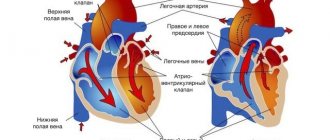
High blood pressure is far from uncommon even for young people; they are increasingly faced with the unpleasant symptoms of hypertension. Therefore, everyone should know what to do to cope with this problem, how to prevent subsequent pressure surges.
The first thing that is important to remember: if your blood pressure has increased, you should not hope that the condition will improve on its own; you must immediately contact a doctor for examination and receive recommendations for treatment.
Since hypertension is a chronic disease, it requires constant attention to oneself. When high blood pressure has become a constant companion of the patient, he needs to follow the prescribed treatment for life. If the tonometer shows high numbers only from time to time, the patient should take preventive measures.
High blood pressure includes:
- change in lifestyle;
- changing food and bad habits;
- moderate physical activity;
- minimizing nervous feelings.
Otherwise, one day your blood pressure will rise sharply, causing severe health problems. Such conditions are called hypertensive crisis.
Causes of pressure 200 to 100
For each person, depending on age and the presence of chronic pathologies, blood pressure varies from the norm to 120/80. Therefore, an attack of malaise can occur even with a slight excess. But when blood pressure rises to 240 or even higher, this threatens complications. Internal organs such as kidneys, heart, and brain are affected. Such an attack can lead to consequences in the form of poor vision or its complete loss. The reasons for this pressure may be:
- constant worries, stress;
- genetic disposition;
- environment;
- high fat content in the diet (butter, sour cream, sausage, cheese, cakes);
- a large amount of alcohol consumed, which directly affects the heart rate (changes towards an increase);
- high salt content in food, which leads to fragility of blood vessels;
- sedentary work, sedentary lifestyle;
- smoking;
- overweight;
- complication after illness.
Enter your pressure
Move the sliders
Norm or pathology
In some cases, a slight deviation of indicators from the norm by 5-10 units, both up and down, is acceptable. But blood pressure 240 over 120 (240 over 130, as well as blood pressure 240 over 140) cannot be called a minor deviation. This is a serious pathology called hypertensive crisis.
It is worth paying attention not only to increased systolic and diastolic indicators, but also to the difference between them. With normal blood pressure, this difference should be 40 units. In this case, the “run” is more than 100 units. Such a difference is dangerous not only for the heart, but also for the entire body as a whole.
High blood pressure is stress for the whole body, because it works in an enhanced mode
The disease requires immediate intervention by a specialist and an urgent reduction in blood pressure. The reasons for this phenomenon can be stress, heart and vascular diseases, diabetes, obesity, etc. The greatest risk factor is the elderly, but it is possible that a hypertensive crisis can occur at a young age.
Note. The normal blood pressure for a healthy adult is 120 over 80, and the pulse is 60-80 beats per minute. If, with minor deviations, any symptoms begin to bother you, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Symptoms with a pressure of 200 over 100
If high blood pressure persists for long periods of time and very rarely returns to normal on its own, then due to its changes, the speed of blood flow increases and the walls of blood vessels become thicker, and because of this, the lumen in them decreases. During this period, the sick person has the following symptoms:
- pain in the back of the head, a feeling of pulsation, especially in the temporal part;
- blurred vision, pathological changes in the fundus, dilated blood vessels;
- constant fatigue, even in the morning;
- noise in ears;
- rapid heart rate, aching pain in the heart area;
- swelling of the eyelids, face, hands;
- redness of the facial skin, appearance of vascular networks;
- memory impairment;
- numbness of the limbs, sweating;
- involuntary urination, urine analysis reveals albumin proteins;
- sudden changes in pressure - hypertensive crisis.
Advanced hypertension negatively affects all human organs, namely:
- Brain. With hypertension, the lumen in the blood vessels narrows, which leads to oxygen starvation of this most important organ, and as a result, a stroke may ultimately occur.
- The cardiovascular system. High blood pressure provokes severe stress on the vessels, they wear out more quickly and fatty plaques are deposited on their walls. With changes in the healthy functioning of blood vessels, the nutrition of the heart muscle stops, and this entails angina pectoris. If left untreated or improperly treated, high blood pressure will lead to a heart attack.
- Urinary system. With changes in its operation, the filtering function deteriorates. A large amount of protein and other substances entering the circulatory system are detected in the urine. If treatment is ignored in older people, this leads to kidney disease.
- Organs of vision. High pressure negatively affects the microvessels located in the human eyeball. Due to frequent changes in pressure, irreversible changes in the retina occur.
Often there are no signs of increased blood pressure of the hypertensive type, which is why developing hypertension is also called the “silent killer”. It’s just that one day a person suffers a heart attack or stroke due to another surge in pressure, even an insignificant one against the background of the general excess. Interruptions in heart rate, nausea, causeless anxiety, heart pain, darkness before the eyes followed by loss of consciousness, migraine, loss of coordination - all these are symptoms of hypertension.
You cannot ignore the symptoms of high blood pressure; they will help prevent the dangerous consequences of hypertension in time.
Symptoms of hypertensive crisis
Enter your pressure
130
on
90
Search in progress Not found
During an attack of hypertension, many symptoms are observed, but the main sign of the pathological condition is a sharp increase in pressure up to 250-260/120-150 mm Hg. Art. Among other signs it is necessary to highlight:
- cold sweat;
- goose bumps;
- anxiety, restlessness;
- increased heart rate;
- lack of air;
- tremor of the upper extremities;
- nervous overexcitement.
At the very beginning, the patient will experience severe pain in the head, which is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fear of light, tinnitus, and dizziness. Head pain may worsen if a person sneezes sharply.
Hypertensive crisis develops in different ways. Some patients become overly irritable, whiny, they develop a feeling of fear, and red spots appear on the skin of the chest.
It happens that the functioning of the digestive tract is disrupted, diarrhea and frequent urge to urinate appear. The patient's systolic pressure will increase, reaching extremely high levels - from 230 and above. This provokes:
- increased heart rate;
- increase in pulse and venous pressure.
An uncomplicated attack can last several days, but it has less acute symptoms. The patient's consciousness is confused, a feeling of drowsiness, stupor appears, and a headache.
If severe vomiting and nausea begin, this means that diastolic pressure has increased, but systolic pressure has remained within normal limits.
Treatment
The correct therapeutic course can only be prescribed by a specialist after a complete diagnosis. As a rule, therapeutic measures are aimed at treating the underlying disease that causes arterial hypertension.
Only a doctor can prescribe a course of treatment, because every body is individual.
Also prescribed are medications that lower blood pressure, improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and relieve symptoms. Most often used:
- Beta-blockers - Atenolol, Vasocardin, Anaprilin;
- Calcium antagonists - Amlodipine, Nifedipine, Verapamil;
- ACE inhibitors - Captoril, Enalapril, Capoten;
- Diuretics - Furosemide, Indapamide, Hypothiazide.
In addition to these drugs, sedatives are often prescribed, as well as medications to eliminate symptoms. In case of vomiting - antiemetic, if there is a headache - antispasmodics, and other drugs depending on the patient's condition.
Generalization and directions for further research
Many clinicians express concern when the SBP response exceeds the “normal” range, but in such cases there is insufficient empirical evidence to make clinical recommendations. Moreover, arbitrarily set upper blood pressure values for stopping CST have the same drawback. We argue that the clinical utility of BP measurements can be improved under the following conditions:
In addition to the maximum/peak values obtained with CST, consider the rate of change of BP (slope of the curve), and establish the level of agreement between these two measurements.
Possibility of influence of age, gender, health status, medications and CST protocol on blood pressure values obtained in the test.
Standardize BP measurements as recommended by Sharman and LaGerche (1):
- Measure at the end of each CST step.
- Measure before ending the test, and if not possible, immediately after stopping the test.
- Use an automated device that can measure on the move (65). This limits interobserver variability. Prefer DBP data from auscultatory devices over oscillometric devices. However, caution is needed as there is little reliable data on these devices, mostly from small studies of healthy people.
- Manual measurements are suitable for experienced assessors. There are no empirical data to inform the threshold effects of training, but regular BP measurement during exercise is likely to be more beneficial than sporadic BP measurement.
Future studies should record and report BP values at which acute cardiovascular events occur during CST to properly assess risk and establish evidence-based upper limits.
What to do with high blood pressure 240?
If the pressure rises to 240 to 140, before starting to take many medications, the patient needs to calm down and pull himself together. Fear is one of the manifestations of hypertension. Medicinal tinctures of valerian and motherwort and Corvalol will help overcome anxiety. Be sure to call an ambulance and take the following measures before paramedics arrive:
- Provide fresh air. To do this, you need to open all windows.
- A few deep breaths. This will help restore breathing, enrich the lungs, and therefore the blood, with oxygen.
- Take a reclining position.
- Measure blood pressure every 10–15 minutes.
If an attack occurs, it is necessary to call an ambulance as quickly as possible and give the victim medicine for high blood pressure. Most often, the drug Capoten is used for these purposes. In the first hour, you can reduce the pressure by no more than 20-25% of the existing values.
Capoten quickly reduces blood pressure and improves well-being
To do this, you need to place one tablet of the drug under your tongue. If the dosage of the medicine is 25 mg, then you can take 2 tablets at once. It is also possible to use Nifedipine. Dosage - 1 tablet under the tongue. If the pressure does not decrease, then you can take another tablet 15-20 minutes after the first. Also, to improve the patient’s condition, it is necessary:
- Place him in bed on a high pillow.
- Ventilate the room (fresh air normalizes breathing).
- It is important not to let the victim panic.
- Apply mustard plasters to the feet, calf muscles and the back of the head (for no more than 15 minutes).
- For headaches, give the patient a No-Shpa tablet or another antispasmodic.
- If your heart hurts, then a Nitroglycerin tablet (under the tongue) will help.
Cold hand baths, breathing exercises, and hot foot baths help reduce blood pressure. Cold compresses can be applied to the forehead and sides.
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day.
High blood pressure is far from uncommon even for young people; they are increasingly faced with the unpleasant symptoms of hypertension. Therefore, everyone should know what to do to cope with this problem, how to prevent subsequent pressure surges.
The first thing that is important to remember: if your blood pressure has increased, you should not hope that the condition will improve on its own; you must immediately contact a doctor for examination and receive recommendations for treatment.
Our readers successfully use ReCardio to treat hypertension. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Since hypertension is a chronic disease, it requires constant attention to oneself. When high blood pressure has become a constant companion of the patient, he needs to follow the prescribed treatment for life. If the tonometer shows high numbers only from time to time, the patient should take preventive measures.
High blood pressure includes:
- change in lifestyle;
- changing food and bad habits;
- moderate physical activity;
- minimizing nervous feelings.
Otherwise, one day your blood pressure will rise sharply, causing severe health problems. Such conditions are called hypertensive crisis.
The doctor is talking about a hypertensive crisis if the blood pressure has reached 250 to 120 or even 250 to 150 millimeters of mercury. However, it should be understood that these numbers may be individual for each patient.
There are many reasons for the development of this condition, the main one being the presence of arterial hypertension. Often, sudden surges in blood pressure to high levels occur when you stop taking antihypertensive drugs; doctors call this phenomenon withdrawal syndrome.
In addition, blood pressure increases for the following reasons:
- excessive physical activity;
- hypokalemia;
- stress;
- cerebral ischemia;
- excessive sensitivity to changing weather conditions;
- addiction to alcoholic drinks.
If a woman suffers from hypertension, her blood pressure may rise to 120 or higher during menopause.
Approximately the same symptoms occur with exacerbation of coronary artery disease, circulatory disorders in the brain, and acute heart failure.
There are two types of hypertensive crisis: complicated, uncomplicated. In the first case, the risk of damage to internal organs, stroke, and heart attack increases. In this condition, it is important to know what to do to provide the patient with quick emergency care.
During an attack of hypertension, many symptoms are observed, but the main sign of the pathological condition is a sharp increase in pressure up to 250-260/120-150 mm Hg. Art. Among other signs it is necessary to highlight:
- cold sweat;
- goose bumps;
- anxiety, restlessness;
- increased heart rate;
- lack of air;
- tremor of the upper extremities;
- nervous overexcitement.
At the very beginning, the patient will experience severe pain in the head, which is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fear of light, tinnitus, and dizziness. Head pain may worsen if a person sneezes sharply.
Hypertensive crisis develops in different ways. Some patients become overly irritable, whiny, they develop a feeling of fear, and red spots appear on the skin of the chest.
It happens that the functioning of the digestive tract is disrupted, diarrhea and frequent urge to urinate appear. The patient's systolic pressure will increase, reaching extremely high levels - from 230 and above. This provokes:
- increased heart rate;
- increase in pulse and venous pressure.
An uncomplicated attack can last several days, but it has less acute symptoms. The patient's consciousness is confused, a feeling of drowsiness, stupor appears, and a headache.
What to do if blood pressure rises above 250/120? Treatment must be carried out in several stages; during an attack, prompt assistance should be provided, even before the medical team arrives. After this, doctors will decide what to do - hospitalize the patient or leave him for home treatment.
First, you need to position the patient so that he is in a semi-sitting position. If the patient is lying in bed at this time, a couple of pillows are placed under his head to ensure free breathing and prevent suffocation, which often happens during a hypertensive crisis.
When a patient previously consulted a doctor to prescribe medications against hypertension, he needs to take the medications that were recommended by the doctor. To reduce blood pressure quickly and effectively:
- the tablets are placed under the tongue;
- slowly dissolve.
Additionally, it is important to take blood pressure measurements as often as possible and monitor the indicators; they must decrease smoothly. After just 30 minutes, the pressure drops by 30 units, after 1 hour – by 50. If the optimal pressure level is reached, there is no need to take any other measures.
The pressure should not be reduced too sharply, as this will cause circulatory problems in the brain.
During a hypertensive attack, it is important to do everything so that the patient quickly gets rid of feelings of fear and anxiety. To normalize overexcitation and psycho-emotional state, it is recommended to take a sedative. Other medications are taken only after the ambulance team arrives, after the doctors have selected the right medicine.
Traditional methods
In addition to medications, it is recommended to practice traditional methods of normalizing blood pressure. They are especially good for emotional stress, when the patient needs to calm down.
Each herb is crushed, take a tablespoon of the mixture, pour 250 ml of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. After this, the product is filtered and consumed half a glass before meals three times a day.
To lower blood pressure to 120 and below, use a tincture of other herbs: hawthorn, horsetail, cucumber, motherwort, birch leaves, adonis. It is prepared in the same way as the previous remedy, take half a glass 3 times a day, always before meals.
Beetroot juice, which you drink 100 ml three times a day after meals, helps with high blood pressure. The duration of such treatment will be 3 weeks. To increase efficiency, natural honey and lemon are added to the juice in a ratio of 1 to 2. Treatment is taken in half a glass 2 times a day, preferably 1 hour after meals.
Hawthorn juice has medicinal properties and is consumed 30 minutes before meals. To dilate blood vessels, take cranberry juice, grind a glass of berries with sugar or honey, eat a tablespoon 3 times a day before meals.
The menu should also include seafood, dairy foods and lean meat. Watermelon helps get rid of excess moisture in the body, and as a result, blood pressure decreases.
After suffering a hypertensive crisis, when the pressure is approximately 120/80, the patient must completely give up smoking, alcoholic beverages, and foods that greatly increase blood pressure. In order to promptly identify changes in your blood pressure, you need to purchase a tonometer, systematically measure your blood pressure, and monitor your lower and upper pressure readings. And the video in this article will answer the important question about deciphering the numbers of your upper blood pressure.
Low blood pressure is considered to be pressure below 100/60 mm Hg. Art.
The main symptoms of low blood pressure are drowsiness, weakness, and dizziness. To increase it, you can drink a cup of strong tea or coffee. If the described complaints persist for several days against the background of low blood pressure, that is, excluding other possible causes for the appearance of the above symptoms, such as changes in weather, colds, overwork, it is necessary to consider the issue of adjusting therapy.
Important! If the patient has previously been prescribed medications for arterial hypertension, then they must be taken strictly according to the doctor’s prescription. Often, exceeding dosages leads to a sharp decrease in blood pressure to critical levels and to the development of dangerous pathologies.
Why does blood pressure rise?
The doctor is talking about a hypertensive crisis if the blood pressure has reached 250 to 120 or even 250 to 150 millimeters of mercury. However, it should be understood that these numbers may be individual for each patient.
There are many reasons for the development of this condition, the main one being the presence of arterial hypertension. Often, sudden surges in blood pressure to high levels occur when you stop taking antihypertensive drugs; doctors call this phenomenon withdrawal syndrome.
In addition, blood pressure increases for the following reasons:
- excessive physical activity;
- hypokalemia;
- stress;
- cerebral ischemia;
- excessive sensitivity to changing weather conditions;
- addiction to alcoholic drinks.
If a woman suffers from hypertension, her blood pressure may rise to 120 or higher during menopause.
Approximately the same symptoms occur with exacerbation of coronary artery disease, circulatory disorders in the brain, and acute heart failure.
There are two types of hypertensive crisis: complicated, uncomplicated. In the first case, the risk of damage to internal organs, stroke, and heart attack increases. In this condition, it is important to know what to do to provide the patient with quick emergency care.
An uncomplicated crisis does not require hospitalization, but it is also necessary to know what to do.
Consequences of pressure 240 to 120 mm Hg. st
When a hypertensive crisis occurs, it is necessary to take all measures to lower blood pressure without delay. Indicators of 240 to 120 are very dangerous for human life.
With such indicators, the heart and blood vessels begin to work harder, which often leads to irreversible consequences. If you do not consult a doctor in time and start treatment, there is a risk of dangerous pathologies. Such as:
- Serious disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- Pulmonary edema;
- Angina;
- Clouding of consciousness;
- Convulsions and paralysis (complete or partial);
- Myocardial infarction;
- Stroke;
- Impaired kidney function;
- Development of pathologies in the endocrine system.
Such pressure is dangerous for any age category. Pregnant women are no exception. Blood pressure of 240 over 120 is dangerous not only for the expectant mother, but also for the baby inside the womb. Often, due to a hypertensive crisis, premature birth (miscarriage) begins.
If high blood pressure is not treated, life expectancy may be reduced by 10-15 years.
conclusions
Hypertension is a leading cause of cardiovascular mortality and morbidity, but clinical BP measurements alone underestimate its prevalence in healthy individuals considered normotensive at these levels (66). We argue that CST BP measurements serve as a complementary assessment for clinical and outpatient assessment of hypertension and CVD risk, diagnosis, and prognosis. However, this approach is still hampered by the unreasonableness of previously proposed values and the lack of empirical diagnostic indicators of BP. To facilitate accurate classification of normal and excessive BP responses, existing guidelines need to be reinterpreted. Clinically significant abnormalities in BP response should be defined in terms of the rate of change in BP relative to workload or cardiac output in addition to peak values obtained during exercise. It is important to note the modulating influence of age, gender, level of training, health status and medications taken, which may be a consequence of an adaptive state (higher level of training), and not a connection with pathology. Finally, without positive clinical results, there is no need to stop CNT at high blood pressure thresholds, since there is no scientific evidence that such a reaction is associated with adverse events.
Source:
https://link.springer.com/
Features of specific pressure values
| Blood pressure value (mm Hg) | Peculiarities |
| 220 by 120 | Dangerous pressure, which is most often associated with serious disorders of the cardiovascular system. With such indicators, tachycardia, arrhythmia, and heart pain are most often associated. If you do not call an ambulance in time, there is a risk of stroke, heart attack, hemorrhage and other pathologies. |
| 230 by 120 | A hypertensive crisis with such indicators is almost always accompanied by a rapid heartbeat and increased pulse pressure. The condition is life-threatening. In this case, immediate first aid to the victim and medical intervention are required. |
| 240 by 120 | This form of hypertensive crisis usually develops due to high-risk arterial hypertension. If you do not call an ambulance in time and do not begin to lower blood pressure in a timely manner, then most often such pressure will leave consequences - disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys, adrenal glands, heart, brain cells and other target organs. |
| 250 by 120 | A pressure of 250 over 120 is defined as a hypertensive crisis and most often occurs due to self-cessation of prescribed medications for hypertension. With a systolic reading of 250 units, the heart muscle is overstrained, and the vessels are constantly working “to the point of strain.” In almost all cases, after stopping the attack, some consequences remain. But the sooner you call an ambulance, the greater the chances of avoiding dangerous pathologies. |
| 260 by 120 | If you do not start lowering your blood pressure readings, then often during a hypertensive crisis with an upper pressure reading of 260 mm Hg. st recorded death. This form of attack is extremely dangerous for human health, as some of the brain cells die. In addition, if blood pressure is not lowered urgently, in most cases vascular rupture occurs. |
Any of these values is dangerous for human life, so immediate emergency assistance and calling a doctor are required. For some indicators, the consequences remain regardless. However, with timely assistance, the condition of the victim can be significantly improved and his life saved.
There is no point in trying to eliminate a hypertensive crisis using traditional medicine. In this case it is a waste of time. Treatment can only be medication. You can turn to folk remedies only after the attack has stopped. This would be a good complementary therapy.
Any of these values is dangerous for human life, so immediate emergency assistance and calling a doctor are required. For some indicators, the consequences remain regardless. However, with timely assistance, the condition of the victim can be significantly improved and his life saved.
Introduction
Blood pressure (BP) measurement during clinical exercise testing (CST) is a necessary adjunct to electrocardiography (ECG) and heart rate (HR) assessment, as abnormal responses may reveal underlying pathology. Given the difficulty of measuring BP during exercise, accurate measurement techniques are required to ensure optimal clinical interpretation (1). Widely accepted contraindications to continued CST for safety include upper blood pressure limits (2,3). However, definitions of “normal” BP during exercise and a safe “upper limit” are based on a limited number of studies dating back to the early 1970s (4, 5). Since then, our knowledge of phenotypic variations and possible links to pathology of abnormal BP responses has evolved significantly. Despite this, BP responses in CST that exceed the recommended norms often pose a dilemma due to unclear clinical consequences, especially when other tests are normal. There is compelling evidence that excessive increases in systolic blood pressure (SBP) or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) during CST, called the hypertensive response (2, 3), are associated with a 36% increased risk of cardiovascular events and mortality (6), masked hypertension, despite clinically normal blood pressure (7), and an increased risk of latent hypertension in normotensive people (8 – 18). These observations highlight the potential clinical diagnostic and prognostic utility of exercise BP measurements, but they are not yet widely used in clinical practice due to limitations of previous studies (19), lack of standardized methodology, and limited empirical data in the general population.
The purpose of this review is to critically analyze the evidence contained in current guidelines for CST AD. We will show that the criteria used to define “normal” and “abnormal” responses are largely arbitrary and based on insufficient empirical data. We will also identify key factors influencing BP responses during exercise and how to increase their explanatory value in individual responses to CST. Finally, we will provide recommendations for future studies on exercise BP measurement to expand the evidence base and facilitate its adoption into clinical practice.