Any adult measured their blood pressure. The normal value of the parameter should be within 120 to 80 mmHg. If the number increases, it is called hypertension. If the value is reduced, hypotension is detected. It is important to know what these numbers mean to understand the patient's condition.
Upper and lower pressure value
Blood pressure is the value of the degree and strength of systemic blood flow spreading inside the vessels. It helps to identify the condition of the following parts of the cardiovascular system:
- arteries, veins;
- arterioles, venules;
- capillaries;
- heart.
The characteristics of blood pressure depend on the following indicators:
- blood resistance;
- the volume of circulating blood formed after a single contraction of the heart muscle (systole);
- quality of myocardial contraction.
The following types of blood pressure indicators are distinguished:
- the highest
- observed during the period of contraction of the left ventricle, leading to the ejection of blood; - the lowest
is the transition of blood flow to the right atrium with relaxation of the myocardium (diastole).
Systolic or upper pressure is the degree of saturation of blood vessels that occurs during the contraction of the heart muscle. This is an indicator that characterizes the quality of heart activity. Activity is generated due to the functioning of large arteries. The most important of them is the aorta. Systolic pressure indicators depend on the following factors:
- left ventricular stroke volume;
- degree of elasticity of the aortic walls;
- the maximum rate of blood ejection from the heart into the vessels.
Diastolic or lower pressure is an indicator that indicates the resistance that forms during the passage of blood through the vessels. At this point, the aortic valve becomes closed, so blood does not move back into the heart. But during this period, the heart tissues prepare for the arrival of other blood, which is already saturated with oxygen. Therefore, re-cutting is required. Biological fluid moves through the heart and blood vessels passively.
Mildronate is a cardioprotective, antihypoxic, angioprotective drug based on meldonium. It is a derivative of gamma-butyrobetaine, that is, it is a synthetic version of B vitamins. Read more in the article: “cheap analogues of mildronate in tablets.”
The following factors influence diastolic pressure:
- number of contractions of cardiac tissue in 1 minute,
- peripheral vascular resistance.
The difference between systolic and diastolic pressure in a healthy human body should be 30-40 mmHg. This indicator depends on the person’s well-being and the state of the cardiovascular system.
Retinal detachment is an eye disease in which the retina separates from the underlying lining of the eyeball. Without timely and correct treatment, the pathology leads to blindness. Read more in the article: “retinal detachment as the eye sees.”
Since each organism is individual, the numbers cannot be identical for each patient. But we can judge the presence of the following criteria for blood pressure:
- upper
- 120 mmHg; - lower
- 80 mmHg.
These indicators are typical for a normal blood pressure within 120 to 80 mmHg.
The following factors influence the overall blood pressure:
Advertising:
- quality of lifestyle;
- food consumed daily by a person;
- the presence or absence of bad habits;
- stress, depression, nervous tension.
For example, some types of food can increase or decrease the indicator. Caffeine increases blood flow through the vessels.
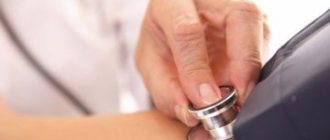
How to measure blood pressure correctly?
To obtain reliable blood pressure readings, you need to take measurements in a quiet environment at room temperature. For about an hour, it is not advisable to smoke or drink strong coffee or tea. For half an hour you need to eliminate physical activity. Your feet should be on the floor and your hands should rest freely at heart level.
There are a few more simple rules:
- During the measurement, you cannot move, talk or cross your legs;
- The cuff should fit snugly on the arm, but not squeeze it;
- If several measurements are required, at least 5 minutes must elapse between them;
- The cuff is selected so that it covers at least 80% of the shoulder circumference. If you have to hold the Velcro with your hand, the results will be incorrect;
- In the absence of back support, the indicators may be overestimated.
Doctors often refer to the so-called “working pressure”. The fact is that, depending on the state of the body and its individual characteristics, the interval of the upper and lower indicators may differ for different people. Working blood pressure is the blood pressure at which a person remains in good health. This could be, for example, 130/90 or 115/80.
There is only one way to determine your working pressure: measure it regularly. Then you can find out what values the tonometer shows when a person feels well. This is an important nuance, since with a reduced operating pressure the same 130/90 can be considered as a significant increase, although the numbers themselves are within the norm.
The need to determine blood pressure
If the flow of blood into the heart and the tension in the blood vessels increases, each time the blood pressure increases by 10 mmHg. This leads to an increased risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies. If the patient suffers from chronic arterial hypertension, the following pathologies may develop:
- cardiac ischemia;
- hypertonic disease;
- stroke, heart attack;
- vascular damage in the lower extremities.
Initially, with an increase in blood pressure, dizziness, headache, and a sharp loss of strength appear. In this case, you need to consult a doctor, constantly check the indicator, and begin timely treatment.
Reasons for the growth of indicators
Increased diastolic pressure is most often accompanied by an increase in systolic pressure with a pulse difference of about 40 mmHg. Art. This may be due to both physiological factors, such as overwork, stress, changing weather conditions, overeating, hypothermia, etc., and to a number of serious pathological processes, namely:
Why is low blood pressure high?
- hormonal disorders;
- problems in the functioning of the heart, both congenital and acquired;
- poisoning;
- allergic reactions;
- atherosclerosis;
- changes in blood composition;
- tumor processes.
Increased blood pressure is typical for women during pregnancy and menopause. This is a normal reaction of the body to changes and hormonal fluctuations occurring in it. The risk group for developing hypertension includes people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, do not adhere to generally accepted dietary rules, consume large amounts of salt, smokers and alcoholics.
The symptoms of hypertension at the initial stage are blurred and are usually mistaken by a person for banal fatigue at work. Later, as the disease develops, high blood pressure is accompanied by:
- severe headaches;
- the appearance of black spots before the eyes;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- chest pain that gets worse with exercise;
- shortness of breath;
- feelings of anxiety and panic.
When the pulse difference is low (20 mmHg), this indicates that diastolic blood pressure is increasing without reference to the upper one. This picture is typical for diseases of the kidneys, thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
Method of measuring blood pressure
Advertising:
Blood pressure is examined using a specialized blood pressure monitor. It is recommended to adhere to step-by-step methods of carrying out the procedure so as not to obtain overestimated or underestimated results.
- Select a cuff size that fits the shoulder.
- Provide the best conditions. The person should not be under stress or physical activity. The temperature should be room temperature, not cold or excessively warm.
- Taking into account additional factors. It is recommended to measure the indicator 1 hour before active physical activity, eating food and coffee, or smoking.
- Select the optimal table level. It should be of such a height that the cuff on the arm is located in the area of the intercostal line. If it moves by 5 cm or more, the degree of blood pressure will decrease or increase. The error will be 4 mm.
- Location of the pressure gauge scale. It should be at eye level so that the patient does not make mistakes during the procedure.
- Patient location. He should sit straight, leaning on the back of the chair. The body should relax, the legs should be placed straight, and should not be crossed. The hand for measuring pressure is placed on the table and relaxed. Parts of the body should not be tense during the procedure.
- Air pumping. The approximate state of the patient's blood pressure is assessed. During the pumping process, wait until the numbers on the tonometer reach this limit, then pump up another 30 mmHg. If the patient pumps the tonometer above this value, severe pain will begin in the arm.
- Reset. The first sound is formed, which is called the Short tone phase. This is an indicator corresponding to the upper value of blood pressure. When these tons completely disappear, phase 5 will form. This indicator will correspond to the lower pressure criterion.
- Repeated study. It can be carried out only 5-7 minutes after the initial use of the tonometer. During the analysis, the average indicator is calculated, which will be the most accurate and optimal for the patient. A one-time procedure may show an error.
- The first analysis is performed on both hands at once. A secondary study is carried out on only one upper limb.
If the heart rhythm is disturbed, measuring blood pressure becomes difficult. Therefore, it is recommended to evaluate the indicator only with the help of medical personnel.
Causes of high blood pressure
Doctors most often record an increase in blood pressure in people with a hereditary predisposition and/or diseases of other organs and systems (pheochromocytoma, hyperthyroidism, atherosclerosis, diabetes, etc.), leading to the development of hypertension as a symptom.
The mechanism of blood pressure increase is realized in two ways:
- neurogenic – vasoconstriction through the response of the sympathetic nervous system;
- humoral – release of vasopressors (catecholamines, renin-angiotensin, etc.) into the blood.
Also important is the disruption of the depressor system, which is responsible for vasodilation.
At the same time, a number of factors that trigger the process of hemodynamic disturbances have long been identified:
- excess weight;
- little daily activity;
- poor nutrition, including preference for fast food, snacking on carbohydrate foods;
- chronic intoxication caused by smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction;
- mental and physical stress;
- lack of sleep;
- hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, menopause;
- abuse of salt in the diet;
- elderly age;
- harmful working conditions;
- taking medications that can indirectly affect blood pressure (for example, hormonal contraceptives , appetite suppressants, etc.)
With high blood pressure, it is important to monitor the reduction of the influence of these factors in everyday life, which will help reduce the risk of developing the most threatening complications - stroke and heart attack.
Evaluation of results
Advertising:
After receiving the results, it is important to evaluate 1 parameter:
- presence of normal blood pressure:
- arterial hypertension;
- arterial hypotension.
In 1999, a table was developed, according to which it is possible to determine the norm and increase in the level of pressure that negatively affects the patient.
| Pressure parameters | Upper, mmHg | Lower, mmHg |
| The best | 120 | 80 |
| Normal limits | 130 | 85 |
| Increased performance | More than 130 | More than 85 |
Attention! To assess the quality and degree of activity of the cardiovascular system, they look at the upper and lower values in combination. If they differ significantly, choose the parameter that has increased.
The table shows the degree of development of arterial hypertension, hypertension and pressure indicators:
| Degrees of hypertension | Upper value, mmHg | Lower value, mmHg |
| 1 | 140-160 | 90-100 |
| 2 | 160-180 | 100-110 |
| 3 | More than 180 | More than 110 |
| Border | 130-140 | No more than 90 |
| Systolic hypertension | More than 140 | After 90 |
Normal diastolic pressure
The optimal values of cardiac and renal pressure directly depend on a person’s age, gender, lifestyle, and weight. But if we talk about the average indicators of lower pressure, they are as follows:
- 90 mmHg Art. – upper limit of normal;
- 91-105 mm Hg. Art. – arterial hypertension at the initial stage;
- 106-115 mm Hg. Art. – hypertension of the second severity;
- above 115 mm Hg. Art. – severe stage of hypertension;
- 130 mmHg Art. – a malignant form of hypertension that is practically uncorrectable.
Normal blood pressure by age – from birth to 64 years and older
Treatment of high blood pressure
The main goal of therapy for high blood pressure is to reduce its levels to normal and the maximum possible correction of risk factors (fighting smoking, alcoholism, losing excess weight, doing morning exercises), as well as slowing down the damage to other organs.
Taking into account anamnestic and objective data, various medications are prescribed for hypertension; their main groups are presented below:
- antihypertensive medications to lower blood pressure;
- disaggregants that reduce the risk of hemorrhagic complications;
- statins for correction of lipid metabolism;
- diuretics that indirectly reduce blood pressure;
- according to strict indications, a and/or β-blockers to correct myocardial contractility.
If high blood pressure is a sign of pathology in another organ, then treatment of the underlying disease will be key.
An important aspect in the treatment of high blood pressure is a balanced diet, in which you need to limit salt intake, eat more vegetables, nuts, fruits, healthy vegetable oils (olive, pumpkin). If possible, replace red meat with fish. Reduce the amount of calcium-rich dairy products in your diet.
Symptoms of diastolic hypertension
Hypertension, both systolic and diastolic, is usually manifested by the following symptoms:
- dizziness, cephalalgia, feeling of heaviness in the head;
- throbbing pain in the occipital or temporal region, often radiating to the eyeballs;
- pulsation in the head;
- “floaters” before the eyes and noise in the ears;
- facial skin hyperemia;
- tremor and numbness of fingers;
- irritability, anger, increased excitability;
- decreased performance;
- chills;
- sweating;
- tachycardia.
Attention!
Each patient may exhibit signs of high blood pressure individually. If you have frequent attacks of hypertension, you must have a blood pressure monitor and regularly monitor your condition.