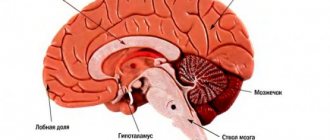
Stroke is a serious condition that is characterized by an acute disruption of the blood supply to parts of the brain and leads to morphological and functional damage to the central nervous system. Depending on the type of damage, hemorrhagic and ischemic types are distinguished. The brain stem includes the medulla oblongata, midbrain and pons. It is a connecting structure between the spinal cord and the brain and is of great importance, since the structures that ensure the vital functions of the body are concentrated in it. In case of damage to the brain stem, the statistics are disappointing: no more than 25% of such patients survive, and only 2% of them can count on a full recovery without severe complications.
Brainstem stroke is the least favorable type of cerebral stroke. The structures of the trunk are responsible for providing the following life support functions: breathing, blood circulation and cardiac activity, vital reflexes. Patients who have had this stroke have a poor prognosis, which is further worsened by hemorrhage. Mortality reaches 75%. Diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms and MRI data.
Among the clinical signs, disturbances of consciousness and bulbar syndrome prevail. The standard for diagnosis is MRI, which gives an idea of the topography and volume of the lesion. At the same time, rehabilitation and partial restoration of lost functions are possible with timely diagnosis and immediate initiation of therapy. The Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with a ventilator, necessary during the acute period of a stroke, and simulators for restoring motor skills.
The effectiveness of treatment most of all depends on the timing and quality of the treatment measures.
Causes of brainstem stroke
The following factors contribute to the development of the disease:
- Hypertonic disease. It is the most common cause of vascular damage to the brain stem. With high blood pressure, the walls of the arteries become brittle, which in turn leads to their rupture and hemorrhage.
- Atherosclerosis, thrombosis. When the lumen of a vessel is blocked by an atherosclerotic plaque or thrombus, the blood supply to the surrounding tissue is disrupted, which leads to the development of ischemia.
- Aneurysms, collagenosis, vascular malformations. Pathological changes in the structure of the vascular wall increase the risk of its rupture. This anomaly can cause a stroke at a young age.
- Diabetes mellitus, rheumatological diseases, heart pathologies, blood clotting disorders, etc. Features of the course of some diseases lead to the development of atherosclerosis, blood clots, macro- and microangiopathy.
- Lifestyle. Smoking, alcohol abuse, physical inactivity, poor diet, stress, and chronic fatigue increase the risk of vascular accidents.
- Age. Each subsequent 10 years increases the likelihood of developing ischemia or hemorrhage by 5-8 times.
- Genetic predisposition. Cohort studies have revealed that the risk of stroke increases by 30% if a person has a history of this disease in their family.
Make an appointment
Right side
If the right side is affected, the most dangerous consequence is damage to the brain stem, in which a person's chances of survival are close to zero. This department is responsible for the functioning of the heart and respiratory system.
Diagnosing a hemorrhagic stroke on the right is quite difficult, since the centers of orientation in space and sensitivity are located in this part. This lesion is determined by speech impairment in right-handed people (in left-handed people the speech center is located in the left hemisphere). In addition, there is a clear relationship: if the functionality of the right half of the brain is impaired, the left side suffers and vice versa.
How does a stem lesion differ from other types of stroke?
Depending on the location and extent of the pathological process, disruption of the blood supply to the trunk can have a variety of clinical manifestations.
The first signs of the disease may be severe pain in the back of the head, dizziness, and in 70-80% of cases loss of consciousness occurs. The clinical feature of vascular damage in this particular department is expressed in the appearance of alternating syndromes - damage to the cranial nerves on one side in combination with motor and sensory disorders on the opposite. The functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and thermoregulation are disrupted, and paralysis of the muscles of the face, pharynx, and muscles of the limbs develops. The development of “locked-in person” syndrome is possible. All symptoms are severe and, if timely medical care is not provided, lead to death in the first two days of the disease. An imbalance of blood circulation in this part of the brain brings serious consequences associated with a person’s life. Basic health parameters are affected. In particular, the following symptoms result from a stroke:
- dysfunction of the heart muscle. There is a change in the heartbeat rhythm, which causes bradycardia, arrhythmia or fibrillation. A distinctive feature of damage to the stem structure is a poor prognosis for rehabilitation;
- failure in the respiratory system. Shortness of breath and inability to take in air appear. In such a situation, the presence of an artificial respiration apparatus is of great importance, otherwise death is possible;
- speech and swallowing problems. The first is more harmless in nature due to the inability to pass saliva. The latter leads to profuse salivation, and some body positions allow fluid to enter the oxygen-receiving organs, thereby provoking the onset of pneumonia.
In addition to all of the above, there is a possibility of problems with vision and coordination, and a decrease in muscle activity.
If timely assistance is not provided, the outcome can be fatal. In ICD-10, brainstem stroke is designated by code G 46.3. According to WHO statistics, stroke occupies a leading position in the structure of morbidity and mortality. Every year, cerebrovascular accidents are detected in 3 people per 100 thousand population. Death at the onset of the disease occurs in 15–30% of cases. With a second episode of stroke, the mortality rate is 70%. According to statistics, the five-year survival rate after a stroke is 40–60%. The prognosis is influenced by the form of cerebrovascular accident. Brainstem stroke affects the brainstem. Doctors consider this type of disease to be the most dangerous.
To diagnose stroke, the Yusupov Hospital uses modern equipment. CT and MRI are considered the most informative ways to determine the localization of a pathological focus in the brain. Therapy includes methods of drug treatment and surgical intervention if indicated. The drugs used meet quality and safety standards. The duration of rehabilitation is determined by the severity of the condition.
Thanks to an individual approach to each patient, positive results are achieved in the shortest possible time.
Expert opinion
Author: Andrey Igorevich Volkov
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Brainstem stroke is the least favorable type of cerebral stroke. The structures of the trunk are responsible for providing the following life support functions: breathing, blood circulation and cardiac activity, vital reflexes. Patients who have had this stroke have a poor prognosis, which is further worsened by hemorrhage. Mortality reaches 75%.
Diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms and MRI data. Among the clinical signs, disturbances of consciousness and bulbar syndrome prevail. The standard for diagnosis is MRI, which gives an idea of the topography and volume of the lesion.
At the same time, rehabilitation and partial restoration of lost functions are possible with timely diagnosis and immediate initiation of therapy. Patients with brainstem stroke are less likely to lose interaction and communication skills, allowing them to participate in their own recovery.
The Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with a ventilator, necessary during the acute period of a stroke, and simulators for restoring motor skills. The effectiveness of treatment most of all depends on the timing and quality of the treatment measures.
What it is?
Hemorrhagic stroke is an acute hemorrhage in the brain due to rupture or increased permeability of blood vessels. This cerebrovascular accident differs from classic (ischemic) stroke, which is more common (70% of patients).
The nature of changes in blood vessels during an ischemic stroke is the blockage of their lumen by blood clots, resulting in gradual necrosis of brain cells, and in a hemorrhagic stroke there is a violation of the integrity of the vascular wall, as a result of which the brain tissue is saturated and compressed by the gushing blood.
Hemorrhagic cerebral stroke is a dangerous and insidious disease. It is characterized by:
- High mortality (60–70% of patients die within the first week after the onset of the disease).
- Suddenness (in 60–65% of patients, hemorrhage occurs without any previous symptoms).
- Profound disability of surviving patients - 70–80% of people are bedridden and cannot care for themselves, the remaining 20–30% have a less pronounced neurological deficit (the function of the limbs, walking, speech, vision, intelligence, etc. is impaired)
More than 80% of brain hemorrhages are associated with increased blood pressure (hypertension). By taking antihypertensive drugs (blood-lowering drugs), you can reduce the risk of stroke, the amount of hemorrhage and the severity of brain damage. If patients are admitted to a medical facility within the first 3 hours, this increases the chances of survival. Specialized rehabilitation centers help restore lost brain functions as much as possible after a stroke. Complete cure is rare, but possible.
Characteristic symptoms
The fact that the pathological process has affected the brainstem can be understood in 95% of cases from examination data.
Focal neurological manifestations can be observed in the first hours of the disease and during the recovery period. The clinical picture of brainstem damage appears suddenly and develops at lightning speed, compared to other parts. The prognosis for recovery is usually worse. Signs of brain stem pathology are directly related to its purpose. It belongs to the nervous system and is its central part. Responsible for perspiration, heart function, body temperature, swallowing and chewing. Therefore, brainstem strokes are extremely dangerous, even fatal. The defeat of the department manifests itself sharply. The state of health quickly deteriorates, temperature fluctuations begin, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, loss of consciousness, and coma often occurs.
In medicine, indicators for a disorder of this type are divided into two groups, depending on the form of the ailment, but there is a more general list suitable for all types:
- speech dysfunction;
- failure to regulate body temperature;
- poor coordination;
- muscle paralysis;
- change of voice after swallowing;
- change in pulmonary ventilation;
- inflammation of the respiratory tract;
- bradycardia or tachycardia;
- deterioration of vision of space;
- clouding of consciousness;
- poor sensitivity of the limbs;
- loss of consciousness;
- coma.
Hemorrhages occur suddenly, and the speed of assistance plays a big role. As soon as the severity of symptoms becomes obvious to others, you need to immediately call an ambulance. Most often, loss of consciousness or complete paralysis occurs. Particular attention should be paid to the quality of breathing.
Dizziness and loss of coordination
The harbinger is a feeling of pain in the skull or dizziness, accompanied by deterioration in coordination of movements and loss of balance.
This is often the earliest symptom of a pathological process in the trunk. Due to a persistent feeling of dizziness and pain in the back of the head, it is difficult for a person to stand on his feet and maintain balance. In such cases, the patient may suddenly fall or be forced to take a horizontal position. Coordination of movements suffers: the patient may not understand the position of body parts, an unsteady gait develops, hand movements are uneven and slow, and handwriting changes. All manifestations have a similar picture, but there are signs that are more noticeable than others or appear earlier. Unfortunately, a symptom such as dizziness will not allow you to accurately determine the cause of its occurrence, but will help you prepare for all possible outcomes. If the patient exhibits the described signal, place him in a lying or sitting position and wait for improvement. If none are noted, call a team of medical workers.
Make an appointment
Movement disorders
A brainstem stroke causes motor problems that become noticeable in the period following the stroke.
It occurs due to damage to the area of the brain responsible for cognitive activity. At the initial stage, programmatic decay manifests itself, which is expressed in changes in gait, frequent motor errors and focusing increased attention on arbitrary objects. Morphological damage in the nervous tissue of the trunk leads to impaired motor activity. This defect can progress and provoke structural disintegration of the statolocomotor system, which leads to disorganization of dynamic control of movement. At the final stage of development, the basic characteristics of the central generator of the step rhythm are affected. In this case, the patient experiences asymmetry in movements of both legs and arms, as well as freezing in place while walking. In other cases, while consciousness is preserved, a person is struck by paralysis of one half of the body (hemiparesis) or spreads to all limbs (tetraparesis). The prognosis for the restoration of motor functions is more favorable in the first 2-3 months of the disease.
Swallowing disorders - dysphagia
This is a severe manifestation of an acute disorder of cerebral blood supply.
It is observed in 65% of patients with brain stem stroke. When the nerve center is damaged, vital parameters, for example, the swallowing of saliva, are significantly affected. These tasks involve a significant number of muscles that can fail due to illness. Imperfect swallowing is called dysphagia. The danger of this complication is associated with a high risk of developing respiratory disorders and aspiration pneumonia. Most of these patients require tube feeding. The prognosis is usually unfavorable. In approximately 85% of cases, the ability to swallow is restored on its own within 2-3 weeks after the incident. Rarely does this defect remain for the rest of one's life. In this case, complications will follow:
- poor nutrition will lead to a deterioration in overall health;
- constant inflammation of the lungs due to unwanted microorganisms entering the respiratory tract;
- suffocation.
Timely treatment will allow you to get rid of all possible consequences and recover. To do this, it is recommended to contact a speech therapist, he will determine the severity and prescribe appropriate complex therapy.
Speech disorders - dysarthria
The cause of this disorder is a violation of the motor functions of the muscles of the tongue, facial muscles, and pharynx.
It is observed in approximately 30% of cases and manifests itself in changes in sound pronunciation, timbre, and intonation. Speech is distorted, losing intelligibility and articulation. In severe cases, speaking skills are completely lost. Dysfunction is accompanied by paralysis of the facial muscles located on the face and responsible for the ability to speak. This phenomenon is medically called dysarthria. The ability to communicate is lost due to disturbances in the brain stem. Associated symptoms are as follows:
- poor facial mobility;
- distorted, unintelligible speech;
- uneven speed of pronunciation;
- stops in the middle of a phrase;
- lack of emotional coloring.
To restore speech functions, the supervision of a speech therapist is required. Based on clinical information about the patient, he will select a personal plan of classes and exercises, after which he will begin rehabilitation. It is worth noting that the speed of recovery directly depends on the moment you contact a specialist.
Eye symptoms
If the part where the oculomotor center is located is damaged, the patient loses the ability to control the movements of one or both eyeballs.
This is reflected in the inability to fixate on an object, double vision, strabismus, outward deviation of the eyes and drooping eyelids. Sometimes fields of vision may disappear. Vision plays one of the main roles in the perception of surrounding information. It allows you to distinguish colors, objects and significantly affects the quality of life. Damage to critical areas leads to deterioration of visual perception. The described disadvantage can be determined by the following characteristics:
- black spots before the eyes;
- difficulty concentrating on one object;
- impossibility of recognition.
A problem with seeing the environment can haunt the patient throughout his life and cause disability, but it is not uncommon for him to be restored through medical practice.
Alternating syndrome - paralysis and distorted face
This symptom complex occurs as a result of dysfunction of the cranial nerves on the side of the lesion and conduction disorders on the opposite side of the body. Due to paralysis of the facial muscles, the patient on the affected side experiences sagging skin, drooping of the corner of the mouth and upper eyelid. In this case, the upper and lower limbs from the opposite area of the body remain immobilized. Paralysis or distortion of the face is one of the main symptoms of the disease. This has a significant impact on the ability to speak, causing dysarthria or dysphagia. To confirm, ask the victim to smile. If asymmetry is observed, then specialists should be called immediately.
Disorders of breathing, heartbeat and thermoregulation
Damage to the respiratory, vasomotor centers and thermoregulation center in a large percentage of cases ends in death.
Impaired respiratory function during a trunk stroke manifests itself in the form of severe shortness of breath or complete loss of the ability to breathe independently. Such patients are completely dependent on a ventilator. In other cases, when the center is not completely affected, the period of wakefulness may be accompanied by spontaneous breathing, but during sleep periods of apnea are observed. A change in the functioning of the cardiovascular system is expressed in an increase in heart rate, which is then replaced by bradycardia and a drop in blood pressure. Arrhythmias and fibrillations may develop. Taking traditional antiarrhythmic drugs in such cases is ineffective. Unstable thermoregulation is observed in rarer cases and is characteristic of the most severe degree of the disease. It manifests itself in the form of a sharp and persistent increase in body temperature to 39ᵒC and above, and cannot be corrected with medication.
In other cases, critically low temperatures may occur. Both options have a disappointing prognosis for recovery.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke are varied and are divided into two large groups: general cerebral and focal. Also, the symptoms strongly depend on the location of the hemorrhage, its size, the somatic condition of the patient and many other factors.
General cerebral symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke include the following:
- Impaired consciousness (stunning, stupor, coma). The larger the focus, the lower the level of consciousness. However, with damage to the brain stem, even a small focus of hemorrhage leads to severe depression of consciousness.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Headache.
- General weakness.
- Breathing disorders.
- Hemodynamic disorders.
Predominantly focal symptoms include the following:
- Paresis or plegia in the limbs, hemiparesis is more common.
- Paresis of facial muscles.
- Speech disorders develop mainly with damage to the left temporal lobe.
- Visual impairment (including the development of anisocoria).
- Hearing impairment.
A stroke should be suspected if the patient has any type of speech impairment, weakness in the arm and leg on one side, the development of epileptic seizures without provoking factors (for example, such factors include alcohol consumption), impaired consciousness up to coma. In any suspicious cases, it is better to play it safe and call an ambulance. Behavior and assessment of the situation when a stroke is suspected should be considered in a separate article.
Diagnosis of brainstem stroke
Diagnosis of the disease begins with examination data and collection of the patient’s medical history. Based on the characteristic symptoms, a brain stem stroke can be suspected in the first minutes. Such patients are hospitalized on an emergency basis. In a hospital setting, a number of procedures are performed to confirm the diagnosis. The following have the greatest diagnostic capabilities:
- Computed tomography is an x-ray method for studying the layer-by-layer structure of organs and tissues. With a high probability it helps to recognize foci of hemorrhage in the brain.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is an effective method for detecting pathological lesions using nuclear magnetic resonance. Allows you to assess the degree and volume of tissue damage.
- Doppler ultrasound. Using ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and brain, pathological changes (stenosis, occlusion) can be detected in the carotid and vertebral arteries, as well as in their branches.
- Electroencephalography. It is also a non-invasive diagnostic method. By recording bioelectrical activity, it reflects qualitative and quantitative changes in the function of the cortex and deep structures of the brain.
In addition, it is possible to conduct laboratory tests of the composition of blood and cerebrospinal fluid. According to indications, a neurologist is able to draw up an almost complete clinical picture, which reflects the depth and localization of the damage that has occurred. But to confirm the diagnosis, additional studies are required using CT or MRI, which will show:
- type of disorder;
- the extent of the pathology;
- presence of hematoma or ischemia.
The more fully and accurately the factors of change are identified, the easier it is to draw up a rehabilitation plan.
Consequences
If patients can be saved, they experience neurological deficits—symptoms caused by damage to the area of the brain where the hemorrhage occurred.
These may be consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke:
- paresis and paralysis - impaired movement of the limbs on one half of the body, since they are constantly in a half-bent position and it is impossible to straighten them;
- speech impairment and its complete absence;
- mental disorders and irritability;
- constant headaches;
- movement coordination disorders;
- inability to walk or even sit independently;
- visual impairment up to complete blindness;
- facial distortion;
- vegetative state - the absence of any signs of brain activity (consciousness, memory, speech, movements) with preserved breathing and heartbeat.
Symptoms of the disease and their duration depend on the location of the hemorrhage and its volume. The first 3 days are the most dangerous, since during this time severe disorders occur in the brain. Most deaths (80–90%) occur during this period. The remaining 10–20% of patients die within one to two weeks. Patients who survive recover gradually from a few weeks to 9–10 months.
Providing emergency first aid
A stroke occurs suddenly and requires immediate outside help.
The first step is to call a team of medical workers, and while it is on its way, take care of the victim, providing him with support. The process is often accompanied by vomiting, and the accumulated masses interfere with breathing. If problems with perspiration are detected, it is necessary to clear the pathways through which oxygen enters the lungs. To do this, the person should be laid on his side and with a finger wrapped in gauze or a piece of clothing, clean the oral cavity. If you have instruments with you that can measure pressure or blood sugar levels, it is recommended to record the values of these parameters and report them to the arriving doctors.
An important indicator is the moment of onset of symptoms. It would not be amiss to note the time of its occurrence. The use of drugs aimed at lowering blood pressure is contraindicated. Increased pressure after a circulatory disturbance in the brain stem is a normal reaction of the body necessary to adapt to an emergency situation. Eating food or water is also contraindicated; there is a possibility of a negative effect that will aggravate the matter. If a person loses consciousness, it is allowed to be moved, despite existing myths that state the opposite.
The place should be arranged in such a way that the upper body and head are raised, and clothes are unbuttoned to facilitate the flow of oxygen into the lungs. If the incident occurred in a confined space, it is advisable to open the windows and provide fresh air and peace.
If the victim experiences convulsive muscle contractions and foamy discharge from the mouth, it is necessary to place a pillow or rolled up clothing under the head, and also monitor the position of the arms and legs so that the patient does not injure himself and others. Holding the limbs while contracting is strictly prohibited; this will lead to worsening of the situation. The person providing assistance must be prepared for repeated attacks and remove foam from the mouth in a timely manner.
You cannot take measures to restore consciousness, much less use ammonia for this. Its effects can cause lung failure and ultimately death. During the period of pre-medical measures, it is necessary to monitor the heartbeat and pulse. If cardiac arrest is determined, immediate resuscitation is required through chest compressions and mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose artificial respiration.
Memo on providing first aid to the elderly for ischemic stroke
At the first manifestation of symptoms of an ischemic stroke, it is necessary to call a team of doctors to provide emergency medical care. The effectiveness of further treatment directly depends on the timeliness of these actions. While the ambulance is traveling, you should prepare the elderly patient and take certain actions:
- The victim should be laid so that the shoulders and head are located above the body, this will help reduce blood pressure on the vessels of the brain. You cannot move or shift an elderly person - this can only make him worse.
- You should not give the patient anything to eat or drink while waiting for doctors because of the likelihood that the usual swallowing function will be disrupted; the person will choke or choke.
- It is strictly forbidden to give any medications before the ambulance arrives; you may not alleviate, but, on the contrary, aggravate the condition of an elderly relative.
- The oral cavity must be cleared of any secretions and objects (saliva, blood, mucus, food).
- Provide all conditions for free breathing: increase access to fresh air, remove tight clothing.
- If a person has lost consciousness but is breathing on his own, he must be turned on his side, his head resting on his arm and slightly tilted forward, and his leg bent at the knee so that it does not allow him to accidentally roll over.
- If there is no breathing, the elderly person is placed on his back and given artificial ventilation. If there is no pulse, cardiac massage is added to this procedure. For every two breaths there should be 30 heartbeats (2/30). These measures should be carried out only if you have the necessary skills and abilities until the victim begins to breathe on his own or until the ambulance arrives.
The development of ischemic stroke in older people occurs very quickly, which is why it is so important to provide qualified medical care literally in the first minutes and hours of the disease. Treatment must necessarily take place in the intensive care unit, where all efforts will be devoted to carrying out the necessary medical procedures. The faster this happens, the more favorable the prognosis and outcome of the disease. The optimal time for first aid and treatment is 2–4 hours from the onset of an attack. If you manage to carry out the necessary therapy in this short period of time, you may be able to avoid many complications.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment is an integral part of patient resuscitation, prevention and recovery. The therapy provided should be comprehensive and aimed at preserving the vital functions of the body. The main directions for this: Correction of disorders of the respiratory system. If necessary, connection to a ventilator. In the acute period, infusion therapy with plasma preparations and rheopolyglucin is carried out.
Normalization of blood pressure indicators. At high blood pressure levels, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed, making sure that changes to normal values occur smoothly and gradually. The main drugs used are from the group of ganglion blockers and ACE inhibitors. In case of severe hypotension, glucocorticosteroids and dopaminomimetics are administered. Reducing body temperature is carried out using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Reducing intracranial pressure and cerebral edema - with the help of diuretics. In some cases, a hypertonic saline solution is administered.
Restoring blood supply to the affected areas and preventing thrombosis. Here they use drugs from the group of antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants.
Improving the nutrition of brain tissue and intracellular metabolism is carried out with the help of nootropics, antioxidants, and cytoprotectors.
The treatment of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke has its own characteristics. In case of hemorrhage, the use of anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents is contraindicated. The main treatment is aimed at stopping the bleeding and removing the hematoma. Treatment with medications is carried out in the intensive care unit. The following substances are prescribed:
- diuretics aimed at preventing edema;
- sedatives;
- oxygen therapy - if the patient is able to breathe on his own, catheters are installed, otherwise a special support device is connected;
- muscle relaxants to prevent seizures;
- blood thinners that increase blood flow;
- antihypertensive drugs to prevent recurrent vascular ruptures.
At first, all drug therapy is aimed at eliminating repeated attacks and severe consequences.
Doctors keep an eye on the patient until the body’s functioning is completely normalized, and when the patient’s well-being improves, they are transferred to a ward for further recovery. Make an appointment
Types of ischemic stroke in older people
Acute ischemic cerebrovascular accident has several stages. Each develops in its own way and has its own characteristics.
1. Acute stroke.
It is considered the initial period of development of ischemic stroke and lasts no more than 21 days. Pathogenetic changes in brain tissue occur especially quickly during the first 6 hours of illness. In 5–7 minutes, a nucleus is formed from damaged cells; after an hour and a half, the penumbra around it increases by 50%, and after 6 hours – by 80%.
If the necessary medical care is provided in the first 6 hours, the ischemic cerebral infarction will pass, leaving almost no serious negative consequences for older people. Since as a result of pathogenetic processes, brain cells begin to die from the first minutes, if treatment does not start on time, apoptosis will spread exponentially. And after 3–5 days, necrosis of the damaged cells will occur.
Intensive therapy during the first 6 hours includes:
- improving blood supply to brain tissue;
- protecting cells from destruction;
- improving viscosity, coagulability and microcirculation of blood in the smallest vessels of the brain;
- prevention of cerebral edema.
In addition to acute, there are other, more complex types of brain disorders.
2. Major stroke.
Large vessels supplying blood to the brain are susceptible to extensive ischemic stroke. A condition in which many small areas of brain tissue or, conversely, a large fragment is affected, is also considered a major stroke. This is a serious disease with obvious symptoms of brain damage in older people:
- depression of consciousness;
- cerebral edema;
- hemiparesis or hemiplegia on the opposite side of the lesion;
- paresis of gaze towards paralyzed limbs;
- disorder of consciousness;
- autonomic disorders;
- trophic disorders.
The manifestation of certain symptoms is affected by the location of the damaged hemisphere - on the right or on the left. A common sign of ischemic stroke in older people is deep fainting, during which you should carefully look at the patient’s pupils, shining a light directly into his eyes. If the pupils do not react to light and do not dilate, then perhaps a massive stroke is beginning. An elderly patient can only be saved by urgent hospitalization in the intensive care unit, where he will be connected to a life support system.
3. Lacunar stroke.
The most common type of cerebral vascular pathology is lacunar. But it can only be determined in a hospital, albeit in the very early stages. A lacunar stroke damages the deep layers of brain tissue, resulting in the appearance of cavities (lacunae) with a diameter of 1 to 15 mm. Small lacunae, merging, form larger ones, and blood or plasma and fibrin can already accumulate in them.
The development of lacunar ischemic stroke does not impair vision, speech, consciousness, or other functions of the cerebral cortex, since all pathological processes occur deeper. There are no symptoms of brain stem damage. Such differences distinguish this type of stroke from other types of disease.
Recommended articles on this topic:
- How to prevent stroke using folk and medical remedies
- Brain medications for older people: top 10 best drugs
- Caring for older people after a stroke: features, rules and recommendations
Sudden jumps in blood pressure can trigger the occurrence of lacunar ischemic cerebral infarction in older people. Therefore, at risk are those patients who have the following pathologies:
- hyaline dystrophy AG;
- atherosclerosis;
- infectious inflammation of arterioles;
- diabetes;
- vasculitis.
The consequences of lacunar ischemic stroke in older people are very sad: memory loss, impaired spatial orientation, deep depression, and subsequently dementia.
Surgical intervention
Any surgical intervention on the brain is a high risk and can often lead to serious complications, including the death of the patient. Therefore, surgical treatment is carried out in the presence of strict indications:
- Swelling or compression by hematoma of the medulla oblongata, which leads to the progression of neurological symptoms. In this case, to save the patient’s life, craniotomy is performed using a certain technique.
- Pathological changes in cerebral vessels (aneurysms, malformations), accompanied by bleeding. For treatment, special clips are used, which are surgically applied to the neck of the aneurysm.
- For ischemic stroke, when conservative therapy is ineffective, carotid endarterectomy followed by stenting can be performed. The operation is performed endovascularly (without incisions).
In the postoperative period, the patient's condition remains unstable for a long time. It can often be complicated by swelling of the brain tissue, which lasts up to two weeks. In the future, therapeutic measures are carried out aimed at restoring lost functions and preventing a recurrent stroke.
Modern surgical treatment for hemorrhagic stroke
Only in specialized centers is it possible to conduct a thorough diagnosis and adequate surgical or therapeutic treatment of hemorrhagic acute stroke. However, most often a free ambulance will take the victim to the nearest city hospital, where first aid will be provided, limited by the capabilities of the institution. And surgical treatment of stroke, unfortunately, can not be performed in all hospitals.
Therefore, relatives of patients are increasingly turning to specialized advisory services that can provide:
- safe transportation;
- rapid hospitalization;
- expert monitoring of victims in intensive care units and departments of medical institutions.
Only in highly qualified centers will they conduct the necessary research, assess all the risks, and then choose the necessary treatment tactics.
Another important point that affects the patient’s further capacity is rehabilitation and care after surgical treatment of hemorrhagic stroke. The success of postoperative therapy largely depends on the experience of specialists and the availability of modern equipment.
Prognosis after brainstem stroke
The type of stroke, the extent of the pathological process, and the timeliness of medical care are of great importance for the prognosis.
The ischemic type is more favorable - mortality is about 25%. In case of hemorrhage, according to statistics, every second patient dies within a month. The main reasons: cerebral edema with entrapment in the foramen magnum, death of stem structures. Even if life is preserved, the majority of such patients remain deeply disabled. According to research, a negative outcome is more often observed in cases of respiratory failure, persistent bradycardia, changes in thermoregulation, and loss of speech. An uncertain prognosis is given if the patient has dysphagia, movement disorders, or impaired eye movement functions. In any case, treatment of patients with brainstem stroke requires competently selected therapy and the use of all possible rehabilitation methods.
The prognosis of brainstem stroke and further condition is determined by the degree of manifestation of symptoms. Doctors see the most favorable recovery in patients with less pronounced signs of the disease, but, of course, there are always exceptions. The most skeptical view of complete recovery is captured by the following observations:
- problems with speech and breathing;
- dysregulation of blood pressure and body temperature.
A more positive prognosis can be heard when:
- weakness of swallowing;
- complete or incomplete paralysis of the limbs;
- problems with eye rotation;
- frequent dizziness.
Important factors when forming a prognosis are the speed of referral to specialists and the age of the patient. The older a person is, the more difficult the recovery process is.
Mechanism of brainstem stroke
Brainstem stroke may result from hemorrhage or ischemic injury. In the first case, a hemorrhagic form of acute cerebral circulation disorder is diagnosed. Most often, the pathological focus is localized in the bridge, but another location may be observed. Massive hemorrhage often ends with a breakthrough into the cavity of the fourth ventricle. Multiple hemorrhagic foci in the brain tissue significantly complicate diagnosis, blurring the clinical picture.
Disturbance in the flow of arterial blood to the brain structures causes the ischemic form of the disease. In this case, nerve cells begin to die from lack of oxygen and nutrients. The resulting reactive inflammatory process is accompanied by swelling of brain tissue, difficulty in venous outflow and pinching of the medulla oblongata in the foramen magnum. Without adequate therapy, the prognosis is extremely unfavorable, and the disease quickly ends in death.
What are the prognosis for ischemic cerebral stroke in elderly people?
Statistics on the manifestations of ischemic stroke in older people are disappointing. Only 10% of patients fully recover after a cerebral infarction, another 25%, although they receive visible signs of the illness, generally return to normal life. About 20% of people die in the first hours of the disease or later in the hospital, without leaving a coma. Another 40–50% remain disabled, more or less able to care for themselves. With age, the likelihood of a disastrous outcome increases.
A favorable prognosis depends on the speed of providing the patient with qualified medical care. Therefore, at the first signs of an ischemic stroke or even at the slightest suspicion of the onset of the disease, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance. It is better that the panic turns out to be false, and you will have to pay for the arrival of doctors, than to lose precious hours and minutes that could save a person’s life and give a chance for recovery. The likelihood of severe consequences of an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke is too high to take risks.
We recommend
“Care for the elderly after a stroke: features, rules and recommendations” More
Positive results in rehabilitation will be achieved by those elderly people who have the desire and opportunity to engage in physical therapy and speech restoration. The most persistent and purposeful patients are completely rehabilitated; nothing reminds them of the disease they suffered. All you need to do is conscientiously perform all the exercises prescribed by the rehabilitation doctor. Folk remedies and healers are unlikely to help.
Everything mentioned above was taken from English-language sources (and is typical for Western reality). In the countries of the post-Soviet space, the forecast is not so optimistic; the following factors have a negative impact: unsatisfactory work of the ambulance service, poorly equipped intensive care wards, and the lack of qualified doctors to treat brain disorders. In the West, special programs are funded for long-term rehabilitation of patients after a stroke. In Russian-speaking countries, there is currently virtually no government support for the families of victims; people, as a rule, are left alone with the problem, but perhaps the situation will soon change for the better.
After blockage of the cerebral vessels, the condition of the patient admitted to the hospital cannot be assessed. During the first few days, doctors try not to make any predictions, for fear of giving false hope to relatives. The situation becomes clearer later. Even with partial paralysis, when mobility is lost on one side of the body, older people can hope to restore lost functions with the help of physical therapy. Success is achieved only by that part of patients who diligently and purposefully perform the exercises. Practice shows that it is easier to restore the function of a paralyzed leg than an arm. But if some physical limitations cannot be removed within a year after the stroke, most likely they will remain for the rest of your life.
Consequences of ischemic stroke in older people
A disease associated with brain damage necessarily affects the condition of older people. It’s good that the patient survived at all. But his future fate may develop differently. Ischemic stroke left some disabled for life, others were luckier: there were minor changes in the body that did not reduce the quality of life. You can adapt to them or try to recover.
We recommend
“Recovery of elderly people after a stroke: tips and practical recommendations” Read more
Possible consequences of ischemic stroke in elderly people:
- Impaired swallowing function - the patient cannot easily swallow either liquid or solid food, he chokes, this can lead to aspiration pneumonia, and then to death.
- Mental disorders - often those who have suffered an ischemic stroke develop deep depression. Even small changes in the quality of life cause a serious blow to the psyche. Especially if an elderly person has partially lost some everyday skills and needs outside help to do what was previously done without much difficulty. The fear of remaining disabled and becoming a burden for loved ones becomes the cause of a depressed state. A person’s mood changes for no reason, he cannot compose himself, he is timid, and sometimes aggressive.
- Impaired motor function in older people – arms and legs may not immediately regain their former strength and dexterity. Weakness and uncertainty in the legs when walking will force you to pick up a cane; unruly hands will not allow you to perform usual actions - dressing yourself, holding a spoon, etc.
- Loss of sensation in the limbs and face . If muscle strength in the arms and legs is restored quite quickly after an ischemic stroke, then sensitivity does not return to normal for a long time. This is due to the different structure of the nerve fibers (through which impulses travel) responsible for movement and sensitivity.
- Speech impairment may not remain in all older people who have had an ischemic stroke. This complication makes it difficult to communicate with family; a person cannot express his desires or tell his family anything, sometimes uttering a set of incoherent sounds. With right-sided brain damage as a result of ischemic stroke, such complications rarely occur.
- Impaired coordination in space - an elderly person cannot walk confidently, he staggers without assistance, becomes dizzy, and falls during sudden movements and turns.
- Epilepsy – up to 10% of older people after an ischemic stroke are susceptible to unexpected seizures of epilepsy.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs - the mechanisms of bowel and bladder emptying are disrupted; after an ischemic stroke, an elderly person cannot always independently control these processes. That is why understanding and careful care from relatives or a caregiver is so important.
- The consequences can manifest themselves in the form of cognitive impairment - memory lapses occur, older people forget familiar things: the names of relatives, telephone numbers, home address, even their name. Their behavior is sometimes no different from the reaction of a small child; patients inadequately assess the current situation and confuse the time and place in which they are located.
We recommend
“Rehabilitation of the elderly: get a taste for life again” More details It is possible
to change the patient’s condition or influence the consequences of an ischemic stroke of the brain, to restore the impaired functions and capabilities of an elderly person only in the first year after the incident. Long-term rehabilitation over several years is not effective and simply does not make sense.