August 23, 2021
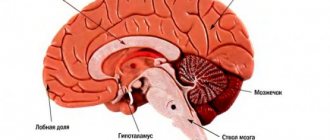
A stroke is a disease in which cerebral circulation is disrupted due to a disruption in the blood supply to the brain (or spinal) cord or a rupture of a vessel. Due to an “accident”, areas of tissue in the brain are damaged or killed. This disrupts the functioning of the human body - leads to impairment of motor and cognitive functions.
There are also unique symptoms that depend on the location of the lesion in the brain. If we dive into this in detail, then, for example, with a stroke in the region of the caudate nucleus, in addition to general symptoms, a person will clearly notice mental and emotional inertia, a decrease or absence of motor activity in conversation and normal daily activities. And with a stroke in the temporoparietal region, the patient will experience psychosis and, possibly, epileptic seizures.
But these details are seen and diagnosed by specialists; for an ordinary person who has experienced a stroke, it is enough to understand the difference between a stroke of the right hemisphere and the left, and what kind of rehabilitation is needed for each of them. We will talk about this in this article.
What are the features of a right hemisphere stroke?
The right hemisphere controls the left half of the body. The same is true on the opposite side - the left side of the brain controls the right side of the body. The exception is deep unconscious sensitivity - understanding the position of the body in space. This sensitivity persists even after a stroke, since there are certain features of the transmission of this type of sensitivity to the brain.
The system of such cross-work is relevant for the physical functioning of a person, for example, if the localization of a stroke is the right hemisphere of the brain, then the person will experience paralysis (in the form of severe weakness or, conversely, high tone of the muscles of the arms and legs) of the left half of the body.
It is also important that the right side of the brain is responsible for psychological state, emotions, imagination and spatial orientation. Due to disruption of the right hemisphere, a person’s spatial thinking and understanding of objects are impaired, creative abilities are lost, and it becomes difficult to control emotions and connect the imagination.
A right hemisphere stroke is so serious that its consequences can ruin a person's life, so it is important to begin rehabilitation as soon as possible to maximize recovery.
Differential diagnosis
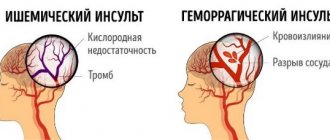
First of all, ischemic stroke should be distinguished from the hemorrhagic type of stroke. Neuroimaging techniques for studying the disease play a significant role in differential diagnosis. In some cases, it may be necessary to distinguish between ischemic stroke and acute hypertensive encephalopathy. Ischemic stroke should also be distinguished from toxic or metabolic types of encephalopathy, from brain tumors, abscesses, encephalitis and other brain lesions of an infectious nature.
What are the features of a left hemisphere stroke?
As we said above, the left hemisphere of the brain controls the right half of the human body. If the left hemisphere of the brain is damaged, paresis (paralysis) of the right limbs will be noted.
The left hemisphere also controls speech (for all right-handers and half of left-handers, and for the other half of left-handers, the center of speech is located in the right hemisphere of the brain), memory and cognitive functions, so during a stroke the patient may have problems with speech, he will lose memory, and mood swings, behavior will change - he will become slow and cautious.
Infarctions in the vertebrobasilar blood supply
The cause of infarctions that occur in the vertebrobasilar blood supply is the occlusion of the perforating branch of the artery, which is called the basilar. The main symptoms of such infarctions are lesions of the CN from the ipsilateral part. The process of occlusion of the vertebral type of artery, as well as branches, which are often called penetrating, that is, directed from the distal part, often contributes to the occurrence of lateral medullary syndrome, which in neurology is called Wallenberg syndrome.
Outcome of right hemisphere stroke
If a stroke occurs in the right hemisphere of the brain, the consequences will affect not only the physical condition of the person, but also cause psychological, emotional and behavioral difficulties.
What to expect after a stroke on the right side? The consequences after the “blow” will be as follows:
- Hemiplegia or hemiparesis
A person will feel paralyzed on the left side after a stroke. He has paralysis and severe weakness in the limbs of the affected side.
- Unilateral spatial neglect
The patient does not perceive one side of the body when performing everyday tasks, ignores part of the left space, and even from memory can only describe the left side of an object or room.
- Loss of body control
The patient loses the ability to move his left arm, leg or smile, and the mobility of the left corner of his mouth decreases.
- Denial syndrome (a person cannot critically assess his condition)
The patient may think that he is fully functioning, despite the fact that in reality this is not the case. A person with this syndrome may become severely injured while trying to perform an activity, or may refuse to undergo rehabilitation, thinking that he is healthy.
- The problem of orientation in space
The patient cannot determine his location in the room. He may also not understand the distance from his hand to an object; this manifests itself during meals, when moving from a bed to a chair, or when changing clothes.
- Emotional Indifference
Due to changes in the emotional state, the patient may not perceive himself in new realities and behave as if nothing had happened.
- There is no way to read the hidden meaning
A person who has had a stroke may have trouble hearing certain sounds and may not be able to grasp the intonation and tone of speech. A person after a stroke does not understand humor and sarcasm.
- Lack of concentration
The patient cannot fully concentrate on the action; it takes him a long time to “gather his thoughts.” The most difficult time for a person to concentrate is when he is given instructions, asked to fulfill a request, answer questions, or solve a simple problem.
If a stroke occurs on the right side, the consequences and how long the rehabilitation will last will depend on the degree of impairment of the person’s physical and psycho-emotional functions. It also depends on when the patient will begin rehabilitation.
The ideal time for rehabilitation is the first 3 months after a stroke, and the most intensive training should be done in the first month after discharge from the hospital.
Causes of development of cerebrovascular accidents
The cause of the development of right-sided ischemic stroke is the cessation of blood supply to the hemisphere. This condition occurs due to blocking of the lumen of the vessel by an atherosclerotic plaque, embolus or thrombus. The area of damage directly depends on the size of the lumen of the blood vessel.
Ischemic stroke of the right hemisphere is a studied disease. The main reasons for its development are:
- the age of the patient, the risk of developing the disease is higher in older people;
- gender - up to 80 years of age, the likelihood of ischemic stroke is higher in men, but after this age the opposite trend is observed;
- chronic stress, increased anxiety;
- burdened heredity, this reason is confirmed by numerous studies devoted to the issues of vascular accidents in people whose family members have suffered a stroke.
Doctors identify causes that can be corrected in order to prevent ischemic stroke:
- high blood pressure;
- irrational lifestyle and use of toxic substances, overeating;
- increased body weight;
- taking combined oral contraceptives;
- atherosclerotic vascular lesions.
Primary prevention of ischemic stroke is aimed at correcting lifestyle, increasing human activity, and reducing body weight.
Outcome of left hemisphere stroke
Along with the typical consequences of a stroke in the right hemisphere, there are also unique consequences after a “stroke” in the left hemisphere.
The consequences of a stroke in the left hemisphere of the brain are as follows:
- Hemiplegia or hemiparesis
A person will feel paralyzed on the right side after a stroke. He has paralysis and severe weakness in the limbs of the affected side.
- Aphasia - speech disorder
Because the speech center is located in the left hemisphere of the brain, a person who has had a left-sided stroke will have incoherent speech, may rearrange sounds in words, repeat words, and not understand the meaning of phrases. He may also not understand spoken speech or understand everything, but be unable to say anything.
- Apraxia of speech - difficulties in communication
Apraxia is a condition in which a person is unable to control muscles and perform normal activities. With apraxia of speech, the patient experiences difficulty moving the muscles around the mouth, which interferes with the formation of sounds and words. Although he may cognitively know what he wants to say, he cannot force his mouth to form words. Therefore, this is a motor problem, not a language problem.
- Dysphagia
The patient has impaired swallowing function
- Verbal memory impairment
The patient forgets names and cannot remember them, he is unable to retell the story he just heard, and he does not perceive and understand information well.
There are other consequences that occur after a stroke, but the disorders listed above are the most common for patients.
Recovery after a stroke of the left hemisphere takes a long time. Sometimes it is possible to return to the previous quality of life during the early rehabilitation period (the first 3 months after a stroke), and sometimes the consequences of a stroke remain with a person for the rest of his life.
The timing of the start of rehabilitation is of enormous importance; under no circumstances should rehabilitation be postponed. Recovery should begin right in the hospital. At the neurological departments of city hospitals there are exercise therapy instructors and massage therapists who are engaged in restoring the patient’s physical activity while he is in hospital.
And immediately after discharge from the hospital, the patient must be provided with home-based or outpatient (if he can move independently) rehabilitation, as well as equip the environment for the needs of the person faced with this terrible situation.
Neuroprotection
Speaking about the treatment of ischemic stroke, one should also mention a type of therapy such as neuroprotection. Its main focus is the use of special drugs that have neurotrophic and neuromodulatory functions. The most famous such drug today is Cerebrolysin (it belongs to the neurotrophic series of drugs). As is known, the central nervous system and spinal cord lack such an important property as storage. In other words, if you stop blood flow in these areas for 5 minutes, the neurons will begin to die. Therefore, the need to introduce neuroprotectors is mandatory. It should be carried out in the first minutes after the onset of an ischemic stroke.
Treatment of ischemic stroke will be successful with an integrated approach: basic therapy, rehabilitation, neuroprotection and reperfusion.
Treatment
A patient who has suffered a stroke requires emergency care and hospitalization. Numerous studies of this disease confirm that treatment carried out in the first three days is most effective, since the activity of nerve cells surrounding the lesion is high.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital begin treating the consequences of a stroke after a comprehensive examination of the patient. The treatment and rehabilitation programs developed by our specialists are based on the principle of the individuality of each patient, however, if the blood supply to the brain is impaired, the following measures are mandatory:
- monitoring of cardiac activity and blood pressure;
- prevention of early contractures, pneumonia;
- ensuring the required level of blood oxygen saturation and removing excess carbon dioxide;
- maintaining homeostasis - equilibrium of the internal environment;
- monitoring the condition of the intestines and bladder;
- swallowing control;
- skin care and prevention of bedsores.
Treatment of patients after pneumonia involves the use of drugs and non-drug methods. To take into account contraindications, cardiologists, neurosurgeons and resuscitators take part in drawing up the treatment program.
Drug therapy after a stroke involves the use of the following drugs:
- antihypertensive drugs for high blood pressure;
- osmotic diuretics and dexazone are used for cerebral edema, as well as to prevent increased intracranial pressure;
- anticoagulants, which include heparin, help control blood clotting;
- antiplatelet agents (trental, beta blockers, calcium antagonists) are used to identify signs of insufficient blood supply;
- drugs with a neuroprotective effect are used to restore neurons.
The Yusupov Hospital creates comfortable conditions for every patient. After a stroke, patients need professional care, which is provided by the staff of the neurology clinic:
- introducing fluids and nutrients into the body;
- turning the patient from one side to the other every 2 hours;
- performing cleansing enemas once every two days;
- wiping the skin every 8 hours with camphor alcohol;
- cleaning the nasopharynx and oropharynx using suction and then rinsing them.
Prevention
Knowing your risk factors for stroke, following the advice of highly trained professionals, an annual comprehensive body check-up and a healthy lifestyle are the best steps you can take to prevent stroke. If you have had a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), these steps may help prevent another stroke.
The help you receive in the clinic plays a significant role in stopping the acute period of a cerebral infarction.
The risk factors for possible complications after an attack will depend on how qualified and prompt assistance a team of neurologists, cardiologists, neurosurgeons, rehabilitation therapists and physiotherapists will provide you.
Many stroke prevention protocols are the same as cardiovascular disease prevention protocols. Basic recommendations for a healthy lifestyle include:
- Constant blood pressure monitoring. This is one of the most important things you can do to reduce your risk of stroke. If a patient has already had a stroke, lowering blood pressure may help prevent a subsequent TIA or stroke.
- Exercise, manage stress, maintain a healthy weight, and limit sodium, alcohol, and tobacco. In addition to recommending lifestyle changes, our doctor may prescribe medications to treat high blood pressure, as well as a vitamin and mineral supplement and fish oil.
- Reduce the amount of cholesterol and saturated fat in your diet. Eating less cholesterol and fat, especially saturated fat and trans fat, can reduce plaque in the arteries.
- Quitting tobacco use. Smoking increases the risk of stroke for smokers and nonsmokers exposed to secondhand smoke. Quitting tobacco use reduces the risk of stroke.
- Diabetes control.
- Maintaining a healthy weight. Excess weight contributes to the development of other risk factors for stroke, such as high blood pressure, heart disease and diabetes.
- A diet rich in fruits and vegetables. A diet containing five or more daily servings of fruits or vegetables may reduce the risk of stroke.
- Exercise can lower blood pressure. It will also help you lose weight, control diabetes and reduce stress.