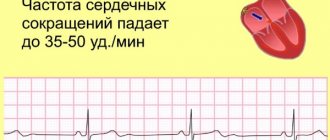
If you are often worried about dizziness, increased heart rate, or pressure surges, then first of all you need to consult a neurologist (neurologist). It is an experienced neurologist at the EXPERT Clinic who will be able to carry out the differential diagnosis necessary to exclude other diseases with symptoms similar to VSD.
Neurologist Bezukh Svetlana Mikhailovna - Doctor of Medical Sciences, professor with 37 years of medical experience. The accumulated experience allows her to quickly formulate a diagnosis, prescribe only the necessary examination and effective treatment.
During the consultation, the doctor will conduct an examination and ask you in detail about your complaints - how, where exactly, in what situations your head hurts and feels dizzy, whether there are pressure surges, attacks of nausea, fainting, how long the attacks last and other questions.
The neurologist will also prescribe the necessary instrumental and laboratory examinations, which can be partially or fully completed immediately after the consultation:
- ECG
- Ultrasound of bracheocephalic vessels (head and neck)
- 24-hour ECG and blood pressure monitoring
- x-ray of the spine
- blood and urine tests.
Additionally, you may need to consult related specialists - a cardiologist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist.
The influence of VSD on exercise tolerance
Playing sports with VSD is permissible in almost all cases, but with some restrictions.
The load should be chosen in consultation with the attending physician and depending on the state of health. With a mild course, maintaining the ability to work, good tolerance to physical activity, and minimal pain, it is allowed to engage in almost all types of sports. The diagnosis of “vegetative-vascular dystonia” does not limit activity in any way.
Permitted types of loads:
- run;
- fitness;
- yoga;
- Pilates;
- a ride on the bicycle;
- step aerobics using a low platform;
- swimming;
- skating;
- fitball
The average severity of the pathology with some decrease in working capacity and periodic vegetative crises does not cancel sports activities. You should monitor your heart rate and if it increases, stop training and rest.
A severe degree with severe respiratory disorders, frequent vegetative-vascular crises, and pressure changes implies refusal to exercise in the gym. For such patients, the doctor must select a complex of exercise therapy.
An approximate set of exercises:
- describe circles with your hands in different directions;
- put your palms together in a locked position and press them against each other for fifteen seconds;
- tilting the head in different directions for five to six approaches;
- circular movements of the shoulders, slightly turning the torso to the right and left;
- hands on the belt, fix the leg bent at the knee for 4-5 seconds, do seven approaches for each limb.
If the load causes darkening in the eyes, increased heartbeat, chest pain, dizziness, severe weakness, you should stop immediately, drink water and a sedative. Further tactics should be discussed with your doctor.
Physical activity for VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia and sports are completely compatible concepts, although it is still not advisable to engage in some sports. Doctors are also wary of recommendations to continue professional sports training with VSD. But moderate physical activity is even welcome, because it increases the effectiveness of therapy. Let's take a closer look at which sports are not dangerous for VSD, and which sports activities should be continued with caution.
- Allowed
With VSD, running, swimming, step aerobics, morning exercises, yoga, and badminton are among the sports that are allowed.
- Forbidden
Martial arts, weightlifting, powerlifting, arm wrestling, kettlebell lifting, bodybuilding, discus throwing are on the black list for the diagnosis of VSD.
Chess is also prohibited for people with VSD. The whole point here is not physical, but emotional stress. In addition, a chess player can sit in one position for hours. A surge of emotions against the background of a lack of muscle load can lead to a hypertensive crisis during VSD.
If you have vascular dystonia and you are going to the gym, here is what you need to remember. The entire lifestyle is of great importance: with VSD, you need a correct daily routine, including at least seven hours of sleep and good nutrition. At the same time, there is no overload on the body. Moreover, it is necessary to forget about overloads during training. When playing sports, it is important not to forget about your pulse and blood pressure. However, do not control them manically, otherwise you will develop neurosis and the effect of the stress will decrease.
Best Sports Workouts
Let's take a closer look at what sports are recommended for VSD.
The best form of physical activity for VSD is running. It uses more than 80% of the muscles, the whole body works. All its systems and internal organs are better supplied with oxygen. If you approach the process correctly, think through a plan for regular training to run, gradually increasing the load, you can easily reduce the symptoms of VSD.
This is because with a gradual increase in loads, the heart muscle will slowly learn to pump a larger volume of blood. The functioning of the brain will also improve, which will begin to receive more oxygen, thought processes will accelerate, and the consequences of neurosis, psychosis and depression will go away. All this will help you more easily survive stress during VSD. With all its advantages, running has one more huge advantage - it is the most accessible sport and in order to practice it, you do not need subscriptions to expensive gyms or expensive equipment. All you need is sneakers and a desire to play sports.
Fitness is an effective way to maintain good physical shape. It represents a set of measures that will help strengthen all muscle groups, the immune and cardiovascular systems, lose weight, and maintain tone. With the help of fitness, you will become more resilient, strong and flexible, rejuvenate your body, and forget about stress and irritability. With the help of fitness, you can also reduce the symptoms of VSD.
Horseback riding, cycling and skiing
Equestrian sports and cycling also have no restrictions in the presence of VSD. But we must remember about the smoothness of movements. In winter, swap your horse or bicycle for skis or skates.
The autonomic system is part of the central nervous system and is responsible for the functionality of all internal organs and their interaction within the system. She is responsible for the following functions:
- ensuring the interaction of reflexes and brain signals;
- perception of the environment, relaxation or tension depending on the factors affecting the psyche;
- the first solution is to activate the parasympathetic department of the autonomic nervous system: nutrition, rest, sleep;
- the second is the sympathetic department: defense and attack of the body.
The ANS consists of two departments, each of which is responsible for its own functions. One allows the body to relax, the other allows the body to tense up.
VSD and charging
To prepare the body of a patient with dystonia for regular heavy exercise, it is necessary to simply do exercises at home for the first month. Just 15–20 minutes daily will give positive results within a month. For hypothalamic dysfunction, it is recommended to perform the following set of exercises:
- Side bends from a standing position. Help strengthen the oblique abdominal muscles and increase blood flow.
- Abdominal exercises from a lying position. Strengthens the spine and abdominal muscles.
- Stand in side and horizontal plank for 1 minute.
- Exercise "bicycle". Increases vascular tone in the legs and improves venous blood flow from the lower extremities to the heart.
- Stretching exercises.
- Lifting dumbbells with your hands.
- Pushups.
A competent approach to organizing physical activity for patients with dystonia is a direct path to improving overall well-being. Along with physical hardening comes optimism and self-confidence.
Sports against the backdrop of VSD
VSD refers to pathological signs associated with impaired functioning of autonomic reactions. Their list can be very extensive. We list the most common ones found in the clinic:
- headache;
- fluctuations in blood pressure and temperature;
- emotional lability;
- excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis);
- periodic and reversible sensitivity disorders (paresthesia);
- chilliness, or periodic feeling of heat;
- redness or paleness of the skin;
- panic attacks, or “vegetative storms”, which are accompanied by the fear of death.
Sport with such symptoms is a controversial issue.
Some doctors try to convince patients that physical activity is undesirable for them and can aggravate the condition.
But there are exercises to normalize the functioning of blood vessels. Therefore, VSD and sport are often interconnected. And in the end, life is movement. And for functional disorders, it is quite possible to choose the right exercises that will not cause unpleasant symptoms.
Recommended types of exercise
When making a diagnosis related to dysfunction of the autonomic system, you need to start every day with physical activity. Immediately after waking up, you need to perform several correctly selected exercises aimed at:
- to strengthen the heart and blood vessels;
- to work with breathing;
- to develop coordination;
- to improve muscle stretching.
Each exercise must be performed slowly, without unnecessary effort, trying to feel muscle pleasure. For concomitant diseases, a set of exercises is selected taking into account not to cause harm. If you have symptoms of cardiovascular diseases such as high or low blood pressure, you must exclude:
- sudden movements;
- increased cardio loads that make you short of breath;
- jumping and shaking, etc.
General recommendations
If the vegetative-vascular system is disordered, you can choose different sports, with the exception of those that cause a heartbeat above normal, shocks and concussions. This could be: Nordic walking, swimming, gentle jogging, cross-country skiing. Training should be regular and moderate. But with VSD, physical therapy (physical therapy) must be included in the adaptation course. The advantages of this type of physical activity are that they:
- performed from a standing or lying position;
- aimed at all muscle groups;
- train breathing and develop coordination and flexibility.
Physical therapy for VSD should be performed regularly. It is better to exercise in the morning, an hour after a light breakfast, an hour before a second breakfast or snack. Exercises should be selected in such a way that strength loads, stretching and relaxation movements alternate. They should be performed slowly, until you feel slightly tired, excluding overwork.
For those who have a diagnosis of VSD, moderate and quiet exercise in the gym is useful, but only in cases where there is a tendency to hypotension: if you have high blood pressure, you cannot exercise on exercise machines.
When putting together a complex using simulators, you must definitely select exercises to improve or correct your posture. Most often, VSD develops in people with poorly developed back muscles. The condition of the spine causes incorrect position of the internal organs, their normal blood supply and function deteriorate. All this aggravates the condition of the patient, who definitely needs to strengthen his back.
Swimming with VSD
Swimming for vegetative-vascular disorders is necessary. This is one of the most gentle and at the same time effective sports. The main goal of water exercises is to develop general endurance and at the same time normalize the functioning of the central nervous system. Calm swimming, without racing for distance and speed, will bring benefits.
Compliance with the contraindications noted by experts for people with VSD can significantly improve the quality of life of the latter and save them from exacerbations of the negative symptoms of this disease.
How to plan a training regimen for a patient with VSD?
Classes begin with stretching, smooth movements, controlling breathing and heart rate. First, the exercises are performed for 7-12 minutes. When training, you should avoid positions with your legs raised up. It is important to combine aerobic and anaerobic exercise to engage all muscle groups.
There is no need to allow yourself to become exhausted; only a feeling of slight fatigue is possible . You should not exercise in a stuffy room; if you feel unwell, it is recommended to temporarily stop training.
Breathing requirements when playing sports:
- smooth inhalation through the nose and exhalation through the mouth;
- breathe with your diaphragm;
- The breathing rhythm must correspond to the movements performed.
What is VSD
VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia) is an outdated name for autonomic dysfunction. The term is used only by domestic doctors in relation to a variety of dysfunctions of internal organs, different in manifestation and origin, caused by a violation of their nervous regulation.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is often first identified at school age, which is explained by the increased pace of life and increased workload during study. An organism that is unable to withstand such pressure, defending itself and demanding a break, “gets sick.” This is expressed in the form of neurosis, accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, imitating the characteristic symptoms of chronic diseases. The condition worsens significantly if it is accompanied by depression or hysteria, anxiety, hypochondria and bad habits.
Restrictions in sports activities for patients with dystonia: when and how to introduce them?
Vegetative-vascular dystonia and sports are incompatible professionally. Patients with any type of VSD should avoid super-intense exercise, since extensive symptoms limit the endurance and performance of the athlete.
You should not participate in professional team sports, especially playing for results at any cost. This could trigger a crisis.
Weightlifting or powerlifting is prohibited for dystonic patients. Any wrestling, boxing, or sparring in martial arts is prohibited. These sports involve sudden lunges without respite, which leads to increased blood pressure, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
The following types of load are contraindicated:
- barbell bench press;
- parachuting;
- acrobatics.
Is it possible for a teenager to play sports with vegetative-vascular dystonia?
Sports are recommended for teenagers for better physical development, as well as a way to relieve psychological stress. But if a child has been diagnosed with VSD, then parents have a question about the possibility of serious training.
Are the symptoms of VSD dangerous for a child?
VSD in adolescents often manifests itself as headaches, fainting, impaired attention, attacks of palpitations and hyperventilation, night terrors, and unmotivated aggression. Such symptoms may cause restrictions. The teenager is protected not only from professional sports, but sometimes also from school physical education. Does such measures make sense?
A full medical examination is necessary to understand the risks. Upon admission to any sports section, children undergo a medical examination. But in addition to standard procedures, a teenager with suspected vegetative-vascular dystonia should be examined at least by a cardiologist and a neurologist, and be tested for the condition of the thyroid gland. The results obtained will allow you to assess your health objectively. If VSD is ultimately confirmed, then the symptoms from the heart and other organs do not pose a danger to life.
Features of training for juniors with dystonia
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia in a teenager may appear for the first time precisely against the background of active training. This happens because the tone of the sympathetic nervous system increases under high loads, and an imbalance between the parts of the autonomic nervous system makes itself felt. Of course, adolescence is conducive to such problems, but with thoughtful training tactics, the onset or exacerbation of symptoms can be avoided.
With regular and feasible exercise, playing sports will only bring benefits. The development of physical qualities helps eliminate imbalances in autonomic regulation and reduces the role of emotions in the formation of body reactions. Psychologically, a teenager who has the slightest achievement in sports feels much better and more self-confident. The coach has objective criteria that measure achievements, which is very important at this age for self-esteem.
Taking amino acids, which improve adaptation to stress and protect the heart, will help to establish the training process for vegetative-vascular dystonia. Glutamic acid, cystine and glycine are the material for the production of glutathione, a strong protective substance that is synthesized in the body. from the Eltacin® and act as efficiently as possible, so it is recommended for constant use by young athletes with VSD.
Reasonable loads for a teenager, together with enhanced amino acid protection, will help eliminate the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia and improve health indicators in adulthood.
Why children don't want to go to physical education
Having discovered that the child has vegetative-vascular dystonia, parents rush to get a certificate giving an exemption from physical education.
The reasons for this behavior of loving relatives are that the child is weakened, he does not like this subject, which means that he needs to be relieved of unnecessary stress.
Children do not like physical education lessons and dream of being exempt from it because:
- they are afraid of not coping with the teacher’s task and becoming a laughing stock among their peers;
- value their attractiveness to the opposite sex. This is especially true for girls, for whom not all teachers give concessions on menstrual periods. Girls who have not yet formed are afraid that they might get their uniform dirty, and their classmates will see it;
- the child is really sick and this prevents him from doing certain exercises;
- Classes are just boring.
Such reasons are rarely voiced by students from schools where:
- boys and girls are engaged in physical education separately;
- teachers respect the physiological characteristics of little women;
- instead of traditional physical education lessons, you are given the opportunity to choose a sport (swimming, aerobics, volleyball, etc.).
Group I
Clinical examination is a comprehensive medical examination of the population, designed to identify diseases and risk factors, as well as a general assessment of the health status of citizens of the Russian Federation, including: examination of patients, laboratory tests, promotion of a healthy lifestyle and drawing the attention of citizens to the state of health of their body.
Persons under 18 years of age undergo medical examinations annually, and the majority of the adult population - once every three years, starting at established age periods (21, 24, 27, etc. until 39) and annually after 40 years.
In this article we will look at what health groups are distinguished based on the results of medical examination of adults and children, and how they differ.
Health groups for adults
Clinical examination is the main activity for research and monitoring of the health level of the adult population. Based on the information obtained as a result of the medical examination, the doctor or paramedic assigns each citizen a health group in accordance with the requirements and criteria defined in Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated March 13, 2021 N 124n “On approval of the procedure for conducting preventive medical examination and medical examination of certain groups of adults population"
The normative act distinguishes four health groups of the adult population - 1, 2, 3a and 3b.
I includes persons who do not have any chronic diseases, as well as risk factors for the development of such diseases, or who have the indicated risk factors with low or average absolute cardiovascular risk and who do not need clinical observation for other diseases (conditions). ).
The results of laboratory examinations of this group of people are within normal limits. As you might guess, this category includes citizens with the most favorable level of well-being.
Based on the results of the medical examination, preventive consultations and other therapeutic and health measures are carried out for people in this category, with the main goal of promoting a healthy lifestyle and compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards.
Group II
This category includes people who do not have any chronic diseases, but are at increased risk of acquiring them. In addition, this includes people who are predisposed to developing cardiovascular diseases. This group is the largest in number, which is associated with a large number of factors that negatively affect the human body (bad habits, poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, climate pollution, etc.).
This category of citizens is diagnosed by conducting a generally accepted standard health examination, as well as additional studies of individual risks, if any.
II includes citizens who have not been diagnosed with chronic non-infectious diseases, but have risk factors for the development of such diseases
- with high or very high absolute cardiovascular risk,
- as well as citizens who have been diagnosed with obesity and (or) hypercholesterolemia with a total cholesterol level of 8 mmol/l or more, and (or) persons
- smoking more than 20 cigarettes a day,
- and (or) persons with an identified risk of harmful alcohol consumption and (or) a risk of consuming narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances without a doctor’s prescription, and who do not need dispensary observation for other diseases (conditions).
Citizens with health group II with high or very high absolute cardiovascular risk are subject to dispensary observation by a doctor (paramedic) of a department (office) of medical prevention or a health center, as well as a paramedic of a paramedic health center or a paramedic-obstetric station, with the exception of patients with total cholesterol levels 8 mmol/l or more, which are subject to dispensary observation by a general practitioner.
For citizens with health group II, if there are medical indications, the general practitioner prescribes medications for medical use for the purpose of pharmacological correction of identified risk factors.
Group III (a and b)
Group IIIa includes persons suffering from chronic non-communicable diseases (CNCDs), which require dispensary observation and highly qualified medical care. The bulk of citizens in this category are people over 40 years old, whose ailments are directly related to age and aging of the body. Medical examination of such persons is carried out for the purpose of secondary prevention, namely to prevent complications and exacerbations of an existing disease.
Category III b includes persons who have not been diagnosed with chronic non-diseases, but who require the establishment of dispensary observation or the provision of specialized, including high-tech, medical care for other diseases, as well as citizens suspected of having these diseases who require additional examination.
Citizens with III a and III b are subject to dispensary observation by a general practitioner and medical specialists with preventive, therapeutic and rehabilitation measures.
Health groups for children
The health groups identified based on the results of clinical examination of the children's population differ significantly from those of adults. First of all, it is worth saying that there are as many as 5 categories for classifying children (as opposed to 3 for adults).
This amount is associated with the increased vulnerability of the child’s body to various diseases, which is why their clinical examination requires more attention and thoroughness, which ultimately leads to the receipt of a significant amount of information for classification into categories.
1 group
This category includes physically and mentally healthy children who have high body resistance to disease. They can also sometimes get sick, but at the time of examination they do not have any pathologies. In fact, group 1 includes children who are not sick at all, but in practice there are very few such children.
2nd group
This category includes children who do not suffer from chronic diseases, but have reduced immunity. Such babies can suffer acute infections several times a year, but nothing more. They are usually divided into several subgroups according to the type of risk. For example, category “A” includes children with problematic heredity, and “B” includes children at risk of developing chronic diseases.
3 group
Category 3 includes children with any chronic disease. However, patients in this category are distinguished by the fact that such a disease occurs in a state of compensation. This means that, despite the presence of pathology, the child does not face severe consequences or exacerbations of the disease and can lead a normal life.
4 group
This health category denotes children with chronic illnesses in the subcompensation stage. In this state, there is already a significant deterioration in well-being, disruption of the functioning of some organs and reduced body resistance. Such children often need constant treatment and rehabilitation, while their diseases are most often expressed in some kind of physical disability, and their neuropsychic development is normal.
5 group
This category includes children with serious chronic diseases in a state of decompensation. These are disabled children with severe developmental problems or reduced functionality. It is worth noting that diseases of this group are not always congenital. An absolutely healthy child after an illness, surgery or injury can receive group 5. Such children almost always require constant supervision and assistance.
Conclusion
Thus, health groups represent a scale by which the condition of the body, both an adult and a child, is determined.
Taking into account examinations by specialized specialists, the health group is determined by a pediatrician or therapist, who, in turn, carries out a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the human body.
Read also:
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated December 30, 2015 No. 2158 “On conducting clinical examination of certain groups of the adult population of the Republic of Crimea in 2016”
- Stages of medical examination
- Regulatory acts
- Health groups for adults and children
- Clinical examination. Question answer
- Results of medical examinations and medical examinations in clinical hospital No. 1 for 9 months of 2016
- Working ahead. How medical examination improves health
- Results of medical examinations and medical examinations in KB No. 1 for 2021
- Why undergo medical examination if you feel healthy?
- Free medical examination of the population in 2021: what does it include and who has the right to undergo it?
- Complete information about medical examination
- Ministry of Health: medical examination allowed to increase the detection of cancer by 72%
- All-Russian medical examination has started
- Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated March 13, 2019 N 124n “On approval of the procedure for conducting preventive medical examination and medical examination of certain groups of the adult population”
- What diagnostic studies are carried out as part of medical examination at the first stage by age?
- What diagnostic studies are carried out as part of the medical examination at the second stage?
- Medical examination goals
Fitness for hypertensive type of VSD
This type of VSD is characterized by excessive vascular tone and high blood pressure (more than 140/90 mm Hg). If this condition is not controlled, it can develop into hypertension. A person is worried about fatigue, headaches and palpitations. In contrast to ordinary hypertension, numerous signs of vascular disorders appear: redness of the face and neck, “marbled” coloring of the skin, coldness in the legs and arms.
“For this type of VSD, breathing exercises, meditation, stretching are great - anything that promotes relaxation,” says Anastasia Yurkova. And to strengthen muscles and form correct movements - Pilates. For cardio, I would recommend walking in the park, swimming, cycling.”
Most trainers recommend completely abandoning strength and interval training. An exception can only be made by those who are already accustomed to such fitness. But they should also reduce the load by 30% and constantly monitor their pulse and blood pressure. Even with a slight deterioration in well-being (pressure and pulse increase after training and at rest), this type of training should be canceled, replacing it with a gentle one - the already mentioned Pilates, tai chi, yoga, walking.
Summary
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is not a disease, but it can be a manifestation of:
- diseases of the central or peripheral nervous system;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular or endocrine systems;
- chronic stress, overstrain, overwork.
Therefore, when identifying VSD, you should be thoroughly examined to identify serious diseases with similar symptoms.
Exemption from physical education during VSD can have a negative effect - physical activity is important for the harmonious development of a person. You need to talk with your child, watch him and find the sport that is right for him. Some teachers agree and allow you to replace physical education lessons with regular attendance at sports sections, subject to successful completion of the required standards at the school.
We recommend watching:
We recommend reading:
Insomnia and VSD
Previous article
Cancerophobia or fear of getting cancer
Next article
Fitness for hypotonic type of VSD
With this type of VSD, vascular tone is reduced, and accordingly, symptoms of vascular insufficiency predominate. Pressure 100/60 mm Hg. Art. and below provokes weakness, pallor, a feeling of lack of air, rapid breathing and yawning. Fog in the eyes, dizziness and even fainting are possible when moving from a horizontal to a vertical position. Also characteristic are redness or cyanosis of the face and neck, “marbled” coloring of the skin, and an unreasonable drop or rise in temperature. “Light cardio is recommended for such people,” says Anastasia Yurkova. This could be a walk, swimming and, of course, yoga, which will help strengthen muscles and work with breathing.”
If you are used to fitness, try training according to your usual pattern, but reducing the load by 25-30%. Definitely avoid exercises that involve sudden changes in body position (jumping, burpees, exercise on a high step platform) and those where the head drops below chest level (bending over, deadlifts, etc.). Also avoid lifting your legs while lying down (to pump up your abs, use an incline bench on which you lie with your feet down). Even if these exercises are included in a generally gentle lesson (Pilates, fitball class), ask the instructor to give you a safe analogue.
[new-page]
Fitness for cardiac type VSD
Doctors talk about the cardiac type of VSD if a person is bothered by pain in the heart, but ECG, EchoCG and other diagnostic methods indicate the absence of cardiac pathologies. Most often, this type of VSD manifests itself during stress and hormonal changes in the body. Sensations in the heart area can be very different: sharp, stabbing, burning pain or, conversely, arrhythmia, diffused throughout the heart. A characteristic feature is that pain may appear and disappear, but does not progress, that is, the person’s general condition does not worsen. “In this case, the emphasis should be on basic cardio,” says Anastasia Yurkova. — Uniform training with a pulse zone of 50-55% of the maximum heart rate and a duration of 45 minutes or more. This intensity is typical for walking, cycling, skiing, rollerblading, relaxed breaststroke swimming. As experts say, health needs to be improved.
When doing fitness for different types of VSD, always listen to yourself. Feeling good and in a good mood during and after the activity indicate that it was beneficial. But unpleasant sensations (especially a rise or fall in blood pressure and pain in the heart) are a reason to refuse such training. And instead of them, for example, just walk more in the fresh air.