Bradycardia is a type of arrhythmia when the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle is less than 60 beats per minute. It can occur as a norm in athletes, but bradycardia often indicates various cardiac pathologies. One of the characteristic manifestations is weakness, fainting and short-term loss of consciousness, cold sweat, pain in the heart, dizziness, and instability of blood pressure. If the patient has severe disease (less than 40 heart beats per minute), heart failure may develop. In this case, for the effective treatment of cardiac bradycardia, surgery to implant a pacemaker is indicated.
Symptoms and signs
Bradycardia has clinical symptoms and objective signs. Objective signs of bradycardia are pulse rate and changes in ECG readings. Clinical manifestations include various complaints of poor health. Among the symptoms of bradycardia, the most common are:
- feeling of lack of air;
- swelling;
- lowering blood pressure;
- fainting;
- pallor of the mucous membranes and skin;
- state of general weakness;
- convulsions;
- fast fatiguability;
- short-term visual impairment;
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- low concentration, absent-mindedness.
The symptoms of bradycardia presented above, as a rule, have different levels of severity. It is worth noting that with bradycardia, both all of the listed symptoms, and only some of them, develop. They are not specific, so they are often mistaken by patients for signs of other diseases or aging. If sinus bradycardia is maintained at a level of 40–59 beats per minute, the person does not experience any clinical symptoms. If the heart rhythm disturbance reaches 30–40 beats/min, fatigue, weakness occurs, attention and memory deteriorate, shortness of breath, swelling, dizziness appear, vision is impaired, and the skin turns pale. When the heart rate decreases to 30 beats per minute or less, a person may experience seizures or fainting. In case of loss of consciousness due to severe bradycardia, urgent medical assistance should be provided to prevent respiratory arrest with further death.
Hot flashes during menopause
The most constant and early symptom is hot flashes during menopause - periodically occurring redness of the skin and a feeling of heat in the face, neck, and chest. Hot flashes are often accompanied by sweating, headache, palpitations and insomnia. Based on the number of hot flashes per day, the following forms of menopausal syndrome are distinguished:
- mild - up to 10 hot flashes per day,
- average - 10-20 hot flashes with characteristic symptoms,
- severe - over 20 hot flashes and other pronounced manifestations.
It should be noted that the variety of symptoms of menopausal syndrome is often due to a psychosomatic component, in particular, the anxious attitude of the woman herself to the changes occurring in her body. Therefore, with competent help from a psychotherapist or psychoneurologist, many manifestations of menopause can be mitigated even without medications.
Causes
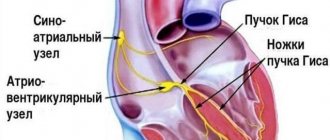
The most common cause of bradycardia is atrioventricular block of the sinus node. The reason for this process lies in the degenerative change in muscle fibers, which are responsible for excitation and conduction of electrical impulses. It is important to consider that bradycardia can be associated with rheumatism, chronic heart disease, myocarditis and other diseases.
The medical history of a patient with sinus bradycardia may include information about the use of drugs that slow the heart rate (HR). There may also be evidence of impaired blood circulation in the brain due to vascular disease. The distal blockade directly influences the onset of the disease.
The causes of bradycardia can be not only specific, it can be caused by:
- excessive pressure on the carotid artery (tie or tight collar) or eyeballs (Aschner reflex);
- increased intracranial pressure (meningitis, bruises, swelling or swelling of the brain);
- ulcer of the duodenum and stomach.
There is a medicinal type of sinus bradycardia, which appears due to taking various drugs, including cardiac ones.
Another form of the disease is the consequences of poisoning the body with organophosphorus compounds, hepatitis, sepsis, typhoid fever, uremia, and chemicals. Intoxication helps slow down the conduction of electrical signals to the heart. This category also includes bradycardia, which is provoked by disturbances in potassium balance or calcium levels in the body.
Some of the most common reasons are:
- coronary heart disease (CHD), acute myocardial infarction, heart disease, arterial hypertension.
- changes in the heart muscle that occur with age.
- reflex effects, in particular being in cold water, powerful blows to the chest or neck.
- drug overdose.
Features of heart block
The blockade is associated with a slowdown or cessation of the passage of electrical impulses through the structures of the heart muscle. The root cause may be any myocardial damage, congenital heart disease, atherosclerosis, overdose of certain drugs, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, menopause, etc. The blockade is of the following types:
- depending on the course - transient (passing) or intermittent (arising and disappearing many times during ECG recording), progressive or constant;
- depending on the location - sinoauricular, intraatrial, interatrial, atrioventricular, intraventricular (bundle branch block, conduction disturbance in the myocardium).
Symptoms of heart block, the treatment of which is often necessary, include periodic loss of pulse, fainting, and convulsions.
Diagnostics
Characteristic signs of sinus bradycardia can be identified by interviewing the patient and subsequent objective examination. The examination allows you to determine a rare pulse and respiratory arrhythmia. For patients with a more obvious degree of development of the disease, consultation with a cardiologist is recommended.
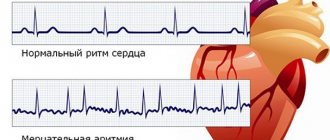
Thanks to an electrocardiographic study, it is possible to establish a rare heart rate, the presence of atrioventricular or sinoatrial block. If no episodes of bradycardia were detected during ECG registration, the method of 24-hour ECG monitoring is used.
If it is organic (not caused by external factors) sinus bradycardia, an ultrasound of the heart is prescribed. Load bicycle ergometry allows you to evaluate the increase in heart rate in accordance with a given physical load.
When it is impossible to detect transient blockades using ECG and Holter monitoring, the doctor prescribes a transesophageal electrophysiological study of the cardiac conduction tract. With its help, it is possible to determine the functional or organic nature of the course of sinus bradycardia.
Types of pathology
Cardiologists distinguish five forms based on etiology:
- extracardiac;
- organic;
- medicinal;
- toxic;
- sinus sports.
The extracardiac type develops under the influence of neurogenic factors, the organic type develops against the background of pathological lesions of the heart. Medicinal and toxic forms of the disease occur when the patient enters the body of toxins or medications in excessive dosages. Sinus bradycardia in athletes is the result of many years of training aimed at achieving maximum heart rate during physical activity.
Pathological types can occur in acute or chronic forms. In the first case, the cause of heart rate disturbances are heart attacks, myocarditis, and intoxication. Chronic bradycardia becomes the result of age-related sclerotic lesions of the heart muscle.
Treatment
Treatment of bradycardia is carried out individually, based on the specific pathology present, as well as the characteristics of the patient’s experience of this disease.
If the decrease in heart rate is insignificant and sinus bradycardia is moderate, therapy is not required; other cases (organic, extracardiac, toxic forms) suggest a transition to treatment of the disease that provokes bradycardia. The drug variety can be eliminated by stopping the drugs or adjusting their dosage.
To move to the active phase of treatment for bradycardia, the fundamental manifestations are distinguished - ventricular arrhythmia, angina pectoris, arterial hypotension, heart failure.
If the patient has fainted against the background of detected sinus bradycardia, it is necessary to consult with a cardiologist about the need to install an electrical pacemaker, which plays the role of an artificial amplifier of the heartbeat rhythm in accordance with the standard physiological frequency. The pacemaker allows you to return all hemodynamic parameters to normal. To diagnose sinus bradycardia, it is necessary to consult not only a cardiologist, but also a therapist.
General information
The pathology develops against the background of the inability of the sinus node to produce the number of electrical impulses necessary for a normal heart rate. Moderate sinus bradycardia may not lead to hemodynamic disturbances. A severe form of pathology provokes insufficient blood supply to tissues. Oxygen starvation of organs develops.
Professional athletes may experience physiological bradycardia, which is considered normal by cardiologists. At rest, trained people record 50-60 heart beats per minute. In a dream, this value drops by 25-30%.
Prevention
Sinus bradycardia requires constant prevention. To do this, you need to visit a cardiologist once a year in order to promptly detect and treat cardiac bradycardia.
In order to reduce the risk of disease, you must follow simple rules:
- to give up smoking;
- normalization of blood pressure;
- control diabetes and maintain blood sugar levels close to normal;
- reduction of high cholesterol levels;
- maintaining normal weight;
- eating heart-healthy foods;
- maximum restriction of alcohol consumption;
- daily exercise;
- reducing the risk of stress factors.
If you are concerned about a low heart rate, you should not delay visiting your doctor. Any disturbances in the functioning of the heart can lead to serious consequences. That is why you should not postpone drug treatment for bradycardia. Make an appointment at our clinic. Highly professional doctors with extensive experience in the treatment of bradycardia will work with you. You can find out details about the location of our branches on the “Clinic Addresses” page, as well as by phone +7 (495) 223-38-83.
Discharge during menopause
During premenopause, menstruation gradually loses its former regularity: it may occur later or earlier than expected. Their intensity changes - and it can either decrease or increase. Occasional intermenstrual discharge is possible - light, “spotting”, brownish in color.
So-called menopausal bleeding, associated with impaired production of sex hormones, develops in women aged 40-50 years, before menopause. Typically, such bleeding begins after a missed period, but it may coincide with the expected period or even begin a little earlier. It differs from regular menstruation in its long duration - up to several weeks.
The intensity of such bleeding may vary and may be repeated. Sometimes they are quite abundant, even threatening health and life.
Menopausal bleeding requires treatment in a hospital, usually responds to hormone therapy, but surgery may also be required. As a rule, diagnostic curettage is required to clarify the diagnosis in such cases. This is necessary in order not to miss possible hyperplasia (overgrowth) of the endometrium, its polyps and other conditions that are also manifested by uterine bleeding. Treatment tactics will depend on the correct diagnosis.
Uterine bleeding that occurs in postmenopause is much more dangerous, as it often indicates a serious illness. For example, spotting in a woman not receiving hormone replacement therapy that occurs several years after menopause can be caused by uterine cancer or ovarian tumors. In this case, it is necessary to undergo a thorough medical examination as quickly as possible with mandatory separate diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervix and body of the uterus. Early diagnosis allows for timely successful treatment.
Urinary incontinence during menopause
Urinary incontinence is a fairly common manifestation of menopausal syndrome. The fact is that the work of the bladder, urethra and the tone of the pelvic floor muscles depend on the level of estrogen in the body. And their deficiency can lead to weakening of the muscles responsible for urinary control. The following violations may occur:
- stress urinary incontinence - involuntary leakage of a small amount of urine during sudden movements, jumping, lifting heavy objects, coughing, sneezing, laughing;
- Urgent (induced) urinary incontinence, in which the muscles of the bladder contract untimely, which causes the involuntary release of a large amount of urine (an irresistible urge is felt, the woman simply does not have time to run to the toilet);
- pain, burning when urinating;
- frequent urination, the need to urinate even several times a night.
We must also not forget that the cause of urinary dysfunction in women in adulthood can be not only menopause itself, but also urinary tract infections. Age-related weakening of the sphincters contributes to their occurrence. The condition of the urinary tract can also be affected by concomitant diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, cerebrovascular accidents and many other factors.
Urinary problems should not be accepted as an inevitable part of aging. You should not hesitate to discuss this problem with a gynecologist and urologist, and also undergo a detailed examination of the pelvic region and urinary system. Specialists will help you find out the true causes of problems and suggest ways to solve them.
Typically, for urinary incontinence, the following are recommended:
- strengthening the pelvic muscles using Kegel exercises, which are based on prolonged contraction and subsequent relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles;
- “training” of the urinary tract using special simulators;
- limiting caffeine consumption;
- fight against excess weight;
- biofeedback method, electrical stimulation of the pelvic muscles;
- drug therapy, local use of hormones;
- surgical intervention.