Application of Mildronate
Mildronate is recommended for the treatment of the following diseases in adults:
- Coronary artery disease – damage to the myocardium of the heart;
- Heart failure - impaired myocardial functionality;
- Overtraining syndrome in sports – the appearance of persistent pain;
- Increased mental stress, decreased concentration and memory;
- Hangover syndrome – the appearance of symptoms of alcohol withdrawal;
- Dysfunction of cerebral circulation;
- Decreased performance, chronic fatigue syndrome;
- Hemophthalmos - penetration of blood or blood clots into the vitreous body of the eye;
- Retinopathy is damage to the retina of the eye.
As a result of the action of Mildronate, blood circulation improves and myocardial contractility is normalized, therefore the drug is used in the complex therapy of cardiovascular diseases. In sports, Mildronate is taken by athletes to increase physical strength and improve metabolism.
Experience of using Mildronate in cerebrovascular diseases
N.V. PIZOVA
, MD, PhD, Professor,
Department of Neurology and Medical Genetics with a Course of Neurosurgery, Yaroslavl State Medical Academy In recent years, the results of various clinical studies of drugs that have shown their effectiveness in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases have been published.
The article discusses the results of using the drug Mildronate (meldonium) in the treatment of ischemic brain lesions, provides research data confirming the cytoprotective effect of the drug on a number of pathogenetic factors that determine the death of brain cells during ischemia. Cerebrovascular disease refers to various lesions of the nervous system against the background of atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension. Less commonly, cerebrovascular disorders occur against the background of rheumatism, polyarteritis nodosa, systemic lupus erythematosus, and giant cell arteritis. Ischemic stroke (IS) complicates blood diseases (polycythemia vera, sickle cell anemia, leukemia), congenital heart defects in the stage of decompensation, myocardial infarction, neck vascular injuries, etc. The social significance of cerebrovascular disease is increasing due to the increase in risk factors among the population development of cardiovascular pathology: old age, sedentary and sedentary lifestyle, high-calorie diet, obesity, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, dyslipoproteinemia. The widespread use of smoking and oral contraceptives has virtually equalized the risks of developing cerebrovascular accidents in men and women. In the last decade of the 20th century there was a significant increase in the number of patients with vascular diseases of the brain. In economically developed countries, mortality from such diseases ranks 2nd-3rd in the structure of overall mortality. Over the past 40 years, in countries with high per capita income, the incidence of stroke has increased by 42%, while in countries with middle and low income it has increased by more than 100% [1]. As a result of studies conducted in Russia, it was found that the incidence of stroke is one of the highest among all types of cardiovascular diseases, and the mortality rate from it consistently ranks second in the structure of overall mortality of the population, second only to cardiac pathology. In some regions of Russia, stroke is more common than myocardial infarction. On average, 60% of stroke survivors become disabled, and most of them are dependent on others or require outside care. By the end of the first year after a stroke in Russia, every second patient dies, and after 7 years, almost 80% of patients die [1].
The basis of IS therapy is two directions: reperfusion and neuronal protection. Reperfusion is associated with the restoration of blood flow in the ischemic area. Neuronal protection is implemented at the cellular level and is aimed at preventing the death of weakly or almost no longer functioning, but still viable neurons located around the heart attack (the “ischemic penumbra” zone). The main methods of reperfusion are thrombolysis. The main methods of neuroprotection include restoration and maintenance of homeostasis; drug protection of the brain and non-drug methods such as hyperbaric oxygenation, cerebral hypothermia. Antithrombotic drugs, including anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents, are mandatory for all patients who have undergone IS. Neuroprotective therapy is aimed at interrupting or slowing down the sequence of damaging biochemical and molecular processes that can cause irreversible ischemic brain damage.
In recent years, the results of various clinical studies of drugs that have shown their effectiveness in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases have been published. One of these drugs is Mildronate (3-(2,2,2-trimethylhydrazinium) propionate dihydrate; meldonium) - a drug that corrects metabolism and energy supply to tissues, belongs to the group of cytoprotectors/antihypoxants, provides protection and energy supply to various cells of the body in conditions of ischemia and increased load. The largest number of studies and publications are devoted to the effects and results of Mildronate treatment of ischemic brain lesions, which explain the complex effect of Mildronate on a number of pathogenetic factors that determine the death of brain cells during ischemia. We can distinguish two main ways of Mildronate’s influence on the nervous system, which are realized by several parallel mechanisms ( Table 1
).
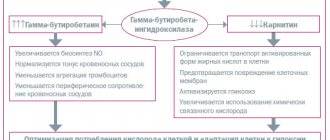
| Table 1. Mechanism of action of Mildronate |
| Improving cerebral circulation and eliminating the influence of risk factors 1) positive effect on the functional ability of the myocardium; 2) correction of nitric oxide biosynthesis processes: has a positive effect on smooth muscle cells of blood vessels - cholinomimetic effects and systemic vascular reactions by stimulating the formation of γ-butyrobetaine esters and activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase; 3) participation in the regulation of glucose metabolism: influences diabetes as a risk factor for cerebrovascular accidents and other diseases of the nervous system; 4) participation in lipid metabolism and inhibition of atherosclerosis processes; 5) effect on the aggregation of formed elements and rheological properties of blood. Protecting neurons and promoting neuromodulation 1) influence on neuronal metabolism at the mitochondrial level, ATP utilization, lipid oxidation and glucose uptake; 2) neuroprotective effect by suppressing the formation of free radicals as products of lipid peroxidation, during ischemia, endogenous neurotoxins and xenobiotics; 3) normalization of the expression of proteins involved in the processes of neurodegeneration, inflammation and apoptosis; 4) potentiation of the action of insulin as a hormonal neuroprotector; 5) implementation of anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory mechanisms, especially in the case of brain reperfusion; 6) a hypothetical possible neurotransmissive cholinergic effect in the brain through the formation of γ-butyrobetaine esters that activate acetylcholine receptors. |
The above mechanisms underlie the neuroprotective or protective, as well as neuromodulatory or restorative effects of Mildronate in various pathological conditions in both the central and peripheral nervous systems: in the treatment of acute and chronic cerebrovascular accidents, brain injuries, improvement of cognitive and motor functions in patients who have suffered a stroke, brain injury and chronic cerebrovascular diseases. The positive effect of Mildronate on the activity of the cardiovascular system through a carnitine-dependent mechanism cannot but have a beneficial effect of the drug on cerebral circulation, as the activity of the heart increases, the need of the heart and skeletal muscle for oxygen decreases. At the same time, the nitric oxide-dependent mechanisms of action of the drug are realized and have a positive effect on the functional ability of smooth muscle cells in the walls of blood vessels, including in the brain [2].
One of the first neurological diseases, taking into account the early proven positive effect of Mildronate on the cardiovascular system, were cerebral circulatory disorders. It was experimentally shown that intravenous administration of Mildronate to rabbits with local brain damage at a dose of 25 mg/kg for 14 days caused a more rapid restoration of cerebral blood flow and vascular reactivity, which was accompanied by an accelerated rate of improvement in brain activity [3]. During an experiment on rabbits, using electrodes implanted into the cerebral cortex, thalamus and hypothalamus, the effect of Mildronate on hemodynamics and water-electrolyte balance in these brain structures was studied using a model of cerebrovascular disorders. Prophylactic administration of Mildronate (10 mg/kg, orally) significantly prevented the development of hemodynamic disorders and optimized oxygen balance. At the same time, the severity of cerebral edema also decreased, which the authors of the study explained by improving the rheological properties of blood, microcirculation and known metabolic effects on cell membranes. These effects of Mildronate were enhanced by its simultaneous use with Riboxin [4].
Another experimental work was devoted to measuring cerebral blood flow and oxygen saturation (pO2) in rats with short-term ligation of the common carotid artery (5 min) using laser Doppler flowmeter methods in the frontal cortex and an oxygenation monitor through the lateral ventricle and observation during the reperfusion period (30 min ). The authors showed that after pre-administration (10 minutes before artery ligation) Mildronate at a dose of 200 mg/kg, a protective effect of the drug on reducing blood supply and oxygen supply to the brain was noted compared to the control group receiving saline solution [5].
The first studies of the effect of Mildronate on cerebral circulation in IS were carried out by Vinnichuk S.M. [6], who revealed an improvement in cerebral hemodynamics and restoration of neurological functions after intravenous administration of Mildronate (5 ml of 10% solution) for 10 days followed by oral administration of 250 mg daily for 2-3 weeks. Other authors [7] observed positive effects even with a single administration of the drug (25 mg/kg, intramuscularly) in the form of improvement in cerebrovascular reactivity around the site of ischemic brain damage.
Russian scientists conducted an extensive study of the clinical effectiveness and antioxidant activity of Mildronate [8]. The study included 60 patients aged 42 to 75 years with IS in the carotid system during the first 48 hours from the onset of neurological symptoms. The main vascular disease in the examined patients was a combination of atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension. This study was conducted using a comparative method. The active treatment group (Mildronate) consisted of 30 patients, the control group (reopolyglucin) - 30 patients. All patients received basic antiplatelet, antihypertensive, cardiac and antidiabetic therapy. During the course of treatment, therapy with vasoactive, nootropic and psychotropic drugs was excluded. During the first 20 days of IS, daily intravenous infusions of Mildronate at a dose of 1,000 mg (10 ml of 10% solution per 250 ml of saline) or rheopolyglucin 400 ml were prescribed. Mildronate was then prescribed at a dose of 1,000 mg (2 capsules twice daily) for 8 weeks. Using single-photon emission computed tomography, an increase in cerebral perfusion was recorded in areas of its initial decrease, corresponding to ischemic foci of damage according to magnetic resonance imaging, as well as a statistically significant decrease in the severity of neurological disorders in the group receiving Mildronate.
Quite a large number of studies have been devoted to studying the effectiveness and safety of Mildronate in patients with chronic forms of cerebrovascular diseases. One of the first was the work of Enini G.I. et al., who used Mildronate intravenously, 5 ml of a 10% solution once a day for 5-14 days, then 0.5 g orally for 7-30 days [9]. According to the results of the study, an improvement in cerebral hemodynamics was noted; in patients, headaches also decreased, performance increased, vigor appeared, mood improved, and asthenia decreased. Similar data were obtained by L.A. Dzyak and V.A. Golik when studying the effects of Mildronate (10 ml of 10% solution intravenously for 10 days, then 750 mg daily in capsules for 20 days) on the condition of patients with chronic cerebrovascular ischemia [10]. The effectiveness of Mildronate (daily for 20 days intravenously in a dose of 5 ml of a 10% solution (i.e. 500 mg) in 200 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution) was also noted in the treatment of dyscirculatory encephalopathy in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [11] in the form of improvement in both subjective and objective neurological symptoms, with the cochleovestibular, asthenoneurotic and cephalgic syndromes of the disease undergoing the most clear dynamics.
Since the core of the clinic of chronic disorders of cerebral hemodynamics is cognitive impairment, the work of I.V. is interesting. Damulina et al. [12]. The authors assessed the effects of Mildronate on the cognitive functions of elderly patients with chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency, using a battery of generally accepted neuropsychological tests and electrophysiological parameters (cognitive evoked potential P300) and showed that a course of Mildronate therapy (6 weeks, 250 mg 2 times a day, then 6 more weeks, with 20 patients taking 250 mg 2 times a day, and the remaining 20 patients taking 500 mg 2 times a day) reduces memory and attention disorders, improving the overall cognitive status of patients, and has a positive effect on the parameters of cognitive evoked potential RZ00 in the form of an increase in the value of its amplitude and a shortening of the latent period. The results of the study indicate a positive effect of Mildronate on the cortical-subcortical interaction, which suffers primarily in chronic cerebral circulatory failure.
The effectiveness and safety of long-term use of the drug was noted against the background of continuous and course therapy with Mildronate at a daily dose of 500 mg on indicators of cognitive function in elderly patients with arterial hypertension and cognitive deficits [13, 14]. An open randomized controlled comparative study in parallel groups (continuous administration for 52 weeks, course therapy - two three-month courses over the course of a year) included 180 elderly patients with arterial hypertension and cognitive deficit. For neuropsychological testing, the following tests were used: Brief Mental Status Assessment Scale, Reitan test, Wechsler test, speech activity test, memory (10 words) and serial counting, kinetic test, MFI-20 scale (to assess the severity of asthenia). The Beck Depression Inventory was used to assess the severity of depression and the Taylor Anxiety Inventory. Continuous therapy with Mildronate turned out to be the only treatment regimen that significantly improved all indicators of cognitive function compared to the baseline and the control group, and a decrease in asthenic and anxiety disorders was also noted.
Thus, the results of the above studies indicate the potential use of Mildronate in the treatment and prevention of acute and chronic cerebrovascular disorders.
It has been established that its therapeutic effect in acute and chronic disorders of cerebral circulation is associated mainly with an increase in the content of NO in the body, the vasodilating properties of which contribute to an increase in cerebral blood flow and oxygenation of the brain. In IS, Mildronate® reduces the severity of neurological deficits, improves cognitive functions, reduces asthenia and dysphoria, and improves quality of life. In dyscirculatory encephalopathy, in addition to this, the drug reduces the severity of cephalgia, vestibuloataxia and dyssomnia. The data accumulated to date require further confirmation in larger placebo-controlled international studies. Literature
1. Klochikhina O.A., Stakhovskaya L.V. Comparative analysis of epidemiological indicators of stroke based on data from a territorial population register for 2009–2012. Neuronews, 2015, 2(5): 1-6. 2. Logina I.P., Kalvinsh I.Ya. Mildronate in neurology. Riga, 2012: 56. 3. Gaĭdar BV, Parfenov VE, Vaĭnshteĭn GB. Ways to optimize the cerebral circulation during extreme actions on the brain. Fiziol Zh SSSR Im IM Sechenova. 1989 Nov, 75(11): 1568-75. 4. Sapegin I.D., Beketov A.I., Mametova A.N., Polevik I.V. Comparative characteristics of the cerebrovasoprotective effects of Mildronate, Riboxin and their combination in modeling cerebral hemodynamic disorders. Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology, 2000, 6: 18-21. 5. Zvejniece L, Svalbe B, Makrecka M, Liepinsh E, Kalvinsh I, Dambrova M. Mildronate exercises acute anticonvulsant and antihypnotic effect ects. Behav Pharmacol, 2010, 21(5-6): 548-55. 6. Vinnichuk S.M. Efficacy of Mildronate treatment in patients with ischemic stroke. Physician Science, 1991, (7): 77-79. 7. Moskalenko YE, Gaidar BV, Parfenov VE. Strategy for pharmacological correction of cerebral ischemia: Systemic approaches. In: J. Kriegslein, H. Oberpichler-Schwenk (Eds.). Pharmacology of Cerebral Ischemia. 1999, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesselschaft GmbH Stuttgart. 8. Maksimova M.Yu., Kistenev B.A., Domashenko M.A., Fedorova T.N., Sharypova T.N. Clinical efficacy and antioxidant activity of Mildronate in ischemic stroke. Russian Journal of Cardiology, 2009, 4 (78): 54-62. 9. Eninya G.I., Timofeeva T.N., Egere D.A., Maiore I.Kh. Therapeutic effects of Mildronate and indications for its use in neuroangiology. Experimental and clinical pharmacotherapy, Riga, Zinatne. 1991, 19: 164-171. 10. Dzyak L.A., Golik V.A. The use of Mildronate in the treatment of patients with dyscirculatory encephalopathy against the background of stenotic lesions of the main arteries of the head. Medical Science, 2003, (5-6): 98-101. 11. Suslina Z.A., Maksimova M.Yu., Kisteneev B.A., Fedorova T.N., Kim E.K. Antioxidant therapy in patients with dyscirculatory encephalopathy, aggravated by type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmateka, 2005, (12): 68-70. 12. Damulin I.V., Koberskaya N.N., Antonenko L.M. The effect of Mildronate on cognitive impairment in dyscirculatory encephalopathy: a clinical and electrophysiological study. Neurological Journal, 2006, a(1): 1-6. 13. Statsenko M.E., Nedogoda S.V., Turkina S.V., Tyshchenko I.A., Poletaeva L.V. Possibilities of Mildronate in the correction of cognitive impairment in elderly patients with arterial hypertension. Russian Journal of Cardiology, 2011, 4(90): 124-128. 14. Nedogoda S.V., Statsenko M.E. Therapist's capabilities in correcting cognitive impairment in arterial hypertension. Pharmatheka, 2010, (10): 21-27.
Source
: Medical Council, No. 5, 2015
Mildronate - a little history
Mildronate is also known as Meldonium. Actually, meldonium is the active ingredient of mildronate.
Meldonium was developed in the 1970s by Ivars Kalvins - then director of the Institute of Organic Synthesis of the Academy of Sciences of the Latvian SSR - one of the leading research institutes in this field in the USSR. It was his scientists who were instructed to make a “product for household use” from meldonium, which then had a military purpose.
Initially, the development was called “mildronate”. It was registered in 1976, and began to be used in 1984. On December 7, 2011, by order of the government of the Russian Federation, meldonium was included in the list of vital and essential drugs.
As of January 1, 2021, meldonium is banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) for pre- and non-competition use by athletes. Then, many famous Russian athletes, for example, tennis player Maria Sharapova, were disqualified for using meldonium, although they claimed that they last took it in 2015. The international doping scandal was just beginning to gain momentum...
By the way, L-carnitine, a popular dietary supplement that is freely sold in many countries and is not on the list of prohibited drugs, has properties similar to meldonium.
How Mildronate works
The active substance meldonium, acting in several directions at once, establishes a balance between the cells’ need for oxygen and its delivery, removes accumulated toxins and neutralizes their negative impact on the body. Thanks to this, a person taking Mildronate becomes more resilient to mental and physical stress and gets an improved metabolism.
Other results of using Mildronate:
- normalization of cerebral circulation;
- improvement of blood circulation in the area of ischemia;
- slowing down the formation of the necrotic zone;
- elimination of functional disorders of the nervous system;
- reduction of the rehabilitation period in the treatment of heart disease, stroke and alcoholism
Mildronate is easily absorbed and excreted from the body after 3-6 hours. Although traces of it can still be found for several months.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Meldonium
A synthetic analogue of γ-butyrobetaine, inhibits γ-butyrobetaine hydroxylase, reduces the synthesis of carnitine and the transport of long-chain fatty acids through cell membranes, prevents the accumulation in cells of activated forms of unoxidized fatty acids - derivatives of acylcarnitine and acyl coenzyme A. Under conditions of ischemia, it restores the balance between oxygen delivery and its consumption in cells, prevents disruption of ATP transport; At the same time, it activates glycolysis, which occurs without additional oxygen consumption. As a result of a decrease in carnitine concentration, γ-butyrobetaine, which has vasodilating properties, is intensively synthesized. The mechanism of action determines the variety of its pharmacological effects: increased performance, decreased severity of symptoms of mental and physical stress, activation of tissue and humoral immunity, cardioprotective effect. In case of acute ischemic damage to the myocardium, it reduces the size of the necrosis zone and shortens the rehabilitation period. In heart failure, it increases myocardial contractility, exercise tolerance, and reduces the frequency of angina attacks. In acute and chronic ischemic disorders of cerebral circulation, it improves cerebral circulation and promotes the redistribution of blood in favor of the ischemic area. Effective for vascular and dystrophic pathology of the fundus. It also has a tonic effect on the central nervous system and eliminates functional disorders of the somatic and autonomic nervous system in patients with chronic alcoholism during the period of abstinence. After oral administration, it is quickly absorbed, bioavailability is 78%. The maximum concentration in blood plasma is achieved 1–2 hours after administration. Metabolized in the body to form two main metabolites, which are excreted by the kidneys. The half-life when taken orally is 3–6 hours.
Use of Mildronate in sports
Mildronate is highly valued by athletes for its ability to improve cellular metabolism, as it accelerates the removal of toxins and free radicals from the body. Thus, Mildronate has an antioxidant effect: it improves well-being, slows down the aging process of cells and helps rapid muscle recovery.
Athletes take the drug to reduce pain and recover faster after training. As a result of taking Mildronate, symptoms of overtraining are relieved and fatigue goes away. The athlete’s general condition improves, which can affect his personal performance.
The benefits of the drug are difficult to overestimate during periods of intense physical activity, when training goes on almost without a break, for example, before a competition, and the body does not have time to rest.
Mildronate is recommended to be taken for up to 6 weeks without a break, so as not to cause addiction to the drug. To obtain good results, taking Mildronate should be combined with proper nutrition and daily routine.
Mildronate caps 250 mg in blister pack No. 10x4
Name
Mildronate.
Description
The active substance of the drug Mildronate® is meldonium dihydrate (meldonium). Meldonium is a structural analogue of a substance found in every cell of the body - gamma butyrobetaine. The action of this drug is based on a positive effect on the body’s energy metabolism, as well as a slight activation of the central nervous system. During exercise, Mildronate® restores the balance between oxygen delivery and consumption in cells and activates metabolic processes in them, which require less oxygen consumption to produce energy. Usually, under conditions of increased stress, the body quickly becomes exhausted, but as a result of using the drug Mildronate®, the body gets used to withstanding the load, using oxygen economically and quickly restoring energy reserves in preparation for new loads. Mildronate®, performing the functions of gamma butyrobetaine, can accelerate the transmission of nerve impulses in the body, and therefore all responses are accelerated and the overall metabolism in the body is improved. Therefore, when using the drug Mildronate®, a tonic effect is felt - memory improves, thinking speeds up, dexterity of movements increases, and the body’s resistance to harmful conditions increases.
Main active ingredient
Meldonium
Release form
White hard gelatin capsules. 10 capsules in a blister made of polyvinyl chloride film with polyvinylidene chloride coating and aluminum foil. 2 blisters along with instructions for medical use in a cardboard pack.
Dosage
250 mg
Indications for use
The drug Mildronate® is used as part of complex therapy in the following cases: - with physical and psycho-emotional overload, accompanied by a decrease in performance; - during the recovery period after cerebrovascular diseases, traumatic brain injury and encephalitis (as recommended by a doctor).
Directions for use and doses
Always use the drug in full accordance with the recommendations of your doctor or pharmacist. If in doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist. Due to the possible stimulating effect, it is advisable to use it in the first half of the day. Recommended dose Adults The daily dose for adults is 500 mg (2 capsules). The entire dose can be taken in the morning in one dose, or divided into 2 doses (1 capsule each). The duration of the course of therapy is determined by the doctor. Special groups of patients Elderly patients For elderly patients with impaired liver and/or kidney function, the dose of Mildronate® may be reduced. Patients with Renal Impairment Since the drug is eliminated from the body through the kidneys, patients with mild to moderate renal impairment should use a lower dose of meldonium. Patients with hepatic impairment Patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment should use a lower dose of meldonium. Use in children and adolescents There is no data on the safety and effectiveness of Mildronate® in children and adolescents (under 18 years of age), so this drug should not be used in children and adolescents (see Do not use this drug). If you have taken more Mildronate® than you should. There are no data on cases of overdose of Mildronate®. The drug is low-toxic and does not cause severe side effects. In case of low blood pressure, headaches, dizziness, accelerated heart activity (tachycardia), and general weakness are possible. In case of overdose, consult a doctor immediately. If you forgot to take the drug Mildronate® If you forgot to take the next dose of the drug Mildronate® on time, do it immediately. However, if your next dose is approaching, skip the forgotten dose and continue to use the drug as recommended at the usual dosing intervals. Do not use a double dose to replace a forgotten dose. If you stop using the drug Mildronate® When you stop using this drug, no adverse reactions are observed. If you have questions about the use of the drug, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning a pregnancy, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine. Animal studies are insufficient to assess the effect of Mildronate® on pregnancy, embryo/fetal development, childbirth and postpartum development. The potential risk for humans is unknown, therefore Mildronate® should not be used during pregnancy (see Do not use the drug). It is unknown whether the drug is excreted into human breast milk. A risk to newborns/infants cannot be excluded and this drug should not be used while breastfeeding (see Do not use this drug).
Precautionary measures
Before using Mildronate®, consult your doctor or pharmacist. Tell your doctor if you have had liver and/or kidney failure, as liver and/or kidney function tests may need to be monitored. Children and adolescents This drug should not be used in children and adolescents under 18 years of age, as there is no data on the safety and effectiveness of meldonium in these age groups. There is no data on the effect on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
Interaction with other drugs
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or may start using any other medications. — Mildronate® can be used together with drugs against angina, cardiac glycosides and diuretics (promote the formation and excretion of urine from the body). — Mildronate® can be combined with anticoagulants (delay blood clotting), antiplatelet agents (prevent the formation of blood clots in blood vessels), drugs that eliminate heart rhythm disturbances and other drugs that improve microcirculation (blood circulation in small blood vessels). — Mildronate® can enhance the effect of drugs containing glyceryl trinitrate, nifedipine, beta-blockers, and other drugs that lower blood pressure and dilate blood vessels. — With the simultaneous use of meldonium with lisinopril, a positive effect of combination therapy is observed. -Additional effects are observed when meldonium is used in combination with orotic acid to reverse damage caused by ischemia/reflow. — As a result of the simultaneous use of Sorbifer and meldonium in patients with anemia caused by iron deficiency, the composition of fatty acids in red blood cells improves. — For patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), in addition to azidothymidine or other drugs for its treatment, the doctor may prescribe meldonium, since the combined use of these drugs has a positive effect on the treatment of AIDS. — An overdose of meldonium can increase the toxic effect of cyclophosphamide on the heart. — Carnitine deficiency resulting from the use of D-carnitine (an inactive isomer of carnitine)-meldonium may increase the toxic effects of ifosfamide on the heart. — Meldonium exhibits protective effects against indinavir cardiac toxicity and efavirenz-induced neurotoxicity. Do not use this drug with other drugs that contain meldonium because the risk of side effects may increase.
Contraindications
- if you are allergic to meldonium dihydrate or any other components of the drug; - with increased intracranial pressure (in case of impaired venous outflow, intracranial tumors); - if you have severe liver and/or kidney failure (there is insufficient data on the safety of use); - during pregnancy and lactation; - children and adolescents under 18 years of age (safety of use has not been verified).
Compound
— active substance – meldonium dihydrate. One capsule contains 250 mg of meldonium dihydrate, - excipients: dried potato starch, hydrated silicon dioxide (Siloid 244 FP), calcium stearate. Capsule (body and cap): titanium dioxide (E 171), gelatin.
Side effect
Like all medicines, Mildronate® can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them. If you experience any unwanted reactions, consult your doctor or pharmacist. This recommendation applies to any possible adverse reactions, including those not listed in the instructions. The following are undesirable reactions observed in previously conducted clinical studies (marked *), and undesirable reactions that were reported during the period after registration of the drug. Common (may occur in no more than 1 person in 10): • allergic reactions*; • headache*; • digestive disorders*. Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people): • hypersensitivity, allergic dermatitis, urticaria, angioedema (difficulty breathing or swallowing, or swelling of the throat, face, arms and legs, lips and/or tongue), anaphylactic reaction (sudden general allergic reaction, the symptoms of which are itching, hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, rapid drop in blood pressure, dizziness, loss of consciousness, shock); • excitement, fear, obsessive thoughts, sleep disturbances; • feeling of “pins and needles”, trembling, decreased sensitivity, tinnitus, dizziness, gait disturbances, lightheadedness, loss of consciousness; • changes in heart rhythm, increased heart rate, atrial fibrillation, chest discomfort/chest pain; • increase/decrease in blood pressure, hypertensive crisis (rapid increase in blood pressure), increased blood flow to tissues (hyperemia), pallor; • sore throat, cough, difficulty breathing, short-term cessation of breathing; • disturbances in the sense of taste (metallic taste in the mouth), loss of appetite, retching, nausea, vomiting, gas accumulation, diarrhea, abdominal pain; • general/macular (limited, without elevation)/papular (small, dense with elevation) rashes, itching; • back pain, muscle weakness, muscle spasms; • frequent urination; • general weakness, chills, weakness, swelling, swelling of the face, swelling of the legs, feeling hot, feeling cold, cold sweat; • changes in the electrocardiogram (ECG), acceleration of heart function, eosinophilia (increase in the number of specific white blood cells)*. Upper abdominal pain and migraine have also been reported in connection with the use of Mildronate®. Reporting Adverse Reactions It is important to report suspected reactions after marketing authorization of a medicinal product to ensure continuous monitoring of the benefit-risk profile of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are encouraged to report any suspected adverse drug reactions through the national adverse reaction reporting systems of the member states of the Eurasian Economic Union. In the Republic of Belarus, it is recommended to report adverse reactions to the information database on adverse reactions (actions) to drugs, including reports of ineffectiveness of drugs (UE "Center for Expertise and Testing in Healthcare" of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus, website rceth.by).
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Store in original packaging to protect from moisture. Keep out of the reach of children. Do not use the drug after the expiration date indicated on the package after “Best before”. The expiration date is the last day of the month. Do not throw medications down the drain. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medications that you no longer need. These measures will protect the environment.
Buy Mildronate caps 250 mg in blister pack No. 10x4 in the pharmacy
Price for Mildronate caps 250 mg in blister pack No. 10x4
Instructions for use for Mildronate caps 250 mg in blister pack No. 10x4
Composition of Mildronate and release forms
The composition may vary depending on the form of release.
- Mildronate ampoules contain meldonium and water for injection.
One ampoule contains 5 ml of the drug, which contains 250 mg of the active substance. Available in cardboard packaging of 10 ampoules.
- Mildronate capsules:
- meldonium;
- potato starch;
- calcium stearate;
- colloidal silicon dioxide;
- titanium dioxide and gelatin in the shell.
Capsules come in two types: with 250 mg and 500 mg of active substance. Sold in cardboard packs of 40 and 60 pieces.
- Mildronate in syrup:
- meldonium;
- purified water;
- cherry essence;
- glycerol;
- dyes;
- propylene glycol.
Two packaging: 150 ml and 250 ml. 5 ml (one dose) of the medicine contains 250 mg of the active substance. Available in cardboard packaging with a 5 ml measuring spoon.
Mildronate enters the blood most quickly in ampoules, immediately after administration of the drug. The syrup also has a good absorption rate. But capsules are more convenient to take.
pharmachologic effect
- Mildronate acts as an angioprotector: dilates blood vessels, reduces tissue swelling, stimulates metabolism in cells, restores blood composition;
- Cardioprotector: strengthens the heart, accelerates cell regeneration, removes toxins;
- The drug has an antihypoxic effect: reduces tissue oxygen demand, activates cellular metabolism, stimulates regeneration, improves tissue nutrition;
- Antianginal effect: prevents and relieves attacks of angina, transports oxygen to the myocardium.
The high effectiveness of Mildronate is the result of a complex effect on the body. The particular benefits of the drug are often discussed by athletes who note an improvement in metabolic processes after its use.
Instructions for taking Mildronate
You can take the drug only on the recommendation of a doctor. As a rule, in the first half of the day, as it has a tonic and stimulating effect. Dosage and rules differ depending on the release form.
Capsules
Reception depends on the purpose.
- For the treatment of cardiovascular diseases in complex therapy, take 0.5-1 grams per day for up to 6 weeks. 250 mg capsules are taken up to 4 per day, 500 mg tablets - up to 2 per day. The daily dose should be divided into 1-2 doses.
- For the treatment of chronic dysfunctions of cerebral circulation, the dosage is the same. During the year, no more than 2 courses lasting up to 6 weeks each.
- For the treatment of chronic alcoholism and detoxification, take 500 mg 4 times a day. The duration of therapy reaches 10 days.
- To increase endurance and physical strength, athletes take 1-2 capsules twice a day before training. Duration of treatment is 21 days, during competitions – up to 14 days.
To make swallowing easier, drink with water.
Syrup
- For the treatment of heart diseases and deterioration of cerebral circulation, take 1 scoop of syrup twice a day.
- The dosage for athletes is selected individually, based on the daily norm of 1 gram (4 scoops), divided into two doses.
Ampoules
The solution in ampoules is administered intravenously, intramuscularly and by injection into the eye.
- Diseases of the heart and brain: 2 ampoules into a vein per day, 1 ampoule 2 times. The course is from 4 to 6 weeks.
- Chronic alogolism: 1 gram per day for 10 days intravenously or intramuscularly.
- Athletes need to administer 500 mg intravenously once, up to 3 weeks.
- Diseases of the retina: eye injection of 0.5 ml of solution per day, up to 10 days.
How to restore strength after viral diseases?
Take your doctor's recommendations seriously
Follow all recommendations and instructions of your attending physician. If you are prescribed physical therapy or other procedures, do not skip sessions. Having coped with the disease, we want to be as far away from medical institutions as possible. But remember that your health depends on how diligently you follow the recommendations.
Eat foods rich in fiber
Fiber is food for our immunity. Feel free to include foods rich in fiber in your diet (white cabbage, avocado, raisins, dried apricots, white bread, beans, wheat bran).
Select the necessary vitamins or medications
After a viral disease, the body experiences a lack of vitamins. Find the right vitamins to fill these gaps, such as: Vitamin C helps strengthen the immune system, Vitamin D is good for bones and teeth, and Vitamin A improves vision.
You can also choose medications that will help restore and maintain performance. Such a drug could be “Mildronat® capsules 250 mg” - it will help you increase physical and mental performance, and also improve memory function.
Don't deny yourself the pleasures
Eat your favorite treat—don't worry about the calories. Go to a concert of your favorite artist or go on an interesting excursion - don’t waste your time. Be a little more kind to yourself - do not deny yourself pleasures, because they will have the most beneficial effect on your mood.
Say no to extra workloads
The rehabilitation period after a viral illness is a difficult period for you, both physically and psychologically. During this period, you should not adhere to a strict diet, engage in extreme sports, take on extra work, etc.
Love sports
We mentioned above that during rehabilitation you should avoid extreme sports, but nothing prevents you from starting to run in the morning, ride a bike or, say, sign up for a swimming pool. These and similar sports activities will help you keep your body in good shape and give you a lot of pleasant experiences.
Be surrounded by friends and loved ones
A well-known saying says: “Houses and walls heal.” And if at home you have not only your own walls, but also close people who are always ready to support you, then the recovery process becomes easy and painless. Friends and family sincerely love you and are ready to surround you with care and attention - and this is exactly what you need now.
Set yourself a new goal
Let a new interesting thing appear in your life to which you can devote time: start blogging, sign up for cooking courses, learn the basics of programming - the choice depends on your desires and preferences.
A new goal will help you make your life richer and more interesting, thanks to it the rehabilitation period will no longer seem like an unpleasant event.
If you are active, do not neglect the recommendations of your doctor, in a word, take on board the above tips, you will be able to quickly restore strength after a viral illness.
We wish you good health and self-confidence!
Contraindications, side effects, overdose
Mildronate is prohibited for use:
- Under the age of 18;
- Pregnant and breastfeeding;
- With increased intracranial pressure;
- With a brain tumor;
- If you are sensitive to substances contained in the drug.
The drug is strictly contraindicated in liver failure. In chronic forms of diseases, it can be taken for a short period and after the course, an examination can be carried out in case of complications.
Acute renal failure is noted as a contraindication. In case of chronic kidney disease, the drug should be taken for a long time with caution, monitoring the condition of this organ. Clinical studies of the drug's effects on the kidneys have not been conducted.
It is also not recommended to combine Mildronate with drinking alcohol. You can drink alcohol 12 hours after taking the drug so that the active substance is removed from the body.
Side effects are observed either due to individual intolerance to the components of the drug, or when taken incorrectly. Among them:
- skin rashes;
- malaise;
- decrease or increase in blood pressure values;
- excitability;
- diarrhea.
If any disturbances are observed, you should consult a doctor and possibly change your therapy.
Keep in mind that tachycardia is possible when taking Mildronate simultaneously with nitroglycerin and nifedipine or antihypertensive drugs. In general, Mildronate combines well with other medications, especially with drugs against pulmonary diseases and arrhythmia.
There is also no data on the adverse effects of the drug in case of overdose. But it is better to rinse your stomach and consult a doctor.
Mildronate is well tolerated by the body without causing toxicity. Rarely, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, nausea, and weakness are possible.
Store the drug at a temperature not exceeding 25 degrees Celsius and out of the reach of children.
Drug interactions Meldonium
Enhances the effect of coronary lytics, some antihypertensive drugs, cardiac glycosides. Can be combined with antianginal drugs, anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, antiarrhythmic drugs, diuretics, bronchodilators. Due to the possible development of moderate tachycardia and arterial hypotension, caution should be exercised when combined with nitroglycerin, nifedipine, α-adrenergic receptor blockers, antihypertensive agents and peripheral vasodilators.
List of pharmacies where you can buy Meldonium:
- Moscow
- Saint Petersburg
Mildronate. Analogs, prices
There are many analogues of Mildronate on the market; if a replacement is necessary, your doctor will help you make a choice.
- Vasomag - from 200 rubles;
- Cardionate – from 170 rubles;
- Meldonium - from 230 rubles.
- Melfort - from 500 rubles;
- Midolat - from 128 rubles;
- Metonate – from 300 rubles;
- Riboxin - from 37 rubles.
The cost of the drug depends on its release form and region. For example, prices in Moscow:
- ampoules – from 417 rubles;
- syrup - from 300 rubles.
- Capsules - from 300-550 rubles.