Heart attacks, cardiac arrest and strokes are all serious conditions related to the heart, but too often people use the terms interchangeably without understanding the differences between the three. While the disorders are all (usually) related to the heart, they have different causes and symptoms, and it's important to know the characteristics of each so you can better identify and treat problems if they occur in your loved ones, or even yourself.
What is the difference between the three conditions?
Heart attack
It is a circulatory problem that occurs when arteries become blocked and the normal flow of oxygen through the blood to the chambers of the heart is prevented. The attack occurs when the coronary arteries, which are responsible for transporting blood to the heart, become smaller due to the accumulation of fatty substances, calcium and protein in them.
Over time, these deposits form a plaque that hardens on the outside. This can lead to rupture, causing blood clots to form around them. When these blood clots block the coronary arteries completely, blood cannot reach the heart, which ends up starving for oxygen. When this happens, the muscle cells in the heart begin to die and can become damaged, which is what constitutes a heart attack.
Location of the heart
Location of the heart in the body
Let's consider in detail:
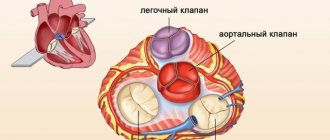
The heart is a hollow muscular organ with an approximate weight of 250-300 grams, located at the level of 5-8 thoracic vertebrae with a predominant displacement to the left half of the chest, and has four chambers in its structure, separated by thick muscular partitions. Between these partitions are the heart valves, which allow blood to flow in only one direction. The size of the heart can increase as a result of the development of a number of certain diseases, as well as during intense physical activity, for example, when playing sports.
The heart has reliable protection - the pericardial sac or pericardium. This is the top layer of the heart wall. Next comes the dense muscle layer or myocardium. The inner lining of the heart is called the endocardium.
Our heart constantly needs nutrition in the form of oxygen and nutrients. This nutrition is provided by the coronary vessels through the circulatory system, in which the heart performs the pumping function. As we see, the heart is a complexly organized organ that contracts continuously, with short pauses for rest, which are measured in seconds. Therefore, this organ requires careful treatment and regular examination, especially after 40 years.
The classification of heart diseases is quite large, ranging from various heart rhythm disturbances, inflammatory diseases of the membranes, hypertension, malformations (congenital or acquired), heart vascular diseases and ending with acute vascular disorders that develop mainly against the background of coronary heart disease, which we will talk about in this article.
Heart disease has become younger. Nowadays you won’t surprise anyone with “young” heart attacks, which are more common in men even at the age of twenty.
Stroke
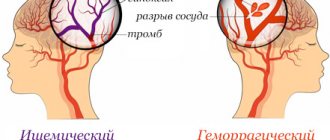
Stroke, also known as CVA, is actually a brain disorder that is often (but not always) caused by heart problems. This occurs when blood flow to the brain is reduced to the point where cells in the brain begin to die. There are two main types of stroke:
Ischemic: Resulting from blockages in the arteries, resulting in a lack of blood flow to the brain and the death of brain cells. This type of stroke involves the heart and circulatory system and is often confused with a heart attack or cardiac arrest.
Hemorrhagic: Caused by bleeding, usually caused by a rupture of an artery in the brain itself. They can sometimes be associated with traumatic injuries to the head, although the impact may occur long after the initial incident.
What are the symptoms of each condition?
All of these conditions can develop very suddenly, but there are often a number of indicators that people can use to help identify a developing problem. Some of the symptoms may be shared between the two conditions, but there are some differences that can help you tell them apart:
First aid
First aid:
On this topic ▼
How to call an ambulance or intensive care unit correctly
- Call an emergency team immediately.
- Calm yourself or calm the victim. Allow him to take a position that is comfortable for you (optimally in a lying position).
- Take a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue. This can be done three times, with an interval of 5 minutes.
- Provide the victim with a flow of fresh air, unfasten the collar and belt.
- If the arrival of doctors is delayed and the pain is unbearable, you should take an analgin tablet.
- Measure the victim’s pulse and blood pressure every 5 minutes.
- Talk, encourage the person, introduce a set of distracting procedures (put the victim’s legs in a basin of warm water or place heating pads on the calf muscles).
Attention! For elderly and senile people, an attack of myocardial infarction can be painless!! This, in most cases, makes it very difficult to make a diagnosis.
Always remember that a person’s life depends on your quick and decisive actions.
But, as you know, a person is the master of his own destiny and his health. A few simple preventive measures that should go with you throughout life will help you maintain a healthy heart into old age.
Heart Attack Symptoms
Symptoms that indicate a heart attack may come and go, but the condition may also worsen over time. They are also likely to be more acute during physical activity.
- Chest pain: Also known as angina. Sufferers often describe a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the chest. This feeling often comes and goes and can easily be confused with indigestion.
- Pain and numbness in other areas of the body: Feelings of pain or discomfort in the arms, neck, or jaw are common indicators of cardiovascular disease. The left side of the body is more likely to experience more pain than the right side.
- Unexplained difficulty breathing, hoarseness, and extreme weakness.
- Fast or irregular pulse or heartbeat.
- Dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
- Intense and often unexplained feelings of anxiety.
Signs of a heart attack
Signs of a heart attack
The main manifestations are characterized by:
- Prolonged chest pain that is not relieved by nitroglycerin.
- Shortness of breath, sudden severe weakness, cold, sticky sweat.
- A feeling of fear, even to the point of psychosis. The person completely loses control over his actions.
- Increased body temperature.
- Reducing criticism of your condition.
- Thread-like pulse, drop in blood pressure.
Symptoms of cardiac arrest
In more than half of cases, cardiac arrest occurs without symptoms, as a “sudden event.” However, some patients experience a range of symptoms in anticipation of the problem. These include:
- Rapid heartbeat or extreme heartbeat.
- Feelings of dizziness and disorientation.
- Loss of breath and chest pain.
Although these indicators can predict cardiac arrest, most people will be alerted to it by the most severe symptoms, such as sudden weakness or loss of consciousness. In most cases, it is therefore very difficult to distinguish a stroke from a heart attack in advance.
Life-threatening dangers and complications of myocardial infarction
Death before arrival at the hospital occurs in 25% of people with a heart attack; the remaining 75% are at risk of complications after a heart attack, which are:
- stroke;
- arrhythmia;
- heart failure;
- blood clots in the legs or heart;
- aneurysm.
It is worth noting that people who survive a heart attack without complications a few hours after the heart attack have a high chance of making a full recovery.
Recovery from a heart attack is always a difficult process, since any heart attack weakens the heart to a greater or lesser extent. Depending on the severity of the heart attack, further scarring of the heart, and the speed of medical care, a heart attack can lead to:
- heart failure, in which the heart cannot pump blood properly;
- arrhythmias or abnormal heart rhythms;
- cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac death (heart stops beating);
- cardiogenic shock (in which the heart is so damaged that the person is in shock);
- of death.
Symptoms of a stroke
Many of the early symptoms of a stroke are neurological and may begin to appear in the weeks and months before the attack. Symptoms to watch out for include:
- Severe headaches that may be accompanied by a feeling of dizziness.
- Confusion, forgetfulness and memory loss. Inability to speak clearly or remember anything from the past.
- Blurred vision in one or both eyes and slurred speech.
- Coordination problems leading to problems walking or lifting objects.
- Nausea, illness and excessive sweating.
- Partial or complete loss of feeling and function in the arms, legs and mouth. It usually affects one side of your body.
What is commonly confused between these disorders?
It should be noted that during a heart attack the heart continues to beat, but during cardiac arrest it stops altogether (or the power of the beating is significantly reduced) due to an electrical malfunction. Those who have previously had a heart attack are at greater risk of cardiac arrest.
Doctor
A heart attack is also more likely to occur as a result of symptoms gradually developing and worsening over time (although sometimes, people can have a heart attack despite having no symptoms at all - a condition known as a "silent" heart attack).
Stroke symptoms, meanwhile, vary and usually affect the sufferer's head or motor skills. Since the causes of stroke can be attributed to the heart's inability to pump enough blood to the brain, it actually occurs as a result of sudden cardiac arrest (which is actually one of the main causes of stroke).
What should you do?
You do not need to live in fear because of any disorder, but you should always contact your doctor if you have any concerns that you have such symptoms. Heart attacks and strokes in particular do often provide notice of an upcoming event, and treatment can prevent disaster.
The best ways to ensure that you do not have such problems are to live a healthy lifestyle, avoid bad habits, eat well and exercise regularly. Also, see your doctor for regular checkups, especially if you have any symptoms that may be related to these conditions.
Prevention of myocardial infarction in men and women
The main risk factor for myocardial infarction is coronary heart disease.
You can reduce the risk of heart disease and a heart attack in the following ways: 1. Quit smoking. 2. Monitor your blood pressure. Remember that people with high blood pressure (hypertension) have an increased risk of heart attack and heart disease. 3. Monitor your blood sugar levels. Diabetes carries a risk of developing heart disease. 4. Monitor your blood cholesterol levels. If you don't know what your cholesterol level is, it's time to get tested. 5. Watch your weight. Obese people are known to be at greater risk of dying from heart disease than people of normal weight. 6. Be active. It has been found that regular physical activity is an excellent way to prevent heart attacks and other heart diseases. 7. Eat right. More fruits, vegetables and omega-3 acids. Remember that to select the right diet, you need to consult a specialist, since your body is unique. 8. Don't get stressed. Learn to manage stress, such as through yoga or meditation. 9. Communicate. The social support you receive from family and friends is an excellent way to prevent heart attacks and many diseases. 10. Learn to manage your anger. Do not suppress anger, but direct it in the right direction, give the right outlet to emotions. Be vigilant, do not ignore the dangerous signs of a heart attack! Remember that timely assistance is the only way to survive a heart attack! Cardiologist Liliya Avkhatovna Yapparova
Prevention
- First of all, you need to follow a diet. Limit the amount of fats and sugars in your diet, but at the same time, increase the amount of foods containing Omega-3. (fish, vegetables, fruits, seafood, vegetable oils).
- Limit alcohol and tobacco consumption.
- Moderate physical exercise will bring undoubted benefits to your health.
- Try to avoid stressful situations, treat everything with a clear head, calmly, and balancedly.
- If the doctor, according to your diagnosis, has prescribed you medications that need to be taken long-term or for life, then you need to do so. You cannot skip taking medications!
- It is necessary to increase potassium-rich foods in your diet: dried apricots, raisins, baked potatoes. It has been proven that 2-3 dried apricots per day completely satisfy the body's potassium needs.
- Let there always be nitroglycerin in your first aid kit or purse. If necessary, it can be used for self-help or to help others. A drug such as Corvalol, Valocordin or Valoserdin will also not hurt. You can have motherwort or valerian preparations. It is also necessary to have analgin or another painkiller. If necessary, you can use it.
Causes of heart attack at 30 years of age in women and men
The main cause of myocardial infarction is a sudden cessation of blood supply to one of the areas of the heart, which are commonly called stacks. The latter are divided into three, depending on the main artery that carries blood here. The anterior interventricular artery gives life to the anterior wall of the heart (as well as the apex and interventricular septum), the circumflex artery gives life to the lateral wall, and the posterior interventricular artery gives life to the posterior wall (lately it is more often called inferior). If the “dam” occurs at the very top, in the trunk of the left coronary artery, an extensive circular infarction develops, affecting almost all areas of the myocardium and most often ending fatally.
Now about the reasons that cause blockage of the artery. Most often, this is a rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to thrombosis in this area. The blood supply to the underlying sections of the myocardium stops; moreover, small fragments of blood clots “fly away” downstream and form additional foci of necrosis. If professionals do not intervene in the situation within a couple of hours (for example, they perform thrombolysis or install walls in the affected area of the artery), the myocardium will die, and the heart will remain weakened forever.
Causes and risk factors for heart attack before age 30
1. Is it just me or is it really so: young people are dying more often from heart attacks?
Indeed, atherosclerosis has been rapidly growing younger in recent years. This is noted by both foreign and domestic experts. In the West, atherosclerosis and its complication, coronary heart disease, are called the “disease of civilization” of the twenty-first century. No wonder.
After all, all risk factors (poor nutrition with an abundance of quickly digestible carbohydrates and animal fats, a sedentary lifestyle, smoking) not only come into the life of a modern person, but penetrate into it from childhood. And if we add to this the deterioration of the environment, it becomes clear why a heart attack at the age of thirty ceased to surprise doctors in the emergency department.
2. My husband died at the age of 35 from a heart attack. Should I worry about the health of my son, who is already thirty years old today?
If the patient’s family, especially direct relatives - father, mother, grandparents, older brothers, have cases of sudden death at a young age, especially if it is proven that the cause of death was a heart attack, then the risk of early development of coronary heart disease is extremely high. Since purely external risk factors for such an early heart attack are not enough. There must be some other reason. Most often, it is caused by unfavorable heredity.
Often, poor heredity is caused by a very specific substrate, for example, a disorder of lipid metabolism transmitted in the family - hereditary dyslipidemia. Many variants of the disease have been described in both men and women, but the result is the same - since childhood, constantly elevated cholesterol levels have been recorded, which can reach two or even three norms with a predominance of the “bad” fraction. Such patients need a strict diet, and from their youth they are prescribed cholesterol-lowering drugs - statins.
The prognosis for a heart attack in young men and women under thirty years of age is often more serious than in middle-aged and elderly people. First of all, this is due to the delay in seeking medical help and worse diagnosis, both of which lead to the loss of precious time, and the reason is the disbelief of both the doctor and the patient himself that a heart attack is possible at such a young age.
Prevention of early heart attacks
3. My son has juvenile diabetes. The endocrinologist advised me to have my heart examined regularly. Why?
There is an increased risk of early heart attack in young women and men who have had type 1 diabetes since childhood and are on constant insulin therapy. Especially if they have additional risk factors - smoking, excess body weight, sedentary lifestyle. These patients should periodically undergo examination of the cardiovascular system for the early development of atherosclerosis; a screening study is considered to be Doppler ultrasound (USD) of the neck vessels, in particular the carotid arteries. The appearance of even small atherosclerotic plaques in this area can serve as an indirect sign of atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries and will require additional examination of the heart, most often a stress test is used for this.
4. I heard that athletes involved in bodybuilding often die from heart attacks. Why do people who seem to lead a healthy lifestyle end up with such sad endings?
Because we should not forget about other causes of heart attack in young men that are not associated with the early development of atherosclerosis. In the case of patients under thirty years of age, and especially men, they can be the most unusual. And they are often associated with the effects of various substances, including toxic ones, on the cardiovascular system. These may be narcotic substances, energy drinks and stimulants (especially in combination with alcohol), as well as anabolic steroids used to quickly increase muscle mass. These substances often cause dehydration, followed by thickening of the blood and spasm of the heart arteries, due to which thrombosis and associated myocardial infarction can occur even without the previous development of vascular atherosclerosis.
You can always tell your doctor about your health in the Doctis mobile application. The first consultation is free! Download now!