14.11.2018
A.A.
(Last update: 07/10/2019)
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation required
Blood pressure is a very important indicator of human health. Any deviation in the values on the tonometer indicates some kind of malfunction in the body. They can be caused by various pathologies or result from exposure to negative external factors.
Many people think that only high blood pressure is dangerous. Indeed, hypertension can cause acute situations, which often cause deaths and the development of diseases in target organs. In addition, at least a third of humanity suffers from hypertension.
However, hypotension also requires attention. Especially if the numbers on the tonometer are significantly lower than normal. After all, a pressure of 80 to 40 causes the patient severe weakness and discomfort, and also has a negative effect on the entire body.
Do not self-medicate. Consult a specialist:
It has been proven that low blood pressure can also cause heart attacks and strokes. Therefore, it is so important to promptly diagnose and treat hypotension.
What do these pressure readings indicate?
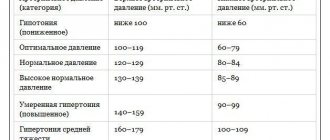
The ideal human blood pressure is 120/80. At the same time, there are people whose working pressure may deviate 10 units in one direction or another. This is also a completely normal phenomenon, which does not indicate the development of any pathologies in the body.
If the values on the tonometer deviate from these indicators, then this indicates that some kind of malfunction has occurred in the body. It should be borne in mind that if the decrease or increase in pressure was short-term, and occurred during sports training, after a sleepless night, etc., then this is a temporary phenomenon that usually passes quickly without causing harm. If this situation occurs every day, then this is a serious reason to consult a doctor.
If the pressure is 80/40, then this is a serious reason to “sound the alarm.” After all, these values are significantly below the norm. Therefore, in this state, the patient will feel severely unwell, and the internal organs will suffer from hypoxia. The risk of developing life-threatening situations in this case is very high.
You need to understand that low blood pressure indicates that the vessels are in a relaxed state, and their resistance to blood flow is reduced. At the same time, the heart is not able to “displace” blood throughout the body with sufficient force. This leads to the fact that all tissues suffer from a lack of oxygen. And the heart and brain are especially susceptible to this negative influence.
Indicators of 80/40 are very low pressure. And if they drop even more, this can cause death.
It should be borne in mind that in very young children a pressure of 80/60 is quite normal. Therefore, when assessing a person’s condition, it is important to take into account his age.
Treatment
Conservative therapy is, first of all, routine measures: sufficient fluid intake, reasonable consumption of coffee and black tea. It is advisable to use elastic stockings or bandages that improve the return of blood from the lower extremities to the heart.
Pharmacological therapy consists of the use of drugs that act on the vascular walls, leading to their narrowing, therefore, to an increase in pressure.
Important! The underlying cause of hypotension should be treated.
If the cause of a chronic disorder is a drug effect, you should contact your doctor to adjust the dose of the drug, change the treatment, or stop the drug completely.
Signs of a sharp decrease in blood pressure
As mentioned above, at a pressure of 80/40, hypoxia of all internal organs develops. Since the blood cannot deliver oxygen to the tissues in sufficient quantities.
Interestingly, this phenomenon is also observed at high blood pressure. Therefore, the symptoms of these conditions are very similar. And it is quite problematic to determine by the signs in which direction the blood pressure values have deviated. Thus, only a tonometer can accurately determine whether the malaise is caused by hypertension or hypotension.
There are characteristic symptoms that can tell a person about a failure. This will help him take timely measures to avoid complications. A one-time decrease in pressure causes temporary discomfort. And such unpleasant sensations disappear after the causes are eliminated.
You need to understand that it is the brain that is most susceptible to the effects of low blood pressure. Therefore, most negative sensations will be associated with hypoxia in this organ.
Signs of hypotension with readings of 80/40:
- Painful sensations in the head. Usually this sensation affects the temporal region and is dull, constant or pulsating in nature; in some cases, the pain can also affect the frontal area of the head. Sometimes such pain is observed only in the left or right area of the head.
- Lack of oxygen. With such low values on the tonometer, the patient will suffer from a lack of air, which is why there will be a constant desire to yawn.
- Dizziness. This symptom is also a consequence of oxygen deficiency
- Prostration. With low blood pressure, performing even simple tasks is problematic, and there is severe drowsiness and lethargy.
- Fainting or semi-fainting conditions. With a blood pressure of 80/40, such conditions occur quite often.
- Feeling nauseous. With very low blood pressure, vomiting may also occur.
- Heartbeat disturbances. The pulse in this state can either slow down or become faster.
- Vision problems. There may be darkening or the appearance of “dots” in the eyes.
- Paleness of the skin. The skin of the face, upper and lower extremities is especially susceptible to this.
Typically, with a blood pressure of 80/40, most of the above symptoms are present. However, they disappear after the values on the tonometer are normalized.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
True hypotension is a pathological decrease. A drop in levels below those that are normal for a person. The following are signs of low blood pressure:
- occipital headaches;
- weakness, malaise, weakness, lethargy;
- vomiting, nausea;
- chills;
- shortness of breath, increased sweating;
- lack of air;
- In the morning, when getting out of bed, dizziness begins.
- Masks for hair growth and thickness are the best and most effective. Recipes with oils, cinnamon, pepper, etc.
- Symptoms of a brain tumor in the early stages
- Washer and dryer - rating of the best with price. How to choose a washing machine with drying function with reviews
What signals indicate long-term hypotension?
You need to understand that symptoms of low blood pressure and signs of long-term hypotension are not the same thing. Indeed, with chronic hypotension, the functioning of some internal organs is disrupted, as evidenced by constantly present problems.
Symptoms of chronic hypotension:
- Deterioration of memory and brain function, absent-mindedness. This is due to the frequent occurrence of hypoxia of this organ.
- Sensitivity to weather changes and magnetic storms. Such natural phenomena lead to serious discomfort and a sharp drop in blood pressure.
- Chronic fatigue. Hypotonic people quickly get tired even when performing simple tasks. Insomnia or increased sleepiness is often present.
- Depressive states, irritability. Constantly bad mood and tearfulness are also characteristic of long-term hypotension.
- Malfunctions of the heart. Low blood pressure also has a bad effect on the “pump of our body.” This leads to heartbeat irregularities, regardless of the influence of external factors, as well as pain in the chest area.
- Sensitivity to changes in ambient temperature. Most people suffering from hypotension are constantly cold. Their hands and feet are always cold.
Such symptoms indicate that problems with blood pressure have been present for quite some time. In this case, visiting a doctor is simply vital.
Signs of low blood pressure
The main consequences of this condition are associated with impaired blood circulation in the vascular system of the brain. The person will feel unwell, there will be pain (throbbing) in the temples, and in some cases in the occipital region. Patients note the occurrence of unpleasant sensations in the forehead, nagging pain in the temporal region. Migraine-like pain may occur on one side of the head. These phenomena are constant and dull in nature; nausea and vomiting may be added. The following are signs of low blood pressure:
- Significant deterioration in health when the weather changes, during magnetic storms.
- Hypotonic people suffer from rapid fatigue, weakness, and their performance is noticeably reduced by the end of the day.
- When suddenly rising from bed or chair, darkening and dizziness appear in the eyes;
- Very low blood pressure can cause fainting;
- Hypotonic patients complain of memory impairment and absent-mindedness. Due to a decrease in blood flow, a person with low blood pressure tends to experience depression, increased irritability, and mood swings.
- A decrease in vascular tone can lead to abnormalities in the functioning of the heart muscle. Both the heart itself and behind the breastbone may hurt. Such symptoms are accompanied by palpitations that are not associated with physical or nervous stress.
- With severely low blood pressure, a person constantly experiences a lack of air, often yawns, and experiences drowsiness.
- Hypotonics are very sensitive to heat or cold; they are characterized by coldness, numbness of the arms and legs.
Causes of hypotension
Hypotension occurs much less frequently than hypertension. However, it is less likely to develop into life-threatening situations. However, this does not make it any less dangerous.
It is also worth noting that most diseases that affect the state of the cardiovascular system and hormonal levels lead specifically to hypertension. But those that cause 80/40 blood pressure are usually the most dangerous.
Pressure may decrease due to the negative impact of external factors. In this case, it is important to normalize your lifestyle and eliminate outside influences that cause such disruptions. This will be enough for the condition to improve.
But hypotension can also be the cause of pathologies occurring inside the body. However, many of them are no less dangerous than hypotension itself.
And the sooner we start fighting such diseases, the better the prognosis for their treatment will be. This is why it is so important to be examined promptly if chronic hypotension occurs. Sometimes this can even help save the patient's life.
Causes
Most often, blood pressure decreases due to cardiovascular diseases. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, metabolic disorders, infections, and poisoning of the body with drugs or alcohol can also affect this indicator.
And also read on our website: What does blood pressure 190 over 120 mean - causes, symptoms, what to do and how to bring down high readings?
In pregnant women
During pregnancy, a number of the following factors can affect the decrease in blood pressure:
- Toxicosis in the first trimester, accompanied by vomiting and loss of fluid.
- In the second half of pregnancy, inferior vena cava syndrome may appear. It occurs due to the growing uterus, which, when lying on the back, compresses the vena cava and prevents blood flow to the heart. A woman may even lose consciousness. However, when changing position, the pressure is restored.
- The presence of extagenital diseases that affect blood pressure.
The danger of this condition during pregnancy is spontaneous abortion in the early stages or premature birth. Knowing about a woman’s pathology, the doctor must constantly keep in touch with her.
In adults and older people
Sometimes at a pressure of 80/40 mm Hg. Art. a person has to be hospitalized, especially if such a condition appears in a hypertensive patient, since a stroke or heart attack can occur with a sharp rise in blood pressure.
The cause of pressure 80 to 40 in an elderly person can be the following circumstances:
- Having suffered a serious illness.
- Operations performed.
- Long rehabilitation, forcing a person to spend a long time in bed.
- Taking certain medications.
To identify the exact cause of the appearance of pressure 80 to 40, it is necessary to undergo a full medical examination.
In children and adolescents
The most common causes of low blood pressure in children and adolescents are:
- Hereditary factors.
- Anatomical congenital or acquired features - for example, thickening of the skull bones, birth trauma, improper overgrowth of the fontanel, etc.
- Hormonal changes and puberty in adolescents.
- Psycho-emotional pressure on the child.
- Chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract, such as sinusitis, bronchitis, tonsillitis, etc.
- Insufficient nutrition, limited intake of fortified foods.
Why can a sharp drop in blood pressure occur?
External factors usually lead to a strong decrease in blood pressure. And to normalize the condition, it is enough to simply eliminate them. If a person encounters such negative phenomena infrequently, then this usually does not lead to the development of any serious pathologies.
Why blood pressure may increase:
- Malnutrition. Often girls who follow “strict” diets suffer from hypotension.
- Medicines. Some medications can lower blood pressure. And this applies not only to drugs aimed at treating hypertension. There are drugs for which hypotension is listed as a side effect.
- Lack of sleep or oversleeping. Both mistakes can lead to the development of chronic fatigue and decreased blood pressure.
- Excessive physical and mental stress. In some cases, such factors lead to loss of strength and hypotension.
- Stressful situations. This is one of the most common reasons for changes in blood pressure readings.
- Colds. During flu and colds, all the body's forces are aimed at fighting the disease, so a decrease in blood pressure may be observed.
- Lack of indoor air and tight clothing. Under such conditions, the body begins to suffer from hypoxia, which leads to a decrease in pressure.
- Being in a room with high temperature and high humidity.
- Contact with chemicals. Some chemicals can lower blood pressure, affecting the functioning of the cardiovascular system and brain.
- Head injuries. Especially often, a decrease in pressure is observed with a concussion.
- Alcohol intoxication.
- Long sunbathing on the beach. Sunstroke and overheating of the body can lead to a decrease in pressure.
Why does blood pressure change in pregnant women?
The body has to adapt to a special condition - pregnancy. A woman’s body weight gradually increases, and additional blood circulation is activated between the uterus and placenta. The functioning of the heart and blood vessels at this time is affected by:
- Changes in hormonal levels;
- An increasing volume of blood circulating in the body;
- Increased tone of the central nervous system;
- Changing the location of the diaphragm, which rises upward;
- Increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity;
- Displacement of the heart in the chest;
- Increased heart rate.
The body directs all its efforts to improve blood flow in the placenta and in the uterus, because this is necessary to provide the developing fetus with oxygen and nutrients. Under these circumstances, blood pressure changes.
Pathologies leading to hypotension
If hypotension is constantly present and is not caused by the factors described above, then this is a really serious reason to visit a doctor. In this case, there is a high probability that it is a consequence of the course of serious pathological processes in the body.
Some of them pose a serious threat to the patient's life.
Causes of hypotension:
- Heredity. Primary hypotension has no known cause. In this case, it is an independent disease.
- Tumor neoplasms. Hypotension can occur against the background of both malignant and benign tumors.
- Obesity. If you are overweight, your body is constantly under increased stress. This can lead to the development of secondary hypotension.
- Hormonal diseases. For example, Addison's disease, which is characterized by adrenal insufficiency and their inability to produce the required amount of aldosterone, adrenaline and cortisol, can lead to such a problem. Also, some thyroid pathologies can cause hypotension.
- Internal bleeding. With blood loss, acute hypotension always develops.
- Serious kidney disease. It is the kidneys and adrenal glands that are responsible for the production of most hormones, as well as the processes necessary to regulate blood pressure.
- Poisoning.
- Heart diseases. This problem occurs especially often in cardiac asthma and failure of this organ.
- Serious allergic reaction. A sharp decrease in blood pressure can occur during anaphylactic shock.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Hemorrhoidal bleeding.
- Serious inflammatory and infectious diseases. For example, tuberculosis, sorcaidosis, etc.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Is this condition dangerous?
For prolonged hypotension, a doctor's consultation is necessary. Otherwise, the process may become chronic.
The danger of pressure 80 to 40 and even 85 to 55 is that a person may not feel it for a long time. While the pathological processes in his body continue to progress.
The most dangerous consequence of hypotension is myocardial infarction.
Other unpleasant consequences of low blood pressure include:
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Opening of gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Decreased functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
And also read on our website: Is blood pressure reading 130 over 80 considered normal or not - what should men and women do?
Pregnancy and blood pressure
While pregnant, women often experience a decrease or increase in blood pressure. For them, this situation also poses a danger, but it is not always a consequence of pathologies occurring inside the body.
During pregnancy, serious hormonal changes occur in the body. This also affects hormones that regulate blood pressure. Therefore, a short-term deviation of the tonometer readings in one direction or another is a common occurrence during this period.
Also, a pregnant woman’s body is more sensitive to various external influences. After all, it is constantly subjected to increased physical stress, and in the later stages, pressure from the enlarged uterus is exerted on all organs.
You need to understand that, despite the fact that in an “interesting situation” low blood pressure is not uncommon, this symptom cannot be ignored. Especially if the pressure is 80/40 - during pregnancy.
Severe hypotension can lead to fetal hypoxia and even miscarriage, so it is very important for pregnant women to monitor their condition and try to avoid negative external influences. They need proper nutrition, proper rest, walks in the fresh air and complete peace of mind.
How to deal with the problem?
If hypotension develops in a healthy person due to excessive stress and stressful situations, these negative factors should be eliminated, and within a few hours or days everything will return to normal.
Often blood pressure decreases due to anemia, pathologies of the nervous system and thyroid gland. In this case, the disease that caused the hypotension is treated directly.
A healthy lifestyle plays a big role in normalizing blood pressure. The following rules must be adhered to:
- Take frequent walks in fresh air.
- Stick to moderate physical activity.
- Take a daily contrast shower.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Night sleep should last at least 8 hours.
If, despite a decrease in blood pressure to 80/40, a person feels unwell, it is necessary to urgently call a doctor . While waiting, you can offer the patient a glass of sweet tea or coffee, or a few drops of tincture of radiola rosea, lemongrass or eleutherococcus.
Raising blood pressure and keeping it at the required level is often much more difficult than lowering it.
Low blood pressure as normal
In some cases, low blood pressure may not be a sign of any abnormality at all. Sometimes this phenomenon is quite normal and does not require correction.
In children, the cardiac system is in the formative stage. In newborns up to 2 months, even indicators of 80/60 are considered normal. And only by the age of 12 their working pressure reaches the generally accepted norm. Therefore, in this case it is very important to pay attention to the age of the child.
Also, low blood pressure may be a variant of the norm in trained athletes. Over time, additional elements of the circulatory system are formed in their heart muscle. Therefore, their working blood pressure indicators are lower than those of ordinary people.
In the cases described, it is important to pay attention to how much the pressure deviated from the norm for a given group of people. However, you need to understand that indicators as low as 80/40 require increased attention in any situation.
Normal blood pressure in pregnant women
Blood pressure levels in pregnant women also depend on the trimester. In general, the optimal indicator is 120-130/80-85. The upper permissible limit is 130-139 mmHg. for systolic and 85-89 mm Hg. for diastolic pressure. Blood pressure exceeding 140/90 is considered elevated.
By trimester, the table of normal values looks like this:
| Pressure norm | Index |
| First trimester | 110-120/70-80 |
| Second trimester | Not higher than 130/85 |
| Third trimester | From 140/90 to 100/60 |
It is important to consider that each body is individual, and each woman has her own normal blood pressure. That is why blood pressure readings should be compared not only with norms, but also with the usual pressure at which a woman feels good.
Why is hypotension dangerous?
Many people mistakenly think that low blood pressure is less dangerous than high blood pressure. This is one of the most common mistakes! Yes, hypotension develops much less frequently than hypotension, but this does not make it any less dangerous.
With hypotension, organs and tissues experience no less hypoxia than with hypertension. With a prolonged course of this condition, the functioning of internal organs gradually deteriorates. Over time, this can lead to the development of serious pathologies.
The organs that are most susceptible to the negative effects of hypotension are called target organs. These include the brain, heart and kidneys. It is in them that the consequences of hypoxia first appear.
However, other organs are also susceptible to the negative effects of hypotension. Indeed, with insufficient blood circulation, which is present at low pressure, diseases of the bones, joints, liver and other organs and systems of our body can develop.
In addition, it has been proven that acute hypotension can cause life- and health-threatening situations. And the lower the readings on the tonometer, the higher the likelihood of their occurrence.
What dangerous situations can arise due to hypotension:
- Heart attack. Moreover, in the hypotonic form of this condition, its painless course is possible. It is especially dangerous due to the fact that it is not always possible to recognize it in time;
- Coma and collapse;
- Stroke. There is medical information about the occurrence of hypotonic stroke;
- Miscarriage;
- Heart failure;
- Worsening cardiac ischemia;
- Angina;
- Fetal hypoxia. This may lead to a delay in its development;
- Death of brain cells. This situation can cause dementia;
- Placental insufficiency. This condition also poses a threat to the fetus.
Blood pressure control is the key to the health of mother and child
Often problems with pressure do not manifest themselves until the situation becomes truly threatening. Sometimes pregnant women attribute the deterioration in their health to their “interesting situation” and hormonal changes and fatigue. But pressure surges during such a period can have quite serious causes and dangerous consequences.
The sooner such prerequisites are identified, the easier it will be to normalize the state of health. This is why pregnant women are advised to regularly monitor their blood pressure, especially since it is very easy to do this with modern home blood pressure monitors.
Diagnosis for hypotension
If hypotension is caused by negative external influences, then it is enough to simply eliminate the external factor and take an antihypotensive drug to eliminate it. However, if we are talking about chronic hypotension, then most likely its cause lies in internal pathological processes.
Hypotension caused by internal pathologies cannot be eliminated by symptomatic treatment alone. In this case, the patient's condition will constantly worsen. Therefore, when designing therapy, it is very important to take into account exactly what disease caused the deviation in the readings on the tonometer.
You also need to understand that with prolonged hypotension, pathologies in the internal organs may develop. And even if the condition normalizes, they will progress, worsening the patient’s condition.
That is why doctors, before prescribing treatment to their patients, conduct a thorough diagnosis of their condition. Various methods can be used for this.
Diagnostic methods used for hypotension:
- Usually the patient is prescribed daily monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate. This examination is carried out in a hospital, where the doctor records the indicators he needs using sensors attached to the patient’s body.
- ECG. It can be used to check the correct functioning of the heart. Based on the results of such diagnostics, further examinations are prescribed.
- MRI and CT. These diagnostic methods are necessary to check the condition of organs that may cause low blood pressure. First of all, this method examines the pituitary gland and other parts of the brain.
- Ultrasound. This examination option is considered the most suitable for considering the condition of the heart, kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Stool examinations. This material is usually analyzed for the presence of blood particles if a bleeding ulcer or hemorrhoid is suspected.
- Blood and urine analysis. Blood and urine are examined for signs of inflammation, hormones, and microelements.
These are basic studies that are carried out at low pressure. However, the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic options to clarify the details of the diagnosis.
Where does high blood pressure come from?
High blood pressure can accompany a woman during pregnancy if she was previously diagnosed with hypertension. In this case, it is doubly important to monitor your condition and listen to all the doctor’s recommendations. You should not take the same medications that were prescribed before pregnancy, as they may affect the development of the fetus. There are medications that do not have side effects on the baby; your doctor will select them for you.
There are medications for blood pressure that do not have side effects on the baby; your doctor will select them for you.
You can also “acquire” high blood pressure as a result of constant stress, heredity, smoking, overweight or obesity, diabetes mellitus or other concomitant diseases of the kidneys, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland. In any case, consultation with a specialist is necessary to minimize the risk of developing hypertension while expecting a child. To do this, it is advisable at the stage of pregnancy planning to eliminate all provoking factors, cure concomitant diseases, and get rid of bad habits.
What to do if the pressure is 80 to 40
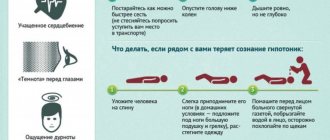
Blood pressure 80/40 is very low. And even if they do not decrease further, then long-term ignoring of this condition can lead to irreversible consequences. Therefore, in this case, the patient really needs first aid.
What to do if the pressure is 80/40:
- First of all, it is necessary to ensure free access of oxygen and a comfortable temperature in the room. To do this, you need to open the windows, turn on the fan or air conditioner. If the victim is wearing tight clothing, it must be removed.
- The patient must be transferred to a horizontal position. In this case, you do not need to put a pillow under your head, but you need to raise your legs up.
- You need to take a hypertensive drug. This can be a modern medicine or a proven folk remedy that is at hand. For example, the patient can be given strong, sweet coffee.
- If this does not help, then it may be necessary to administer saline solution to increase the volume of biological fluid circulating throughout the body. This drug is administered intravenously, by drip.
If this method does not help, then the patient needs to call an ambulance. Further treatment will be carried out in a hospital.
If low blood pressure is constantly present, then a trip to the doctor is inevitable. The specialist will identify the cause of the ailment and prescribe the necessary treatment.
The Dangers of Hypotension in the Elderly
The main complication of low blood pressure in an elderly person is injuries caused by fainting. This can happen on the street, on public transport, at home... If you fall, there is a risk of head injury; Without first aid, the consequences can be serious.
Modern medicine
Treatment of hypotension is usually not limited to just normalizing the readings on the tonometer. After all, chronic low blood pressure is usually a consequence of pathological conditions in the body. Therefore, in this case, therapy is selected according to the diagnostic results.
However, even if the cause of hypotension is various internal pathologies, at the initial stages of their treatment, the values on the tonometer may still be reduced. In this case, drugs are used that help eliminate this symptom and normalize the patient's condition.
Tonics are used to increase blood pressure. Vasoconstrictor drugs also have hypertensive properties.
What drugs are most often used to increase blood pressure:
- Eleutherococcus (40 drops);
- Pantocrine (40 drops three times a day);
- Apilak (you need to take one tablet three times a day);
- Tincture of pink radiola (15 drops).
These products have a fairly mild effect. Therefore, they can be used at home for first aid.
At the moment, there is an opinion that primary hypertension occurs as a result of nervous disorders. Therefore, it is often practiced to treat such a disease with antidepressants and psychotropic drugs.
How to measure blood pressure during pregnancy
The blood pressure measurement procedure takes only a few minutes, but can help prevent very serious health problems. Modern automatic blood pressure monitors do almost everything themselves; you need to use them regularly and follow some rules:
- Take measurements at the same time of day so that the indicators do not change under the influence of hormonal fluctuations and biological rhythms of the body;
- Do not measure blood pressure immediately after exercise, including walking - in this state the pressure may temporarily increase, there is nothing to worry about;
- Do not take measurements less than an hour after eating - due to the active activity of the digestive system, the blood volume is redistributed, so the result will be biased;
- Measure the pressure in a sitting position, the hand lies on the table top, the muscles are relaxed;
- Do not move or talk during the measurement.
You should not measure your blood pressure in a state of strong excitement. First you need to calm down, lie down for a few minutes. Repeated measurement is carried out no earlier than after 10 minutes, if necessary.
Folk remedies that are always at hand
Medicines with hypertensive properties are not always available. Fortunately, when you have low blood pressure, you can use some products that are easy to find in almost everyone's kitchen.
Folk remedies for increasing blood pressure:
- Hot coffee. The patient can be given a cup of strong, sweet, hot coffee to drink. Caffeine is very good for raising blood pressure.
- Strong black tea with sugar. This drink contains an analogue of caffeine - tannin, so tea will also help increase blood pressure.
- Hot green tea with sugar. Green tea should be hot, since this cold drink has the opposite properties.
- Ginseng also helps increase blood pressure. You can use ginseng tea or tincture from this plant.
- Schisandra chinensis. It is also used in the form of decoctions and tinctures.
All drinks for hypotension should be hot. After all, it is in this form that they have the most pronounced hypertensive effect.
It is also important to add sugar to such drinks. Glucose helps increase blood pressure and also provides the body with the energy it needs when feeling weak.
How to lower blood pressure?
Self-medication during pregnancy is contraindicated.
Drugs that have helped someone close to you may have a negative impact on your health and the health of your baby. Therefore, all medications should be prescribed by a doctor after a comprehensive examination. It is worth abandoning the independent choice of herbal medicines and dietary supplements. Pregnancy is a contraindication for taking most of them. They can enhance or slow down the effect of the medications you take, cause allergies and a number of other complications. In order for your blood pressure to remain normal, it is important to control your weight, exercise (of course, within reasonable limits and after consulting a doctor), eliminate foods that increase blood pressure (coffee, strong black tea, chocolate) from your diet, and give up bad habits. High blood pressure is a condition that can and should be dealt with, especially during pregnancy. To prevent the development of complications associated with hypertension, it is enough to control your blood pressure and follow simple doctor’s recommendations. And then you and your baby will be healthy. Tags:
- Pressure
- pregnancy
- complications
To leave a comment you must be an authorized user
GESTOSIS IN PREGNANT WOMEN: Issues of diagnosis and obstetric tactics
Is gestosis in pregnant women an independent disease?
What determines the course of gestosis?
What degrees of nephropathy are usually distinguished?
What pathogenetic therapy is prescribed for gestosis in pregnant women?
Preeclampsia in pregnant women is a syndrome of multiple organ functional failure that develops as a result of pregnancy or is aggravated in connection with pregnancy. Its main symptoms are: pathological weight gain, edema, arterial hypertension, proteinuria, seizures and/or coma. Gestosis in pregnant women is not an independent disease, it is a syndrome caused by a mismatch in the capabilities of the adaptive systems of the mother’s body to adequately meet the needs of the developing fetus. This discrepancy is realized through varying degrees of severity of perfusion-diffusion insufficiency of the placenta.
Isolating hypertension and proteinuria separately in the group of gestosis, most foreign authors, with a combination of symptoms (edema, proteinuria, hypertension), regardless of their severity, define this condition as preeclampsia. This emphasizes the difficulty of determining the severity of gestosis.
Our country has adopted a classification that includes four clinical forms of gestosis: dropsy, nephropathy, preeclampsia and eclampsia. Some authors recognize the existence of another monosymptomatic clinical form - hypertension in pregnant women, and also divide late gestosis into “pure” and “combined”, that is, developing against the background of chronic diseases that existed before pregnancy.
The prevalence of gestosis remains high (about 12-27%) and does not tend to decrease. Its course largely depends on previous diseases, and therefore uncomplicated and combined (complicated) forms of gestosis are distinguished.
Preeclampsia due to kidney disease is difficult and has adverse consequences for the fetus and newborn. In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of cases of renal pathology in pregnant women. Thus, gestational pyelonephritis is detected in 6-8% of pregnant women, glomerulonephritis - in 0.1-0.2%.
Preeclampsia due to kidney disease develops from 18-22 weeks of pregnancy. The early onset of gestosis should always be alarming - we may be talking about a combined form of the disease. The presence of this diagnosis should be clarified, since the treatment of combined forms has its own, very significant features. Pregnant women with kidney disease and gestosis, especially with severe hypertension, often (5-6%) experience premature abruption of the normally located placenta with serious consequences for the health of the mother and fetus.
As a rule, gestosis is severe due to hypertension. Even neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypertensive type in combination with gestosis in some women determines the severe course of the disease.
Preeclampsia apparently develops as a result of an imbalance between maternal antibodies and the antigenic structure of the fetus. During pregnancy complicated by gestosis, the production of antibodies and the number of circulating immune complexes increase. The deposition of these complexes on the surface of the endothelium causes platelet aggregation, tissue damage, and fibrin deposition. In addition to the direct damaging effect of antibodies, they reduce the synthesis of prostacyclin and thereby disrupt the ability of the vascular wall to prevent vascular spasm, platelet aggregation and intravascular thrombosis. The decrease in prostacyclin occurs in parallel with damage to endothelial cells. Immune vasculitis occurs with choriodecidual damage, release of tissue thromboplastin, fibrin, fibrinogen. Damage to the endothelium causes a number of negative consequences, which are most clearly manifested in the form of hypertension, proteinuria and edema. Damage to the endothelium is quite common, which makes it possible to classify severe gestosis as a group of endothelial diseases and justify the inevitability of the development of multiple organ failure in this pathology of pregnancy.
The ability of endothelial cells to produce prostacyclin decreases with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity, so gestosis occurs more quickly against the background of concomitant extragenital pathology and is always accompanied by severe multiple organ failure. In pregnant women with pyelonephritis, the level of endotoxin in the blood increases with a simultaneous decrease in antiendotoxin antibodies. Against the background of immune vasculitis, the production of prostacyclin decreases and the amount of thromboxane increases, which, with an increase in pulmonary and peripheral vascular resistance, leads to an increase in arteriolar tone, cerebral vasospasm, platelet aggregation and disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
An important point is determining the severity of gestosis. There is no doubt that the combined form of gestosis can be considered the most severe. Early onset of gestosis and its presence for more than three weeks should be taken into account as unfavorable prognostic signs.
It is customary to distinguish between grade III nephropathy. In grade I, swelling of the legs occurs, blood pressure is increased by 25-30% (about 150/90 mm Hg), and moderate proteinuria is noted (up to 1.0 g/l). In stage II of the disease, pronounced swelling of the legs and abdominal wall is detected, blood pressure increases by 40% compared to the initial level (170/100 mm Hg), proteinuria is more pronounced (from 1.0 to 3.0 g/l) . Stage III is characterized by pronounced swelling of the legs, abdominal wall, face, an increase in blood pressure relative to its initial level by more than 40% (above 170/100 mm Hg) and severe proteinuria with protein content in the urine (more than 3 .0 g/l). This division does not always justify itself in practice, since even with grade II nephropathy (and sometimes grade I), severe complications and development into preeclampsia and eclampsia are possible. Therefore, many obstetricians distinguish between mild and severe forms of nephropathy. Severe nephropathy may be considered preeclampsia; In this case, patients need intensive therapy, and if its effectiveness is insufficient, immediate delivery.
The classic “triad” of symptoms is observed in 28-50% of cases. Currently, the clinical course of gestosis is characterized by a gradual progression and an increase in the number of low-symptomatic, atypical forms of the disease. However, these forms of gestosis are no less dangerous than a complication with severe symptoms.
The diagnosis of the disease and determination of its severity should be based on an assessment of changes in the cardiovascular system, liver function, kidneys, lungs, nervous system and fetal condition. The main symptom of gestosis is hypertensive syndrome. What is important is not the absolute numbers of maximum and minimum blood pressure, but the increase in pressure compared to the initial one, as well as studying it over time.
Of particular importance are an increase in diastolic pressure and a decrease in pulse pressure (up to 30 mm Hg and below). A relationship was revealed between the severity of gestosis and the degree of blood pressure asymmetry: the more pronounced the asymmetry, the more severe the gestosis. Even with a mild course of gestosis, central hemodynamics are significantly disturbed. The volume of circulating blood, central and peripheral venous pressure decreases, cardiac output decreases, peripheral vascular resistance increases, and metabolic disorders in the myocardium are noted. High hematocrit values (more than 0.42 mg/l) indicate a severe degree of gestosis.
The severity of gestosis can be judged by renal dysfunction. To determine the severity of proteinuria, it is advisable to study the daily portion of urine, since protein excretion during the day can vary significantly. The concentration function of the kidneys suffers earlier than others. In parallel with the increase in the severity of gestosis, daily diuresis decreases. Violation of the nitrogen excretory function of the kidneys during gestosis is judged by the increase in the concentration of urea and creatinine in the blood.
The most characteristic signs of liver damage are disturbances in its protein-forming and antitoxic functions. The amount of protein in the blood plasma in patients with gestosis is significantly reduced, as is the value of colloid-oncotic pressure of the plasma. The albumin content decreases most sharply. Hypoproteinemia is not only a consequence of a violation of the protein-forming function of the liver, but also depends on the loss of protein into the extracellular space and its excretion in the urine due to increased permeability of the vascular wall.
Changes in the central and peripheral nervous system can occur periodically and quickly disappear, but in some cases they are persistently pathological. Headache, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, and varying degrees of impairment of consciousness are signs of hypertensive encephalopathy.
Progressive gestosis with prolonged disruption of microcirculation ultimately leads to the development of intracranial hypertension, acute cerebrovascular accidents, the appearance of convulsive readiness, the development of eclampsia and coma.
In patients with severe forms of gestosis, respiratory dysfunction is observed, and with eclampsia, acute respiratory failure may develop, manifested by motor agitation, cyanosis, shortness of breath, and respiratory rhythm disorder.
Thrombocytopenia of varying severity is observed in almost 1/3 of pregnant women with gestosis. Moreover, thrombocytopenia may be several weeks ahead of other manifestations of this complication. The more severe the gestosis, the more pronounced the decrease in the number of platelets. Thrombocytopenia can also occur in the absence of detectable changes in the coagulation system. Therefore, it is recommended that a platelet count be performed as part of a general examination in order to assess the condition of pregnant women and care for them in late pregnancy. The degree of thrombocytopenia corresponds to the degree of risk to the fetus, regardless of the severity of the patient’s clinical condition.
Vascular disorders characteristic of gestosis entail a deterioration in the delivery of oxygen and other metabolites to the tissues of the mother and fetus. There is a direct relationship between the degree of disruption of oxygen supply to tissues, the condition of the fetus and the severity of gestosis. There are pronounced dystrophic changes in the vascular endothelium (angiitis obliterans), edema and sclerosis of the villous stroma, as well as thrombosis of their vessels and intervillous space, ischemic nephritis, hemorrhages in the decidua and villous stroma, retroplacental hematoma, necrosis of individual villi, thickening of the trophoblast basement membrane. At the same time, the content of estrogen hormones and progesterone in the placenta decreases, which is probably due to its hypoxia (with severe placental ischemia, progesterone synthesis is blocked). Along with destructive lesions in the placenta during gestosis, compensatory and adaptive changes such as hypervascularization, plethora of villi, proliferation of the epithelium, and development of new villi are found. However, despite the increase in placental mass, these changes cannot fully prevent fetal hypoxia.
With gestosis, activation of lipid peroxidation (LPO) processes is observed. LPO products are highly toxic substances that damage membranes. It is known that the hypoxia of the mother and fetus that occurs during gestosis creates favorable conditions for the so-called oxygenase pathway of oxygen utilization. In addition, preeclampsia is accompanied by a decrease in the content of endogenous antioxidants such as vitamins, especially vitamin E. Therefore, it is advisable to include vitamins in the complex therapy of preeclampsia.
Diffusion insufficiency of the placenta is mainly associated with thickening of the syncyticapillary membrane (edema, inflammatory infiltration), which, of course, complicates gas exchange through the placenta and significantly impairs its non-gas exchange functions (barrier, filtration and purification, thermoregulatory, metabolic, endocrine, immune, etc.) or changes the physicochemical characteristics of the tissue that makes up the placental membrane (fibrosis, etc.). Perfusion and diffusion disorders are closely related to each other. But there is also placental perfusion-diffusion insufficiency with the syndrome of mosaic placental lesions, with thrombosis and ischemia in one area, with hemorrhage and edema in another.
An important aspect is the indications for delivery of pregnant women with varying degrees of severity of gestosis. The prolonged course of gestosis often turns out to be a more unfavorable factor for the mother and fetus than the severity of its clinical manifestations. With a long course of the disease, chronic hypoxia and chronic disturbances of peripheral circulation with the development of DIC syndrome are inevitable. The more severe the disease, the shorter its treatment should be, the sooner the question of delivery should be raised. Often, delivery is the main method of treating gestosis, and sometimes the only way to save the mother and fetus.
Delivery for patients with gestosis represents an additional burden, and therefore the patient should be prepared for it by using intensive therapy and carefully assessing its effectiveness. It must be remembered that delivery is one of the elements of complex therapy and is carried out much more carefully with appropriate preparation.
Immediate delivery must be ensured in case of eclampsia, severe complications of gestosis (eclamptic coma, acute renal-liver failure, cerebral hemorrhage, retinal detachment).
Urgent delivery is indicated in the absence of effect from intensive therapy for preeclampsia within 4-6 hours, severe nephropathy - 1-2 days, moderate nephropathy - 5-7 days, mild nephropathy - 12-14 days. An additional indication for delivery is signs of fetoplacental insufficiency (intrauterine hypoxia and fetal malnutrition). If delivery is necessary in pregnant women with nephropathy and the body is ready for childbirth (with the biological “maturity” of the cervix), the method of choice is labor induction after amniotomy. In the absence of labor within 2-3 hours after amniotomy, induction of labor should be started by intravenous drip administration of oxytocin, prostaglandin, or a combination thereof. With an “immature” cervix, it is more advisable to use prostaglandins to induce labor. If it is impossible to induce labor, the issue is resolved in favor of abdominal delivery.
In some patients with gestosis, surgical delivery by cesarean section is most appropriate. When deciding on a cesarean section in patients with severe forms of gestosis, the condition of the mother, fetus, and the effectiveness of intensive care should be carefully assessed. It is advisable to perform a caesarean section in women with severe nephropathy with an unprepared birth canal, in the absence of effect from intensive therapy within 24 hours. It is also indicated in the absence of effect from induction of labor in a patient with severe nephropathy, as well as in the event of abnormalities in labor; in a patient with eclampsia during labor in the absence of conditions for rapid delivery through the natural birth canal. Caesarean section is the method of choice for preeclampsia that is not amenable to intensive therapy for 3-5 hours, and when delivery through the birth canal is impossible.
During childbirth, the course of gestosis, as a rule, worsens, and non-severe nephropathy can acquire signs of severe nephropathy with a questionable prognosis and the possibility of severe complications. In this regard, the details of labor management in patients with gestosis deserve special attention.
During childbirth, it is necessary to carefully monitor the state of hemodynamics, respiration, renal function, liver and biochemical parameters, labor and the condition of the fetus.
In case of fatigue of the woman in labor and insufficient efficiency of labor, the use of therapeutic obstetric sleep is indicated.
Part of pathogenetic therapy is labor pain relief, which must be thorough and adequate. The choice of method of labor anesthesia depends on the severity of gestosis. For grade I nephropathy, the use of promedol in combination with antispasmodics and sedatives is sufficient. For grade II-III nephropathy, the method of choice is long-term epidural anesthesia.
The risk of eclampsia, hemorrhage in the brain, and retina of the eye especially increases in the second stage of labor due to the sharply increasing physical and emotional stress during pushing, leading to an increase in blood and intracranial pressure. For pain relief in the second stage of labor, inhalation of nitrous oxide with oxygen and pudendal anesthesia can be used.
Sedative, analgesic, ganglion-blocking and antispasmodic drugs used to treat gestosis simultaneously regulate the contractile activity of the uterus, since they lead to the normalization of disturbed neurodynamic processes in the higher parts of the central nervous system, which are one of the main causes of abnormalities in labor forces. At the same time, it must be remembered that excessive use of large amounts of sedatives and narcotics can cause a violation of autoregulation with a subsequent deterioration of such vital processes as hemodynamics, respiration, endocrine regulation, etc. Such a condition is difficult to control at the present stage. In order to reduce intrauterine and intra-abdominal pressure, early opening of the amniotic sac is indicated.
Antihypertensive therapy during childbirth is carried out by intravenous administration of magnesium sulfate, dibazol, and antispasmodic drugs. As labor progresses, antihypertensive therapy should be carried out more intensively, since blood pressure tends to increase.
If blood pressure rises and there is no effect from previously used antihypertensive drugs, it is advisable to use ganglion blockers under constant monitoring of blood pressure. The decrease in blood pressure under the influence of ganglion blockers is a consequence of an increase in the vascular bed. As a result of a decrease in peripheral resistance, blood is redistributed into small vessels of the systemic circulation.
The appearance of neurological symptoms (headache, nausea, vomiting), insensitivity of the woman in labor to drug therapy, signs of threatening fetal asphyxia are indications for the end of labor using obstetric forceps or extraction of the fetus by the pelvic end (in case of a dead fetus - a fetal-destroying operation) under anesthesia. In case of gestosis, vacuum extraction of the fetus is not used, since it does not meet the main goal - eliminating pushing - and can lead to injury to the fetus.
Currently, the indications for caesarean section for eclampsia have been expanded. These include - the lack of a quick effect from the use of complex intensive therapy in pregnant women and women in labor in the first stage of labor (within 1-2 hours), unprepared birth canals in pregnant women even if there is a sufficient effect from complex intensive therapy, complicated course of labor (violation contractile activity of the uterus, acute fetal hypoxia, etc.).
If the birth canal is prepared and the pregnancy is full-term, labor can be induced by amniotomy and the administration of oxytocin and prostaglandins. In the second period, switching off pushing using obstetric forceps is indicated. In the case of an immature fetus, the decision on the optimal time of delivery for a pregnant woman with eclampsia is made taking into account the degree of risk of prematurity and, on the other hand, the danger of continuing pregnancy for both the mother and the fetus.
In recent years, the tactics of preventive cesarean section in pregnant women with eclampsia have been revised due to the availability of methods for monitoring the functional state of vital organs and systems of the mother and fetus. It has been established that the contractile activity of the uterus after convulsive seizures in most women is not impaired, therefore, delivery through the vaginal birth canal with assisted ventilation and complex intensive care is possible.
Anticonvulsant and antihypertensive therapy with adequate analgesia should continue throughout labor. The patient must be in a lateral position to prevent the development of inferior vena cava syndrome. Epidural anesthesia should only be used when necessary and should only be performed by an experienced anesthesiologist.
In the third period and immediately after birth, blood pressure often increases due to an increase in peripheral resistance caused by cessation of uteroplacental blood flow and autotransfusion of blood in the uterus. To prevent complications, all patients with severe hypertension should be examined within the first 60 minutes after birth; blood pressure and heart rate should be measured every 15 minutes. If there is a tendency to arterial hypertension, the dose of antihypertensive drugs is increased and anticonvulsant therapy is continued for 24 hours after delivery.
From a practical point of view, it is not the severity of arterial hypertension that is dangerous, but the complications associated with sharp fluctuations in blood pressure, which are the cause of fetal death, developmental delay, hypoxia, premature birth, and premature abruption of a normally located placenta. Therefore, if persistent hypertension is detected, pregnant women are hospitalized and prescribed the following treatment:
- bed rest in the lateral position to avoid aortocaval hypotension and provocation of renal ischemia;
- sedatives that have a calming effect, suppress feelings of anxiety, internal tension, and reduce increased excitability;
- antihypertensive drugs used in combination with agents that improve intraplacental perfusion.
V. N. Kuzmin, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor MGMSU, Moscow