Hematocrit - what is it, what does it depend on
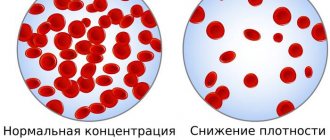
Hematocrit analysis provides data on the ratio of the volume of red blood cells to the total volume of blood; sometimes this indicator refers to the ratio of the volume of all formed elements to the total volume. There is no particular difference between the interpretations; 99% of the blood cell volume is made up of red cells. More often, hematocrit is recorded as a percentage of the total volume, less often as a ratio of cell volume to total blood volume.
This indicator is determined as part of a general blood test complex. It is classified as secondary and is calculated based on data on the number of red blood cells. Occasionally, direct measurement of hematocrit is performed by centrifuging the sample. This procedure allows you to separate plasma from formed elements and directly measure this indicator.
Increased hematocrit
An increase in hematocrit occurs with an increase in the number of blood cells - polycythemia - and a lack of fluid in the body. An increase in the indicator may indicate serious diseases accompanied by blood thickening and thrombotic complications.
Causes
Hematocrit increases due to stress, taking corticosteroid drugs and diuretics, traumatic shock accompanied by intense pain, as well as when climbing to high altitudes, smoking, or playing sports using anabolic steroids to gain muscle mass.
An increase in the indicator may indicate the following diseases:
- dehydration due to vomiting, profuse diarrhea, overheating or heat stroke, excessive sweating, insufficient fluids;
- heavy bleeding in the midst or immediately after it stops;
- pathologies accompanied by a decrease in blood plasma volume, for example, peritonitis, thrombosis, diabetes, burn disease;
- renal dysfunction - hydronephrosis, oncology, polycystic disease;
- vitamin B12 or iron deficiency anemia;
- leukemia;
- erythrocytosis;
- defects and coronary heart disease, heart failure;
- intestinal obstruction;
- bronchial asthma, pulmonary emphysema, obstructive bronchitis.
Symptoms
An increase in blood viscosity leads to thrombus formation. The latter can manifest itself in the form of tingling or various pains and numbness in the limbs. If the cause of increased blood viscosity is not determined in time, serious complications such as myocardial infarction, stroke, gangrene and even death may develop.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out not for the changed hematocrit level itself, but for the conditions or diseases that caused these changes. In some situations, when serious causes for a slightly changed hematocrit level have been excluded, no treatment is required. But usually such situations are short-lived, in the case of physiological reasons for changes in hematocrit levels.
Indications and preparation for analysis
Indications for hematocrit analysis are symptoms indicating the development of anemia or other diseases of the blood or hematopoietic system. These include:
- Pale or jaundiced skin
- Enlarged spleen, liver
- Changes in the size of lymph nodes
- Digestive disorders
- Skin and hair problems (rashes, ulcers on mucous membranes, hair loss or brittleness)
In addition to identifying anemia, the analysis allows us to identify other diseases, for example, polycythemia (a chronic disease in which the bone marrow produces an excess amount of red blood cells) of various origins. This study is also used when it is necessary to assess the need for blood transfusion and calculate the required volume of transfusion.
No special preparation is required for the hematocrit test. It is necessary to follow the standard rules for conducting a general blood test:
- Blood is drawn early in the morning.
- You should not eat food 6-10 hours before the test.
- Avoid alcohol 2-3 days before the procedure.
Patients who smoke are advised to abstain from smoking for at least 2-3 hours before blood collection. If these recommendations are not followed, the analysis may give unreliable results. This is due to the fact that the composition of the blood is subject to strong fluctuations depending on the action of various environmental factors.
Hematocrit test information
The hematocrit value shows the ratio of blood cells to plasma, expressed as a percentage. The research methodology is quite simple. It is necessary to collect venous blood from a small patient and place it in a tube with divisions. After which the tube with the test material is placed in a centrifuge and centrifuged at sufficient speed. As a result, the blood in the tube is stratified: formed elements (cells) settle at the bottom, and plasma accumulates on top of them.
Previously, when assessing the hematocrit value, the laboratory assistant independently assessed the height of the column of formed elements in the tube. The plasma-to-cell percentage was calculated manually. This could lead to some errors and inaccurate analysis results.
Currently, modern centrifuges are connected to computers that automatically read data and display it on a monitor screen. This eliminates the possibility of inaccurate data and makes the error minimal. However, instrument error, which varies among different measuring devices, should not be excluded. Therefore, if repeated tests are necessary, you should contact one laboratory department.
Main article: What is hematocrit in a blood test and its norms
When should I get tested?
The study is relevant for children with a routine visit to the clinic for examination. Hematocrit values are determined as part of a clinical blood test, which is prescribed to the child at each visit. Despite the low specificity of the study, it helps to make a preliminary diagnosis and get an overall picture of the state of health.
Hematocrit in the blood of children is measured after prolonged dehydration, as well as during bleeding in order to assess its severity. A final decision on the need for donor blood transfusion is impossible without the laboratory analysis in question. Analysis plays an important role in establishing the effectiveness of the methods that were chosen for the treatment of blood diseases.
Invalid analysis results
Having received a result that deviates from the norm, the pediatrician will prescribe a repeat test for the child. This is necessary to exclude false results that were obtained due to improper preparation of the child for the study or violation of the rules for collecting biomaterial.
Biomaterial for analysis is submitted on an empty stomach. It is permissible for children aged 1-2 years not to feed for 2-3 hours before taking biomaterial; for children 3-5 years old it is allowed to take a break after the last meal for 3-4 hours. Older children will have to refuse food for 8 hours. Therefore, it is advisable to take the test in the morning. You should give your child plenty of clean and unsweetened water. This will greatly facilitate the venipuncture process for a young patient and will avoid the need for repeated blood draws.
Venipuncture is an unpleasant and painful process for children. Many children get scared and cry a lot. In this condition, it is quite difficult to detect a vein for blood sampling. Incorrect application of a tourniquet for a long time leads to distortion of the obtained laboratory analysis results.
It should be emphasized that a deviation from the norm of one indicator is not enough to establish the exact cause of the disease. If a child's hematocrit is found to be elevated in duplicate tests, they will not be treated immediately. The pediatrician will select additional laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. Only after collecting anamnesis and collecting data from a comprehensive study, a final diagnosis is established and the necessary treatment is selected.
Blood test for hematocrit
The manipulation is performed in the morning, blood is taken from a vein or from a finger. At the Medart clinic, the most modern equipment is used for analysis, so the sampling is most often done from a vein.
To obtain the material, special vacuum containers (vacutainers) are used. This is a modern syringe replacement that provides a number of benefits for the patient:
- Virtually painless procedure.
- Minimum time to obtain the required amount of blood.
- Accurate calculation of the amount of reagent and blood.
- Minimum time for conducting the study and issuing results to the patient.
Modern technologies allow the procedure to be carried out as quickly as possible, without consequences for health.
What does it mean and what does it mean if the hematocrit is elevated in a child?
The main reasons why a child’s hematocrit increases:
- an increase in the total number of red blood cells in the blood (erythrocytosis);
- decrease in blood plasma volume;
- dehydration;
- leukemia
Let's take a closer look at each of the reasons - what causes them and how to treat them correctly.
Erythrocytosis
An increase in the level of red blood cells is observed in polycythemia vera in children. This is a benign pathology, which is characterized by an overly active process of red blood cell formation. Along with red blood cells, but to a lesser extent, the level of leukocytes and platelets increases. The resulting red blood cells have the correct morphological structure and are able to fully exhibit functional activity.
In patients, blood viscosity increases significantly, which disrupts the normal blood supply to organs and tissues. The supply of oxygen slows down, which over a long period of time can lead to organ hypoxia.
Polycythemia vera is a disease of adults, the average age is 55 years. However, the pathology can also affect children. The peculiarity of the course of the disease in them is a more severe condition and severity of clinical symptoms. Main symptoms:
- change in skin color to red or cherry, tongue and lips - to bluish-red;
- feeling of severe itching after hygiene procedures in warm water;
- short-term severe pain at the ends of the fingers or toes;
- frequent fatigue and headaches;
- decreased visual acuity;
- increased blood pressure.
When diagnosing pathology, the doctor pays special attention to blood tests, external signs of the disease and an increased tendency to form blood clots in the vessels.
For treatment, methods are used that are aimed at reducing the degree of blood viscosity. The leading method of therapy is bloodletting. It allows you to reduce the total volume of blood (red blood cells) and return the hematocrit to normal values. A well-known technique is erythrocytepheresis, when certain blood cells, in particular red blood cells, are removed from the patient.
Decrease in blood plasma volume
A similar condition is observed in burn disease and peritonitis.
Burn disease develops in people whose skin lesion area exceeds 10%. In children, the percentage of affected area for the development of the disease may be reduced. A favorable outcome is expected with timely and competent provision of medical care. After restoration of functional activity, the patient may require transplantation of the affected areas of the skin.
Peritonitis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the peritoneum, which is normally sterile. The condition poses a serious threat to life and is accompanied by an extremely serious condition.
In children, the pathology develops rapidly and is much more aggressive than in adult patients. In 75% of cases in newborn babies, peritonitis leads to death. Therefore, the provision of medical care must be urgent.
A particular difficulty for timely diagnosis is that the child cannot specifically identify the area that hurts. Babies with peritonitis cry non-stop and do not latch on to the breast. They have blood clots in their stool and a constantly elevated temperature. The cause of the disease in newborns is intestinal volvulus or ischemic infarction.
Norms
The normal hematocrit level depends on the age and gender of the person. For a mature woman it is 37-50%, for a man 34-45%. For newborns, this figure may be higher and ranges from 35 to 65%. As people grow older, the hematocrit decreases, reaching minimal levels in the elderly. This is the result of decreased bone marrow activity and decreased production of blood cellular elements.
A decrease in normal hematocrit in women is associated with regular blood loss during menstruation. High values in children are a manifestation of active processes in the development of red bone marrow and other hematopoietic organs.
It is important to consider that after massive blood losses and blood transfusions, determining the hematocrit level will give results with a large error. To reliably assess this indicator in such cases, it is necessary to wait a certain time.
It may take up to 3 months for complete physiological restoration of red blood cell levels to normal levels. This period is the life cycle of red blood cells, during which the cellular composition of the blood is renewed.
Symptoms
The clinical picture is fully dictated by the etiological factor. However, each variant of the pathology described has several specific external manifestations.
If the hematocrit in the blood of children is increased, the following symptoms may appear:
- severe or mild dizziness;
- breathing problems – parents note that the child has difficulty breathing;
- numbness of hands and feet;
- constant nausea that does not end with vomiting;
- weakness that persists on a permanent basis;
- fast fatiguability;
- decreased physical activity;
- partial loss of orientation in space.
A low level of hematocrit in the blood is represented by:
- general malaise;
- shortness of breath, appearing even at rest;
- rapid fatigue;
- increased heart rate;
- constant headaches;
- increased tearfulness;
- pale skin;
- deterioration of hair condition.
It is these signs that should arouse suspicion among parents and become an impetus for seeking help from a pediatrician.
- High hematocrit in a blood test in adults and children - what diseases is it a symptom of, and their treatment
Hematocrit increased
An increase in the level of red blood cells detected in a hematocrit analysis may indicate various pathological conditions. The most common:
- Primary erythrocytosis. It occurs as a result of overactive production of red blood cells, including immature forms. May indicate the development of tumors in the bone marrow.
- Secondary erythrocytosis. Develops as a consequence of pathologies of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems (heart defects, respiratory failure).
- Reduced plasma volume. May indicate the development of peritonitis, leukemia, kidney disease. Often occurs with extensive burns, when blood plasma sweats through the damaged dermis.
- Dehydration. Observed in uncompensated diabetes mellitus, it can result from diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating and lack of fluid in the diet.
Erythrocytosis can develop in heavy smokers, especially if smoking has led to secondary damage to the respiratory system and heart. In this case, the body turns on mechanisms to compensate for insufficient oxygenation due to a significant increase in the number of red cells.
An increase in hematocrit is not always a consequence of disease. An increase in the number of red blood cells is considered normal for residents of mountainous areas and professional climbers. When exposed to high altitude conditions for a sufficiently long time, the body compensates for the lack of oxygen and atmospheric pressure by increasing the production of red blood cells.
Erythrocytosis is often asymptomatic and is discovered by chance during a blood test for other reasons. Only with a significant increase in hematocrit are the following observed:
- Pain in joints, muscles.
- Dyspnea.
- High blood pressure.
- Ringing in the ears and dizziness.
- Increased sweating, sleep disturbances.
These symptoms are not specific, so if such ailments occur, you should consult a doctor for further diagnosis.
To restore the physiological level of hematocrit, it is necessary to find out the reason that led to an increase in the amount of blood cells and eliminate it. For example, if erythrocytosis was caused by dehydration (lack of water in the body - dehydration), it is enough to restore the normal amount of fluid to normalize this indicator.
There is no need to self-medicate; only a specialist can accurately determine the cause of the increase in hematocrit and prescribe the correct diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, if there are any changes in the blood test, you should consult a specialist and strictly follow the recommendations received.
Hematocrit norm
A blood viscosity test is prescribed for people who have severe symptoms of dehydration, severe vomiting due to poisoning, or diarrhea. Biological indicators are affected by the age and gender of a person. Doctors have a special formula used to establish the hematocrit number. It is calculated as follows:
- The content of red blood cells is determined as a percentage or as a fractional component.
- The result obtained is multiplied by 0.001.
A high hematocrit in newborns is considered normal. The value of this indicator is 20-30% higher than in adults. Then the number of red blood cells decreases sharply. It is considered normal when the hematocrit value in the blood is 40-45%. In pregnant women, the number of red blood cells begins to decrease from the 20th week, and then returns to normal after childbirth. Sometimes the hematocrit number refers to the number of leukocytes, platelets and red blood cells. The number of the latter elements predominates in the blood.