What does tachycardia mean in a child?
Pediatric cardiologists consider it a disease when the number of heart beats per minute exceeds the norm by 20-30.
On a note! An impulse originates in the sinus node in the right atrium, which spreads to the atria and causes them to contract. The impulse is briefly delayed in the atrioventricular node between the ventricles and atria and transmitted to the ventricles, causing them to contract. The sinus node independently creates impulses within itself at a certain frequency. This is called "sinus rhythm."
Tachycardia is not an independent disease, but a sign of some other pathology. However, there is physiological tachycardia, which occurs during physical activity, emotional arousal, during eating, and when body temperature rises. This condition is completely harmless and does not threaten the child’s life. Tachycardia can occur even in a newborn child if he laughs, tries to make movements that are new to him, etc.
Critical age periods
For young patients, there are critical periods during which an elevated heart rate is often observed. Most often, the child cannot explain exactly how bad he feels and what is the reason for such physiological changes. He feels pressure in his chest, dizziness, sometimes chills, and may even lose consciousness. You should not allow such frequent reactions to occur, and you should visit a pediatric cardiologist in Saratov as soon as you notice the first symptoms. A small patient may be afraid that his body reacted this way to running, watching his favorite movie and the fact that he received a gift that he had dreamed of for so long.
Types of heart rhythm disorders
Tachycardia is divided into three main types :
- Sinus is the most common. With it, the heart rate in the sinus node increases. Most often appears during physical activity. However, it may be the first sign of vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypertensive type and other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Paroxysmal (ectopic) - a sharp increase in the number of heart contractions by two or three times. Manifested by shortness of breath, abdominal pain, cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes. Source: E.L. Boqueria Ectopic atrial tachycardia in children: clinical picture, diagnosis and treatment // Annals of Arrhythmology, 2006, No. 3, pp. 16-19
- Chronic – a condition in which a child’s blood pressure decreases, convulsions, suffocation, and chest pain occur. Treatment is usually lifestyle changes. Parents should protect the child from psycho-emotional and physical stress, monitor his daily routine, ensure proper nutrition and general hardening of the body.
What does a low heart rate mean?
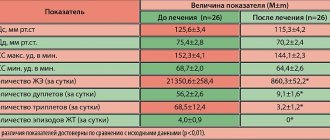
A decrease in heart rate below normal indicates bradycardia. With this disease, dizziness, pale skin, and high fatigue are often observed. Along with a low pulse, the development of hypotension cannot be ruled out. Here you can ask: “What should the child’s blood pressure and pulse be?” The pulse indicators are shown in the table above, and the pressure in a child aged 11 years should be in the range of 70-82 mmHg. Art. - diastolic; 110-126 mm Hg. Art. - systolic.
Left untreated, it can lead to heart failure. To prevent this from happening, you need to know what the normal heart rate is for children 11 years old.
Causes of the disease
Let us consider separately the causes of pathology in infants and preschoolers, schoolchildren, and adolescents.
Infants and preschoolers
In infants, severe tachycardia is considered to be a heart rate of more than 200 per minute. For preschoolers - depending on age, more than:
- six months – 185;
- 1 year – 160;
- 2 years – 150;
- 3 years – 140;
- 4 years – 135;
- 5 years – 120;
- 6 years – 115.
The reasons may be:
- fetal hypoxia during childbirth;
- anemia;
- dehydration of the body;
- fever;
- overheat;
- colds;
- congenital heart defects, which are diagnosed before birth and require constant monitoring. Source: A.I. Safina, I.Ya. Lutfullin, Z.A. Gainullina Heart rhythm disturbances in newborns // Practical Medicine, November 2010, No. 6(45), pp. 75-79
Often preschoolers do not want to do an ECG or even go to the doctor; they are capricious, worried, and cry. Under such conditions, an electrocardiogram will certainly show that the child has tachycardia. Therefore, it is better to conduct the study during sleep or after maximum calm.
Preschool children
Indicators of severe tachycardia are as follows (more than beats per minute):
- 7 years – 110;
- 8-10 years – 105;
- 11 years old – 104;
- 12 years old – 102.
The main reasons for an increase in heart rate at this age are emotional and physical stress. However, there are a number of diseases that cause such symptoms in this age group:
- myocarditis;
- primary rheumatic fever;
- long QT syndrome;
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
In the last two syndromes, the tachycardia is not sinus. In Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, it is supraventricular, and the heart rate increases to more than 140 beats per minute. With an extended QT interval, paroxysms (increased) of ventricular tachycardia appear, fainting may occur, and the heart rate increases to more than 140 per minute. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6595346/ Ranjit I. Kylat and Ricardo A. Samson Permanent junctional reciprocating tachycardia in infants and children // J Arrhythm. 2021 Jun; 35(3): 494–498
Teenagers
Severe tachycardia at this age is indicated when the pulse becomes more than (beats per minute):
- 13 years old – 100;
- 14-15 years old – 98.
The main reasons for an increase in heart rate in a teenager:
- rapid growth causing iron deficiency anemia;
- passion for diets;
- psychophysical fatigue;
- bad habits;
- poor physical fitness;
- excess production of thyroid hormones;
- high blood pressure;
- chronic pathologies of the heart and lungs.
Decoding the results
The normal pulse of a 17-year-old teenager can be found in the table. After the measurement, the value should be compared. If the indicator deviates slightly from the norm, it is impossible to say with a 100% guarantee that the child has some kind of disease.
Normal heart rate in teenagers, children and adults
This may be due to physiological reasons or incorrect measurement.
Symptoms of tachycardia in children
Symptoms and their intensity vary depending on the type of disease and its duration.
Main manifestations:
- vague discomfort in the heart area;
- feeling of heartbeat, heartbeat in the ears;
- lack of air, shortness of breath;
- pallor or blue discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes (in severe cases);
- weakness, fatigue, sluggish sucking in newborns;
- nausea due to dizziness;
- crying, anxiety;
- emotional arousal;
- faintness, loss of consciousness;
- sweating
Diagnostic methods
- Electrocardiography (ECG). After examining the printout, the doctor will be able to determine the type of tachycardia and see, for example, heart failure.
- Daily Holter monitoring is intended to detect paroxysmal tachycardia. Electrodes are attached to the baby's skin and connected to a compact device that takes readings around the clock. Sometimes it takes more than a day.
- Ultrasound of the heart (Echo-CG) - allows you to see the structure of the heart, structural abnormalities, visualize large vessels and heart valves and chambers, the thickness of the walls of the organ, and evaluate its contractile function. Ultrasound allows you to see heart defects.
- A clinical blood test aimed at detecting anemia. With it, a compensatory acceleration of heart rate occurs.
- Biochemical blood test for glucose levels and electrolyte composition.
- Blood test for thyroid hormones.
- Electroencephalography (EEG).
- MRI of the heart - in rare cases.
- Electrophysiological study (EPS) of the heart is necessary to evaluate electrical activity and find the source of impulses in the paroxysmal type of tachycardia.
Treatment of the disease
How to treat tachycardia will become clear after the cause is identified in the child. This pathology is treated by a cardiologist and other highly specialized specialists, depending on the results of the examination. For example, in case of problems with the thyroid gland, this will be an endocrinologist.
Important! If you find tachycardia in a child, then before consulting a doctor, exclude any stimulants from his diet - tea, coffee, chocolate, and protect him from stress as much as possible.
Therapy is selected individually, taking into account the underlying disease that caused the tachycardia. If a child has central nervous system dysfunction, a neurologist will prescribe sedatives. For heart pathologies, therapy is carried out by a cardiologist. At the same time, there are a lot of heart diseases, so treatment approaches vary. So, if an infection provokes myocarditis, then you will need to take an antibiotic. For autoimmune diseases that lead to arrhythmia, cytostatics and glucocorticosteroids are prescribed. Also, for any disease that causes tachycardia, the cardiologist can in any case prescribe a drug that will make the heart rate slower in order to relieve the load on the heart.
What to do if a child has an attack of tachycardia before the doctors arrive?
Until the ambulance arrives, there are several ways to alleviate the child’s condition:
The most important thing is to calm the child down, open a window or vent so that fresh air can enter the room. The following measures can then be taken:
- Wipe the child's face with cold water, and then place a cloth soaked in cold water on his face.
- Have your child close his eyes and then gently apply pressure to his eyeballs for a few seconds. This will provoke a reflex in which the heart rate decreases.
- Perform a Valsalva maneuver - the child should close his mouth and nose tightly and strain as if he wants to exhale.
- Massage the carotid sinus, that is, the place where the carotid artery divides into two branches - external and internal. This place is located approximately where the thyroid cartilage is on both sides of the neck. It’s easy to feel the thyroid cartilage; in men it’s called the “Adam’s apple.” After this, move your fingers slightly downward, and immediately under the Adam’s apple you will feel the carotid sinus with a characteristic pulsation. Apply pressure and massage for a few minutes. Source: L.A. Balykova, I.S. Nazarova, A.N. Silence Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in children // Practical Medicine, September 2011, No. (53), pp. 30-37
How and under what conditions does it appear?
A normal heart rate for a 15-year-old teenager can range from 61 to 81 beats/min. The indicator appears in the body due to the work of the heart. Its life activity is similar to a pump. That is, the heart pumps blood into the arteries.
Pulse waves are formed at the mouth of the aortic valve when fluid exits the left ventricle into the aorta and then spreads through the vessels at high speed. Stroke volume of blood occurs when systolic pressure increases, that is, the diameter of the arteries expands. And during diastole, the walls are restored to their original size.
The further the vessels are from the heart, the lower the pulse. For example, in capillaries it is impossible to feel the wave at the level of arterioles (small arteries).
Disease prevention
In order for not only the heart, but also the entire body to be strong and healthy, you must first normalize your diet. It is necessary to exclude all caffeine-containing drinks, as well as chocolate, fried foods and reduce the amount of sugar. The best diet is plant-based and dairy. Fruit juices and fresh vegetables are beneficial. Vitamin complexes will help reinforce the effect of the diet. The child must take magnesium and potassium, which normalize the heart rate. Consult your doctor first. And be sure to include moderate physical activity in your child’s daily routine, such as morning exercises. It stimulates the heart and increases its resistance to the release of excess adrenaline. As a result, irritability decreases and the emotional background normalizes. At the same time, you should not overexert yourself; any activity should be moderate. Swimming, for example, is very useful.
Sources:
- E.L. Boqueria. Ectopic atrial tachycardia in children: clinical picture, diagnosis and treatment // Annals of Arrhythmology, 2006, No. 3, pp. 16-19.
- A.I. Safina, I.Ya. Lutfullin, Z.A. Gainullina. Heart rhythm disturbances in newborns // Practical Medicine, November 2010, No. 6(45), pp. 75-79.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6595346/ Ranjit I. Kylat and Ricardo A. Samson. Permanent junctional reciprocating tachycardia in infants and children // J Arrhythm. 2021 Jun; 35(3): 494–498.
- L.A. Balykova, I.S. Nazarova, A.N. Silence. Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in children // Practical Medicine, September 2011, No. (53), pp. 30-37.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a cardiologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Electrocardiography (ECG) | 1400 rub. |
| Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) | 3500 rub. |
Amount of water to cleanse the intestines
| Age | Amount of water for cleansing enema (ml) | Amount of water for siphon enema (ml) |
| 1-2 months | 30-40 | — |
| 2-4 months | 60 | 800-1000 |
| 6-9 months | 100-200 | 1000-1500 |
| 2-5 years | 200 | 1000-1500 |
| 6-10 years | 300 | 2000-3000 |
| Adults | 400-500 | 5000-8000 |