Pathological conditions that are manifested by changes in the frequency and strength of heart contractions. They manifest themselves as pain in the heart, rapid heartbeat, irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath and dizziness. Heart conduction disturbances (blocks) are a common finding on electrocardiographic (ECG) examinations. Most often, they do not manifest themselves clinically, but some blockades require the implantation (installation) of a permanent pacemaker (pacemaker).
Many types of intracardiac blockades (for example, incomplete blockade of the right bundle branch) are a normal variant.
Cardiological examination for cardiac conduction disorders is intended not only to determine the type of blockade, but also to determine whether it is a manifestation of organic heart damage. In addition, not all cases of blockade need to be treated. The main indications for installing a pacemaker are fainting and pre-fainting conditions, but you need to be sure that fainting is caused precisely by cardiac conduction disorders.
Causes of the disease
Heart rhythm and conduction disturbances can occur due to physiological characteristics and cardiac pathologies.
Sinus tachycardia, for example, develops during physical and emotional stress. Respiratory bradyarrhythmia is normal. Atrial fibrillation and flutter are dangerous. They usually develop against the background of diseases of the cardiovascular system. As a rule, heart rhythm and conduction disturbances occur when:
- coronary heart disease;
- vices;
- arterial hypertension;
- cardiomyopathy.
Non-cardiac diseases such as:
- acute poisoning;
- fever;
- stomach ulcer;
- hyperthyroidism;
- adrenal tumor.
Risk factors for the development of pathology include:
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- obesity;
- concomitant diseases (mainly the endocrine system).
What it is
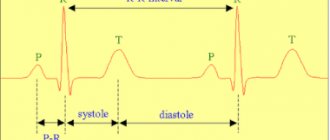
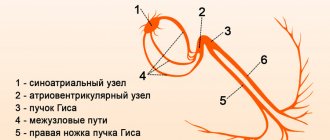
Normally, the impulse originates in the sinus node of the right atrium - where the superior vena cava flows into it.
Next, the wave travels through the atria and ends up at the next control point - the atrioventricular localization node. From here the excitation goes through the His bundle and gradually spreads to the apex. His fibers are special cells of the interventricular septum that form three branches. The right bundle branch (RBBB) delivers signals to the walls of the right ventricle. Along the left (LNPG), which is divided into anterior and posterior branches, there is coverage of the left ventricle. At the end, the branches divide into Purkinje fibers. This structure allows the impulse to be transmitted without loss and ensures uninterrupted heart function.
Conduction is slow and impaired - is there a difference?
In a healthy organ, impulses move from top to bottom in a set rhythm, with the required speed. With pathology, their conduction is slowed down or disrupted. If the passage of the signal is inhibited, excitation reaches the end point, but this process occurs at a slower speed. If conduction is disrupted, the impulse is interrupted in a certain area or is completely absent.
Impairment and slowing of intraventricular conduction occur at different ages. We cannot unambiguously estimate how often this pathology is detected. Failures in the conduction system of the heart often remain asymptomatic and are detected accidentally during a preventive examination. According to the medical literature, various types of conduction disorders are diagnosed mainly after 50 years (5–7% of cases). At 60–70 years of age, the frequency of detection of such conditions reaches 30%.
Failure of intraventricular conduction belongs to the group of bradyarrhythmias. Intra-atrial conduction disorders belong to this category. The causes and symptoms of the development of these conditions are similar. An accurate diagnosis can only be made after an examination.
Types of conduction disorders
All pathologies are divided into two groups:
- Changes in rhythm (arrhythmias). Such pathologies can be expressed in the form of atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, bradyarrhythmia, ventricular tachycardia, etc.
- Direct blockade. Some experts classify them as a separate category of pathologies. Blockades are divided into sinoauricular, intraatrial, atrioventricular and intraventricular.
Both types of conditions are equally dangerous.
Symptoms of pathology
Clinical symptoms manifest themselves in different ways. In some patients, the pathology is diagnosed only during an ECG, while others show pronounced signs of disorders.
Pathologies are characterized by:
- slow or increased heart rate;
- feeling of lack of air;
- chest pain;
- general weakness;
- changes in blood pressure;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness.
Any pathology is dangerous because when it occurs, blood circulation is disrupted. As a result, organs and tissues do not receive the required amount of oxygen and nutrients. It is important to pay attention to each symptom and tell your doctor about it. This will allow him to accurately determine the disease you have and begin adequate treatment as soon as possible.
Pathology leads to the development of several complications. This:
- Collapse. This condition is characterized by a sharp drop in blood pressure, pale skin and weakness.
- Arrhythmogenic shock. Occurs when there is a sharp decrease in blood flow. The patient loses consciousness, turns pale, the heartbeat becomes rare, and the pressure drops below 60 mm Hg. Art.
- Ischemic stroke. This pathology occurs against the background of increased thrombus formation. A stroke is characterized by changes in speech, unsteadiness of gait, and paralysis of the limbs.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE). This pathology develops when a pulmonary artery is blocked by a blood clot and is manifested by shortness of breath and suffocation, blue discoloration of the face, neck and chest.
- Acute myocardial infarction. The pathology develops due to the fact that the arteries cannot provide the necessary blood flow to the heart. As a result, oxygen deficiency occurs in the tissues. An area of necrosis forms on the heart. A heart attack is manifested by acute pain in the chest.
- Asystole (cardiac arrest). This condition develops when ventricular fibrillation occurs when the vessels do not receive the required amount of blood.
All these conditions can lead to the death of the patient.
Expert advice: when to install a pacemaker
Installation of a pacemaker is a surgical procedure and is prescribed only when indicated.
There is no point in carrying out the procedure in the absence of obvious symptoms of pathology. If the patient feels well, the introduction of an artificial pacemaker is not indicated. Surgery is not recommended if the identified symptoms are associated with reversible causes. You need to cope with the underlying disease - and the heart muscle will be able to function fully again. Indications for installation of a pacemaker:
- bradycardia with a heart rate less than 40 beats/min and rhythm disturbances in the presence of obvious symptoms;
- complications that threaten the patient's life;
- MAS attacks;
- persistent conduction disturbances after myocardial infarction.
The possibility of installing a pacemaker is being discussed when the pulse is less than 40 beats/min in the absence of obvious clinical symptoms. The procedure is performed at any age.
Prevention of cardiac conduction disorders has not yet been developed. Do not delay treatment, avoid risk factors. This will reduce the chances of developing pathology. To identify the problem in time, regularly undergo preventive examinations with a therapist with an ECG assessment (as necessary).
Diagnostics
The basis of examination for suspected pathology is an ECG. During the examination, the doctor discovers the main signs of a particular condition. Extrasystoles are manifested by altered ventricular complexes, tachycardia paroxysm - by short intervals between us, etc. Do not try to interpret the ECG results yourself. Entrust the procedure to a cardiologist.
An ECG is not the only examination used to diagnose pathology.
Also performed:
- Daily monitoring of ECG and blood pressure.
- Tests with physical activity.
- Transesophageal ECG.
- Transesophageal electrophysiological study.
- MRI of the heart.
- Ultrasound of the heart, etc.
All diagnostic methods are aimed at detecting deviations from normal heart rhythm and recording partial or complete blockades. The patient may also be referred for an examination to assess the patency of various vessels.
Diagnostics: signs on ECG and Holter
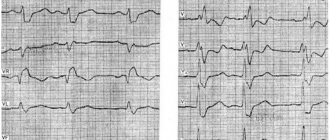
Electrocardiography is the main method for diagnosing the pathological process. Violation of intraventricular conduction on the ECG will manifest itself with specific signs.
A block along the right leg of the heart leads to expansion and deformation (the appearance of notches) in the QRS complex. Such changes are determined through the right chest leads.
Left heart branch block also widens and distorts the QRS, but pathological signs are detected through the left precordial leads. If the left anterior branch is affected, then a deviation of the electrical axis of the heart to the left is observed. The diagnosis can be confirmed by comparing ECG waves - in the second and third leads, S will be higher than R. If the impulses do not go through the left posterior branch, then the axis deviates to the right, S is higher than R in the first lead.
Nonspecific heart blockades deserve special attention. An ECG reveals changes that do not correspond to a specific pathology. For example, the QRS complex changes - it splits and deforms without widening. Such symptoms are observed with local damage to heart tissue against the background of a heart attack, inflammatory process, etc.
Additional information is provided by the following research methods:
- cardiac echocardiography;
- X-ray of the lungs;
- functional tests;
- CT scan.
We obtain significant information about the work of the heart muscle when conducting Holter ECG monitoring. The study lasts 24 hours. This method allows for continuous recording of signals and identification of abnormalities that are not visible on a conventional cardiogram. Such a recording shows changes that occur not only at rest, but also during movement and physical activity. The compact recorder is attached to the belt. The patient leads a normal lifestyle, and the system records the work of the heart in a continuous mode.
It is important to understand: the success of diagnosis will directly depend on whether the blockade is permanent or transient and how often attacks occur in the latter case. If conduction disturbances are observed daily, daily monitoring will reveal this on the ECG. Sometimes cardiogram monitoring is required for 7-30 days.
Treatment
Treatment of pathologies is always carried out comprehensively. The choice in favor of one method or another is determined by:
- the patient's condition;
- his individual characteristics;
- existing concomitant diseases.
If coronary heart disease is detected, patients receive:
- blood thinners;
- nitroglycerine;
- cholesterol-lowering agents.
For hypertension, medications that lower blood pressure are prescribed.
In case of chronic deficiency, it is necessary to take diuretics and glycosides.
If a heart defect is detected, surgical correction may be performed.
Emergency care for patients involves the administration of drugs that restore heart rhythm.
Surgical interventions
If the exact cause of the pathology is identified and the medications are ineffective, the doctor may recommend surgery. As a rule, it is aimed at installing a pacemaker. Such a device does not cure the disease, but can effectively stop attacks and reduce the risk of death.
Other operations may also be performed. Only your cardiologist will tell you about them. Surgical interventions are performed only in advanced cases when symptoms cannot be eliminated in other ways.
Our clinic in Moscow provides complex therapy for pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Experienced doctors can detect all the signs of diseases and identify factors contributing to their development and complications. Therapy is always adequate and carried out at the best price. The cost of services is indicated on the website. Our specialists will also announce prices. The exact cost of therapy will be determined by the doctor after conducting an examination and selecting appropriate tactics and methods.
Heart rhythm disturbances: treatment of arrhythmia
Treatment of most types of arrhythmias is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that provoked the occurrence of systematic failures. Some conduction and rhythm disorders can be eliminated by adhering to a healthy lifestyle: eating right, giving up any strong alcoholic drinks and nicotine, playing sports, avoiding stress and psycho-emotional tension.
If necessary, the attending physician will prescribe medication. For patients with tachycardia, topical pharmacological products from the group of beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, cardiac glycosides. To generally stabilize the patient’s emotional state, sedatives are prescribed.
In some cases, patients are indicated for surgical intervention. The pacemaker is a pacemaker and helps to correct the functioning of the organ in such serious conditions as AV blockade, severe bradycardia that is not amenable to medication, and sick sinus syndrome. The treatment regimen is always selected strictly individually, taking into account the characteristics and needs of each patient.
Prevention
Prevention of pathologies of the cardiovascular system is aimed at:
- adherence to sleep and wakefulness;
- eliminating the risks of stressful situations;
- changing your lifestyle and giving up bad habits.
Moderate physical activity (mainly water procedures) is beneficial. To prevent arrhythmia, it is very important to follow a diet. Diet excludes salty, fatty and spicy foods, coffee and strong tea. Don't get carried away with the liquid. You need to drink 1-2 liters of water per day. It is also important to enrich the diet with vitamins and microelements.
If you have a genetic predisposition to pathologies or a history of them, it is very important to regularly visit a cardiologist and undergo a full examination. Be sure to include in the program such studies as:
- general blood analysis;
- ECG;
- ECG under load.
The examination will not take much of your time, but will help prevent the development of pathology and the occurrence of complications.