- home
- Articles about cholelithiasis
- This is useful to know
- About the structure of the human body
- Catalog of useful medical articles
›
›
›
›
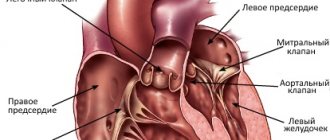
Another heart valve, the tricuspid valve, is located around the circumference of the right atrioventricular orifice.
It connects the right atrium and the right ventricle. Sections of the article
What does the valve consist of?
Valve flaps
Chordae tendineae
Why is a tricuspid valve needed?
Structure, localization, anatomy of the tricuspid heart valve
The tricuspid heart valve is located in the area of the atrium and ventricle on the right side.
Its structure is represented by the following elements:
| Name | Description |
| Fibrous ring | Consists of a large number of elastic fibers. Attached to the interatrial septum. A large number of cardiac conduction channels pass through the annulus fibrosus. Some part of this element is represented by muscle fibers and has a loose structure. As the annulus fibrosus moves away from the interatrial septum, its thickness gradually becomes smaller. |
| Doors | In most cases, the normal development of the heart valve involves 3 main leaflets (anterior, posterior and septal). Sometimes their number increases, according to experts, due to the bifurcation of the rear valve. They all vary in size. The largest door is the main one. The structure of these elements provides for the presence of a base, a body and a closure section. |
| Chordae tendons | There are 3 main elements, each of which performs its own specific functions. |
| Papillary musculature | The muscle is located on top of the interatrial septum. The chordae tendineae emerge from it. |
Tricuspid and other heart valves
The condition and functioning of the tricuspid valve is important for normal blood circulation.
It prevents the backflow of blood into the right atrium.
Description
All heart valves are covered with endothelium. The three layers that form the basis of the valve apparatus have specific characteristics and are called fibrosa, spongiosa and ventricularis. During heart contractions, spongiosa, rich in glycosaminoglycans, facilitates the process of rearrangement of collagen and elastic fibers.
Vacular interstitial cells (VICs) are abundant in all layers of heart valves and contain a variety of dynamically targeted components. The regulation of collagen and other structural components is provided by enzymes synthesized by VIC. The integrity of valve tissue is maintained by the interaction of valve endothelial cells (VECs) with the VIC. Changes and remodeling of the valvular interstitial and endothelial structure contribute to disruption of the valve properties, and subsequently valve function.
Basics of proper operation of the valve apparatus:
- The valves are properly formed and flexible.
- The valves open completely, allowing the required amount of blood to pass freely through the opening.
- The valves close tightly, then blood does not flow back
Work of the organ
The function of the tricuspid heart valve is to maintain normal blood circulation throughout the human body. Passing through all cells and internal organs, the blood gives off oxygen and receives carbon dioxide back. It is also saturated with decay products, due to which it acquires a dark color.
The work of the tricuspid valve is necessary for the separation of jointly functioning elements (left and right ventricles, atria). Venous blood returns through these sections to the pulmonary circulation. Saturated with oxygen through the left atrium, the ventricle flows into the systemic circulation.
Valve functions
The tricuspid heart valve is located on the right side and is an important element in the functioning of the pulmonary circulation.
It performs the following functions:
- During heart contractions, it prevents blood flow from the lower right ventricle to the atrium.
- Takes direct part in the blood circulation process. The tricuspid valve is responsible for the delivery of venous blood to the vessels located in the bronchi.
- Supports gas exchange in the alveoli of lung tissue and heat transfer.
Continuous blood circulation in the human body throughout his life is responsible for the rapid and timely delivery of oxygenated blood to all internal organs and tissues. Through venous outflow, carbon dioxide and decay products leave the body. In medicine, this mechanism is called the cardiovascular system.
The systemic circulation begins from the left ventricle and ends in the right atrium. The pulmonary circulation is directed from the right ventricle to the left atrium.
Normal valve performance
The tricuspid heart valve is located between the right ventricle and the atrium. When the heart muscle relaxes, it opens. When the myocardium contracts, the valve closes. The valves close tightly due to the presence of chordae and muscles. During normal operation of the tricuspid valve, venous blood passes from the right side of the heart to the left. It is then sent to the lungs for gas exchange.
The backflow of blood into the heart cavity from large vessels is not observed due to the correct functioning of this valve. With the development of pathological processes, the entire mechanism is disrupted, as evidenced by the emerging clinical symptoms.
Etiology of aortic insufficiency
The most common causes of organic aortic valve insufficiency are:
- Rheumatism (about 70% of cases);
- Infective endocarditis;
- More rare causes of this defect include atherosclerosis, syphilis, systemic lupus erythematosus (Libman-Sachs lupus endocarditis), rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
With rheumatic endocarditis, thickening, deformation and shrinkage of the semilunar valve leaflets occur. As a result, their tight closure during diastole becomes impossible, and a valve defect is formed.
Infectious endocarditis most often affects previously altered valves (rheumatic lesions, atherosclerosis, congenital anomalies, etc.), causing deformation, erosion or perforation of the leaflets.
Pathologies of the 3-leaf heart valve, causes and symptoms
In most cases, pathological changes in the functioning of the tricuspid valve provoke heart failure or the development of stenosis. Degenerative processes impair blood circulation, resulting in characteristic clinical signs.
| Name | Description |
| Failure | A disease characterized by insufficient closure of the tricuspid valve. In this situation, the blood returns back to the atrium. |
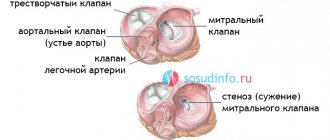
| Stenosis | The pathological condition is characterized by narrowing of the holes located in the tricuspid heart valve. In most cases, problems arise against the background of rheumatism, congenital defects, or after prolonged mechanical impact on the chest. |
| Congenital defects | Pathological changes occur during the period of intrauterine development of the human body, often against the background of hereditary diseases in the mother’s body. |
Pathological processes in the area of the tricuspid heart valve develop as a result of the following provoking reasons:
- complication of rheumatism;
- severe thyrotoxicosis;
- development of myocarditis;
- infective endocarditis;
- cardiomyopathy;
- carcinoid syndrome;
- mechanical trauma to the chest, resulting in damage to the heart;
- surgical intervention in the area of the mitral valve, due to which its leaflets enlarged;
- myocardial infarction;
- increase in diameter of the fibrous ring.
Congenital defects in most cases develop together with other hereditary abnormalities (patent foramen ovale, atrial septal defect).
Tricuspid valve dysfunction is also provoked by tumor growths that have appeared on various internal organs. In this situation, disruption of the functioning of the cardiovascular system occurs as a result of the toxic effects of malignant processes.
Developing pathological changes, taking into account the main reason for their appearance, provoke the appearance of certain clinical signs. Symptoms will help the cardiologist determine the degree of damage to the cardiovascular system and assess its ability to function.
Tricuspid valve dysfunction is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the shade of the skin on the face changes;
- shortness of breath appears;
- breathing is impaired;
- the face swells;
- general weakness occurs in the body;
- the patient is bothered by vomiting; the discharge contains blood impurities;
- metabolism in the intestinal area is disrupted;
- a person gets tired quickly;
- Painful sensations appear in the area on the right side under the ribs.
The liver also enlarges, not only the face, but also the lower and upper limbs swell.
Excess fluid accumulates in the lungs. The intensity of the clinical picture and the presence of certain signs depends on the degree of development of pathological processes. It is important, if any symptom appears, to go to the hospital and undergo a full examination to establish an accurate diagnosis. Properly selected therapy will prevent serious consequences.
What pathologies of the right atrioventricular valve most often occur?
Dysfunction of the right atrioventricular orifice most often takes the form of stenosis or insufficiency. Pathological changes in the valvular apparatus of the heart significantly impair blood circulation, which is manifested by certain clinical symptoms.
Tricuspid valve stenosis
- It is associated with certain diseases of an infectious nature, infection with streptococcal, enterococcal or treponemal infections.
- It is more often detected in patients with rheumatism or syphilis.
- Represents a narrowing and reduction in the diameter of the AV opening (stenosis), which significantly impedes the flow of blood through the valve.
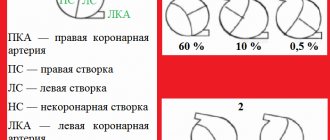
- In 60% it is combined with damage to other valves, mitral or aortic.
- Circulating in the bloodstream, the infection settles in all parts of the heart, affecting the elements of the valve apparatus.
- Due to the progressive inflammatory process, the tricuspid valve becomes sclerotic. The valves, annulus fibrosus, muscular elements and chords fuse, reducing the lumen of the AV foramen.
- Normally, the size of the valve is 3-4 centimeters; with stenosis, the diameter decreases from 3-1.5 cm.
- As a result of changes in hemodynamics, not the entire volume of blood flows from the atrium to the ventricle, and therefore stagnation develops in the pulmonary circulation.
- The examination is characterized by pathological reflux - swelling of the neck veins when pressing on the abdominal area where the liver is located.
- Auscultation of the heart reveals diffuse pulsation and enlargement of the cardiac boundaries, loud pathological murmur in the diastole phase.
- It manifests itself as portal hypertension (increased pressure in large hepatic vessels) with subsequent stagnation of blood in the spleen, intestinal vessels, and stomach.
- Characteristic symptoms are severe weakness, shortness of breath, swelling, cyanosis of the hands and face, irregular heartbeat, increased blood pressure, hemoptysis, swelling of the abdomen and fatty tissue, swelling of the veins around the navel.
- Without treatment, it leads to fatal heart failure and death.
- Drug treatment is ineffective; surgical intervention is indicated to replace the affected valve and save the patient’s life.
Right atrioventricular valve insufficiency
Most often occurs due to rheumatic infection, inflammation of the endocardium of the heart or rupture of elements of the valve apparatus, part of the chords or muscle fibers.- Extremely rare - this is a congenital defect.
- In addition to infection, dysfunction can be caused by changes in the right ventricle, its hypertrophy or dilatation, which leads to a compensatory increase in the diameter of the fibrous ring of the valve and disrupts its closure.
- May occur as a result of dilatation of the heart ventricle due to inflammatory diseases, myocarditis or cardiomyopathy.
- It is associated with opium addiction and its main complication – endocarditis (inflammation of the inner layer of the cardiac membrane).
- It is characterized by incomplete slamming or prolapse (protrusion) of the valve leaflets, due to which blood is constantly thrown back into the right atrium.
- During an ultrasound examination, the doctor sees changes in hemodynamics, the degree of blood reflux and the size of the narrowing of the AV opening.
- Auscultation (listening to the valves during heartbeat) reveals a pathological popping noise.
- Since the atrium does not have great compensatory capabilities, signs of dilatation (expansion) immediately appear.
- As with stenosis, it manifests itself as congestion in the liver, an increase in venous pressure and venous pulse (swelling of the neck veins when the heart contracts).
Stages of dysfunction
The tricuspid heart valve is located on the right side of the organ. Pathological changes develop gradually. In medicine, disorders of the functioning of the tricuspid valve are distinguished, taking into account the complexity of pathological changes and the possibility of their reversal.
There are the following stages of development of organ damage:
| Name | Description |
| Stage I | At this stage of pathological processes, minor disturbances occur that affect the movement of the pulmonary and systemic circulation. |
| Stage II | Pathological processes progress, but if treatment is started in a timely manner, degenerative changes can be reversed. |
| Stage III | Significant problems in the functioning of the tricuspid valve provoke the appearance of specific symptoms, for example, increased blood pressure. |
| IV stage | At the last stage of the disease, the valve structure is affected. The person’s condition is deteriorating, progressive symptoms require urgent hospitalization and strict supervision by the attending physician. |
At the last stage of valve damage, pathological processes are irreversible. Properly selected therapy will improve the patient’s quality of life and prevent complications.
Diagnostic methods
A comprehensive examination will help the doctor establish the correct diagnosis and select the most effective treatment regimen.
Patients with damage to the tricuspid heart valve are prescribed the following diagnostic methods:
| Name | Description |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | An examination method that will assess the functioning of the heart and identify existing pathological abnormalities. Also determine the volume of the atria. |
| Phonocardiogram | During the examination, the specialist identifies systolic murmurs. |
| X-ray examination | Using the images, the doctor will determine the dilatation of the affected ventricle or atrium, the size of the organ itself, and identify congestion. |
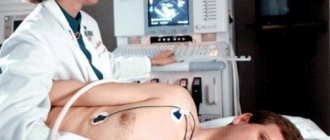
| Echocardiography | The cardiac septa and their movements are observed. Deformation of the valves and the appearance of new formations are also revealed. |
| Spiral computed tomography (CT) | The specialist evaluates the functioning of the main muscle in the human body. |
| Catheterization | The diagnostic method is carried out to determine the pressure in the right side of the heart. |
An important determining point in the diagnosis is the systolic murmur during exhalation. Its presence indicates the development of tricuspid valve insufficiency. Additionally, or before surgery, patients are prescribed coronocardiography. A diagnostic method that will allow you to evaluate blood circulation and detect pathological changes.
Forecast
The life expectancy of patients, even with severe aortic insufficiency, is usually more than 5 years from the moment of diagnosis, and in half - even more than 10 years.
The prognosis worsens with the addition of coronary insufficiency (angina attacks) and heart failure. Drug therapy in these cases is usually ineffective. The life expectancy of patients after the onset of heart failure is about 2 years. Timely surgical treatment significantly improves the prognosis.
Methods of treating diseases
The tricuspid heart valve (located between the right atrium and the ventricle) is treated depending on the degree and stage of its damage, how extensively the pathological processes develop, and the area of their localization. During the period of therapy, it is important to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, without exception, since the disease is life-threatening for the patient.
Drug therapy for damage to the tricuspid heart valve involves the use of the following drugs:
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Diuretics | Britomar, Hydrochlorothiazide | Medicines reduce congestion in the patient’s body and remove excess fluid. The tablets are taken orally, regardless of food, and washed down with plenty of water. Adult patients are prescribed 10-20 mg once a day. If necessary, the dosage is increased to 20-40 mg. |
| Potassium preparations | Panangin, Asparkam | The drugs prevent the accumulation of excess fluid in the patient’s body. The medicine is taken orally 1-2 tablets 3 times a day after meals. The minimum course of therapy lasts 2-3 weeks. In severe situations, the medicine is administered intravenously through a drip. |
| Venous dilators | Corvaton, Nitrosorbide | The drugs reduce the load on the heart and help it accumulate a certain amount of blood. It is recommended to take the tablets at regular intervals and wash down 0.5 tbsp. water. Adult patients are prescribed 1 tablet 1-2 times a day. |
| Anticoagulants | Warfarex, Warfarin | The standard dosage of the drug is 5 mg 1-2 times a day. It is preferable to take the medicine before or after a meal. The course of therapy lasts 6-12 months. |
| Cardiac glycosides | Digoxin, Corglicon | The drugs help eliminate arrhythmia. The medicine should be taken before or after meals. Swallow the tablets whole and take them with plenty of liquid. Take the first dose in a volume of 0.5-1 mg, then every 6 hours at 0.25-0.75 mg for 2-3 days. The maintenance dosage is 0.125-0.5 mg 1-2 times a day. |
| Beta blockers | Diltiazem, Carvedilol | Medicines reduce the contraction of the left ventricle. Adult patients are prescribed 1 tablet 1-2 times a day. The drug is swallowed whole and washed down with a small amount of water. |
During specially selected therapy, patients should also follow the strict recommendations of the attending physician:
- Completely give up bad habits (alcohol, cigarettes).
- Always dress appropriately for the weather to prevent hypothermia or overheating.
- Avoid emotional situations, nervous tension, and severe stress.
- Follow a specially selected diet to reduce the load on a diseased heart.
- Reduce the intensity of physical activity.
Compliance with these recommendations will help not only achieve a positive result in treatment, but also prevent the occurrence of serious complications.
Heart defects in children
If a child is diagnosed with a bicuspid aortic valve, then, despite his age, his condition should be determined and what function is impaired. This indicator is the basis for proper treatment. They also pay attention to the state of the structure of the aorta in children for its expansion and aneurysm.
The diagram below clearly shows standard indicators, based on which you can independently understand the problem and why the doctor prescribed a specific treatment. As you get acquainted, you should understand that the work of the snort is affected by concomitant heart diseases.
Regarding the treatment of this defect in children, doctors assure that drug therapy does not give a positive result, because the valve in an altered state is sensitive to infection and rheumatic processes.
That is, if for medical procedures (dentistry, surgery) it is necessary to administer an anesthetic or antibiotic, then the doctor should be warned about the valve defect.
We can conclude that there is no point in treating the snort; valve preservation or prosthetic surgery should be performed. This will allow the child to continue to live a full life. The preferred surgical procedure in children is the Rhos principle.
In some cases, replacement of the natural valve with a mechanical one is prescribed. However, this will require the child to take blood thinning medications for life.
Therefore, when diagnosed with a bicuspid aortic valve in a female, replacement with a biological one is recommended, because mechanical later causes difficulties when planning pregnancy. Also, if you get snort prosthetics, you will have to give up professional sports.
Indications and types of operations
The indication for surgical intervention is the second degree of pathological changes in the area of the tricuspid heart valve. The same applies to the lack of positive dynamics after drug therapy.
The tricuspid heart valve, depending on the location of the pathological foci, is operated on using the following methods:
| Name | Description |
| Annuloplasty | During medical procedures, the fibrous ring of the tricuspid valve is mobilized. U-shaped sutures are placed on the expanded commissures. |
| Semicircular annuloplasty | The operation is performed in case of severe expansion of the fibrous ring of the tricuspid valve. The surgeon uses a purse string suture. |
| Bicuspidization | Suture annuloplasty of the tricuspid valve, which involves placing U-shaped sutures on the fibrous ring in the area of the posterior leaflet. Teflon gaskets are used during this operation. |
| Prosthetics | A method of surgical treatment that is most often used for stenosis or insufficiency of the tricuspid valve. During surgery, the surgeon excises all the main valves and installs artificial prostheses in their place. |
Surgical treatment is carried out using an artificial device that maintains blood circulation in the patient’s body. The surgical method is selected taking into account the anatomical characteristics of the patient’s body and the provoking factors that caused the development of the pathological mechanism.
Stenosis
Stenosis occurs when valve tissue thickens, restricting blood flow. This often occurs when calcium and other deposits build up on the valve. The heart thickens over time and there is not enough blood supply to keep the heart pumping. This can lead to severe illness and even death.
Problems with the heart valves can cause shortness of breath, especially during exercise. They also pose a risk of heart failure, stroke and sudden death.
A person may be born with valve abnormalities. Valve problems can also develop due to aging or damage from chronic diseases such as diabetes or other diseases such as carcinoid disease. Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as smoking, can also increase your risk of heart disease, including valve problems.
Symptoms of a heart valve problem are similar to those of other heart diseases and include:
- dizziness or fainting
- shortness of breath
- cardiopalmus
- chest pain
Prognosis for pathologies
In most cases, progressive pathological processes with damage to the tricuspid valve lead to serious complications within 5-10 years.
Among the dangerous consequences it is necessary to highlight:
- pulmonary embolism;
- fatal atrial fibrillation;
- congestive heart failure;
- the occurrence of ascites;
- damage to the liver or blood vessels of internal organs;
- development of severe pneumonia;
- the occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension.
As a result of secondary infectious damage to the human body against the background of defects, the risk of complete cardiac arrest increases. Life expectancy for patients with tricuspid heart valve disease is 20-30 years. It is important to constantly be under the supervision of a doctor.
Timely diagnosis of the location of the pathological focus and treatment of the tricuspid heart valve is the main prevention against complications and consequences.
At an early stage of dysfunction, drug therapy will help to cope with disorders. Late stages of disease require surgical intervention. Modern medicine offers enough methods to avoid death and prolong a person’s life.
Not exactly a vice
There is another pathology that does not relate to heart defects, but is considered a minor anomaly of the heart muscle - this is an open foramen ovale. The condition is only congenital and is associated with incomplete closure of the opening between the cavities of the right and left atrium. Normally, the oval window closes during the first or second year of a child’s life; in adults, an open oval window is diagnosed in 25%.
In cases where this pathology provokes a pathological release of blood, surgical treatment is performed. With a small release of blood, the patient’s condition does not suffer, however, he requires observation by a cardiologist and anticoagulant therapy to prevent the formation of blood clots.
The role of the coordinated work of the entire valvular apparatus of the heart can hardly be overestimated. Pathology that arises in any part of the myocardium will inevitably lead to complications, even if it begins unnoticed. Do not forget that heart disease is the main cause of death in the population, so take care of yourself and try to exclude all factors that can adversely affect cardiac activity. Watch your weight, give up smoking and alcohol, get active rest, get enough sleep, don’t get nervous over trifles - and your heart will be healthy.
Did you like the article? Save it!
Still have questions? Ask them in the comments! Cardiologist Mariam Harutyunyan will answer them.
Ivan Grekhov
Graduated from the Ural State Medical University with a degree in General Medicine. General practitioner