied by severe pain, bleeding, and swelling.
External changes are observed only with thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid. The latter falls out of the rectum and cannot be reduced. At the same time, it is red or purple in color and increased in size. At the same time, there are no external signs of internal thrombosis of the hemorrhoid. Changes in the mucous membrane can only be detected by rectoscopy and palpation.
External excision of the hemorrhoid will help relieve acute symptoms. Surgery occurs under local anesthesia. Its essence is as follows: a thrombus is removed from a thrombosed nodule through an incision (5 mm). As a result of surgery to remove thrombosis of the hemorrhoid, the pain goes away almost instantly.
Attention! Surgery only removes the blood clot and the symptoms it causes, but does not in any way affect the cause of hemorrhoids.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hemorrhoidal thrombosis is not difficult. The diagnosis is made by external examination of the anal area .
If the proctologist decides on surgical intervention, it will be necessary to take tests : ___• general blood test, ___• coagulogram, ___• blood glucose level.
It is necessary to tell the attending surgeon about all medications taken, since some medications (oral contraceptives, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.) affect blood clotting.
Contraindications
___• The operation is not performed if the patient’s condition is extremely serious (general exhaustion, complications of cardiovascular diseases, sepsis). ___• Surgical interventions are not prescribed for severe pregnancy (severe anemia, poorly controlled early toxicosis with dehydration, late toxicosis with generalized edema, etc.).
Since thrombectomy is a minimally invasive (low-traumatic) operation, the procedure can be prescribed after the patient’s condition has been stabilized. The decision about surgery or its inadmissibility is made individually, taking into account all risk factors.
Preparation for the procedure
If the doctor decides to undergo thrombectomy, the patient is prescribed a diet that excludes foods that cause gas formation in the large intestine (cabbage, legumes, fresh fruits and juices from them). The ban also includes products that cause a rush of blood to the rectum and/or have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane (smoked meats, spicy foods, alcohol).
Immediately before the procedure (in the morning and evening before the operation), you will need to cleanse the intestines using a Microlax microenema.
Preparation for thrombectomy is carried out when the patient's condition allows it. In case of severe pain and an impressive size of the node, bowel cleansing is not performed, and in the event of a threat of severe complications, surgical removal of the blood clot is carried out on an emergency basis.
How is the operation performed?
The procedure can be performed in a gynecological-style chair or on a couch and takes a few minutes. First, doctors give an anesthetic injection that “freezes” the tissue, just like in a dentist’s office. Therefore, the patient is conscious, but does not feel pain.
The surgical intervention takes several minutes and involves three manipulations: ___• opening the affected node (small incision), ___• removing the blood clot, ___• stopping the bleeding (the wound can be sutured, but more often it is not sutured)
After the procedure you can go home.
The exception is those cases of thrombosis when severe complications occur (gangrene of the node, paraproctitis, severe bleeding) that require hospitalization.
Rules of behavior in the postoperative period
If the evacuation of hemorrhoidal blood clots was carried out against the background of the patient’s satisfactory condition, then the postoperative period does not provide for significant restrictions.
The following are prohibited: ___• physical activity, ___• thermal procedures (bath, sauna, beach holiday), ___• prolonged stay in a sitting or squatting position.
Products that cause a rush of blood to the pelvic vessels or irritation of the mucous membrane are excluded from the diet: spicy, salty, smoked foods and alcohol.
Food should be rich in fiber, which stimulates intestinal function (prunes, apples). It is not recommended to eat foods that can cause constipation (rice and semolina porridge, potatoes, pasta). If stool retention occurs, a mild laxative (for example, Forlax) is prescribed.
After each bowel movement, wash the anal area with warm water and change the sterile napkin. If suspicious symptoms appear (pain, bleeding, discharge from the wound), you should immediately consult a doctor.
Indications for surgery
Thrombectomy from an external hemorrhoid is performed in the following cases:
- Acute hemorrhoids accompanied by thrombosis;
- Necrosis of the hemorrhoid;
- Pain syndrome that is not relieved by medications;
- The desire to get rid of hemorrhoids as soon as possible.
In fact, hemorrhoids can be completely eliminated only through surgery, but minimally invasive methods can only be used at stages 1-2, sometimes 3, of hemorrhoids. In advanced cases, such treatment is ineffective and extensive surgery is required. Therefore, if a patient is diagnosed with hemorrhoids, then the best solution would be to choose laser surgery.
Reviews from patients and recommendations from doctors
We analyzed online reviews of patients who underwent removal of hemorrhoidal thrombosis. The vast majority of patients were satisfied with the procedure. The most common impression: “The procedure itself is not as unpleasant as waiting for it.”
No reviews of complications of the operation were found. The most common complaint is pain in the area of the postoperative suture, which disappears after a few hours, but may reappear during bowel movements.
A more serious drawback is the likelihood of relapse. In order to avoid recurrent thrombosis, you must follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Preparation rules and methodology
Preparation for laser thrombectomy implies the following rules:
- Mandatory additional examination: general blood and urine analysis, blood sugar, liver parameters, fluorography, ECG;
- A week before treatment, it is necessary to exclude the consumption of foods that cause gas formation: brown bread, legumes, carbonated drinks;
- 2-3 days before surgery, you should switch to light, low-fat foods, without seasonings or additives;
- The last meal should be 12 hours before surgery;
- It is recommended not to smoke on the day of surgery;
- Immediately before surgery, a cleansing enema is performed or laxatives are prescribed.
How is the operation performed?
A special feature of laser thrombectomy is the ability not only to remove a blood clot, but also to excise the hemorrhoidal node with the slightest blood loss. Under general anesthesia, the surgeon isolates the affected node and uses a laser beam to cross its base. The laser immediately seals tissues and blood vessels, stopping bleeding.
After the operation, the patient remains in the clinic for several hours, after which he can go home - no long hospitalization is required. You should come back for an examination in a few days. After surgery, it is recommended to stay at home for 5-7 days. From special instructions, it is important to remove physical activity and adhere to a strict diet. When the wound heals, which happens fairly quickly, the patient can go home.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Thrombectomy is a low-traumatic method of treating acute thrombosis of hemorrhoids, which has both advantages and disadvantages. The method involves surgical intervention, so it is prescribed if conservative methods are contraindicated or ineffective.
Positive aspects of thrombectomy: ___• a short list of contraindications, ___• does not require hospitalization, ___• the shortest recovery period with a minimum number of restrictions, ___• minor side effects of the operation (pain, weakness, swelling), ___• complications are extremely rare.
Disadvantages of the method. Thrombectomy does not involve removal of the hemorrhoid, so recurrent thrombosis may develop. For this reason, in case of recurrent thrombosis, a more radical operation to remove thrombosed nodes (hemorrhoidectomy) is indicated.
Prevention of relapse
Basic principles of prevention
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node occurs as a complication of hemorrhoids, therefore, prevention of relapse consists in preventing the occurrence of enlarged hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids are a disease with a hereditary predisposition. Therefore, if there has already been one attack, there is a high probability of relapse. However, the implementation of a negative scenario is possible in the presence of additional risk factors: ___• pregnancy, ___• taking hormonal drugs, ___• overweight, ___• constant diet violations: eating spicy and fatty foods, alcohol, ___• abuse of thermal procedures (bath and sauna) or regular hypothermia, ___• work involving prolonged sitting or heavy physical work.
Necessary precautions
Most often, acute thrombosis occurs as a consequence of prolonged bowel dysfunction (chronic constipation). Therefore, you need to achieve daily bowel movements with a diet rich in fiber.
It is advisable to refrain from physical and nervous overload, as well as from hypothermia and overheating of the lower half of the body. You should not abuse alcohol, as well as spicy, smoked and salty foods.
When working “sedentarily”, you need to take regular breaks, during which you should perform hemorrhoid-preventing exercises. Many chronic diseases can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids, so taking care of your health is a reliable prevention of thrombosis of hemorrhoids.
Dangerous for the development of hemorrhoids and obesity. With this pathology, intra-abdominal pressure increases, the rheological properties of the blood change, problems with stool arise, and hormonal levels are disrupted. Therefore, normal weight is not only beauty, but also health.
Is it possible to do without surgery?
If doctors recommended thrombectomy of the hemorrhoid, this means that conservative therapy is not indicated in your case. You should not try to treat thrombosis with “traditional” methods.
If treatment is inadequate or absent, complications may develop: ___• bleeding, ___• gangrene of the node, ___• paraproctitis (purulent melting of peri-rectal fatty tissue).
In some cases, the affected node may open on its own and free itself from the blood clot. At the site of the “bump,” a fold of skin is formed – an anal fringe, which causes unpleasant sensations (itching, weeping) and is an unpleasant cosmetic defect.
results
- The average age of the patients was 74 years. 62.7% of patients were men. The average National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score was 18 points.
- According to the analysis, a favorable outcome occurred in 60 patients (59.4%) in the mechanical thrombectomy group and in 59 patients (57.3%) in the combination therapy group. There was no statistical difference between groups (difference, 2.1% [1-sided 97.5% CI, −11.4% to ∞]; odds ratio, 1.09 [1-sided 97.5% CI, 0.63 to ∞]; P = 0.18 for noninferiority).
- There were no significant differences between groups in 90-day mortality (8 [7.9%] vs. 9 [8.7%]; difference, -0.8% [95% CI, -9.5%-7 .8%]; odds ratio, 0.90 [95% CI, 0.33-2.43]; P > 0.99).
- According to the safety analysis, the incidence of intracerebral bleeding was lower in the thrombolysis + thrombectomy group compared with thrombectomy (34 [33.7%] vs. 52 [50.5%]; difference, -16.8% [95% CI, - 32.1% - -1.6%]; odds ratio, 0.50 [95% CI, 0.28-0.88]; P = 0.02).
- No statistically significant differences were demonstrated between study groups (6 [5.9%] vs. 8 [7.7%]; difference, -1.8% [95% CI, -9.7%-6.1%]; odds ratio, 0.75 [95% CI, 0.25–2.24]; P = 0.78).