Reasons for the increase
Most often, deviations of the sedimentation index from the norm indicate the development of a disease, but in some cases its increase is associated with natural causes. These include:
- Long-term treatment with certain pharmaceutical drugs.
- Pregnancy. An elevated COE is considered normal in this condition.
- Lack of iron in the body. As a rule, this is observed with poor absorption of iron.
- Ages from 4 to 12 years. In children of this age group, who do not have pathology or inflammation, the ESR often increases. It has been noted that this feature is most common in boys.
- Individual body features. According to statistics, 5% of people experience accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation in the absence of any pathological processes.
Pathological causes of changes in sedimentation rate include:
- Development of rheumatism.
- Temporal arteritis.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Anemia.
- Tuberculosis.
- Hepatitis.
- Operation.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas.
- Inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract.
- Oncological diseases.
The harmful activities of viruses, bacteria, parasites and fungi in the body cause the red blood cells to clump together, and the particles formed as a result of their clumping promote the deposition of red blood cells under the influence of gravity.
Main indications for the study
Indications for laboratory examination of patients:
- regular medical examination;
- hospitalization in a hospital inpatient department;
- preparation for routine vaccination;
- diagnosis of inflammatory processes;
- diagnosis of infectious lesions;
- diagnosis of congenital developmental pathologies, genetic diseases, anemia;
- assessment of the dynamics of recovery, the effectiveness of the therapeutic measures taken.
It is advisable to take a referral for testing from a doctor. But if taking tests is your own decision, the laboratory will accept you and perform all the necessary procedures.
Preparation for laboratory diagnostics
Proper preparation for the examination is of utmost importance. The accuracy of the results directly depends on this. If you know in advance that you have to take tests, then 5-7 days before them you need to give up fatty foods, alcohol, and taking medications.
If you take medications on a regular basis and cannot stop taking them, be sure to warn your doctor so that he takes this into account when interpreting the results. Tests must be taken on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning. If you need to donate in the afternoon or evening, it is important not to eat anything 5-8 hours before blood collection. It is allowed to drink clean still water.
Normal indicators
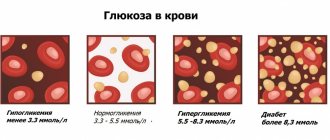
The norms depend on the age and gender of the person. So, in women the normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate is 3-15 mm/hour, and in men 2-10 mm/hour.
In children under 6 months of age, the subsidence rate should be from 12 to 17 mm/hour. In pregnant women, the rate ranges from 20-25 mm/hour, and in people over 60 years old - 15-20 mm/hour.
According to statistics, 40% of deviations from the norm are the result of infectious diseases, 23% of patients with elevated normal values suffer from cancer, 17% of patients have rheumatism, and 8% of patients have anemia, diseases of the intestines, and pancreas. , prostatitis and diabetes.
C-reactive protein (CRP) test
What it is.
A venous blood test in which the concentration of C-reactive protein in a sample is determined. This test is a more accurate indicator of inflammation than ESR because C-reactive protein appears in the blood only during inflammation.
How it works.
The liver produces C-reactive protein in response to the call of immune cells that have encountered a problem, from a bacterial or viral infection to cancer cells. When it encounters dead or dying cells, the protein binds to them and triggers another defense mechanism - it activates the complement system. This means that normally there is either no CRP in the blood, or very little. And if it appears, it means there is definitely inflammation going on somewhere.
Why is it prescribed?
Although CRP is a more reliable marker of inflammation than ESR, the mere fact of its presence in the blood does not indicate anything about the causes of inflammation, so it is not suitable for diagnosis. As a rule, the analysis is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis or to monitor treatment: for example, if a patient with COVID-19 has a CRP level of more than 10 mg/l, then this, along with other signs, may indicate a moderate course of the disease.
“CRP is a more accurate indicator than ESR,”
says another specialist at a Moscow clinic
- it reflects the severity of bacterial inflammation.
If a patient has high white blood cells and high CRP, this strongly suggests that they have a bacterial infection that needs to be treated with antibiotics.” In pneumonia, CRP will reflect the extent of lung damage. The norm is from 0 to 6. If a person has a common cold, it will be in the range of 10-12. But if CRP, for example, is in the range of 100-300, we are most likely talking about serious pneumonia.
“If a person has pneumonia confirmed on an X-ray or CT scan, CRP will fall as they recover,”
explains another doctor.
“At the same time, there are clinical conditions when a person who has recently suffered coronavirus disease maintains a residual temperature within the range of 37.1-37.2°C. If the CRP is normal, this indicates that the patient has actually recovered. And if CRP is high, the person needs further treatment.”
Methods for reducing ESR
There is only one way to reduce the number of red blood cells: treat the disease that caused them to increase.
Self-administration of antibiotics, dietary supplements and anti-inflammatory drugs is under no circumstances recommended, since each disease requires an individual approach to treatment. It should be remembered that only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis.
To determine the cause of exacerbation of SLE symptoms, a comprehensive examination of the patient is necessary. Once diagnosed, your doctor will explain how to reduce the level of SLE in your blood by prescribing appropriate treatment, and you will be referred for a follow-up test within a few days. If the indicator begins to decrease, albeit slowly, the prescribed treatment gives positive results.
Reducing ESR with medications
- If it turns out that the cause of increased SLE is anemia, the first step is to increase the hemoglobin level. To do this, include foods containing folic acid, vitamin B12 and iron in your diet. These foods include green vegetables, salad, grains, liver and beef, rabbit meat, veal, shellfish, legumes, nuts, black currants, rose hips, beets, plums, raisins, etc. To quickly increase hemoglobin and, as a result, reduce COE, your doctor may prescribe a product that contains essential vitamins and minerals.
- Rheumatism is treated with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antihistamines, as well as corticosteroids and other medications. Treatment of rheumatism is long and complex, therefore, to achieve good results, you must strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, follow a diet, and avoid hypothermia.
- In the treatment of acute diseases of the kidneys, pancreas, gall bladder, and respiratory tract, antibiotics are used to help eliminate the causes of these diseases. In chronic cases, accompanied by an increased sedimentation index, it is treated without the use of antibiotics; pharmacological drugs are often combined with the use of traditional medicine.
- When tuberculosis is detected, it should be remembered that this disease takes a long time to treat - from 6 months to two years. After treatment from tuberculosis, blood counts do not return to normal for a long time. Therefore, only 4-6 weeks after recovery can one judge whether the indicator has returned to normal.
- If the patient's test results show an increase in sedimentation rate to 75 mm/h or more several times in a row, the doctor may have reason to suspect the presence of a malignant tumor in the body. In neoplastic diseases, an increased sedimentation rate occurs due to the disintegration of a malignant tumor. In this case, the question of how to reduce the erythrocyte sedimentation rate fades into the background. Intensive treatment is aimed at combating the disease. If the patient is saved, the subsidence rate will eventually decrease on its own.
Traditional medicine
It should be remembered that reducing the number of red blood cells using folk remedies alone is unacceptable. Some plants have the ability to reduce inflammation, purify the blood and improve blood counts. With the help of these plants, the body will quickly cope with the underlying disease, the composition of the blood will improve, thanks to which the erythrocyte sedimentation rate can be reduced.
So what can you do to reduce the rate of sedimentation at home? To do this, you can use traditional medicine such as:
- Beet.
- Honey.
- Herbal infusions.
- Lemon juice with garlic.
Beet
This plant is known for its blood purifying properties. In case of increased red blood cell count, this medicine should be prepared:
- We thoroughly wash two small dark red root vegetables, peel them, place them in an enamel pan, add 3 liters of water and bring to a boil.
- Cook the beets until fully cooked for 2-3 hours (depending on the size of the root).
- The broth should be filtered and drunk in the morning before breakfast, 100-150 ml.
You can also make fresh beetroot juice or use the grated root with natural honey daily.
This product can only be used if you are not allergic to it. For medicinal purposes, every morning you consume 1 tablespoon of honey diluted in a cup of warm tea.
Herbal infusions
To reduce COE, you can use infusions of chamomile flowers, thyme oil or linden oil. To prepare the infusion, you need to take a tablespoon of crushed raw materials and pour 250 ml of boiling water.
You can use the resulting product after 30-40 minutes, when it is well brewed and the water will reveal the healing properties of the herb. To enhance the effect, it is recommended to drink herbal infusions with the addition of honey.
Lemon juice with garlic
A good effect can be obtained by using a mixture of lemon juice and garlic. To prepare it you need to take 2 large heads of garlic and 2-3 lemons. The garlic should be peeled and crushed, and the juice should be squeezed out of the lemons.
The first time you need to create a drug, you will need to create the drug the same way you create a drug. Use twice daily after meals.
People who are thinking about how to reduce the number of red blood cells using folk remedies do not forget about a healthy lifestyle. Walking in the fresh air and breathing exercises help improve lung function, which means increasing the amount of oxygen in them and normalizing the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Proper nutrition, regular preventive examinations and timely treatment of diseases will help maintain a healthy state of health and, as a result, correct blood counts.
How to prepare
The duration of the analysis does not exceed 5-10 minutes. As a rule, the procedure is accompanied by slight pain and discomfort in the puncture area, but the discomfort passes very quickly. If capillary blood is needed, then before piercing the third or fourth finger of the left hand, the skin in this place is treated with an alcohol cotton ball. After this, using a special medical blade, a small incision is made on the fingertip (its depth does not exceed 3 millimeters). The resulting drop of blood is disposed of with a sterile napkin, after which the laboratory assistant proceeds to collect the biomaterial. Having collected the required amount, the wound surface is lubricated with an antiseptic, and a cotton swab with alcohol is applied to the puncture site.
If the analysis involves taking biomaterial from a vein, then the patient’s forearm is tightened with a medical tourniquet or strap, after which he must work a little with his fist (clench and unclench) for better vascular filling. The site of the intended puncture is treated with an alcohol wipe, after which a needle is inserted into the selected vessel, to which a test tube is connected to collect the released blood. Having collected a sufficient amount of biomaterial, the needle is removed, and a cotton swab with alcohol is applied to the wound.
To calculate ESR, an anticoagulant is placed in the biological material to prevent clotting. Then it is sent to a vertical container for 60 minutes. Since the specific gravity of red blood cells exceeds the weight of plasma, gravity forces them down to the bottom of the container. Because of this, 2 visible layers are formed in the test tube: the upper (colorless plasma) and the lower (erythrocyte accumulations). Then the laboratory assistant takes measurements of the top layer. The indicator corresponding to the mark between the red blood cells and the plasma zone on the test tube scale is ESR (indicated in mm/h).
Today there are 2 main ways to detect ESR:
- Panchenkov's method. The capillary is divided into exactly one hundred compartments, and later 5% sodium citrate is added to it to the “P” level. Then the capillary is filled with biomaterial up to the letter “K”. The resulting mixture is mixed and installed vertically. The assessment takes place after 60 minutes.
- Westergren method. Here, venous blood is used, mixed with sodium citrate 3.8% in a ratio of 4:1. It can be mixed with Trilot B followed by the addition of sodium citrate or saline solution in an amount of 4:1. The study is carried out in test tubes equipped with a 200 mm scale. The result is assessed after 60 minutes. This technique is used everywhere, and its main distinguishing feature is the type of test tubes and measuring scale used.
Despite the coincidence of the results of these methods, the Westergren method is famous for its greater sensitivity to exceeding the ESR indicator, and therefore it is considered highly accurate and informative.
Prevention of cancer
Unfortunately, at this point in time it is not possible to completely prevent the development of cancer. But following some preventive rules can reduce the risk of disease to a minimum:
- Complete cessation of smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Diet;
- Sports activities;
- Maintaining a daily routine;
- Reducing time spent in direct sunlight;
- Annual follow-up with a doctor, especially for those at risk.
Tumor markers
Tumor markers are specific proteins produced by malignant tumor cells. Normally, humans do not have such proteins or contain them in small quantities. Each organ has its own tumor marker; let’s look at the most frequently identified ones:
Tumor marker CA 12 , normal -
Okomarker CA 15-3 , normal
Tumor marker PSA , norm 0 - 4 ng/ml. Detects prostate cancer.
The tumor marker AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) is a marker of liver cancer. Also used in gynecology to determine fetal malformations. The norm for men and non-pregnant women is: 0.5 – 5.5 IU/ml.
Tumor marker Ca 19-9 , normal
Tests for tumor markers are carried out in the morning, on an empty stomach. Blood for analysis is taken from a vein.
Symptoms
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in women
The more common seropositive form of rheumatoid arthritis (SPRA) develops gradually in women. This is a typical course of RA in middle-aged and elderly women.
The first symptoms of SPRA, when they appear, you should consult a doctor:
- morning stiffness that persists for half an hour or more;
- mild swelling and tenderness in three or more small joints;
- the pathological process begins from the metacarpophalangeal joints of the hands or from the metatarsophalangeal joints of the feet; this is confirmed by a positive transverse compression test - pain when squeezing the hand or foot.
Clear signs of SPRA are a reason to consult a doctor immediately!
Joint inflammatory processes progress, joint pain becomes constant, debilitating, stiffness in the morning increases and lasts at least an hour. New small and even large joints may be involved in the process. The lesion remains symmetrical.
A woman’s body temperature may rise, but more often it is a slight (low-grade) rise, and signs of damage to other organs and systems appear. The risk of developing contractures (reduced joint mobility) and ankylosis (complete immobility of joints) increases.
Extra-articular symptoms (not always found, but require immediate medical attention):
- rheumatoid nodules on the skin in the area of the affected joints;
- enlarged, painless lymph nodes;
- decrease in muscle volume;
- inflammation of blood vessels - vasculitis in the form of the appearance of pinpoint areas of necrosis around the nail bed;
- damage to the heart and lungs, accompanied by shortness of breath;
- kidney damage with impairment of their function;
- enlarged liver and spleen;
- low hemoglobin, anemia.
Possible complications - require hospital treatment:
- necrosis of the cartilage of joint bones - arthritis can cause such complications very often as the process progresses;
- loss of calcium in bone tissue (osteoporosis), bone fragility;
- habitual fractures, dislocations and subluxations in the affected joints;
- compression of peripheral nerves by inflamed tissues - tunnel syndromes;
- amyloidosis – deposition of amyloid in the internal organs, which leads to disruption of their function;
- exhaustion.
All the obvious symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in women
Symptoms of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis in women:
- the onset of this disease is subacute or acute with fever, malaise, weakness, headache, muscle pain;
- swelling and pain in one or two large joints (knees, elbows, etc.);
- at the beginning of the disease, the lesions are asymmetrical, but over time, symmetrical lesions of small joints may occur;
- There is no rheumatoid factor in the blood.