Iron deficiency is much more common than deficiencies of other minerals or vitamins. Iron deficiency is especially common in women during pregnancy. Why does this happen, why is low iron level dangerous for mother and child, and how to avoid it?
Iron is one of the most important microelements for the body. After all, iron is part of hemoglobin - the “transport” that carries oxygen to all our cells and tissues. With iron deficiency, the amount of hemoglobin decreases, causing the body to lack oxygen. All biochemical processes slow down, the person feels weak and tired.
In addition to hemoglobin synthesis, iron has other functions; it is necessary for the normal functioning of the endocrine and immune systems.
Symptoms of low hemoglobin
Signs of iron deficiency anemia:
- darkening of the eyes, headaches;
- pale skin;
- lethargy, apathy, weakness;
- low blood pressure, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat;
- chilliness;
- the patient wants to eat chalk and earth;
- massive hair loss;
- brittleness and thinning of nails.
Diagnostics
Hemoglobin levels are checked repeatedly during breastfeeding. While a woman is in the maternity hospital, this test is taken at least three times (on the day of birth, the next day and upon discharge). In the future, the schedule for taking tests is prescribed by the local doctor or visiting nurse. A nursing mother should undergo examinations and donate blood on time to prevent the development of chronic anemia.
The hemoglobin level is determined during a general blood test. In front of it, you cannot eat, smoke, or drink iron-containing medications 12 hours before donating blood.
Causes
The development of anemia during pregnancy and after childbirth is caused by several reasons:
- Sick iron consumption in the third trimester. During this period of development, the baby needs iron in large quantities, so the mother’s body begins to release the necessary vitamins, minerals, including iron.
- Large blood loss during childbirth, usually occurs during caesarean section.
- Diseases of the circulatory system, heart, various types of infections.
- Diet food or poor diet.
The most common cause of anemia is a strict diet. Most women who have given birth quickly want to return to their former shape, so they go on a strict diet. At the same time, they do not think that they are endangering their health and the baby. This can lead not only to the development of anemia, but also to exhaustion of the body.
Concomitant factors for the appearance of anemia after childbirth are stress, fatigue, bad habits (abuse of tea, coffee) and frequent childbirth (there should be a break of at least 3 years between pregnancies). In this condition, raising hemoglobin to the required level is much more difficult.
Some experts believe that the cause of iron deficiency anemia is an internal conflict in the body. This disease is more likely to affect women who suffer from a lack of care, attention, support and the fear of not being able to cope alone. Against this background, lethargy, weakness, headaches and darkening of the eyes appear. Thus, the body itself suppresses the woman so that she lies down and does not struggle with her problem.
According to Louise Hay, there are two psychosomatic causes of this disease:
- lack of self-confidence and low self-esteem;
- fear of life or complete lack of joy in it.
V. Zhikarintsev adds one more reason to this list - claims to the surrounding world.
Liz Burbo believes that blood is life itself. If a person has lost the taste for life, then this disease manifests itself. In confusion and ignorance, a person simply becomes lost and depressed, which negatively affects his health, including the functioning of the hematopoietic system.
Sh. Shalila and B. Baginski, famous healers, also believe that anemia is the result of a lack of joy.
A. Torsunov interprets this as follows:
“The human body, which tends to be sad and sad often, stops producing the required number of red blood cells. Passivity and pessimism lead to disruptions in the functioning of the circulatory system. But excessive fuss and overexcitement can also provoke this disease.”
Therefore, not only laziness reduces the activity of blood cells, but also passionate desires. Thus, the degree of activity of blood cells depends on the determination and positive attitude of a person. The more you enjoy and are satisfied with life, the more likely it is that your circulatory system will function properly.
Another example from Torsunov: it often happens that a child is unwanted, but due to circumstances, a woman carries it and gives birth. After giving birth, she falls into a deep depression - the child becomes a burden and a burden for her. Excessive fatigue and despair lead to the development of anemia. But if a woman enjoys motherhood, the number of red blood cells produced increases.
How does iron deficiency affect a child?
Iron is necessary for normal fetal development. It is required for the formation and development of several vital body systems, including the central nervous system. A review of research published in the Journal of Nutrition suggests that iron deficiency can affect the brain, which can negatively affect a child's future intelligence, cognitive abilities and emotional well-being [Grantham-McGregor S, Ani C A review of studies on the effect of iron deficiency on cognitive development in children. Journal of Nutrition. 2001].
When the embryo is formed and begins to grow, the main part of the iron is used for the synthesis of hemoglobin. Experience from developing and developed countries suggests that iron deficiency anemia in an expectant mother can lead to low birth weight in the newborn. This is evidenced by a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. The study also suggests that risks to the baby can be reduced by starting iron supplements early in pregnancy.
Infants born to mothers who took iron supplements have been found to have a lower risk of developing iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia in the first years of life.
An important factor for a newborn's hemoglobin level is the volume of blood that is transferred from the placenta before the umbilical cord is clamped. It is recommended to wait at least 2 minutes after birth before clamping the umbilical cord - this helps increase the newborn's blood volume by about 30% and reduces the risk of iron deficiency in infancy. Be sure to discuss this point with the doctor who will deliver the baby!
How to deal with anemia
The first thing you need to do is adjust your diet. If you have no contraindications, drink freshly squeezed juices from beets, carrots, pomegranates and apples. They can be mixed or diluted with boiled water.
The most valuable sources of iron:
- pomegranate;
- amaranth and alfalfa sprouts;
- Jerusalem artichoke;
- green buckwheat;
- rye;
- legumes;
- chlorophyll from nettle leaves, leafy greens, beet and carrot leaves;
- Milk thistle meal.
Among vegetables, tomatoes, herbs, pumpkin, beets and green vegetables will help increase hemoglobin. Fruits that contain large amounts of iron are quinces, peaches, apples, plums, apricots, persimmons and pears. Berries in the diet should include currants, cranberries, strawberries, strawberries and blueberries.
Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of acute anemia, you need to follow simple rules:
- If there is prolonged bleeding, consult a doctor. Minor but long-term blood loss can lead to iron deficiency.
- Avoid blood donation in the first year after childbirth and for 6 months from the date of the end of the guard.
- Eat right - your diet should be rich in foods that contain a lot of iron.
- Avoid stressful situations, try not to get nervous.
- Boost your immunity and avoid getting sick.
Important! Low levels of ascorbic acid in the body can lead to problems with iron absorption, so it is recommended to take preventive courses of vitamin C during breastfeeding.
A nursing woman should take care not only of the child, but also of her body, because the condition of the baby will depend on her health. When the first symptoms of anemia appear, you need to take a blood test and consult a doctor. The diet of a nursing mother should be rich in red meat, beef and rabbit liver, eggs, grapes, cabbage, tomatoes and red peppers.
Healthy recipes
There are several recipes that will help restore iron levels in the blood:
- Pour a glass of boiling water over 4 clover flowers, an hour after steeping, strain. Take ½ glass three times a day on an empty stomach for 30 days.
- Take a glass of walnut kernels and green buckwheat, chop in any convenient way, add honey, stir. Take 1 tbsp daily. l.
- Mix aloe leaves ground in a meat grinder with honey in equal quantities. Close the lid tightly and keep in a dark place for 5 days. Take 1 tbsp. l. in the morning, at lunch and in the evening before meals every day until you use it up.
- Make a mixture of honey, prunes, dried apricots and raisins - 500 g of each component. Take 3 tbsp. l. per day for a month. Mix dry nettle leaves with pollen and natural honey in a ratio of 3:1:2. Take 1 tsp. on an empty stomach half an hour before meals, washed down with water.
- You can increase hemoglobin using chyawanprash.
- Take 1 tsp on an empty stomach. milk thistle with a small amount of water.
For better absorption, iron must be taken with vitamin C (ascorbic acid), as well as preparations or products containing copper, zinc and manganese. These include tomatoes, lettuce, raisins, spinach. Some vegetables and fruits contain a complex of essential substances - iron and components that promote its absorption.
To increase hemoglobin, it is useful to take a long walk in the fresh air and give the body moderate physical activity, for example, yoga, swimming under water.
In addition to proper nutrition, it is necessary to reconsider your views and beliefs: a positive and optimistic person is less susceptible to this disease.
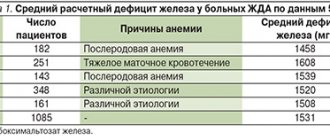
Laboratory indicators
In the last trimester of pregnancy, the hemoglobin level decreases by 10-15 units from the norm for a healthy, non-pregnant woman. When breastfeeding, reference standards are also reduced by no more than 20 units. If there was a large blood loss during childbirth, then hemoglobin may drop to 90 g/l, but these indicators should return to normal by 10 days after birth.
| Laboratory indicators of hemoglobin levels in the blood of women | |
| Healthy non-pregnant woman, 18-65 l | 120-150 g/l |
| 32-45 weeks of pregnancy | 110-115 g/l |
| Difficult birth | 90-100 g/l |
| The first three months under guards | 110-120 g/l |
| 4-12 months guards | 120-130 g/l |
For laboratory testing of hemoglobin levels in women after childbirth, a capillary (from a finger) or venous method of blood sampling is performed. In both cases, the test should be taken on an empty stomach, and medications containing iron and animal blood serum should be avoided.
What is hemoglobin and what does it affect?
When we inhale air, oxygen enters our lungs, which must be distributed to all organs and tissues. Hemoglobin acts as a “transport” that delivers oxygen. This is a protein of complex composition found in red blood cells. Having “delivered” oxygen to its destination, hemoglobin “carries back” carbon dioxide, which is expelled out through exhalation.
Thus, the existence of an organism without hemoglobin is simply impossible. And a change in its quantity, both up and down, affects well-being. When hemoglobin levels decrease, “oxygen starvation” occurs, which affects general well-being.