Hypertension and its consequences are one of the most common causes of mortality. According to Rosstat, diseases of the circulatory system rank first in the number of deaths. They account for 46.8% of all cases. Therefore, high blood pressure cannot be ignored. Even in the absence of severe symptoms, it is recommended to regularly take measurements with a tonometer. And if deviations from the norm appear, consult a doctor immediately.
Hypertension and high blood pressure
Blood pressure (blood pressure) is the pressure that blood creates on the walls of blood vessels from the inside. From the outside, the vessels are compressed by the atmosphere. So that blood can circulate and the vessels do not close under the influence of external force, the heart pumps blood at a pressure exceeding atmospheric pressure. Measurements are taken in millimeters of mercury. There are arterial, venous, capillary, intracardiac, and pulse pressures. Normally, the work of the heart muscle ensures a blood pressure of 120/80 mmHg. Art. The first number shows the systolic pressure at the moment the blood is pumped out by the heart. The second number is the diastolic pressure between heartbeats, it shows the resistance of the peripheral vessels to the further movement of blood. The difference between the upper and lower values is called pulse pressure.
During physical activity, sudden changes in temperature, and stress, indicators may increase, but quickly return to normal, as the body adapts to the changed conditions. A persistent increase in blood pressure is called hypertension or hypertension.
Hypertension affects all organs and worsens overall health. Without treatment, it leads to irreversible pathological changes, and in severe cases, death. There are three forms of the disease:
- Easy. Blood pressure readings range from 140/90 – 160/100. At this stage, the risk of organ damage is low. But the danger lies in the fact that a person may not notice or ignore the symptoms, miss the onset of the disease, and it will progress.
- Average. Characterized by pressure 160/100 – 180/110. At such values, damage to the heart, eyes, and kidneys begins. Pathologies can develop over several years. If treatment for hypertension is started in time, changes can be slowed down.
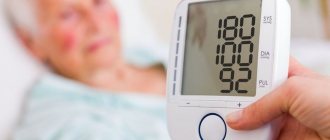
- Heavy. Blood pressure 180/110 and above. This condition is extremely dangerous, as it leads to rupture of blood vessels. Depending on the location of the hemorrhage, stroke, heart attack, blindness, and failure of internal organs occur.
It is important not to miss the first signs of hypertension and keep the readings as close to normal values as possible.
Diagnostics
Increased diastolic pressure is not an independent disease, but develops as a symptom of one or another pathology of the internal organs or endocrine system. Therefore, if an increased lower blood pressure is repeatedly noted, the patient must undergo a detailed medical examination, including:
- consultations with a therapist, cardiologist, nephrologist and endocrinologist;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and thyroid gland;
- ECG;
- Echo-CG;
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels;
- clinical (general) blood and urine analysis;
- determination of the level of thyroid hormones in the blood;
- excretory urography;
- Rehberg's test.
Depending on the results obtained, additional studies of certain organs and systems may be prescribed.
To determine high blood pressure, it is necessary not to measure it once, but to measure it three times
Symptoms of hypertension
Signs of pathology are the following conditions:
- Headache, often in the occipital region. May not respond to analgesics.
- Pulsation in the head, noise in the ears.
- Dizziness may occur with a sudden change in position.
- Decreased visual acuity, darkening of the eyes, sensation of “floaters”.
- Chills, increased sweating, rapid pulse, nausea.
- Nose bleed.
- Redness of the face and ears.
- Feelings of anxiety, restlessness, increased fatigue.
Symptoms may indicate more than just hypertension, but when one or more conditions appear, it is recommended to first measure blood pressure. If the values are higher than normal, consult a therapist or cardiologist.
Normal diastolic pressure
The approximate limits of normal diastolic pressure indicators in patients of different ages are identified. It should be taken into account that fluctuations in these values are also largely due to the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Rare small deviations from the norm may not be a cause for concern, but pronounced diastolic hypertension indicates developing pathologies.
Diastolic pressure indicators
| Patient age | Lower limit of normal | Upper limit of normal | Pathological indicators |
| 15-16 | 51 | 79 | 50 or less, 80 or more |
| 17-29 | 61 | 84 | 60 and less, 85 and more |
| 30-39 | 61 | 89 | 60 and less, 90 and more |
| 40-59 | 61 | 89 | 60 and less, 90 and more |
| 60-69 | 61 | 89 | 60 and less, 90 and more |
| Over 70 | 89 | 65 and less, 90 and more |
Attention!
If a person's blood pressure is regularly higher than normal, the specialist defines this condition as hypertension. This disease can lead to the development of various complications that significantly reduce the patient’s quality of life.
Causes of high blood pressure
When measuring pressure, the state of blood flow is assessed - how correctly the blood circulates through the vessels. Hypertension occurs when circulation is impaired and more force from the heart is required to push blood through the vascular bed. This can happen for several reasons:
- Increased blood volume. In this case, the blood puts more pressure on the vessels. Normally, to compensate for excess fluid, the walls of blood vessels stretch, and the pressure normalizes. But, when tissue elasticity is lost, stretching does not occur or is insufficient. Typically, blood volume increases with increased salt intake.
- Narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels. The cross-section of the vessel becomes smaller, making it difficult for the fluid to pass through. In the short term, this condition develops against the background of stress, physical activity, and a sharp drop in temperature. These are reversible reactions. A common cause of constant narrowing of the lumen is atherosclerosis - the deposition of cholesterol plaques.
- Increased blood viscosity. This condition is caused by dehydration, diseases of the immune system, metabolic disorders, obesity, varicose veins, dietary errors, alcohol consumption and other factors. To ensure that thicker blood circulates, high pressure must be created.
A systemic increase in blood pressure indicates chronic pathology. In addition to normalizing blood pressure, it is necessary to diagnose the cause and carry out complex therapy.
Causes of diastolic hypertension
Increased pressure can be caused by both normal physiological processes in the human body and various developing pathologies. In a healthy person, diastolic hypertension may occur in the following cases:
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages, nicotine, drugs. These substances have a stimulating effect on the nervous system, sharply reducing inhibition processes in the body. As a result, a spasm of the vascular walls occurs, and the number of heartbeats per minute increases. Such changes lead to an increase in pressure, including diastolic. A cool shower, neck massage, or sleep will help relieve an attack of hypertension. If necessary, the patient is advised to use drugs to remove alcohol or drugs from the body.
- Eating fatty and hot foods. Normally, any meal is accompanied by a slight increase in blood pressure. High-calorie foods take a long time and are difficult to digest. At the same time, various digestive processes affect heart rate and blood density. If a patient is prone to diastolic hypertension, he is advised to avoid regularly consuming foods high in lipids.
- An increase in lower pressure is possible as a result of the use of various pharmacological agents. In women, a similar effect is often provoked by hormonal contraceptives. Corticosteroids and anti-inflammatory drugs also lead to hypertension in some cases. If there is a significant increase in diastolic pressure, it is necessary to consult a specialist and replace the medication with another one.
- Staying in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions. Living in regions with polluted air or water leads to the accumulation of toxins in the human body and disruption of the cardiovascular system.
- Playing sports. Any exercise leads to accelerated blood movement through the vessels and more frequent myocardial contractions. Hypertension can be avoided by exercising moderately, without resorting to excessive physical activity.
Diastolic hypertension can also occur due to various diseases. In this case, hypertension should be divided into primary and secondary. In the first case, the pathology develops due to hemodynamic disturbances and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system. Such disorders require long-term complex treatment. In this case, pharmacological agents must be selected taking into account the individual health characteristics of the patient.
Kidney diseases
The kidneys produce the biologically active substances renin and angiotensin. One of their functions is to regulate normal blood pressure in the human body. With the development of various diseases of the urinary system, the patient begins to produce an excess of these hormones. As a result, the lumens of blood vessels narrow, cholesterol plaques are deposited on their walls, and hypertension develops. Most often, a similar clinical picture occurs with pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, or exacerbation of urolithiasis.
Attention!
Disturbances in the urinary system lead to acute fluid retention in the body and the development of intoxication. Such pathologies pose a danger to human life and require emergency diagnosis and medical intervention.
Kidney diseases, in addition to diastolic hypertension, manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- intense pain in the lumbar region;
- disturbance of urination, most often ischuria - urine retention in the body;
- bloating and abdominal pain;
- stool disorders, nausea, intestinal cramps;
- attacks of vomiting that does not bring relief;
- sweating, chills.
Treatment of diastolic hypertension in this case involves careful treatment of the underlying urological disease. The patient is prescribed the following medications:
- antibacterial drugs for pyelonephritis: Amoxicillin, Doxycycline, Ampicillin;
- antispasmodics: No-shpa, Drotaverine;
- analgesics: Nise, Ketorol, Ketanov;
- means for removing stones: Cyston, Urolesan, etc.
When fighting hypertension, special attention should be paid to diet. The patient is advised to minimize the consumption of salt, salty and peppery foods. Excess sodium in the body leads to an increase in the volume of intracellular fluid, thickening of the walls of blood vessels and narrowing of their lumen. This causes an increase in blood pressure.
Attention!
In some cases, to normalize the production of renin and angiotensin, a specialist prescribes drugs to the patient that reduce the activity of the renin-angiotensin system: Omapatrilat, Losartan, Valsartan.
Thyroid diseases
The thyroid gland is one of the most important organs of the endocrine system. At the same time, failures in its work immediately affect a person’s health, since the coordinated work of the whole organism is disrupted.
The follicular cells of the thyroid gland produce two main hormones:
- thyroxine or T4;
- triiodothyronine or T3.
In some cases, the patient begins to produce an excess amount of active substances, as a result of which the following changes occur in the body:
- the heart rate increases;
- vascular tone increases;
- the lumen of the arteries narrows.
As a result, a person’s diastolic pressure increases, weakness, dizziness, and intense headache occur. There may also be an increase in appetite, irritability, overexcitation, and myalgia.
To relieve hypertension, it is necessary to carry out comprehensive treatment of hyperthyroidism, that is, pathological excessive production of hormones. Depending on the degree of development of the disorders, the patient is indicated for conservative or surgical treatment.
Drug treatment in this case is aimed at reducing the secretion of the thyroid gland. Patients are prescribed thyreostatics: Propylthiouracil, Thiamazole. It is also mandatory to follow a diet rich in proteins, carbohydrates and amino acids. In this case, you should limit the intake of foods that excite the nervous system.
If the patient’s condition does not improve, persistent hypertension, disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and severe headaches are noted, then surgery to excise the thyroid gland is prescribed. After the intervention, the patient must take medications throughout his life to maintain normal hormonal levels.
Upper, lower, pulse pressure
The upper, systolic, cardiac pressure indicates the work of the heart at the moment of pushing out blood. An increase in the upper indicator is accompanied by a rapid pulse, discomfort in the chest area, and shortness of breath. High systolic pressure accelerates wear and tear of the heart and leads to structural changes in the myocardium. Long-term hypertension may develop:
- Coronary heart disease is a decrease in blood circulation in myocardial tissues.
- Heart failure is incomplete filling and emptying of the ventricles.
- Infarction is the formation of a necrotic focus in the myocardium.
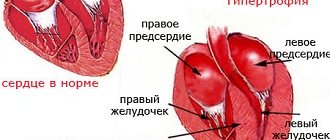
- Left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy is the growth and thickening of muscle tissue, which leads to impaired contractile function, up to sudden cardiac arrest.
Lower, diastolic, renal pressure depends on the condition of the blood vessels. Manifestations of high diastolic pressure are muscle weakness, visual disturbances, and dizziness. Also, the need to control blood pressure is indicated by kidney disease, swelling, difficult diuresis during the day and excessive urination at night.
Consequences of hypertension with high renal pressure:
- Stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation, which may be accompanied by hemorrhage.
- Renal failure - due to tissue nutritional disturbances, the kidneys cannot work normally, intoxication begins with damage to all organs and systems.
- Deterioration in the elasticity of blood vessels - fragility, microhemorrhages, and hematomas appear on the skin.
- Malnutrition of the limbs - peripheral blood circulation is hampered with the possible formation of ulcers and the development of gangrene.
Also important is the difference between the upper and lower indicators - pulse pressure. Normally it is 30-50 mmHg. When it decreases, lethargy occurs, throbbing headaches in the frontal and occipital regions, cognitive function is impaired, and the ability to concentrate decreases. A decrease in the indicator may occur due to:
- Atherosclerosis, aortic aneurysm.
- Kidney nutritional disorders.
- Aneurysms with different localizations, including cerebral vessels.
- Inflammation of the serous membrane of the heart.
- Hemorrhages.
With increased pulse pressure, the myocardium regulates blood circulation with great tension, which provokes disturbances in the functioning of the heart, characteristic of high systolic pressure.
How to protect yourself from blood pressure changes
A healthy lifestyle is what can raise low and lower high blood pressure, bringing it closer to normal levels. This does not mean that a chronic hypertensive patient who stops consuming salt will become absolutely healthy, but he will be able to reduce the number of attacks.
The best foods for heart and vascular health
Measures to prevent both low and high diastolic pressure are as follows:
- Complete cessation of smoking, which makes blood vessels fragile and reduces lung capacity.
- Mandatory physical activity appropriate to the person’s age and health status.
- Reducing the amount of salt in the diet (relevant for hypertensive patients).
- Losing weight if you are overweight, which is one of the main factors that increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
- Regular walks in the fresh air allow you to saturate your blood with oxygen.
- Maintain a sleep schedule (at least 8 hours at night).
- Proper nutrition, taking into account the body's needs for proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements. Thus, by increasing the level of unsaturated fats in the diet and reducing the amount of saturated fats, you can prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques that accompany almost any vascular pathology.
At-risk groups
All elderly people are at risk of developing hypertension due to the natural aging of blood vessels and the heart. At an earlier age, the likelihood of high blood pressure is higher if:
- Diseases of the kidneys and blood vessels.
- Congenital heart defects.
- Obesity.
- Alcohol abuse, smoking.
- Frequent stress, disruption of work and rest schedules.
- Systematic intoxication with harmful substances.
- Eating foods high in cholesterol and salt.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
People who have had head injuries or heart and brain surgery should also monitor their blood pressure.
Ways to lower diastolic pressure
Diastolic hypertension is a condition that can lead to a sharp deterioration in a person’s well-being. Therefore, at the first signs of the development of pathology, it is necessary to take a number of measures aimed at normalizing the functioning of the patient’s body:
- The patient should be placed face down on the couch, and a cold compress or ice pack should be applied to his neck and collar area for 5-10 minutes. This will reduce blood flow tension in the vessels supplying the brain.
- Resort to acupuncture, that is, a procedure for stimulating active points of the body. You need to lightly press on the hollow under your earlobe and move your fingertip to the middle of the collarbone. Repeat the manipulation on the other side of the head.
- Take a cool shower, take a nap. Relieving stress and resting will help lower your blood pressure.
Attention!
All these measures can be used only if the patient feels satisfactorily and does not complain of impaired speech, consciousness, drowsiness or severe dizziness. Otherwise, you should immediately seek emergency medical help.
Drug therapy for diastolic hypertension
Drug treatment for diastolic hypertension should be taken only as prescribed by a specialist. The doctor must take into account the individual health characteristics of the patient, his general well-being, and the presence of chronic or acute diseases. In most cases, the following pharmacological agents are prescribed for the treatment of this pathology:
- Beta blockers: Anaprilin, Atenolol, Metoprolol
and so on. These drugs dilate blood vessels, help to quickly lower blood pressure, and reduce the level of glucose in the blood plasma. These medications are widely used for the treatment of hypertension, but are sold only by prescription. - Angiotensin converting enzymes: Captopril, Enalapril, Quinapril
etc. They are used to treat both systolic and diastolic hypertension. They block the action of an enzyme that causes an increase in blood pressure. - Calcium antagonists: Nifedipine, Verapamil
. These are drugs that are prescribed only for severe hypertension and are used for urgent relief of a hypertensive crisis, that is, to reduce very high blood pressure.
In this case, drug treatment should be comprehensive and long-term. The medications should be taken regularly. Refusal of therapy prescribed by a doctor can lead to a worsening of the condition and the development of persistent hypertension.
Danger to organs and body systems
- Heart. Due to the increased load, the walls of the myocardium begin to grow, especially the left ventricle, which works to eject blood. With tissue hypertrophy, nutritional deficiency begins, wear accelerates, and elasticity decreases. As a result, arrhythmia, bradycardia, ischemia, and heart attack may develop.
- Vessels. Constant tension makes blood vessels fragile, deforms them, and leads to ruptures. Hypertension increases atherosclerotic deposits, up to complete blockage. First of all, the capillaries that provide nutrition to the internal organs, eyes, and limbs are affected.
- Brain. Insufficient brain nutrition in hypertension leads to cognitive impairment. The most common cause of strokes is hypertension.
- Kidneys. Lack of blood circulation leads to the accumulation of toxins. The kidneys cannot cope with excretion in full; they do not have enough nutrients to recover. This leads to the development of kidney failure and further worsens the condition of blood vessels, as harmful compounds remain in the blood.
- Eyes. Hypertension can cause damage to the optic nerve, and in the most severe cases, blindness occurs.
How to Prevent the Dangers of High Blood Pressure
When diagnosed with hypertension, a full examination is required to find the cause due to which the pathology develops. At the same time, it is important to stabilize indicators in order to reduce the risks of developing a crisis and complications.
- You need to measure your blood pressure several times a day, preferably at the same time. It is better to record the data and take it to a doctor’s appointment - this will allow you to track the dynamics and identify patterns.
- Under no circumstances should you stop taking prescribed medications on your own. If persistent improvement occurs during therapy, patients often stop taking medications. You can't do this. Cancellation, reduction of dosages, replacement of one drug with another is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
- It is necessary to adhere to a daily routine and avoid overwork. It is easier for the body when the usual rhythm is not disturbed.
- At the first sign of deterioration, seek help. Fluctuations in indicators and progression of hypertension can cause a crisis, heart attack, or stroke, so any changes should be reported to the doctor to adjust therapy or conduct additional examination.
Since hypertension affects all organs and systems, regular restorative and supportive courses are recommended for blood vessels, heart, and other organs as indicated.
Folk remedies for normalizing high blood pressure
If diastolic pressure has increased slightly under the influence of stress, overwork, or eating unhealthy foods, then traditional methods of treatment can be used to reduce it:
- Valerian tincture. Take 2-3 times a day, 5-10 drops. Has a mild sedative effect.
- Infusion of black currants, pine cones, chokeberry and peony. Mix plant materials in equal volumes. Pour two teaspoons of the resulting mixture into a glass of cold water and heat over low heat until boiling. Leave for 30 minutes, strain. Take a third of a glass 3 times a day half an hour before meals. The infusion contains a large amount of flavonoids, which have a beneficial effect on the condition of the vascular wall.
- Lemon juice with honey. Squeeze the juice of half a lemon into a glass, add a tablespoon of honey. Add warm water to the brim and stir. This drink allows you to quickly reduce high diastolic pressure.
Prevention of hypertension
Prevention of hypertension is not specific. To reduce the risk of developing the disease, it is recommended to adhere to the rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- Stop smoking and do not abuse alcohol. Alcohol and nicotine destroy blood vessels.
- Normalize weight. Obesity itself can cause hypertension. In some patients, weight loss restores normotension without medication.
- Do physical education. Cardio exercise of at least 150 minutes per week and walking are especially effective for strengthening the cardiovascular system.
- Balance your diet in terms of calories and composition. It is necessary to consume fiber daily and reduce animal fats and salt in food.
- Monitor your drinking regime. Insufficient water leads to blood thickening and retention of toxins. The norm for an adult is 2 liters per day.
If possible, it is better to avoid stress and overexertion, get enough sleep and spend time outdoors.
Lifestyle change
Speaking about how to treat high blood pressure, it should be said that in the complex treatment regimen for this pathology, considerable importance is given to lifestyle changes.
First of all, this concerns diet. You should eat food 4-5 times a day in small portions. Chocolate, coffee, table salt, marinades, fatty and spicy foods are excluded from the diet (or severely limited).
The development of arterial hypertension is indicated in cases where three control measurements recorded blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg. Art.
The daily menu should include fresh fruits and vegetables, herbs, dried fruits, foods rich in potassium (nuts, cabbage, tomatoes, baked potatoes, dried apricots), magnesium (buckwheat, fish, dairy products, strawberries, bananas) and B vitamins (yeast , liver, meat, pears, apples, oranges). It is advisable to contact a nutritionist to develop a detailed menu that takes into account the energy needs of the body, the general condition of the patient, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Physical activity. To improve blood circulation, it is necessary to devote sufficient time to physical activity every day. The level of permissible loads is determined by the attending physician, based on the general condition of the patient. Preferably swimming, walking, cycling. General massage is very useful.
Massage is useful for high blood pressure, as it helps normalize vascular tone.
Rejection of bad habits. The patient is advised to completely quit smoking. Nicotine promotes spasm of blood vessels, and hence an increase in diastolic pressure. It is equally important to give up the abuse of alcoholic beverages (it is permissible to drink no more than 50 ml of cognac or 200 ml of red wine per day).
Normalization of sleep and rest patterns. Night sleep should last at least 8-9 hours. You should try to go to bed no later than 10 pm. It is important to adhere to a daily routine, alternating work and rest.
Spa treatment. It is based on the use of climatic and physical factors that normalize the state of the cardiovascular system and thereby stabilize blood pressure.
An increase in diastolic pressure in older people is especially dangerous, since their blood vessels are significantly altered.