The author of the article is Sozinova A.V., a practicing obstetrician-gynecologist. Experience in the specialty since 2001.
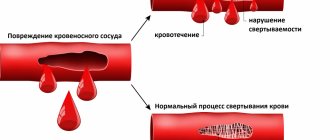
The hemostasis system is a set of mechanisms that ensure the preservation of the liquid state of blood and its fluidity, prevent and stop bleeding, and are also responsible for the integrity of blood vessels.
A blood test that allows you to evaluate its coagulation and anticoagulation abilities is called a coagulogram or hemostasiogram. Coagulation factors, anticoagulant or anticoagulant and fibrinolytic systems are involved in hemostasis.
During pregnancy, the study of a hemostasiogram is mandatory when a woman is registered and at 30 weeks of gestation.
Additional study of the coagulogram is prescribed according to indications.
Disorders of vascular-platelet hemostasis
Disturbances in this part of hemostasis most often manifest themselves as increased bleeding, a tendency to form hematomas (bruises) with the slightest contact, or even spontaneously, for no apparent reason. In some situations, on the contrary, there is a tendency to excessively easy thrombosis.
There are factors that stimulate the formation of a primary thrombus and those that disrupt it. Stimulants include the inflammatory process, because inflammation increases the content of biologically active substances in the blood. We can say that there is a readiness for the formation of a blood clot; it is only a matter of local damage to the vessel. Therefore, in severe infectious diseases, blockage of blood vessels may occur. There is an increased readiness for thrombosis during pregnancy, as well as in some hereditary diseases (thrombophilia). Among food products, table vinegar (marinades) and coffee increase platelet activity.
The process of formation of a primary thrombus is disrupted when the number of platelets decreases (thrombocytopenia) and when there is a qualitative deficiency of platelets (thrombocytopathy). Thrombocytopathy can occur when taking certain medications. First of all, these are anti-inflammatory drugs: aspirin, analgin, brufen, some antibiotics. Thrombocytopathy also develops in kidney diseases. Spices and strong alcohol can also reduce the usefulness of platelets.
The blood coagulation system is actually several interconnected reactions occurring in the form of a cascade, or chain reaction. At each stage of this process, the proenzyme (the inactive form of the enzyme) is activated. Thirteen of these proteins (clotting factors) make up the coagulation system. They are usually designated by Roman numerals from I to XIII.
Features of the hemostatic system during pregnancy
While waiting for a baby, the hemostasis system of the female body acquires its own characteristics. The whole body is rebuilt to work for two. This also applies to the circulatory system. During this period, additional blood circulation through the uteroplacental circulation is required. In addition, the birth process may be associated with significant blood loss. During pregnancy, normal coagulogram values differ from the usual values. Blood clotting levels increase naturally.
Disturbances in the coagulation system
A decrease in the content or activity of coagulation factors may be accompanied by increased bleeding (for example, hemophilia A, hemophilia B, von Willebrand disease). Excessive activation of coagulation hemostasis (for example, Leiden mutation of factor V) leads to the development of thrombosis (thrombophilia).
Hemostasis and pregnancy
Among all the causes of miscarriage, problems in the hemostatic system are in second place in frequency. Second after obstetric and gynecological reasons. What's the matter?
During pregnancy, the expectant mother's body prepares for childbirth. The hemostasis system is also being prepared to minimize blood loss during childbirth. Hemostasis is activated progressively along with increasing gestational age. If a woman’s hemostasis is initially overactive, then during pregnancy microthrombi may form in the vessels of the uterus or placenta, which leads to miscarriage or frozen pregnancy.
Under what conditions can this happen?
- 1. For hereditary thrombophilia,
more often when there is a violation of the metabolism of folic acid and its compounds (folates), when the amount of homocysteine in the blood increases. The reasons for the increase in homocysteine levels may be a lack of folic acid and vitamin B12 in the diet, thyroid disease, and kidney disease. It can also increase in smokers, coffee drinkers and while taking medications such as theophylline (by the way, a relative of caffeine), nicotinic acid. Homocysteine damages the endothelium (inner layer) of blood vessels, and this damage triggers blood clots.
- 2. For antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)
– this is the name of an autoimmune disease in which antibodies are produced to one’s own clotting factors. As a result, blood clots also spontaneously form in the vessels.
Coagulogram - what kind of analysis is this?
The functioning of the circulatory system is perhaps the most important indicator of health. During pregnancy, she requires increased attention. A coagulogram reveals disorders of hemostasis - the system that is responsible in our body for the normal liquid state of blood and for blood clotting to stop bleeding. If hemostasis indicators are reduced, a person will experience large blood losses even due to a minor cut. Too high (hypercoagulation) leads to thrombosis, heart attacks and strokes.
According to doctors, the danger of both anomalies is that they may not reveal themselves in any way in everyday life. But during surgery or childbirth there is a risk of developing a critical situation.
The hemostatic system undergoes some changes during pregnancy. Therefore, the coagulogram before and during pregnancy is different. Nature provides for such a natural restructuring. In the process of bearing a child, a third circle of blood circulation arises in a woman’s body, which is called the uteroplacental. Preparations are underway to increase the amount of circulating blood. This is important also because of the inevitable blood loss during childbirth.
Prevention of bleeding disorders during pregnancy
In order to avoid pregnancy complications, all pregnant women must undergo laboratory tests - a clinical blood test, a coagulogram (blood clotting parameters), and determination of homocysteine levels.
Women who have previously had miscarriages or frozen pregnancies, as well as those pregnant as a result of IVF, are at risk for developing disorders in the hemostatic system. For patients at risk, it is recommended to conduct a complete study of the hemostatic system, blood testing for antiphospholipid antibodies. In the case of IVF (in vitro fertilization), monitoring of blood clotting parameters must be carried out throughout pregnancy. In accordance with the recommendations of the WHO (World Health Organization) expert committee, monitoring of coagulogram and D-dimer must be performed at least once every 2 weeks. Correction of such disorders is carried out jointly by a gynecologist and a hematologist.
Ideally, it is advisable to carry out a full examination not after pregnancy, but at the stage of family planning.
At the Clinic of High Medical Technologies named after. N.I. Pirogov has established and operates a system for diagnosing and treating patients with problems in the hemostatic system. Laboratory diagnostics, including genetic studies, can identify the causes of disorders. Treatment of such patients at the stage of family planning and their management during pregnancy (both physiological and as a result of IVF) is carried out by qualified gynecologists together with a hematologist.
Complexes with this research
Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure RUB 16,590 Composition
Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 11,430 RUR Composition
Coagulogram Study of the functional state of hemostasis 1,390 R Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Miscarriage RUB 31,040
- Female infertility RUB 10,650
- Pregnancy planning. Clinical indicators 4,350 R
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 6,310 RUR
- Extended coagulogram 3,000 R
Content
- Indications for the purpose of analysis
- Increased thrombin time
- Changes in indicator during pregnancy
Thrombin time is an indicator that allows us to evaluate the final stage of the blood clotting process (coagulation), namely, the formation of fibrin from fibrinogen. That is, thrombin time is the time during which fibrinogen is converted into fibrin in citrated plasma after the addition of calcium and thrombin. In this case, the rate of formation of a fibrin clot mainly depends on the amount and usefulness of fibrinogen, as well as the presence of anticoagulants in the blood. Thrombin time is used to assess blood anticoagulant activity and identify dysfibrinogenemia.
Indications for the purpose of analysis
- determination of fibrinogen deficiency or deficiency;
- monitoring the results of therapy with heparin, thrombolytic or fibrinolytic drugs;
- assessment of the patient’s condition with DIC syndrome;
- liver pathology;
- detection of the presence of fibrinogen/fibrin degradation products in the blood;
- in the presence of two spontaneous cases of pregnancy termination before 22 weeks.
Thrombin time depends on the level of fibrinogen in the blood: a decrease in the level of fibrinogen increases thrombin time and for this reason, the analysis of thrombin time is usually combined with the analysis of fibrinogen, as well as other coagulogram indicators. Thrombin time - the norm is 15-18 seconds. However, in various diseases, the thrombin time indicator goes beyond the normal range - the thrombin time is increased or decreased)
When and how to donate blood for a coagulogram for pregnant women
Pregnant women donate blood for a coagulogram several times during the entire gestation period.
In severe pregnancy and frequent hospitalizations, the number of coagulograms increases along with other laboratory tests.
Pregnant women in whom the cause of hemostasis disturbance has been identified and established are specially registered. For example, a genetic factor.
The test is prescribed by the attending obstetrician-gynecologist, and in some cases by a hematologist, if there are obvious blood clotting disorders.
Taking a blood test for a hemostasiogram
- blood is donated in the first half of the day on an empty stomach;
- in the morning you can drink a glass of water (not tea or coffee);
- when using medications, inform the nurse, who will make the appropriate mark on the analysis form;
- Blood is drawn from a vein using a vacuum system (not through a needle and syringe). It has been proven that the preanalytical stage (preparatory) has a further influence on the process of sample preparation and analysis. The result obtained depends on these factors;
- venous blood is placed in a test tube with the reagent and must be mixed.
The following are not subject to analysis:
- hemolyzed blood;
- clots in the sample;
- incorrect ratio of reagent and biological material.
Types of hemostasiogram
Research can be basic or extended. The basic hemostasiogram includes determining the necessary indicators:
- prothrombin;
- fibrinogen;
- INR;
- PtV;
- APTT;
- TV;
- PTI;
- RFMK.
An extended hemostasiogram determines many more indicators: for example, antithrombin III, D-dimer, lupus anticoagulant, etc. An extended study is prescribed according to indications: for example, pregnant women or people with coagulation pathologies.
What the results say
Let's consider what results can be obtained when studying blood coagulation and what can be judged from them.
Normal hemostasiogram indicators during pregnancy
| Indicators | What do they mean | Normal during pregnancy |
| Fibrinogen | The leading coagulation factor preceding fibrin. | 1st trimester: 2.4-5.1 g/l, 2nd trimester: 2.9-5.4 g/l, 3rd trimester: 3.7-6.2 g/l. |
| APTT | Time of formation of a blood clot. | 1st trimester: 24.3-38.9 s. 2nd trimester: 24.2-38.1, 3rd trimester: 24.7 -35.0. |
| Prothrombin | Protein, the second important factor in blood clotting. | 78-142% |
| Platelet count | Nuclear-free blood cells that play an important role in hemostasis. | 1st trimester: 174-391 thousand/µl, 2nd trimester: 155-409 thousand/µl, 3rd trimester: 146-429 thousand/µl. |
| Prothrombin time (PTT) | Time for plasma clot (fibrin) to form. Warns of a tendency to bleeding. | 1st trimester: 9.7-13.5 s, 2nd trimester: 9.5-13.4 s, 3rd trimester: 9.6-12.9 s. |
| Prothrombin index | Determination of plasma clotting time after calcium removal. | 85-115% (or 0.8-1.2 according to international standards). |
| Antithrombin 3 | Protein as part of the anticoagulant system. Responsible for counteracting coagulation in the formation of blood clots. | 1st trimester: 89-114%, 2nd trimester: 88-112%, 3rd trimester: 82-116%. |
| D-dimer | The main marker of thrombosis. Appears during the breakdown of fibrin included in the thrombus. | Increased during pregnancy: in the 1st trimester - 0.05-0.95 mcg/ml, in the 2nd trimester -0.32-1.29 mcg/ml, in the 3rd trimester - 0.13-1.7 mcg/ml ( with a lower limit of not less than 33 mg/ml). |
| INR (international normalized ratio) | Prothrombin time indicators in various laboratories. Shows the effectiveness of anticoagulant treatment. | In the 1st trimester: 0.89-1.05 s, in the 2nd trimester: 0.85-0.97 s, in the 3rd trimester: 0.80-0.94 s. |
| Lupus anticoagulant (in two versions) | Antibodies that promote blood clotting. | During pregnancy from 0.8 to 1.2 g/l |
| Antiphospholipid bodies | A special group of proteins is identified. Prescribed for thrombosis or after several terminations of pregnancy. Their excess leads to cell damage and thrombosis. | Calculation of immunoglobulins G and M. |
| Cuff test | To assess the antithrombotic ability of blood vessels (clamp the arm with a cuff). | About 40-50%. |
| Clotting time | It is detected until a drop of blood has completely coagulated (in a test tube or on glass). | Within 2-4 minutes. |
Thrombophilia test
A test for thrombophilia can be offered to pregnant women as part of a hemostasiogram. It is prescribed according to indications (if there is a tendency to thrombosis or thromboembolism in a woman or her relatives). This is a paid analysis from a number of commercial laboratories, based on determining the composition of genes. The study allows you to identify up to 15 different forms of thrombophilia.
As a result of assessing the hemostasiogram, two main disorders can be identified:
- Hypercoagulation. This condition is typical when:
- increased D-dimer, platelets and fibrinogen;
- decrease in PT, APHR, INR and antithrombin III.
- Hypocoagulation. This conclusion is made with the following changes in the coagulogram:
- increased levels of PTT, APTT, INR and antithrombin III concentration;
- reduced levels of platelets and fibrinogen.
Hypercoagulation is dangerous due to the formation of blood clots in the venous system (usually in the veins of the lower extremities). The hypocoagulation state is dangerous due to bleeding, seriously threatening the life of the mother and baby.
The analysis of a hemostasiogram is complex, and for its correct interpretation, even an experienced doctor often needs additional research.