**
**
There is little blood -> danger of infection -> wash and bandage
Example: skinned knee
- Any colorless liquid that can be drunk is suitable for rinsing
- for the bandage, clean (relatively) cloth
There is a lot of blood -> danger of blood loss -> pressure bandage
Example: struck a knife on a finger
- if blood continues to ooze, then apply another bandage and press harder
- do not remove the already soaked bandage
Fountain -> very rapid blood loss -> pinch the artery, tourniquet
Places of arterial compression:
- Lower third of the shoulder
- Upper third of thigh
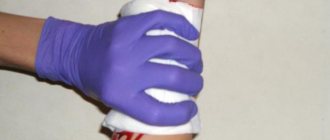
Rules for applying a tourniquet
A tourniquet is applied only in extreme cases (fountain), as it very often causes irreversible damage.
- applied above the wound
- placed on clothing (if there is no clothing, put it on).
- 1 round of the tourniquet - fasten it, then stretch it and apply 3-4 rounds
- Apply the tourniquet quickly, remove it slowly, gradually.
- write the date and time of application of the tourniquet on the forehead (with anything)
- time: in winter - 1 hour, in summer - 2 hours,
- then loosen for 5-10 minutes and apply a tourniquet just above the previous application site
- the tourniquet must be visible!
- check that the tourniquet is applied correctly - there is no pulse in the limb
- see a doctor immediately
What not to do
- Let's not put our hands into the wound!
- We’re not getting anything out of the wound!
- do not remove the already soaked bandage
What to do next
- take the victim to a doctor
- If you are unable to move independently, call an ambulance.
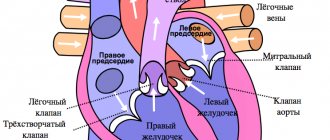
How to stop arterial bleeding?
Injuries that are accompanied by bleeding require urgent measures. Blood loss when a large artery is injured (carotid, brachial, femoral artery, aorta) is such that a person can die in 2.5-3 minutes. Agree, this is quite small. That is why arterial bleeding must be stopped quickly.
It's not that difficult to define. Bright red blood that comes out of the wound in a pulsating stream, sometimes in the form of a fountain.
The very first thing to do is to stop the flow of blood to the wound. To do this, finger pressure is used - the artery is compressed with two to four fingers until the pulse disappears. This measure is temporary; it will prevent the victim from dying from blood loss and will give time to prepare and apply a tourniquet or sterile pressure bandage.
- in case of arterial bleeding, the popliteal artery is pressed onto the lower leg. Pressing is done with both hands. The thumbs are placed on the front surface of the knee joint, and with the remaining fingers they feel the artery in the popliteal fossa and press it to the bone;
- in case of arterial bleeding from the thigh, the femoral artery, which is located on the inner surface of the upper thigh directly under the inguinal fold, is pressed;
- in case of arterial bleeding from the upper limb, press the brachial artery to the humerus at the inner surface of the biceps brachii muscle with four fingers. The effectiveness of the pressure is checked by the pulsation of the radial artery on the inner surface of the elbow;
- when bleeding from a wound located on the neck, press the carotid artery with fingers or a fist on the side of the wound below the wound.
To gain time to prepare the bandage, it is allowed to stop the bleeding by inserting a roller made of gauze, cotton wool or tight soft material into the folds of the limbs. It is also permissible to fix the limbs in a certain position:
- to stop bleeding from wounds of the hand and forearm, the roller is placed in the elbow bend. Bend the victim’s arm at the elbow, while the forearm must be tied tightly to the shoulder and tied with a tourniquet;
- to stop bleeding from the brachial artery, a roller is placed in the armpit and the arm bent at the elbow is firmly fixed to the chest;
- in case of bleeding of the lower limb, the cushion is placed in the popliteal fossa;
- in case of damage to the subclavian artery and bleeding in the armpit, move the arms bent at the elbow behind the back as much as possible and fix them at the level of the elbow joints. This technique cannot be used for fractures of limb bones;
- if the popliteal, femoral, brachial and ulnar arteries are damaged, bend the limb as much as possible.
After the bleeding has stopped and you have time, you need to apply a pressure bandage or tourniquet to the place of pressure. A pressure bandage is used for wounds of small arteries. Several layers of sterile gauze or bandage are applied to the wound and bandaged tightly. As for the tourniquet, if it is not available, you can use a piece of thick fabric, a tie, a rope, a waist belt, etc. A tourniquet is applied to the shoulder, forearm, lower leg or thigh above the bleeding site. The tourniquet cannot be applied directly to an open area of the body, so it is necessary to place gauze or cloth under it, or this is done on top of clothing, having first straightened the folds on it. Make 2-3 turns of the tourniquet around the limb and then tighten it until the bleeding stops and the pulsation of the vessel below the application site can no longer be detected. It is not necessary to tighten the tourniquet excessively, as there is a high risk of damage to the muscles and nerves, which can lead to paralysis of the limb and even its necrosis.
Remember that a hemostatic tourniquet is applied:
- in the warm season (+4°C and above) - for a period of no more than one hour;
- in the cold season (below +4°C) - for a period of no more than half an hour. Moreover, the limb below the tourniquet must be wrapped warmly (artificial heating cannot be used), since it cannot heat itself.
If it is necessary to leave the tourniquet for a longer period, press the vessel with your finger above the wound site, slightly and smoothly loosen the tourniquet for 10-15 minutes, then reapply it slightly higher or lower than the previous position.
Figure 1 — Application of a tourniquet
The place where the tourniquet or bandage is applied should be clearly visible and not hidden by clothing or bandages. To control the elapsed time and make the work of the ambulance team easier, it is necessary to place a note under the tourniquet or attach a note to clothing next to it, indicating the date and exact time the tourniquet was applied, for example, May 12, 11:25 am.
A victim with severe arterial bleeding after applying a tourniquet should be immediately taken to the nearest medical center.
Internal bleeding
- call an ambulance
- cold on the abdominal area
- anti-shock measures
- transport in a sitting position
Signs and symptoms of internal bleeding
- the person becomes weaker, there may be no pain
- paleness, cold sweat, chills
- "floaters before the eyes", dizziness
- breathing is weak, shallow
- swollen, hard, painful belly when pressed, “fetal position”
- there may be a bruise on the stomach
What not to do
- do not anesthetize!
- don't feed
- don't give anything to drink
How to properly apply a hemostatic tourniquet
In order not to harm the victim, it is necessary to approach the process of applying a tourniquet with all responsibility and perform it in accordance with the rules:
- in order to reduce blood flow, the injured limb should be slightly elevated, for example, placed on a rolled up towel;
- to avoid damage to the skin, it is necessary to place a soft cloth under the tourniquet; this procedure will also help reduce pain;
- if the injury is on the leg, then the product must be applied to the thigh area, if the arm is injured, the tourniquet should be attached to the shoulder;
- the tourniquet should be positioned with the concave side inward;
- when pulling the product under the limb, you must ensure that the right side of the tape is slightly longer than the left;
- It is necessary to apply the tourniquet with effort. Each subsequent turn should be slightly weaker than the previous one and should overlap it, which will avoid damage to soft tissues;
- the harness is secured with hooks and a chain located at the ends of the product.
Penetrating chest injury
- close the hole tightly
- apply cold
- not allowed to speak
- breathe deeply
Signs and symptoms of penetrating chest injury
- white or bloody foam at the mouth
- the same one at the wound site
Glue the bag, a piece of plastic with tape or adhesive tape, check: if there is an entrance hole, then there may be an exit hole (in the case of a gunshot wound, it can be 10 times larger than the entrance hole), if it is small, you can seal it.
First aid for venous bleeding
With venous bleeding, a stream of blood comes to the surface at high speed so that it does not allow a blood clot to form and stop the bleeding.
As a result, a person may lose a large amount of blood.
Algorithm for providing assistance:
- Raise the injured limb upward;
- Cover the wound with a bandage or clean cloth folded several times;
- Cover the wound tightly with a bandage.
In case of severe venous bleeding, a tourniquet is applied and then cold is applied to the wound. Next, go to the hospital for help.
Long-term crush syndrome (Crush syndrome)
When a person gets caught in a rubble
- apply a tourniquet above the point of pressure and only then release
- released - tightly bandage the limb and remove the tourniquet
- plenty of warm drinks
- anti-shock measures and urgent hospitalization
This material is part of the School of First Aid course “Space of Safety”. We recommend signing up for classes at the school by calling +7 495 760—9092 or on the website https://www.allsafety.ru
Source: https://www.allsafety.ru/
How to check that the tourniquet is applied correctly
A medical hemostatic tourniquet should be applied so as not to cause harm to the patient.
So, signs confirming that the overlay was completed correctly:
- the first main sign is that the bleeding stops, the blood stops flowing from the wound;
- pulsation in the arterial vessels is not observed;
- the limb becomes pale and cools down.
Attention! If an Esmarch hemostatic tourniquet is applied and the limb turns blue, the procedure must be redone, since the blueness of the limb indicates compression of the vein, and not blockage of the artery.
Sources
- Zideman DA., Singletary EM., Borra V., Cassan P., Cimpoesu CD., De Buck E., Djärv T., Handley AJ., Klaassen B., Meyran D., Oliver E., Poole K. European Resuscitation Council Guidelines 2021: First aid. // Resuscitation - 2021 - Vol161 - NNULL - p.270-290; PMID:33773828
- Gyedu A., Stewart B., Otupiri E., Donkor P., Mock C. First Aid Practices for Injured Children in Rural Ghana: A Cluster-Random Population-Based Survey. // Prehosp Disaster Med - 2021 - Vol36 - N1 - p.79-85; PMID:33491619
- Singletary EM., Zideman DA., Bendall JC., Berry DA., Borra V., Carlson JN., Cassan P., Chang WT., Charlton NP., Djärv T., Douma MJ., Epstein JL., Hood NA ., Markenson DS., Meyran D., Orkin A., Sakamoto T., Swain JM., Woodin JA., De Buck E., De Brier N., O D., Picard C., Goolsby C., Oliver E ., Klaassen B., Poole K., Aves T., Lin S., Handley AJ., Jensen J., Allan KS., Lee CC., De Buck E., De Brier N., O D., Picard C ., Goolsby C., Oliver E., Klaassen B., Poole K., Aves T., Lin S., Handley AJ., Jensen J., Allan KS., Lee CC. 2021 International Consensus on First Aid Science With Treatment Recommendations. // Resuscitation - 2021 - Vol156 - NNULL - p.A240-A282; PMID:33098920
- Singletary EM., Zideman DA., Bendall JC., Berry DC., Borra V., Carlson JN., Cassan P., Chang WT., Charlton NP., Djärv T., Douma MJ., Epstein JL., Hood NA ., Markenson DS., Meyran D., Orkin AM., Sakamoto T., Swain JM., Woodin JA., De Buck E., De Brier N., O D., Picard C., Goolsby C., Oliver E ., Klaassen B., Poole K., Aves T., Lin S., Handley AJ., Jensen J., Allan KS., Lee CC., Schmölzer GM., Morley PT., Nieuwlaat R., Lang E. 2021 International Consensus on First Aid Science With Treatment Recommendations. // Circulation - 2020 - Vol142 - N16_suppl_1 - p.S284-S334; PMID:33084394
- Chang KC., Huang YK., Chen YW., Chen MH., Tu AT., Chen YC. Venom Ophthalmia and Ocular Complications Caused by Snake Venom. // Toxins (Basel) - 2021 - Vol12 - N9 - p.; PMID:32911777
- Coughlin DJ., Boulter JH., Miller CA., Curry BP., Glaser J., Fernandez N., Bell RS., Schuette AJ. An Endovascular Surgery Experience in Far-Forward Military Healthcare-A Case Series. // Mil Med - 2021 - Vol185 - N11-12 - p.2183-2188; PMID:32812042
- Sumardino S., Widodo., Poddar. Analysis of pre hospital emergency management in case of head injury. // Enferm Clin - 2020 - Vol30 Suppl 5 - NNULL - p.228-233; PMID:32713577
- Goolsby C., Rojas LE., Rodzik RH., Gausche-Hill M., Neal MD., Levy MJ. High-School Students Can Stop the Bleed: A Randomized, Controlled Educational Trial. // Acad Pediatr - 2021 - Vol21 - N2 - p.321-328; PMID:32473216
- Menger R., Lin J., Cerpa M., Lenke LG. Epidural hematoma due to Gardner-Wells Tongs placement during pediatric spinal deformity surgery. // Spine Deform - 2021 - Vol8 - N5 - p.1139-1142; PMID:32314179
- Zhao YF., Zhao JY., Hu WZ., Ma K., Chao Y., Sun PJ., Fu XB., Zhang H. Synthetic poly(vinyl alcohol)-chitosan as a new type of highly efficient hemostatic sponge with blood -triggered swelling and high biocompatibility. // J Mater Chem B - 2021 - Vol7 - N11 - p.1855-1866; PMID:32255048
Rules for stopping arterial bleeding
Blood loss during arterial bleeding occurs so rapidly that emergency assistance must be provided from the very first 2-3 minutes after its formation. When large arteries are injured, the time for emergency assistance is reduced to 1-2 minutes. Otherwise, blood pressure will drop with every second, causing the victim to lose consciousness, fall into a coma, or die outright.
In case of arterial bleeding, you should first of all squeeze (squeeze) the site of injury with your fingers or fist, trying to stop the gushing flow of blood.
In this case, certain rules should be followed in pressing and squeezing certain blood vessels:
- The common carotid artery is pressed with the fingers to the spine, namely: to the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae. In this case, you should press on the inner edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle approximately in its middle part.
- The external maxillary artery is pressed with the fingers to the anterior edge of the masticatory muscle.
- The temporal artery is compressed with the fingers slightly forward from the upper edge of the ear.
- The subclavian artery is pressed with fingers or a fist behind the outer edge of the clavicular part of the sternocleidomastoid muscle to the first rib.
- The brachial artery is compressed with the fingers along the inner edge of the biceps muscle towards the bone.
- The femoral artery is pressed with a fist to the pubic bone under the Pupart ligament. In thin people, this vessel can be easily pressed against the thigh.
- The popliteal artery is pressed with a fist in the middle of the popliteal cavity.
After providing emergency assistance to press the vessel in case of damage to large arteries, it is necessary to immediately apply a rubber tourniquet to them. For minor bleeding, bandage the injury with a tight roller or a solid sterile bandage. In extreme conditions, instead of a tourniquet, you can use a belt, scarf, thick rope and other improvised means that can be used to make a pressure bandage. A sterile bandage is applied to the wound itself to prevent infection from entering the body.
In some cases, when there is no bone fracture, forced flexion of the injured limb can be used instead of a tourniquet. With this method of stopping arterial bleeding, the injured limb is bent and fixed in a bent position using a bandage or other available means.