While pregnant, expectant mothers undergo many tests. Such studies help obstetricians and gynecologists identify pregnancy pathologies in a timely manner, prescribe additional tests for women, and, if necessary, hospitalize them. These include a general blood test, the results of which must meet certain standards. If the test result shows an increase in neutrophils, what could this mean? What is the norm for these substances? In what cases do neutrophils decrease?
Let's find out the answers to these questions.
Neutrophils: functions and norm
These substances in the blood are components of leukocytes. Neutrophils are indicators of the state of female immunity. They can warn about the onset of an inflammatory process in the expectant mother’s body. But if, according to the results of the analysis, they are elevated, this is not always evidence of an infectious lesion.
The level of neutrophils can be absolute and relative. The first type is determined by the total number of cells in a unit of blood. The absolute level of neutrophils is 1.8-6.5 * 109 per liter. If we talk about a relative indicator, then the norm of these substances is 45-75% of the total number of leukocytes. Approximately up to 5% are immature forms of neutrophils. But in adult women they are mature, that is, segmented.
Research and its results
When a doctor interprets the results of a blood test, he first checks the ratio of band and segmented neutrophils.
They differ from each other in cytological structure and quantity. During pregnancy, segmented cells increase more often, and band cells increase significantly less frequently. The content of neutrophils is assessed from two points of view: relative to all other types of leukocytes (as a percentage) and the number of cells in one liter of blood (absolute number). The normal absolute cell count per liter of blood is no more than 1.7-6.5*10⁹ units/l. The normal relative content ranges from 40 to 78%. Immature forms - band neutrophils - make up only 6%.
Deviations from the abs (absolute) norm in tests and relative ones have different reasons, so all numbers are assessed only by a doctor.
Carrying out a blood test requires compliance with some recommendations on the part of patients in order for the result to be reliable:
- do not overload the body with physical labor the day before;
- do not take medications;
- avoid hypothermia and stressful situations;
- Do not consume alcoholic drinks or food 8 hours before the procedure.
If these requirements are not met, the results of the study may be distorted. You will need to donate blood again to confirm low or high neutrophils during pregnancy.
Blood analysis
What it is
WARNING!
The information on the site is provided for informational purposes and cannot be used to make a diagnosis or make treatment decisions. Neutrophils are a group of leukocytes that have antimicrobial activity. Determining the number of these blood cells during pregnancy helps confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis.
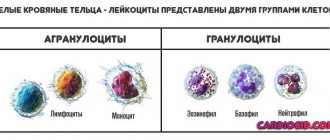
This group of white blood cells is formed from progenitor cells produced by the bone marrow. During growth, the bodies go through 2 stages, at each stage they acquire a specific subtype.
- Metamyelocytes are immature cells that do not leave the bone marrow. If it penetrates into the general bloodstream, the doctor may suspect an acute inflammatory process or leukemia.
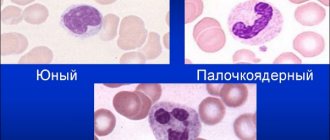
- Band neutrophils - doctors call them “young” defenders of the body of a pregnant woman and not only.
- Segmented neutrophils are the mature form of blood cells. Based on the name, it is clear that they are subject to division into segments.
The life of this type of leukocyte lasts no more than 14 days. They remain in the bone marrow for 6 days. After this, mature white blood cells are released, gradually spreading throughout the body. 10 hours after release, they begin to die.
Diagnosis of neutrophilia
To determine a pathological increase in neutrophil levels, a woman needs to undergo a blood test, which is carried out in any medical institution. It is necessary to donate blood from a vein, always on an empty stomach. Laboratory staff will then use specialized microscopic equipment to determine the number of neutrophils and other blood cells.
The same preparation rules apply to this study as for regular blood donation. That is, a few days before collecting the biomaterial, it is forbidden to eat fatty foods and various smoked foods; you should also exclude alcohol and any medications. Physical overexertion is also prohibited, since it can also distort the true results of the study. If the level of neutrophils significantly exceeds during pregnancy, the mother is prescribed additional tests such as ultrasound diagnostics and bacterial culture, scraping from the surface of the tonsils and laboratory tests of feces and urine.
Depending on the data received, the doctor selects the most optimal, effective and safe treatment, because not all medications and therapeutic procedures are suitable for pregnant women. Neutrophilia is usually caused by inflammatory lesions, so antibiotic drugs that are safe for pregnant women are used for therapy. To eliminate any risks for mother and baby, it is necessary that all appointments are made exclusively by an obstetrician-gynecologist or a doctor of another, more narrow specialization, in accordance with the localization of the inflammatory process.
Is treatment necessary?
Therapeutic measures prescribed for pregnant women depend on the reasons caused by the deviations.
- When the cell level is at the upper limit, there is no need for therapy. Thus, the mother's immune system responds to the development of the fetus. But with large deviations, medication support may be required.
- Therapy of infectious diseases. Antibacterial treatment is used. Medicines are selected taking into account the woman’s current situation. Antibacterial medications should not cross the placenta. Doctors recommend using this kind of treatment only at the onset of the 3rd trimester, when all the baby’s organs are formed.
- When a benign or malignant neoplasm is diagnosed, the woman is advised to terminate the pregnancy or have a premature birth.
- Therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating injuries after they have occurred.
- Control of endocrine disorders with the help of conventional medications that were used before conception. It is possible to adjust the dosage level.
Most medications can cause complications for the growth and development of the fetus or the woman's condition. Therefore, during treatment, ongoing diagnostic tests are carried out and the dosage of medications is adjusted.
During pregnancy, blood counts often change. An excess of neutrophils by a couple of units is a variant of the norm for the state of gestation. All methods of therapy must be agreed with the attending physician so as not to harm the fetus.
Reasons for the increase
If neutrophils are increased in the blood of women during pregnancy, we are talking about a condition such as neutrophilia, or neutrophilia. An increase in the level of neutrophils to 10X10⁹ per liter indicates moderate neutrophilia. If the content reaches from 10 to 20Х10⁹/l, we are talking about pronounced. We can talk about severe if the level of granulocytes is from 20 to 60X10⁹/l. Based on the level of neutrophilia, doctors assess the intensity of the inflammatory process: the higher it is, the more severe the disease.
During pregnancy, you should always monitor your blood counts and take timely measures under the supervision of your doctor.
There may be many reasons, including:
- Segmented neutrophils are increased in the child’s blood and nasal smear. Reasons what to do
- Acute purulent inflammation caused by bacteria. With a localized process, neutrophilia can be moderate or severe. This includes diseases such as tuberculosis, pneumonia, diseases of the ENT organs, tonsillitis, appendicitis, pyelonephritis, salpingitis and others. Severe neutrophilia is observed in generalized processes: sepsis, peritonitis, cholera, scarlet fever.
- Recent vaccination.
- Necrosis (burns, gangrene, strokes).
- Bacterial intoxication without infection by bacteria (for example, when consuming canned food in which the bacteria have died and the toxins have not broken down.
- Alcohol or lead intoxication.
- Disintegration of a malignant tumor.
- A recently completely cured infectious disease.
In pregnant women, neutrophilia is considered a normal variant
There is such a thing as neutrophilia in pregnant women. During this period, elevated neutrophils are a variant of the norm. The fetus developing in the womb is considered foreign to the body, so the immune system produces a large number of leukocytes, including neutrophils. This process is regulated by the female hormone prolactin. As the fetus grows, the amount of its waste products also increases, resulting in even more neutrophils being released into the blood. This is immediately reflected in the leukocyte formula, which shows the growth of band granulocytes.
During this period, it is necessary to monitor blood counts, since high neutrophils can signal a risk of premature birth or miscarriage. When a large amount of toxic waste from the fetus is released into the blood, a change in hormonal levels may occur, and the immune system will try to get rid of the fetus, which it considers a threat to the woman's health.
What is the essence of neutrophilia?
If neutrophils are elevated during pregnancy, this means neutrophilia. This condition is considered normal for a woman if the deviations are not too large from the norm. The organism that develops in utero is initially foreign, in which case the immune system begins to actively produce killers - leukocytes - in huge quantities. This process must be regulated by a special hormone - prolactin. To avoid untimely birth or fetal loss, a woman must constantly monitor her health and be under the close supervision of specialists.
The primary reasons for the increase in neutrophils in the blood during pregnancy
If elevated neutrophils during pregnancy rise to the level of 10X10⁹/liter, then this means normal. When this indicator exceeds the norm and amounts to 20X10⁹/liter, then, most likely, there is severe inflammation in the woman’s body; the more neutrophils in the blood, the more dangerous the disease can be. Let's consider the main reasons for the increase in neutrophils during pregnancy:
- Consumption of preserved food that was unsuitable.
- Bacterial inflammation affecting the respiratory system. For example, such diseases include tonsillitis, nephritis, tuberculosis, appendicitis.
- Recent vaccination.
- Necrosis of various types.
- Intoxication of the body under the influence of alcohol or heavy metals.
- Destruction of the tumor.
- A disease caused by infection.
Why do neutrophils decrease?
This condition is called neutropenia. It is diagnosed when the level of these substances in the blood is 1.6 * 109 per liter or lower. Neutropenia is also divided into three types. And its reasons could be:
- Severe infectious and viral diseases. These are influenza, rubella, tuleryemia, measles, hepatitis.
- Bone marrow lesions. This happens after irradiation, taking certain medications, for example, sulfonamides, immunosuppressants or painkillers.
- Blood diseases, which include leukemia, folate deficiency anemia, cobalamin deficiency in the body.
Expectant mothers should maintain contact with their gynecologists. And if any pathological conditions arise, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy, then you need to go for an unscheduled examination. And if a pregnant woman has questions about test results and prescriptions, then there is no need to hesitate to ask the doctor.