Pathologies and diseases of the spine
Below are the most common pathological conditions and diseases of the spine, accompanied by pain in the back and chest.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis, primarily thoracic, is characterized by severe pain (especially when inhaling) and symptoms such as lumbago radiating to the shoulder or scapular region, discomfort in the ribs and hypochondrium, aggravated by coughing, sneezing or laughing. Osteochondrosis (thoracic, cervical, lumbar) is caused by the following reasons: constant stay in the same position, serious physical activity (work or sports), injuries, age, sedentary lifestyle.
Intercostal neuralgia
With intercostal neuralgia, the chest and back hurt between the shoulder blades or in the middle. Acute pain in these areas is a characteristic sign of neuralgia. Discomfort is caused by hypothermia or lifting heavy things. This is perhaps the only disease that does not pose any particular danger to the body, but causes serious discomfort.
Scoliosis
Curvature of the spine due to scoliosis most often occurs in childhood, at school age, and only progresses over time if treatment is not started in time. Scoliosis not only makes our posture unattractive, but also creates serious discomfort. Pain in the chest in the middle and back appears with 3 or 4 degrees of scoliosis. Severely compressed vertebrae and the load give off sharp pain in the sternum or back.
Injuries
Any injuries sustained (spine, thoracic region or other parts of the body) cause pain in the chest (chest) or back, which can appear alternately here and there, or radiate to both areas at the same time. Injuries occur due to accidents, falls, physical injuries, etc. In such cases, it is better for a person not to move, he should not be moved if possible, since in case of serious injuries and wounds there is a high risk of internal bleeding.
Backache! Attention - osteochondrosis!
Osteochondrosis is a disease in which damage occurs to the cartilaginous surfaces of bones inside the joints. Symptoms of osteochondrosis manifest themselves in different ways. This depends on the degree and nature of changes in the intervertebral discs and surrounding tissues. In addition, the symptoms of this disease largely depend on the location of the lesion.
There are several types of osteochondrosis - these are cervical osteochondrosis, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and widespread osteochondrosis, which affects not only all parts of the spine, but also joints: shoulder, hip and knee. Of all the listed types, the most widespread are lumbar and cervical osteochondrosis.
The causes of osteochondrosis can be infections, hypothermia, stress, exposure to chemicals, decreased physical activity, as well as hormonal disorders and heavy lifting. Incorrect posture (standing, sitting or lying down) and work associated with flexion, extension, rotation and jerking movements of the body can also be the causes of osteochondrosis. The appearance of osteochondrosis is often promoted by falls, injuries, overload and congenital defects of the spine. It is known that sport has a positive effect on human health. But, if these sports and physical education activities are carried out without taking into account the influence of heavy physical activity, then this can also lead to the occurrence of osteochondrosis.
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
The first symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis is a tingling sensation in the shoulder blade, which spreads to the armpit and further to the elbow. At the same time, there may be a sensation as if there is a foreign body behind the sternum. Then the pain begins to surround the shoulder blade and go to the sternum. Pain may appear in the lower chest on the back, which will begin to descend into the groin. In addition, pain is often felt in the upper part of the stomach at night (appears when lying on your back). The pain can be quite severe and begins to intensify with any movements in the thoracic region. As morning approaches, the pain in the stomach begins to subside.
If you do not pay attention in time to the pain that appears in the thoracic spine, it will begin to spread to the middle part of the abdomen. When you turn your body, if you lie on your back or sneeze, this pain begins to intensify, causing pain in the right hypochondrium. If, with thoracic osteochondrosis, the upper lymph node is damaged, then headaches begin to appear, and the neck and face begin to ache. If the lesion affects the lymph nodes of the thoracic region, then the pain that appears in the back may be accompanied by nausea, heartburn, belching, as well as the appearance of pain in the right hypochondrium.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
With lumbar osteochondrosis, pain appears in the thigh, groin, lower leg and knee - on the affected side the leg straightens at the knee with great difficulty and pain. The pain then spreads along the outer surface of the thigh and down to the foot, causing difficulty in standing on the heel with the foot extended. Numbness of the lower leg or foot may occur, and the muscles begin to decrease in volume. There is severe weakness in the legs, and sharp, unbearable pain appears in the lower back, hips and lower legs. In more severe cases, fecal and urinary incontinence and the development of bedsores occur.
With lumbar osteochondrosis, severe pain appears after unsuccessful movement or sleep in the lumbar region, and after a few hours this pain begins to be felt in the leg. If this condition occurs for the first time in a person, then in a maximum of a week it goes away. This pain is associated with muscle spasm, which results in severe compression of the intervertebral disc, which causes such severe pain. To relieve this pain, the patient needs to be kept at rest, take a painkiller, and the sore spot needs to be lubricated with any warming ointment. If the pain does not go away, then you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe a number of measures to eliminate these pains, including acupuncture, manual therapy, laser therapy and electrophoresis . In some cases, a novocaine blockade is performed. After the pain is relieved, the patient must follow a number of preventive measures to prevent the pain from returning. But in many cases these pains become chronic. They begin to appear with any physical activity.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Severe pain appears in the neck, which turns into a headache, spreading to the forehead, eye or ear. Usually such pain appears only on one side. The pain intensifies with any movement of the head, especially with a sharp turn. Dizziness, crunching, nausea, tinnitus appear, and in some cases vomiting begins. The scalp becomes so painful that it is impossible to comb your hair. Hearing loss and vision deterioration may occur. Fainting often occurs when the head is turned suddenly, and there is a sharp increase in blood pressure. With cervical osteochondrosis, pressing pain in the heart may appear, radiating to the area between the shoulder blades. These pains can be quite long-lasting and only go away after taking validol. Unlike pain during an acute heart attack, a person does not experience the fear of death. He remains calm. Cervical osteochondrosis develops gradually, and within six months the pain can spread to the shoulder (swelling and stiffness of the hand appear). Soon these pains become constant and most often intensify at night, spreading along the arm, shoulder blade and neck.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis in typical cases does not present any difficulties. It is necessary to undergo a complete neurological, radiological and orthopedic examination. A neurological examination is prescribed to establish reflexes, since some such reflexes may be absent if the nerve roots are pinched. In order to determine whether there is an inflammatory process in the body, a blood test is prescribed. And, of course, an X-ray examination is prescribed, which will show the displacement of the vertebrae and the degree of their wear. Currently, for the diagnosis of spinal diseases, there are such instrumental research methods as ultrasound, radiography, tomography, myelography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, contrast discography, and electrospondylography.
Electrospondylography refers to modern computer functional diagnostics, which allows identifying the disease at an early stage of its development, as well as determining the level of damage and monitoring the course of the disease.
Ultrasound examination is not one of the main methods for diagnosing spinal disease. Using an ultrasound scanner, it is impossible to obtain a high-contrast and fairly clear image of the spinal structures.
Tomography allows you to view individual parts of the spine as best as possible using x-ray sections.
Myelography uses a contrast agent injected into the spinal canal . This research method is good for examining the spinal cord and nerve roots.
With the contrast discography method, a contrast agent is injected into the intervertebral disc, which can be used to determine the presence of pathological changes. Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern research method in which, using electromagnetic waves, images of organs and tissues can be obtained. This method does not have a negative impact on human health, so it can be used repeatedly as needed. Using this study, pathological changes in the intervertebral discs, disc herniation, and many other spinal diseases are detected.
When carrying out computer diagnostics , as well as when carrying out radiography, X-ray examination is used. Using computed tomography, pathological changes in bone tissue can be detected.
X-ray is a painless examination that allows you to assess the nature of the spinal lesion (traumatic or non-traumatic). X-rays can detect tumors and fractures of the spine, bone growths and other lesions of the spine. This study is the most common in the diagnosis of osteochondrosis.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Treatment of osteochondrosis is a rather difficult task, since treatment methods have not yet been found that could stop the aging process of the human body. But, if you choose the right course of treatment for osteochondrosis, you can not only slow down the development of this disease, but also prevent its complications.
When treating osteochondrosis, it is first necessary to ensure the patient's rest. If the symptoms of the disease are severe, the patient is hospitalized and prescribed bed rest until the period of exacerbation passes. With this disease, it is necessary for the patient’s bed to be hard, so it is recommended to place a shield made of wood under the mattress.
Treatment includes three stages:
- symptomatic treatment, which is prescribed to eliminate the main symptoms of osteochondrosis;
- surgical treatment that eliminates spinal deformities and spina bifida;
- prescription of restorative therapy, that is, rehabilitation of the patient.
In symptomatic treatment, the main goal is to eliminate pain. For these purposes, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics. Timely removal of pain helps prevent depression associated with chronic pain, as well as prevent pathological changes in the spine.
In addition to anti-inflammatory drugs, the patient is prescribed medications that improve blood circulation. These drugs help in time to prevent the occurrence of various changes at the level of internal organs.
A new direction in the treatment of osteochondrosis is the prescription of drugs that restore cartilage tissue. These drugs have a regenerating and anti-inflammatory effect, and also restore damaged cartilage tissue of the joints, as a result of which their mobility improves and the pain that occurs when moving disappears.
In addition to the listed medications, the patient is prescribed antidepressants and a vitamin-mineral complex. Physiotherapeutic procedures, therapeutic exercises and manual therapy are also prescribed.
Surgical treatment of osteochondrosis is prescribed in exceptional cases. Indications for surgical treatment are vertebral subluxations, quite severe deformation of the spinal column, as well as the formation of spina bifida.
Treatment of osteochondrosis in our medical center is carried out using shock wave therapy (SWT) and photodynamic therapy.
An acoustic shock wave with certain characteristics affects pathologically altered tissue areas, promoting the resorption of fibrous areas, the destruction of microcrystals of calcium salts and their removal from muscles, tendons and ligaments. At the same time, there is also a significant increase in microcirculation and metabolism in the affected area.
The effect is manifested in the reduction or disappearance of pain, muscle spasms, increasing the elasticity of ligaments and tendons, which allows increasing the range of motion in the spine and joints.
Before treatment, all patients are examined by an orthopedic surgeon , X-rays of the affected area are taken, and, if necessary, ultrasound examination of joints and tendons, and magnetic resonance computed tomography. Then a diagnosis of the disease and indications for shock wave therapy are established. All patients are given contraindications to UVT treatment .
The high qualifications of our employees and the vast experience they have accumulated in the use of shock wave therapy allow us to achieve the most positive effect in the treatment of osteochondrosis.
Shock wave therapy is carried out using a modern Masterpuls MP 200 device.
In addition to all the studies listed, it is also necessary to undergo an examination by a neurologist, orthopedist and chiropractor. In the diagnosis of osteochondrosis, the patient’s complaints also play an important role. Therefore, before you see a doctor, you need to try to remember all the pains that bother you, as well as how they appear and under what circumstances they subside. All these little things will be needed for a correct diagnosis, since many symptoms are very similar to other diseases.
The course of treatment of osteochondrosis using the UVT method consists of 5-7 sessions.
The session is carried out once every 5-7 days.
Advantages of the UVT method:
- efficiency;
- good tolerability (does not require anesthesia);
- reduces the need to use other methods, especially surgical treatment;
- rapid pain relief without analgesics;
- the ability to use at the chronic stage of the disease and during its primary manifestations;
- It is performed on an outpatient basis, does not require hospitalization, and does not disrupt the patient’s usual rhythm of life.
Prevention of osteochondrosis
To prevent osteochondrosis, as well as to prevent its exacerbation, it is recommended to apply a few simple rules that will help reduce the load on the spine:
1. It is recommended to go swimming and hang on the horizontal bar as often as possible.
2. To prevent back muscles from atrophying, you need to move more often - walk in the fresh air and do physical exercises.
3. If it is not possible to avoid lifting weights, then you should lift them not by bending over, but by crouching.
4. You should always try to keep your back straight.
5. You must try to avoid drafts and hypothermia.
6. It is important to promptly treat diseases of the musculoskeletal system, as they contribute to the appearance of osteochondrosis.
7. It is necessary to change body position frequently, especially if the work involves prolonged sitting.
Proper nutrition plays a major role in the prevention of osteochondrosis. From childhood, you need to include in your child’s diet foods that contain magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, manganese, as well as vitamins A and C. Orange and yellow vegetables and fruits are very rich in vitamin A. And sweet peppers, berries, herbs and, of course, rose hips and lemon are rich in vitamin C. It is also necessary to include fermented milk products, cheese, cabbage, corn, various nuts, as well as eggs, liver and legumes in the menu.
Since ancient times, it was believed that a person’s health depends on his spine. If the spine is healthy, then the person will feel good. Our modern medicine also confirms that human health is determined by the health of the spine. Therefore, in order to maintain your health for many years, you need to spare and take care of your spine from an early age. And if any changes appear on his part, you must immediately seek help in order to prevent the development of the disease in time.
Kravchenko O.M., orthopedic traumatologist of the highest category, medical, Krasnodar.
Cardiovascular diseases
The appearance of any pain in the chest area should alert you, because our most important organs are located here - the heart and lungs. Pain, depending on the disease, can be constant or intermittent, long-term or short-term, and accompanied by other symptoms. If you have problems with the stomach or pancreas, the pain often radiates to the lower thoracic region. Pain syndrome occurs during myocardial infarction
, angina pectoris, pneumonia, bronchitis,
diaphragm hernia
, stomach ulcer, oncology, etc.
Myocardial infarction
With myocardial infarction, the chest and back between the shoulder blades begin to hurt, and the pain can radiate to the left arm or shoulder, as well as to the jaw on the left side.
Angina pectoris
With angina pectoris, a characteristic pressing pain and burning sensation appears in the sternum, and sometimes radiates to the area of the shoulder blades.
Pericarditis
It manifests itself as a sharp change in body temperature, inflammatory processes in the heart area and pain on the left side of the chest.
Myocarditis
The disease is characterized by piercing, aching pain in the chest, as well as gradually appearing weakness throughout the body and difficulty breathing.
Case two
Man B., 40 years old. I visited a neurologist with complaints of severe pain in the lower thoracic spine . The patient reported that he has hernias in this part of the spine and has been treated for this disease for many years. He even provided the conclusion of an MRI study of the thoracic and lumbar spine to confirm his words. And before contacting a neurologist, patient B. independently completed a course of treatment with diclofenac - this course was prescribed to him several months ago by a neurologist at his place of residence. The patient decided to save time and not contact the doctor again; he was treated independently. But after completing the course of treatment, the pain not only did not decrease, it intensified, weakness and malaise appeared, and the patient stopped eating. When we conducted a full examination of the patient, it turned out that the patient had an ulcer penetrating into the pancreas. There is a special type of gastric ulcer when a “hole” forms not on the front surface of the stomach (with this location of the ulcer it can be felt with your hands, i.e. when palpating the projection of the stomach, severe pain will occur), but on the back surface of the stomach (in this case it cannot always be felt) and it “bites” into the pancreas, causing severe pain that extends to the lower thoracic spine. Such pain in the thoracic spine requires urgent treatment from an abdominal surgeon.
Oncological diseases
With cancer, pain appears in different areas of the body and can change location regardless of the location of the tumors. Typically, pain appears in the later stages, when the pathology has spread widely and caused serious harm to the person. The entire chest may hurt with lung cancer, and the pain is worst when you cough or breathe quickly. Another symptom of lung cancer may be coughing up blood. In women with breast cancer, there is pain in the chest and radiates to the back.
Treatment is based on therapy of the underlying disease.
Below we will talk about treatment for the most common causes of back pain - reflex and compression complications of osteochondrosis and myofascial pain.
Treatment of reflex syndromes and radiculopathies (treatment of back pain) due to osteochondrosis is based in the acute period on rest, avoidance of sharp bends and painful positions.
If movement is necessary, you should wear a neck or lumbar corset (fixing belt). You can use physiotherapeutic pain-relieving procedures, rubbing ointments, compresses with a 30-50% solution of dimexide and novocaine, novocaine and hydrocortisone blockades.
Surgical treatment of back pain (removal of a herniated disc) is necessary in those rare cases when compression of the spinal cord or cauda equina roots occurs.
Diagnostics
Since pain in the back and chest can simultaneously be a sign of a large number of diseases and pathologies, it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis only after conducting examinations and passing the necessary tests. The list of diagnostic measures is compiled by the doctor. You cannot engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication. What may be included in the diagnosis when a patient presents with the following complaints:
- collecting information about the patient’s problem and health status;
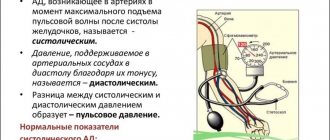
- examination, which includes listening to the heart and lungs, measuring blood pressure and pulse;
- X-ray, which makes it possible to evaluate the work and condition of the heart, lungs, spine and ribs;
- An ECG
is prescribed to evaluate heart function; - CT and MRI
make it possible to clarify the condition of internal organs and the presence of pathologies; - FEGDS and gastroscopy are prescribed for problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Laboratory tests may also be ordered. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after a complete examination of the patient.
Preventive measures for back and chest pain
To prevent back and chest pain, you will need to follow some rules and make some lifestyle changes. The most important measures are:
- correct diet in compliance with BJU and calorie content;
- drinking regime;
- night rest on a flat mattress and anatomical pillow;
- taking vitamin complexes;
- moderate exercise daily;
- active lifestyle (running, swimming, Nordic walking, walks in the fresh air);
- correct posture while walking and working at a desk;
- proper weight lifting;
- comfortable shoes.
Preventive visits to doctors and periodic examinations are also important. In addition, you need the right psychological attitude and positive thinking. By changing your lifestyle, you can reduce the likelihood of developing diseases, including preventing pain in the sternum and back.
Treatment
Treatment is selected depending on the diagnosis and may include both outpatient medication and hospitalization with surgery. The patient can also be prescribed and selected diet, physical activity and other measures for recovery, rehabilitation and reduction of symptoms and pain relief. The timing and number of treatment methods used are individual. If you have pain in the chest and back, go to the doctor. If you consult a neurologist
the problem can be solved either completely or the risk of complications and further health problems can be significantly reduced.
Prevention
To ensure that chest and back pain bother you as little as possible, you must follow some rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- You need to walk and sit correctly; to do this, try to slouch less.
- Avoid lifting objects that are too heavy. Neglecting this point may result in injury and pain. If you still need to lift something, you must first bend your knees so as not to create unnecessary stress on the spinal column.
- If possible, limit your body position to a sitting position. If you work at a computer, you need to get up and stretch your muscles as often as possible. It is better for drivers to periodically stop the car and go for a walk.
- Limit consumption of salt, sweets, fatty and spicy foods. It is recommended to eat foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Develop healthy habits: exercise, sleep at least 6-8 hours at night, eat right. A healthy lifestyle will help you feel a surge of strength and energy, and also relieve pain.
It is worth limiting, or better yet completely eliminating, drinking alcohol and smoking. After all, toxic substances lead to degeneration of all tissues, even bone. After scientific research, it was found that alcohol-containing drinks have the ability to wash out all trace elements from bones.
Causes of pain in the thoracic spine
Unpleasant sensations can be caused by stress and overwork, as well as pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
The most common causes of pain are:
- influenza and acute respiratory viral infections;
- bronchitis;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- osteochondrosis;
- spondylosis;
- arthrosis;
- various types of spinal deformities;
- myositis.