A cancer patient has fluid in the lungs - what does this mean? How dangerous is this? How to treat this condition?
“Fluid in the lungs” is not exactly a medical term. When this phrase is uttered, one of two states is usually meant:
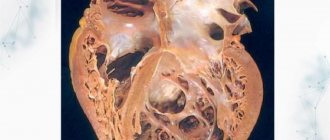
- Pulmonary edema . Lung tissue consists of numerous tiny sacs with a thin wall - alveoli . It is through them that the blood is saturated with oxygen and carbon dioxide is released into the air. If fluid accumulates in them, this condition is called pulmonary edema.
- Exudative pleurisy . In this case, fluid accumulates between the layers of the pleura - a thin film of connective tissue that covers the lungs and lines the inside of the chest cavity.
In this article we will talk about “fluid in the lungs”, which is caused by pulmonary edema.
Causes of fluid in the lung
Pulmonary edema can occur not only with cancer. All causes of this condition are divided into two large groups:
- Cardiogenic - associated with disruption of the heart.
- Non-cardiogenic - associated with other pathological processes in the body, for example, with an increase in the permeability of pulmonary capillaries.
Read more about possible causes of edema:
- Oncological diseases of internal organs
- Various diseases causing sepsis, pneumonia, circulatory congestion
- Overdose of a number of drugs, as well as narcotic drugs
- Effects of radiation on lung tissue
- Heart disease in the stage of decompensation
- Thromboembolism of blood vessels and capillaries of the lungs
In cancer, there are both cardiogenic and non-cardiogenic causes.
Research methods
- Spirometry is a test of pulmonary function that will show changes characteristic of COPD, and can also show impaired pulmonary function in CHF.
- Tests such as a chest x-ray, computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may show signs of CHF or COPD.
Often with CHF, the heart looks enlarged. When CHF worsens, fluid accumulates in or around the lungs, which can be seen on chest imaging.
Imaging tests may show changes in the lungs consistent with COPD, including thickening, inflammation, and bullae (air-filled spaces in the lungs that compress healthy tissue).
- Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) is an ultrasound examination of the structure, structure and mechanical activity of the heart. Using the echo, your doctor can examine the structure of your heart, the blood flow in your coronary (heart) arteries, and the pumping function of the heart muscle itself.
If cardiac function is reduced (often described as low ejection fraction), this may indicate CHF. An echo is not part of the diagnosis of COPD.
Folk remedies
There are many “folk” methods for treating pulmonary edema. Among the recipes that should help relieve swelling, the most common are formulations based on the following plants:
- Cherry
- Linen
- Liquorice root
- Juniper fruits
- Lovage root
- Steelwort root
- St. John's wort
- Dog-rose fruit
- nettle leaves
- Plantain leaves
- bearberry leaf
These and some other plants in various proportions are offered to be brewed, steamed or infused. Such a solution should help in the treatment of pathology.
Some substances contained in these plants may indeed help relieve symptoms, but are not very effective as a primary treatment.
Fluid in the lungs with cancer
In cancer patients, pulmonary edema often occurs as a complication of chemotherapy.
Some anticancer drugs (anthracyclines, cyclophosphamide) and high-dose radiation therapy cause damage to the heart muscle - cardiomyopathy . In this case, the muscles of the ventricles of the heart weaken and cannot adequately cope with their functions, heart failure develops, which leads to pulmonary edema. Symptoms often increase gradually.
Acute non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema can develop during treatment with interleukin-2, mitomycin, and vinblastine. Patients who receive chemotherapy have a weakened immune system and are at increased risk of infections, which can lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome , a condition in which the lungs become inflamed and fill with fluid. Tretonin treatment may cause systemic capillary leak syndrome , a rare condition in which fluid accumulates in the lungs and other organs.
Patients who have had radiation therapy to the chest area have an increased risk of damage to the coronary arteries and heart valves. In this case, the functioning of the heart is disrupted and heart failure develops.
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema can also be caused by the tumor itself during the development of heart failure as a result of the following conditions:
- Metastasis of the lymph nodes in the chest and compression of the heart.
- Metastases of tumors in the cardiac membrane - pericardium .
- Superior vena cava syndrome, when the return of blood to the heart from the upper part of the body is disrupted as a result of blockage of the lumen of the vein by a tumor and blood clots.
Sometimes cancer has nothing to do with it: it is simply combined with severe cardiovascular disease, which leads to heart failure and fluid accumulation in the lungs.
How does COPD develop?
COPD causes inflammation of the lungs. This occurs due to active or passive smoking, exposure to toxins (airborne), and/or repeated lung infections. Over time, repeated damage to the lungs causes the airways to thicken and narrow, making breathing difficult.
Damaged lungs and thickened airways put pressure on blood vessels, leading to pulmonary hypertension (increased pressure in the pulmonary artery). Pulmonary hypertension is a form of high blood pressure in the lungs. It can be caused by many factors, including sleep apnea and COPD. Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a type of pulmonary hypertension in which the walls of the arteries leading from the right side of the heart to the lungs become narrowed. As a result, the pressure in the lungs increases, leading to symptoms such as fatigue and shortness of breath.
When the lungs are severely damaged in COPD, the pressure in the pulmonary arteries becomes very high, causing back-up pressure on the right side of the heart as it sends blood to the lungs. This eventually leads to cor pulmonale, a type of right heart failure caused by airway disease.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary edema?
Fluid in the lungs can build up quickly or gradually. Depending on this, acute and chronic pulmonary edema are distinguished. Their symptoms vary:
| Acute pulmonary edema | Chronic pulmonary edema |
|
|
Diagnostics
The combination of diseases creates many diagnostic problems. Clinical symptoms and signs often overlap. Assessing cardiac and pulmonary function is often problematic and sometimes misleading. Closer collaboration between cardiologists and pulmonologists is required to better identify and treat concurrent heart failure and COPD.
The diagnosis of COPD and CHF is based on history, physical examination, and specific diagnostic tests. Physical examination and test results vary in the early stages of these conditions, but begin to show some similarities in the later stages.
| Physical examination | COPD | CHF |
| Dyspnea | Yes | No |
| Wheezing in the chest | No | Yes |
| Heart murmurs | No | Yes |
| Edema | late stage | Yes |
| Enlarged veins in the neck | late stage | Yes |
| Cyanosis (pale or blue color of fingers, toes, lips) | Yes | No |
| Tachypnea (rapid breathing) | Yes | No |
| Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat) | Yes | No |
| Bradycardia (slow heartbeat) | No | Yes |
| High blood pressure | No | Yes |
How dangerous is fluid in the lungs and what complications are possible?
Acute and advanced chronic pulmonary edema is life-threatening. The lungs cease to cope with their function, oxygen starvation increases in the tissues.
The lack of adequate treatment can result in a number of complications that can threaten the vital systems of the body:
- The development of fulminant edema is a dangerous condition that can cause death within a few minutes
- Airway obstruction due to the formation of large amounts of foam
- Difficulty and depressed breathing
- Tachyarrhythmia and asystole - extreme increase in heart rate
- Destabilization of blood pressure
If prompt treatment measures are taken, many of these complications are treatable.
How to treat a patient who has fluid in the lungs?
The first aid measure for acute pulmonary edema is oxygen supply through a mask. This helps reduce symptoms. Sometimes artificial ventilation is indicated. In order to remove excess fluid from the body, furosemide (Lasix) is prescribed. Morphine and other drugs help reduce shortness of breath and anxiety. Vasodilators (for example, sodium nitroprusside) dilate blood vessels and reduce the load on the heart.
If a patient with pulmonary edema has high blood pressure, they are prescribed drugs that help bring it down; if it is low, they try to increase it.
Treat a condition that causes fluid to accumulate in the lungs. If the cause is side effects of chemotherapy, the doctor may stop the drugs and replace them with others.
Exacerbations
Both conditions can include exacerbations, which are episodes characterized by worsening symptoms.
- In general, COPD exacerbations are characterized by severe shortness of breath and a feeling of suffocation. They can be triggered by infections, smoke and harmful fumes.
- As a rule, exacerbations of CHF progress more slowly and can be triggered by changes in diet (for example, excessive salt intake).
Worsening of both conditions can occur if you do not take your medications as directed by your doctor. Of even greater concern is that exacerbations of CHF and COPD can occur without an obvious trigger. Both types of exacerbations can be life-threatening and require medical attention.
If you have already been diagnosed with CHF or COPD, you may not notice early signs of the other disease due to the similarity of symptoms. If you notice a change in your symptoms, be sure to tell your doctor - it is possible that you have developed another condition in addition to the one you have already been diagnosed with.
Prevention
Prevention of fluid accumulation in the pleura during oncology consists of measures aimed at eliminating the disease that can provoke it. Fluid in the lungs during cancer can accumulate due to diagnoses such as pulmonary tuberculosis, other pulmonary diseases of non-tuberculous origin (pneumonia), and rheumatism. Other measures to prevent it are related to general recommendations for improving the health of the body: a balanced diet, regular exercise, hardening, maintaining a sleep schedule and giving up bad habits that can reduce immunity.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Treatment
Substances contained in plants such as cherries, licorice root, and St. John's wort can alleviate the symptoms of the disease, but they are not suitable as the main means of treatment.
Medicine has in its arsenal such pathology treatment options as:
- Surgical manipulation;
- Chemotherapy;
- Radiotherapy;
- Targeted therapy;
- Immunotherapy;
- Hormone therapy.
To evacuate excess liquid mass in the lungs in acute forms of edema, it is necessary to administer diuretics. An oxygen mask, cardiac and vascular drugs are used.
Ascites - causes, syndromes and treatment
If the cause of the pathology is chemotherapy, it is necessary to discontinue the drugs that led to the pathology and prescribe new ones.