Diseases of the heart and blood vessels are a pathology that most often affects middle-aged and elderly people. The whole problem is that not everyone pays attention to the first symptoms of some diseases, as a result of which an exacerbation stage occurs and they have a detrimental effect on heart health. Sensations of pulsation in the heart area - cardiology patients often complain about this symptom. The reasons for its occurrence are always ambiguous. Let's look at the most popular of them.
In general, if the heart functions normally, then a person does not feel how it beats and pulsates. When a person begins to feel the pulsation of the aorta, this means that a pathology has begun to develop in the body, for example, arterial hypertension, aortic aneurysm, or aortic valve insufficiency.
What is heart pulsation?
In medical terminology there is the concept of pulsation. It stands for: movements of the walls of the heart and blood vessels in the form of shocks, which is characterized by transmission displacements of soft tissues that appear during contractions of the heart muscle.
Ripple is a broader concept than pulse, because it refers only to the pulsation of the walls of vessels pumping blood, which is caused by the passage of a pressure pulse wave passing through the vessel and forming in the aorta.
First aid
If a person observes characteristic signs of frequent contractions of the heart muscle for the first time, or attacks occur very rarely, then one should know about the first steps to facilitate the functioning of the organ. First of all, it is necessary to ensure access of fresh air to the room (open a window, swing open the door, ventilate). Then release your neck and chest from constricting clothing (remove the scarf, unbutton the collar). The face and neck are rinsed with cold water.
If you don't have access to water, you can wipe your face with a damp cloth. You should take a comfortable body position in which you can relax. The best option is to lie down and try to breathe evenly and deeply. If necessary, take special medications to relieve an attack of tachycardia. A good and quick result is provided by an infusion of valerian (20 drops of medicine are added to 50 ml of drinking water). The tincture calms the nervous system and lowers heart rate.
Diagnostics
When a patient contacts a doctor with a complaint of pulsation in the chest and heart area, the doctor initially performs a visual examination. To do this, the doctor slightly turns the patient on his left side and stands at chest level, so that the pulsation in the heart area is better visible.
The most interesting thing is that patients who complain of such symptoms have a history of myocardial infarction. Now the specialist’s task is to find out where exactly the source of the problem comes from: a hypertrophied apex of the heart muscle or an aneurysm.
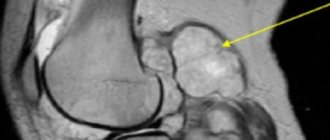
To get a more accurate picture, your doctor may order an x-ray. It is usually not possible to detect an aneurysm on imaging, but in rare cases a pulsatile left ventricular aneurysm can still be seen. On fluoroscopy, you can track the paradoxical pulsation of the aneurysm, which does not coincide with the apex of the muscle. In addition, it is possible to detect protrusion of the left ventricular arch.
In general, there are three possible and most common causes of pulsation: tachycardia, atherosclerosis, and nervous tics.
Treatment methods
To relieve an attack of heart pulsation, eye massage is allowed. This procedure requires 5 to 7 minutes. You should place the phalanges of your fingers on your closed eyelids and apply a little pressure, hold for 10 - 15 seconds, then release. The massage is carried out until the attack subsides.
Medicines based on herbs or chemicals are prescribed. Atenolol, Sedasen, Digoxin, Preductal are widely used. Among folk recipes, the herb St. John's wort, hawthorn, motherwort, and valerian are used. In cases of attacks of pulsation of the heart muscle, you should consult a doctor and find out the cause of the disease.
It is not recommended to self-medicate or drink medications uncontrollably. A serious approach to therapy will ensure recovery and prevent relapses.
Atherosclerosis
The aorta is the largest vessel in the human body, for this reason it is most often affected. It is divided into abdominal and thoracic segments, starting in the left ventricle of the heart and has many branches that feed all organs located near it. In most cases, it is partially affected and has symptoms that always depend on the specific case.
Quite often, atherosclerosis is the cause of many serious diseases of the heart and blood vessels. With this pathology, connective tissue begins to grow in the walls of medium and large arteries, as a result of which the inside of the vessels is saturated with fats, and their walls become denser and thicker. Thus, they lose their elasticity and lumen, and this leads to the risk of blood clots.
Atherosclerosis can develop in absolutely any part of the aorta. When the problem lies in the chest, it pulsates in the area of the heart, namely between the ribs to the right of the sternum. In addition, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- hoarseness of voice and difficulty swallowing;
- burning and squeezing effect behind the sternum and in the heart;
- increased blood pressure;
- radiating pain in the spine, neck, arms and under the ribs;
- paroxysmal pain;
- fainting;
- weakness and dizziness.
When a patient encounters damage to the abdominal aorta, he experiences the following problems:
- weight loss;
- aching pain in the stomach;
- bloating;
- frequent constipation;
- unevenness and hardness when palpating the aorta.
Why do people face this disease? It affects patients aged 40-50 years and older. Moreover, it occurs much more often among men than among women. Smokers are the most potentially dangerous group susceptible to atherosclerosis. In addition, there are other risk factors:
- gout;
- high blood pressure;
- overweight;
- sensitivity to stressful situations;
- genetic predisposition;
- sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity.
Heart disease or pinched nerve?
Therefore, intercostal neuralgia causes pain not only in the heart, but also in the lower back, back, and also under the shoulder blade.
With intercostal neuralgia, irritation or compression of the roots of the intercostal nerves occurs at the point where they exit the spine. Also, pain in the heart area can be caused by excessive tone of one or more muscles of the shoulder, back or shoulder blade.
The causes of neuralgia are varied: exposure to heavy metals, certain medications, bacterial toxins, diseases of the nervous system (polyradiculoneuritis, multiple sclerosis, etc.), trauma, various infections (tuberculosis, influenza, etc.), spinal pathology or congenital anomalies (hernias). discs, osteochondrosis, etc.), allergies.
Another cause of intercostal neuralgia can be changes in the spine, which are caused by hormonal disorders in women. The development of the disease can be affected by alcohol abuse, metabolic disorders of B vitamins, and diabetes mellitus. Older people are susceptible to this disease when all of the above reasons affect the background of age-related changes in the blood vessels.
It should be remembered that nerve endings are everywhere, so intercostal neuralgia can imitate, for example, lung diseases, renal colic, pain that occurs with herpes zoster and, most often, cardiac pathologies. Conversely, other diseases are often mistaken for neuralgia with similar symptoms.
How to eliminate pain
Treatment prescribed for intercostal neuralgia must be comprehensive. First, the causes of the disease should be corrected or eliminated. During an exacerbation, bed rest is required for three days. The bed should be firm and level; it is better to place a shield under the mattress.
During attacks, it is necessary to place mustard plasters on the paravertebral area or wrap the chest with a warm scarf. If the pain intensifies, then you should take analgesics (sedalgin, analgin, etc.). It is also recommended to take B vitamins.
To prevent intercostal neuralgia from becoming chronic, it is necessary to reduce physical activity, try to avoid stressful situations and not abuse alcohol.
How to distinguish intercostal neuralgia from heart disease
Pain during angina occurs quickly and also passes quickly (within 2-5 minutes), it can be relieved with nitroglycerin. Heart pain does not change when moving or changing position, when exhaling or taking a deep breath, it is accompanied by an irregular pulse and an increase or decrease in blood pressure.
To clarify the cause of chest pain, magnetic resonance imaging and radiography should be done.
If pain is felt under the left shoulder blade, you will need a cardiogram. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Tachycardia
Most heart diseases can be fatal. Among them is tachycardia, characterized by disruption of the heart. Symptoms are usually as follows:
- fainting and feeling of lack of strength;
- strong pressure in the temples, neck and heart areas;
- cold sweat and weakness;
- darkening of the eyes and dizziness.
In addition, pulsation in the heart area and deterioration of sleep and appetite are possible. An increased pulse or, conversely, a decreased one is the influence of blood flow. Normally, the pulse should be 60-90 beats per minute, and if it is higher, then there are already signs of tachycardia. It usually occurs due to the following influencing factors:
- endocrine disorders;
- hypotension;
- decreased hemoglobin level;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- exposure to certain medications;
- emotional stress or physical stress.
However, an elevated pulse may not always indicate heart problems. The reasons for increased heart rate and increased pulsation may be the release of adrenaline into the blood, which occurs during fast running, intense physical exertion, excitement and a sudden change in stressful situations. In such cases there is no reason to worry.
Causes
Each person feels pulsation in the heart area with a different number of beats. Some observe at 100 contractions per minute, others only at 120 - 130 times. In medicine, there are several main reasons for increased heart rate:
- Tachycardia. The pathology causes sensations of pulsation not only in the heart area, but also in the neck, temples, toes and hands. Diagnosed at 90 or more beats per minute;
- During the period of hormonal changes;
- When the stomach is full;
- Allergic reaction to medications;
- Colds;
- Increased body temperature;
- Emotional stress, exciting moments in life;
- Increased sports loads;
- Running training;
- Climbing a mountain or using stairs;
- Abuse of drinks and products containing caffeine;
- Exceeding the concentration of nicotine in the blood (smoking abuse).
Most causes are not diseases. Pathological deviations that cause pulsation in the heart area are observed due to the influence of external factors. Physical activity, emotional stress or bad habits cause heart palpitations. This is a normal reaction of the heart muscle. The organ tries to provide enough blood to all organs and tissues. If a characteristic symptom occurs at rest, you should contact a cardiologist for diagnosis. This sign is a deviation from the norm and indicates a malfunction of the heart.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of tachycardia. This may be cardiosclerosis, myocardial dystrophy, arrhythmia. Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine or nervous system. Lack of iron in the body (anemia). Hypoxia, hypertension or congenital heart disease.
Nervous tic
Quite often, patients, at any age, may encounter a similar problem. Sometimes it is associated with contractions of muscle fibers in the chest. They are usually expressed by convulsions and can be attributed to a nervous tic. Such twitching usually occurs when:
- constant emotional instability of a person;
- physical activity on the back;
- scoliosis;
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine;
- uncomfortable body position.
FacebookvKontakteTwitterWhatsApp
Symptoms
Attacks of increased heart rate are often accompanied by accompanying symptoms:
- a person feels pain in the chest;
- there is a feeling of lack of air in the lungs, deep breaths are required;
- there is noise in the ears or completely in the head;
- pulsates in the heart area, in the temporal zone, in the fingers and toes, on the neck.
The above symptoms may be temporary or permanent. If it occurs periodically during stress or anxiety, do not panic. The symptoms will go away on their own. If signs are observed without external factors, you need to consult a doctor. During normal functioning of the organ, pulsation should not be felt.