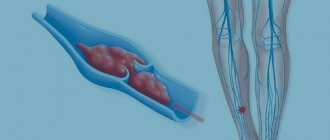
Most often, blood clots form in the deep veins of the lower extremities and heart valves, but theoretically they can affect any other vessel. Once released and transported through the blood, the clot can reach vital organs. This situation, especially in the case of acute pulmonary embolism, can be fatal for the patient.
Prevention of thrombosis, thrombophlebitis and thromboembolism is a vital necessity. It should be understood that preventive measures are much more effective here than therapeutic ones. According to WHO, the immediate mortality rate among people suffering from blood clots is about 6-12% per year. If you are potentially at risk, you can make adjustments to your lifestyle to prevent this from happening.
Causes of thrombosis
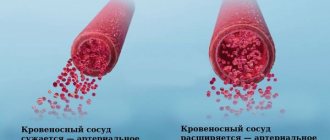
The main cause of arterial thrombosis is atherosclerosis, in which clots of fats or calcium compounds form on the walls of the arteries. They narrow the artery and can completely block blood flow or break off and block smaller vessels.
The development of arterial thrombosis in the vessels of the brain results in strokes, and in the coronary arteries - myocardial infarction.
There are many more reasons for the formation of venous blood clots:
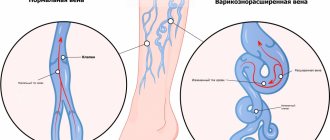
- varicose veins of the lower extremities;
- loss of mobility, both complete and partial;
- bone fractures;
- hypercoagulability and other autoimmune disorders;
- heredity.
Mechanism of thrombus formation
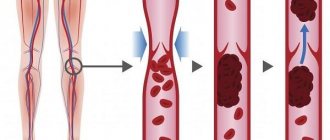
The formation of a blood clot always follows one scenario: first, damage occurs (trauma to the vessel wall), platelets rush to the site of damage, which stick together into a strong clot and adhere to the wound. Next, fibrin threads are formed, and the vessel receives a “patch.” Over time, the tissues are restored, the blood clot dissolves as unnecessary.
A useful mechanism that saves people from blood loss due to injury can become dangerous when there is an excess of platelets - thrombophilia. An excess of these blood cells results in blood clots that are too large for minor injuries. The second important factor in thrombus formation is the very presence of damage. Thrombosis becomes a pathology if it begins in the absence of injury to the vascular wall.
Risk area
The risk of developing vein thrombosis increases with:
- hormonal therapy;
- presence of deep vein thrombosis in relatives;
- pregnancy;
- injury to veins during operations, fractures, cuts;
- physical inactivity;
- increased blood clotting;
- use of venous catheters;
- obesity;
- oncology;
- heart and lung diseases.
Arterial thrombosis is more likely to develop:
- for diabetes;
- high blood pressure;
- obesity;
- low activity;
- bad heredity;
- poor nutrition;
- high levels of bad cholesterol;
Older age increases the risk of both types of thrombosis.
How to prevent a blood clot from breaking off
People whose blood relatives suffered from thrombosis will have a high risk of developing a similar disease. Therefore, you should be regularly examined by a doctor to detect dangerous vascular growths. Modern medicine has all the necessary tools to detect a blood clot and prevent its rupture.
If a person’s blood has increased clotting, he will be prescribed medications (antiplatelet agents). Sometimes they need to be taken for life. It should be noted that only a doctor can recommend them, otherwise you can cause serious harm to your own health.
If the doctor diagnoses a blood clot that is highly likely to break off, the patient is urgently hospitalized and prepared for surgery.
People with thrombosis should strictly follow their doctor's instructions. They are not recommended to take a hot bath, visit saunas and steam baths, as all these procedures increase blood flow through the vessels. A ban is also imposed on visiting massage rooms and using warm compresses.
To prevent blood from stagnating in the veins, it is necessary to move as much as possible, engage in physical exercise, and walk a lot.
If the patient is at risk of blood clot rupture, then strict bed rest is indicated. Self-treatment of thrombosis or wait-and-see tactics in this case is unacceptable.
A menu containing foods that lower blood cholesterol should be a priority. This will prevent the formation of atherosclerotic deposits on the vessels, and therefore reduce the risk of thrombosis. For this purpose, you can include sea fish, seafood, broccoli, spinach, new potatoes, and dairy products in your diet.
Types of thrombosis
The two main types of disease are arterial and venous, but there are two large groups of patients that require more detailed consideration. Many doctors distinguish these variations into separate types of thrombosis.
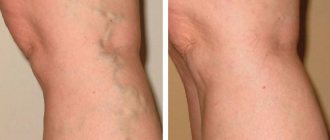
- Superficial vein thrombosis, or SVT, is when a blood clot blocks the superficial veins of the upper or lower extremities. Accompanied by a characteristic pattern of a darkened vein, its obvious relief. About 10% of cases of TPV, for which treatment was not started, result in serious complications, including tissue necrosis.
- Deep vein thrombosis, or DVT, occurs when a blood clot blocks the deep veins in the lower extremities or pelvis. Causes blood stagnation in the lower extremities, reduces the flow of oxygen-free venous blood to the heart, and significantly increases the risk of pulmonary embolism.
Deep vein thrombosis: causes, clinical picture, treatment
The mechanism of blood clot formation allows you to quickly cope with vascular damage, but sometimes the blood clotting process is disrupted, and blood clots occur without external influence, creating a risk to health and life. Deep vein thrombosis most often occurs:
- in older people;
- in patients after laparoscopy or surgery on large joints;
- with severe physical inactivity;
- after fractures and ruptures of internal organs (accidents, fights, etc.);
- during pregnancy and childbirth - in pregnant women, blood clotting is increased;
- with long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- in smokers.
The main symptom of DVT, which occurs when the blood clot is located above the lower leg, is swelling and pain in the affected limb.
General symptoms of thrombosis
The disease is quite difficult to identify in the early stages, but there are a number of signs that should alert the patient:
- swelling of the limbs in the evening;
- the appearance of a network of dilated vessels;
- fast fatiguability;
- sudden lameness after exercise;
- cold extremities;
- difficulty breathing;
- pain in the chest and back after stress and physical activity;
- dizziness and tinnitus;
- problems with coordination of movements;
- bloating, indigestion. abdominal pain without clear localization.
Since the primary signs of thrombosis can also be a consequence of other diseases, a complete diagnosis of the body is necessary. The localization of problematic sensations is not always directly related to the area of thrombus formation. For example, dizziness can also occur with damage to the coronary arteries - due to tissue hypoxia.
Specific signs of a blood clot
If treatment of the disease is not started in the early stages, more distinct signs appear that make it possible to recognize a blood clot:
| Type of thrombosis | Symptoms |
| Deep veins of the leg | cold hands or feet, fatigue, low exercise tolerance, intermittent claudication after a long walk |
| Pulmonary artery | Sudden onset of shortness of breath, bluish skin with a gray tint, drop in pressure, chest pain, heart rhythm disturbances, bulging neck veins, fainting, cough, wheezing, pinkish sputum, increased body temperature, pain in the right hypochondrium. |
| Coronary arteries of the heart | Pain behind the sternum, radiating to the back and neck, occurs during stress, physical activity, and is accompanied by shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat. |
| Arterial network of the legs | Chilliness, numbness of the feet, burning, pain when walking, which stops when you stop, the skin becomes pale, and then the fingers turn blue. |
| Cerebral arteries | Dizziness, unsteadiness, various visual disturbances, unclear speech, decreased muscle strength and sensitivity in the arm and leg, memory loss. |
In general, the main symptoms of extremity vein thrombosis are:
- swelling;
- heaviness in the arms or legs;
- fatigue;
- redness and swelling of the skin in the area of the blood clot;
- pain on palpation along the vein;
- local temperature increase.
Thrombosis of deep veins and internal vessels is much more difficult to determine; as a rule, the patient learns about them from the doctor, and the initial complaint may not have any connection with the formation of a blood clot.
When to see a doctor
The patient’s subjective sensations are extremely important for timely diagnosis of the disease. That is why you should not delay seeing a doctor if:
- there was a feeling of fullness in the legs when walking;
- the limbs are decorated with vascular mesh;
- often the heart hurts or the left side of the body goes numb - angina pectoris;
- there were sudden problems with vision, hearing, diction, swallowing, coordination;
- cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, weakness appeared;
- the kidneys or one kidney are sick. There was blood in the urine.
It is worth noting that a timely visit to a doctor with such signs can protect patients from heart attack, stroke, pulmonary embolism and other complications with high mortality.
Ekaterina Misheneva: “Don’t let the blood stagnate”
Today in Russia, mortality from cardiovascular diseases directly related to thrombosis is twice the European average and amounts to more than 1.5 thousand people per hundred thousand population. Ekaterina Misheneva, a cardiologist at the State Institution of the Republic of Kazakhstan "Cardiological Dispensary", spoke in an interview with Respublika about what kind of disease this is and who is susceptible to it.
– So what is thrombosis?
– Thrombosis is a blockage of a vessel with a blood clot, while blood does not enter the organ, and it may suffer. Most often, a person's limbs are affected. In the body of a healthy person, the formation of such a clot helps stop bleeding. For example, if you cut yourself or have your blood taken for a test, the bleeding will stop after a while. But sometimes it also happens that thrombosis occurs when it should not exist, that is, for no apparent reason. Sometimes this causes myocardial infarction (a blood clot in the arteries that supply the heart muscle) or a stroke (a blood clot in the arteries of the brain). And this can threaten not only health, but also life. Such thrombosis can also occur due to certain characteristics of genes, i.e. hereditary information recorded in the cells of your body. Therefore, if a person wants to connect his life with a profession that involves high-risk situations, for example, working as a rescuer, police officer, or in professional sports, he should undergo a molecular genetic examination. Problems begin when blood clots, attaching to the walls of blood vessels, form a plug, which at any moment can break off, set sail through the veins and arteries and, once in a bottleneck, completely block the blood flow. And the man suddenly dies. Everyone is afraid of plane crashes, but few people know that after a safe landing you can collapse dead right on the plane's ramp - due to a blood clot that has formed in the veins during the flight. It is believed that blood clots form in one of the passengers on every flight. Fortunately, not every case ends in tragedy. According to statistics, 70 percent of people experience thrombosis.
– Why do blood clots occur? Can the danger be identified? And how to protect yourself from the threat?
- Let's figure out why blood clots occur in the veins. For blood clots to form, a combination of three factors is necessary. The first factor is damage to the inner surface of blood vessels (occurs after traumatic, tumor or inflammatory diseases). The second is a slowdown in blood flow (occurs with heart failure, prolonged bed rest and varicose veins). And the third is increased blood clotting (noted during injuries, inflammatory processes, surgical interventions and dehydration). Sometimes one reason is enough. If all three are present, thrombus formation is inevitable. There are two types of thrombosis - venous and arterial. Venous is more common. It is dangerous for its complications, the most severe of which is thromboembolism (blockage of branches) of the pulmonary artery. Surgeons claim that this diagnosis explains a third of cases of sudden death. More than half of patients die in the first two hours after the onset of embolism. Arterial blood clots are less common, but they are more insidious. Being in fast blood flow, they more often come off, first causing disruption of the blood supply to the organ that the artery supplies with blood, and then its death. Thus, thrombosis of the coronary arteries leads to myocardial infarction, and of the cerebral arteries - to a stroke. Veins are quite delicate and easily wounded anatomical formations. Their walls are much thinner than those of arteries of the same diameter. Blood pressure in the veins is much lower, so the middle (muscular) layer is less developed. Veins are less resistant to external compression and injury; they are easily involved in the inflammatory process even without the participation of microorganisms. In addition, the veins have valves, damage to which and stagnation of blood in the area where they are located contribute to the formation of blood clots. Maintaining blood in a liquid state is ensured by the simultaneous operation of a huge number of complex biochemical mechanisms. They maintain a precise balance between the coagulation and anticoagulation systems of the blood. There are a large number of typical situations, well known to doctors, in which venous blood flow is simultaneously disrupted and the coagulation system is activated. For example, during any surgical operation, a large amount of tissue thromboplastin, a substance that stimulates blood clotting, enters the bloodstream from the tissues. The more severe and extensive the operation, the greater the release of this substance. The same thing happens with any injury. This mechanism was formed in ancient times, and without it humanity as a biological species simply would not have survived. Otherwise, any injury to our distant ancestors, and to us, would have ended in death from bleeding. The body as an integral system is indifferent to what caused the wound - the claws of a saber-toothed tiger or a surgeon's scalpel. In any case, the blood clotting potential is rapidly activated. But this protective mechanism can often play a negative role, since it creates the preconditions for the formation of blood clots in the venous system in operated patients.
– It is clear that any operation is a risk.
– On the first day after surgery, it is difficult for the patient to get up, move and walk. This means that the work of the muscular-venous pump is turned off and venous blood flow slows down. In case of injuries, in addition, it is necessary to apply plaster casts, skeletal traction, and connect bone fragments with metal pins, which sharply limits the patient’s physical activity and contributes to the occurrence of thrombosis. Its incidence after surgical operations on the abdominal organs can reach 25-40 percent. With hip fractures, knee and hip replacements, thrombosis in the deep veins of the legs develops in 60-70 percent of patients. The most serious problem is venous thromboembolic complications during pregnancy. The fact is that a woman’s body itself prepares in advance for childbirth, and therefore for blood loss. Already from the early stages of pregnancy, the blood coagulation system is activated. The inferior vena cava and iliac veins are compressed by the growing uterus. Consequently, the risk of thrombosis increases. Acute venous thrombosis may complicate the use of hormonal contraceptives. These drugs seem to deceive the woman’s body, “convincing” it that pregnancy has already occurred, and hemostasis naturally reacts by activating the coagulation system. Although pharmacologists try to reduce the hormone content, primarily estrogens, in these drugs, the incidence of venous thrombosis (and therefore the possibility of pulmonary embolism) in women taking hormonal contraceptives is at least 3-4 times higher than in those taking hormonal contraceptives. who doesn't accept them. The risk of blood clots is especially high in women who smoke, since nicotine releases thromboxane, a powerful blood clotting factor. Excess weight also actively promotes thrombus formation. Venous thrombosis is a common complication of neoplasms, both malignant and benign. Patients with tumors usually have increased blood clotting. This is apparently due to the fact that the patient’s body prepares in advance for the future disintegration of the growing tumor. Often, venous thrombosis acts as the first clinical sign of the onset of a cancer process. Even a long flight in a cramped airplane seat, with legs bent at the knees, and forced inactivity, can provoke vein thrombosis, the so-called “economy class syndrome.” Thus, any surgical intervention, any injury, pregnancy, childbirth, any disease associated with the patient’s immobility, circulatory failure, can be complicated by venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. This is precisely what explains such a high incidence of venous thromboembolic complications, even in countries with well-developed medicine.
– How to determine thrombosis by external signs? And who is more susceptible to this disease?
– The insidiousness of venous thrombosis also lies in the fact that its clinical manifestations do not cause the patient a feeling of great distress. Swelling of the leg, pain, usually of a moderate nature, and slight cyanosis of the limb do not frighten patients, and sometimes they do not even consider it necessary to see a doctor. In this case, without any warning, a blood clot can break away from the vein wall in a few seconds, turn into an embolus - a blood clot that migrates through the vessels, and cause severe thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries with an unpredictable outcome. According to experts, about 100,000 people die annually from pulmonary embolism in the Russian Federation. Thus, this disease claims more lives than car accidents, regional conflicts and criminal incidents combined. Due to its transience and unpredictability, pulmonary embolism is perceived as a bolt from the blue not only by patients, but also by doctors. Fortunately, not every venous thrombosis is complicated by thromboembolism, although their number is very high. Blood clots are more often found in older people. Physical inactivity that accompanies a sedentary lifestyle provokes blood stasis - one of the main risk factors for the disease. One of the common causes of arterial thrombosis is atherosclerosis. Atherosclerotic plaques cause narrowing of the arteries. Blood flow becomes difficult, and favorable conditions arise for the formation of thrombosis. The relationship between smoking and the formation of atherosclerosis, and therefore the occurrence of blood clots, has been proven. But most often people who have a tendency to form blood clots - thrombophilia - are at risk of thrombosis. It can be genetic, associated with gene damage, and be inherited. And in some cases it may be caused by an imbalance of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems.
– Blood clots often form in the summer, why?
– There are several reasons for this. The main thing is travel, or rather, the air travel that accompanies it. Air passengers sit for a long time in uncomfortable positions, veins are pinched, and low pressure and extremely dry air in airplane cabins contribute to blood stagnation and rapid dehydration of the body. To avoid blood clots, before the flight you need to tighten compression hosiery (it improves blood flow in the legs), take a quarter of an aspirin tablet, which reduces blood viscosity. And during the flight, stretch your legs more often: try to get up and walk around the cabin after the plane has gained altitude, every 30 minutes. The second reason is the summer desire to lose weight. Blood clots are more likely to form in women who are on diets (removing excess fluid from the body is the basis of diets, and this is where dehydration of the body begins) or taking birth control pills (they increase blood clotting).
– Is it possible to sense the lurking danger?
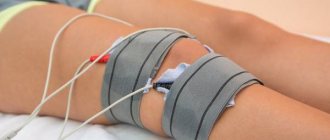
– Symptoms of venous thrombosis are heaviness in the muscles (usually the calf muscles), swelling of only one lower limb, hardening along the veins, bluish skin, pain. If venous thrombosis is complicated by thromboembolism in the pulmonary arteries, then in addition to swelling and pain in one of the extremities, pain in the chest, aggravated by breathing, cough, hemoptysis, and increased body temperature are added. Often such patients are treated by a neurologist diagnosed with intercostal neuralgia or by a therapist diagnosed with pneumonia. Sometimes such “minor” embolism may not manifest itself at all until repeated episodes lead to more severe changes in pulmonary blood flow. Signs of arterial thrombosis depend on where the blood clot is located. With arterial blood clots in the arms or legs, patients complain of sharp pain, coldness in this limb and loss of sensitivity. If it is the arm, then it is often difficult to measure blood pressure or impossible to measure it at all. Blood clots in the abdominal arteries cause vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Thrombosis of the cerebral arteries can manifest as a stroke. Blood clots in the coronary arteries - myocardial infarction - severe pressing or burning pain in the chest. However, about 30 percent of venous thrombosis may be asymptomatic. They are the most dangerous. To detect them, you need to undergo examinations. As a rule, routinely detected blood clots are not removed, but dissolved with special preparations.
– How are thromboses treated?
– The fight against deadly thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries is primarily a fight against acute venous thrombosis. Of course, it is much more effective to prevent thrombosis than to treat it. That is why the problem of preventing venous thromboembolic complications is now attracting the attention of doctors of various specialties. This is why surgeons, oncologists, gynecologists, physical therapy doctors so persistently try to get their patients out of bed the next day after surgery, or even on the same day, in order to take a few steps around the ward (often hearing accusations from their patients of all the deadly sins ). By the way, the common phrase “movement is life” comes to mind in this case. If thrombosis of the main veins has already developed, then doctors direct all efforts primarily to preventing pulmonary embolism. Previous attempts to remove the thrombus completely turned out to be futile, since against the background of altered hemostasis, a new thrombus appears on the inflamed vein wall, more friable and even more dangerous. Venous thrombosis does not threaten the vitality of the leg, since the arteries that pass through the blood flow regularly bring oxygen and nutrients. Venous gangrene is a very rare complication; it develops if blood clots close absolutely all veins, both deep and subcutaneous. Therefore, simultaneously with antithrombotic or anticoagulant therapy aimed at preventing the growth and spread of a blood clot, the patient is examined to identify floating, embolic forms of venous thrombosis. For a long time, only phlebography was used for this, that is, x-ray examination of the main veins using a contrast agent. Currently, most patients can be diagnosed using ultrasound techniques. First of all, this is an ultrasound examination of the veins, which does not require puncture of the veins, the introduction of a toxic contrast agent and, which is very important, especially when examining pregnant women, is not associated with irradiation of the patient. At the same time, the information content of the study is not inferior to phlebography. But the most dangerous, often catastrophic course of the situation occurs when a pulmonary embolism has already occurred. Thromboemboli are usually large in size, and in most patients they close the pulmonary trunk or main pulmonary arteries.
– So how to protect yourself from blood clots?
– First of all, lead an active lifestyle - physical activity improves blood circulation, prevents blood stagnation, and improves metabolic processes in the body. It is necessary to eat properly - the basis of the diet should be plant foods that do not contain cholesterol. The body should not be dehydrated—lack of fluid increases blood viscosity. Take care of yourself: injuries, operations, infectious diseases are a risk factor for blood clots. Get tested on time. Ultrasound duplex scanning of veins, during which the diameter of the vein is measured and the speed of blood flow is determined. Often the blood clot itself can be seen on ultrasound. Donate blood for cholesterol, undergo a coagulogram (blood clotting test). Get a blood chemistry test (a high level of an indicator called D-dimer is a key indicator of thrombosis, but can be elevated in other diseases). In-depth studies for thrombophilia are quite expensive to do for anyone concerned about their health, but we still recommend them when one of the relatives (father, mother, brothers, sisters, uncles, aunts, grandmothers, grandfathers) have had thrombosis in the family or thromboembolism, as well as cases of sudden death of relatives under the age of 55 years. Or in case of thrombosis in a person under the age of 50 years. We also recommend it in case of causeless recurrence of thrombosis of any location. These examinations are necessary to determine a more accurate treatment method. Modern medicine has a wide range of tools for diagnosing and treating acute venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Nevertheless, it should be remembered that the best way to combat this most dangerous complication is prevention, carried out in collaboration between the doctor and the patient. The fight against excess weight, uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs, smoking, physical inactivity, conscious and active implementation of medical recommendations can significantly reduce the frequency of tragedies and misfortunes caused by this disease.
What can a doctor do?
Depending on the severity of the condition, the doctor may:
- Order a test for thrombophilia.
- Prescribe Doppler examination of blood vessels.
- Prescribe an ultrasound of the veins.
- Refer to a more specialized specialist - with DVT to a phlebologist, with intestinal vein thrombosis - to a gastroenterologist, with a threat of coronary artery thrombosis - to a cardiologist.
- In severe cases, ensure urgent hospitalization.
- If you detect a blood clot that has not yet come off, completely covering large vessels, or if the blood clot breaks off, insist on surgical intervention.
- If a blood clot is diagnosed early, conservative treatment should be prescribed. For example, the drug Fazostabil has proven itself well as a means of promoting the resorption of blood clots and preventing their re-formation.
In addition, the specialist will be able to identify other diseases that can produce similar symptoms and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Trust your doctors!
You should not trust doctors in matters of treatment. According to Drobyazgo, medicine has made a huge step forward over the past year. Drugs such as tableted anticoagulants have appeared - these are the drugs that disappeared from the shelves, but have now reappeared.
“Previously, we only had injections, or there were drugs that were quite dangerous. Now there are drugs that have proven themselves very well, there are very few side effects and risks of bleeding, but they still exist, so you need to take them only for the appropriate indications,” the doctor noted.
In addition, doctors are now less and less forced to subject patients to any surgical procedures. In many cases, patients with thrombosis are not even hospitalized, but are left to be treated on an outpatient basis according to the recommendations of doctors.
Press service of NIIZMM DZM /
If the blood clot comes off
The thrombus is not always firmly attached to the wall of the vessel. When a clot is superficially attached, a simple surge in pressure, a blow, or a careless movement is enough for the clot to come off and travel through the circulatory system. Moving through the vessels, the detached thrombus sooner or later reaches the most important organs, and usually the pulmonary vein, if the thrombus was venous, or the left atrium, if arterial.
Pulmonary thrombus
In the most dangerous cases, blockage of the large vessels of the lung occurs, after which death occurs within a few minutes. A less severe option is infarction-pneumonia, when a blocked vessel bursts and the lungs begin to fill with venous blood, which is accompanied by acute pain and hemoptysis. In this case, the patient has every chance of survival.
The mildest case, when a blood clot enters the pulmonary veins, is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure in the lungs, pain, shortness of breath, and suffocation. If you call an ambulance right away, the patient is likely to survive.
Coronary thrombus
If a blood clot located in the left atrium or coronary arteries breaks off, the patient is at risk of: myocardial infarction, stroke if the blood clot enters the brain through the bloodstream, infarction of the intestines or kidneys if the arteries leading to them are blocked, as well as blood stagnation and gangrene with subsequent loss limbs if the blood clot gets into the large arteries of the arm or leg.
What foods should be included in the diet
Foods rich in vitamin E. Vitamin E (tocopheryl acetate) is also called the “vitamin of youth”. It strengthens the walls of blood vessels, making them more elastic - and also participates in the formation of collagen and elastic fibers of the intercellular substance.
In addition, vitamin E ensures tissue regeneration and maintains normal levels of blood clotting - which is especially important in the context of preventing the development of thrombosis.
Vitamin E also has an anti-carcinogenic effect and helps strengthen the immune system. It also protects the cell structure from destruction by free radicals - in a word, a real little guardian of our health!
Treatment of thrombosis
Treatment of thrombosis requires an integrated approach. There are modern techniques that allow you to dissolve a blood clot by introducing special drugs directly into the vessel. This method is justified in cases of immediate threat to life, since it prevents blood clotting for a long time and makes any injury dangerous.
More conservative methods involve the use of compression hosiery, installation of a vena cava filter to catch blood clots, as well as a number of drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid - they help restore normal blood clotting.
The duration of drug therapy is determined by the doctor.
Folk remedies in the treatment of thrombosis
In the treatment of thrombosis, folk remedies that provide thrombus resorption or thrombolysis can be used in parallel with medications. As a rule, doctors recommend:
- Turmeric, which contains curcumin, which helps dissolve blood clots.
- Garlic contains sulfur compounds that are effective in combating clots.
- Peppers: red, chili, hot - contain salicylates and protect against the formation of new blood clots.
- Flaxseed is a storehouse of Omega-3s that improve blood circulation. In combination with fatty red fish, they not only reduce the risk of thrombosis, but also increase the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels.
- Peppermint infusion helps lower blood pressure, reduce blood clotting, and dissolve newly formed clots.
The use of folk remedies must be coordinated with your doctor, since too much blood thinning can lead to internal bleeding and even death!
Prevention of thrombosis and re-formation of blood clots
A number of factors that provoke the formation of blood clots do not depend on the individual, however, even in the case of autoimmune disorders and hereditary predisposition, the risk of thrombosis can be reduced.
- Movement. Stagnation of blood due to a sedentary lifestyle contributes to damage to the veins, so you need to walk, walk, and play active games.
- Nutrition. The development of atherosclerosis and arterial thrombosis is facilitated by the abuse of trans fats, fast carbohydrates, bad cholesterol, alcohol, etc. Switching to a healthier diet will reduce your risk of developing many diseases.
- Wearing compression stockings. Recommended for pregnant women, people with varicose veins, as well as during and after operations. The degree of compression is determined by the doctor.
- When immobile for a long time, for example, on an airplane, it is necessary to wear loose clothing and take the most relaxed postures. Do not cross your legs to avoid blood stagnation.
- Older patients are recommended to take prophylactic medications that reduce the risk of blood clots.
To avoid re-formation of a blood clot, you should follow your doctor’s recommendations and respond as carefully as possible to all sensations in your body.
How does a blood clot form?
Blood is necessary for a person to live. It circulates through the vessels, delivering nutrients and protective elements to the organs, which help in the fight against viruses and bacteria. If a person is injured, the blood clots, thereby blocking their access to the body. The ability of blood to form clots and clog the lumen of a vessel with them can sometimes play a cruel “joke” on a person, which will lead to disability or even death.
Blood has fluidity so that it can clot at the right moment; the mechanisms of the coagulation system are activated. It triggers the formation of protein fibrin threads, which clog the vessel, preventing excess blood from leaking out.
The human body also has an anticoagulant system that fights the formation of blood clots in those tissues that have not lost their integrity. If at some point there is a malfunction in the functioning of these two systems, then blood clots begin to form in the vessels.
They are located near the inner wall of the vein, going through several stages:
- A blood clot begins to grow in the place where the vessel is damaged and inflamed. Most often this happens against the background of thrombophlebitis. The body reacts to an inflamed vessel by activating the blood coagulation system. It triggers the production of fibrin fibers, which are concentrated near the site of inflammation.
- Red blood cells and platelets begin to become entangled in fibrin fibers.
- New blood cells that are brought in with the bloodstream continue to “stick” to the clot, making it larger and larger. It increases in size, becomes denser and can come off at any moment.
Blood clots can also form in arteries when the vessel narrows. Cholesterol plaques that have grown on the arterial walls are an obstacle to normal blood flow, as a result of which a clot of fibrin threads and platelets begins to grow.
Risk factors for blood clots:
- Belonging to the male gender, over 40 years of age.
- Belonging to the female gender, over 50 years of age. An increased risk of thrombosis is caused by menopausal changes in the body.
- Dehydration of the body.
- A cancerous tumor of a malignant nature.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Serious errors in nutrition.
- Taking certain medications. Hormonal contraceptives pose a particular danger in terms of blood clot formation.
- Postponed surgery.
- Disruption of the normal flow of blood through a vessel as a result of its compression.
- Pregnancy.
- Vein injuries in the legs.
- Heart failure.
- Infections.
Blood clots that form in large vessels pose a danger to human life. Their separation will lead to the rapid death of the patient.