Full text of the article:
Pregnancy is a great stress for a woman’s body, so during pregnancy it is necessary to closely monitor your health and try to do everything necessary to ensure that the pregnancy proceeds in conditions favorable for the mother and the unborn baby. You need to give up bad habits, lead a healthy lifestyle, breathe fresh air, eat well and avoid stressful situations.
But it is important to monitor not only external factors that can affect the body, but also the internal processes that occur in it. In particular, it is imperative to control blood pressure and prevent it from jumping. High blood pressure can endanger the life of the unborn child.
What should your blood pressure be during pregnancy?
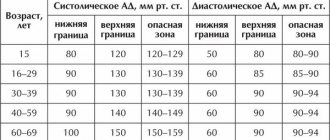
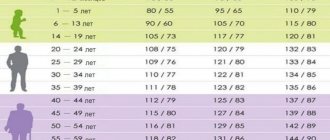
It is difficult to answer this question unequivocally, because people’s “working” pressure can differ significantly. There are average ranges of the recognized norm, but there are also individual characteristics. As a guide, blood pressure in the range from 120/80 to 140/90
.
People with consistently low blood pressure are diagnosed with “ hypotension
,” and people with blood pressure above the maximum normal value are diagnosed with “
arterial hypertension
” (
AH
). Drug therapy and the use of non-drug agents help normalize blood pressure and bring it into the “normal” range. Physical activity, regular walks, proper nutrition, lack of stress, etc. contribute to this.
Doctors try to avoid additional drug load on the female body during pregnancy, so they are calm about lowering blood pressure to the lower limits of the range and even lower (90/60). Unstable blood pressure is considered normal, since the female body undergoes serious restructuring during pregnancy, but it is still necessary to control blood pressure.
If a pregnant woman’s blood pressure has noticeably increased compared to her normal blood pressure or there are surges with a high level of lower pressure, then the doctor will most likely diagnose “ hypertension.”
" This diagnosis requires additional treatment, but it is better to start it earlier than to worsen the situation, so doctors recommend measuring blood pressure daily, and not just during routine medical examinations. You can even keep a “diary” and record the measurement results to see the dynamics.
Hypertensive conditions
High blood pressure during pregnancy has various clinical and pathogenetic forms. There is no generally accepted international classification of this condition, but Russian experts adhere to the following division:
- The chronic form is the one that is detected before the child is conceived or during the first half of pregnancy. It persists for the first month and a half after birth.
- Gestational hypertension is diagnosed in the second half of pregnancy and persists after childbirth. A transient form of gestational hypertension is characterized by the absence of protein in the urine before birth; symptoms disappear during the first 3 months after birth. It can also develop as a chronic form, in which high blood pressure is observed even after 3 months from the date of birth of the child.
- Gestosis superimposed on the chronic form.
- Preeclampsia, preeclampsia, eclampsia.
The level of blood pressure in an expectant mother may increase against the background of multiple pregnancies, with high body weight, against the background of a hereditary predisposition, with diabetes mellitus and antiphospholipid syndrome, heart and vascular diseases, and kidney disease. And also risk factors for hypertension are a history of preeclampsia and eclampsia, a woman’s age over 40–45 years, and an interval between births over 8–10 years.
The protocol of the Ministry of Health states that the diagnosis of hypertension in pregnant women is made based on the lower (diastolic) pressure, since it does not depend as much on the psycho-emotional state of the woman as the upper (systolic).
Why high blood pressure is dangerous for mother and child:
High blood pressure during late pregnancy
- the possibility of developing a hypertensive crisis, late gestosis;
- the appearance of heart failure, pulmonary and cerebral edema;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- risk of premature placental abruption;
- risk of retinal detachment in the mother;
- the occurrence of fetal hypoxia;
- intrauterine growth retardation.
Preeclampsia
This is a group of pathological conditions that are manifested by high blood pressure in pregnant women, the appearance of protein in the urine or edema, or a combination of all these manifestations at the same time. Severe forms are characterized by cerebral swelling and seizures. Late gestosis includes preeclampsia and eclampsia. How these pathologies develop is discussed below.
With preeclampsia, generalized vasospasm occurs, against the background of which vascular resistance in the periphery increases, which, in turn, leads to a decrease in blood supply to vital organs. The result of disruption of the blood supply to the uterus and placenta is a delay in the growth and development of the fetus.
Changes in the renal apparatus are manifested by insufficient supply of oxygen and necessary substances to the glomeruli of the kidneys, which is manifested by the appearance of protein in urine, water retention, and the formation of edema. In severe cases, the level of uric acid, creatinine and urea increases, and the level of blood clotting increases due to platelets sticking together.
Eclampsia is manifested by the symptoms of preeclampsia in combination with seizures, vasospasm and cerebral edema. An increase in cranial pressure occurs, cerebral circulation is disrupted with further ischemic or hemorrhagic damage to the structures of the central nervous system.
Mild preeclampsia:
- systolic pressure – 140–160 mm Hg. Art., diastolic – 90–110 mm Hg. Art.;
- no swelling;
- protein in urine – less than 0.3 g.
Average degree:
- pressure is similar to mild pathology;
- protein in urine – 0.3–5 g;
- Swelling may occur on the face and hands.
Severe preeclampsia:
- upper pressure greater than or equal to 160 mm Hg. Art., diastolic – greater than or equal to 110 mm Hg. Art.;
- protein above 5 g;
- swelling on the face and hands;
- urine is excreted less than 400 ml per day;
- disorders of the central nervous system.
Help with preeclampsia
Mild preeclampsia requires restrictions on physical and mental stress; experts recommend resting more in a position on the left side. It is important to include a large amount of protein products in the menu. Salt and water may not be limited, but dishes should not make you thirsty. Women are prescribed vitamins, iron and calcium supplements.
In case of moderate severity of the pathological condition, medications may not be taken if the pressure was reduced during the period of initial increases in indicators, and it is possible to keep it within acceptable limits. Against the background of chronic hypertension or with persistently elevated blood pressure, antihypertensive drugs (Methyldopa, Atenolol) are used. In the final weeks before birth, therapy includes steroids to prevent fetal respiratory distress.
Treatment of severe preeclampsia is carried out in a hospital setting. Antihypertensive drugs, infusion therapy with magnesium sulfate, and steroids are prescribed. If the birth canal is not yet ready for delivery, specialists take appropriate measures. Diuresis is monitored every hour, and the level of protein in the urine is assessed twice a day.
Treatment of eclampsia
The woman is placed on the couch on her left side, the airway is checked, oxygen is supplied, and pain relief is administered (Fentanyl, Relanium). If a convulsive attack occurs, you should not administer medications, and you should not hold the woman in a certain position. It is important to secure the tongue and prevent aspiration of oral contents into the airway. After an attack, provide oxygen supply.
Immediate infusion therapy with magnesium sulfate is indicated, with additional administration of Diazepam or Thiopental. If the birth canal is not ready for urgent delivery, the choice is to perform a cesarean section. If after childbirth the woman’s condition has not stabilized, she is transferred for observation to the therapeutic department.
Important! After discharge, the woman is under the supervision of a local doctor for one and a half months after giving birth or until her blood pressure readings return to normal.
Treatment of arterial hypertension in pregnant women
Correcting your activity and rest schedule, diet therapy, and taking medications will help lower your blood pressure. Experts recommend limiting any type of stress, measuring blood pressure every 3-4 hours, periodically resting, lying on your left side, and sleeping at least 10 hours a day.
Diet therapy does not provide for strict restrictions: there is no need to reduce the amount of salt, since this can reduce the volume of circulating blood; you need to increase the consumption of foods rich in protein, polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and minerals. Experts do not allow fasting or taking measures to lose weight. And you should also spend a lot of time walking in the fresh air.
Experts identify criteria according to which antihypertensive therapy should be started:
- Blood pressure 140/90 or higher, in combination with or without gestosis, chronic form with damage to target organs, gestational arterial hypertension, which occurred after the 7th month of pregnancy.
- Blood pressure 150/95 or higher without the presence of target organ damage, pregnancy hypertension that occurred after the 7th month of gestation.
- Blood pressure is 170/110 or higher without any associated pathologies.
It is important to remember that not a single drug that is prescribed to combat high blood pressure is completely safe for the fetus. In the first trimester of pregnancy, only Methyldopa can be used. Next, Labetalol, Verapamil, Nifedipine retard, Clonidine, Doxazosin, Hypothiazide are prescribed. When choosing medications, the ratio of benefit to the mother and potential risk to the fetus is assessed.
Why is high blood pressure dangerous for a pregnant woman?
High blood pressure can lead to serious consequences for the body of mother and baby. First of all, the heart and blood vessels react to high blood pressure; arterial hypertension prevents adequate blood supply to the placenta ( preeclampsia
), as a result of which disturbances in fetal development may occur. A child can be born with a whole “bouquet” of diseases.
At the same time, a woman may feel persistent headaches and abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, her vision may decrease, breathing problems may appear, and her weight may increase sharply. Sometimes preeclampsia can be asymptomatic, but the consequences will be just as serious, so it is important not to trust solely your own feelings and sensations, but to monitor your blood pressure and do blood and urine tests in order to seek prenatal care in time.
Preeclampsia
in some cases may be accompanied by additional complications. The worst of them is eclampsia, which impairs blood circulation in a woman’s brain. Eclampsia can cause a sudden, severe seizure that is accompanied by convulsions and can result in coma and miscarriage, and sometimes death of the mother.
Blood pressure at different times
In the first trimester, hypertension in pregnant women is rare, but blood pressure can indeed change upward. This is due to the following reasons:
- The appearance of gestosis, which practically does not occur in the initial stages.
- If hypertension in pregnant women was noted even before the child was conceived, and the woman received appropriate treatment.
- Emotional overload that changes blood pressure for a short time. This condition is typical for expectant mothers, and it is associated with increased reactivity of the nervous system. During this crucial period, it is important to avoid stressful situations that have a negative impact on the developing fetus.
In the later stages, approximately 25% of pregnant girls experience increased blood pressure above acceptable values. It is no more than 160/100 mmHg, but this condition requires treatment, which is associated with the risk of complications. After the birth of the child, all the reasons that provoke pressure surges do not have such a noticeable effect on the woman’s body. Within 5-6 weeks, the indicators will stabilize, and the doctor at this stage may cancel the treatment previously administered to the pregnant woman.
What can arterial hypertension indicate?
High blood pressure is not always an independent problem; sometimes it is only a symptom of another disease or condition, for example, gestosis. Preeclampsia
- This is a complication of pregnancy, sometimes it is also called “late toxicosis”. A symptom of gestosis is not only high blood pressure, but also swelling, as well as an increased level of protein in the urine. Preeclampsia can lead to failure of the kidneys or other vital organs.
High blood pressure may also indicate fetoplacental insufficiency, i.e. interfere with the flow of oxygen to the fetus. “Oxygen starvation” can cause developmental arrest and death of the unborn child. In addition, high blood pressure can trigger premature placental abruption.
What does high blood pressure indicate in the 1st and 3rd trimester?
If in the early stages the pressure reaches 140/90, and such an increase is observed regularly, then we can talk about the presence of hypertension associated with the course of pregnancy itself and disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system.
Frequent high blood pressure in the 3rd trimester may indicate gestosis, which impairs blood flow and the functioning of individual organs. In the risk group, gynecologists include women who have infections, intoxication of the body, and nervous disorders.
Negative manifestations of high blood pressure:
- cardiac arrhythmia
- constant swelling
- vision problems
- constant weakness
- placental abruption
- rejection of the fetus by the female body (in addition to high blood pressure, increased protein in the urine and excessive weight gain are added).
Signs of high blood pressure
The most reliable way to control pressure is by regularly measuring it, but sometimes the pressure may jump unexpectedly, and a tonometer may not be at hand. Indirect symptoms of high blood pressure may also be cause for concern.
, and especially their combinations:
- dizziness and headache;
- noise in ears;
- “flies” before the eyes;
- nausea and vomiting;
- severe swelling;
- the appearance of red spots on the skin after mild physical activity or stress.
If these symptoms appear, you need to measure your blood pressure and, if possible, rest. During pregnancy, a woman’s condition is not stable, but ignoring symptoms of high blood pressure or other atypical symptoms is also dangerous. It is better to consult a doctor and do not miss scheduled visits to the doctor.
How to treat?
There are the following ways to lower blood pressure:
- taking pills (read the instructions carefully or consult a leading gynecologist - Papazol, Egilok, Dopegit and others)
- avoiding stress (for example, you can do yoga for pregnant women)
- traditional medicine (decoctions based on rose hips, dill seeds, taking pumpkin with honey)
- preparation and consumption of vitamin cocktails (beetroot, pomegranate, carrot, pumpkin and cranberry juice)
- exclusion from food of spicy, salty and sweet foods, as well as coffee and chocolate
- place some support under your feet when you are lying down and resting
Thus, eliminating high blood pressure will not be difficult. You just need to undergo an examination and consult with your doctor.
Causes of high blood pressure during pregnancy
If a woman has previously been diagnosed with hypertension, then you should not be surprised at high blood pressure during pregnancy. On the contrary, it is necessary to monitor changes in the condition even more carefully and follow the doctor’s recommendations. If a woman was taking medications regularly before pregnancy, they may need to be changed. At the very least, you will need to make sure that the drugs will not harm the unborn baby. Typically, medications for pregnant women are selected separately and individually.
The causes of high blood pressure can be stress, excess weight, diabetes, smoking and various diseases. Heredity also plays an important role. A predisposition to high blood pressure may not appear immediately, but if it exists, then even at the pregnancy planning stage it is worth taking care to ensure that there are as few factors that provoke arterial hypertension as possible.
Preventing high blood pressure
In such a situation, it is important to understand that all changes are temporary and their reasons lie in the restructuring of the body and preparation for the upcoming birth. During this period, experts advise devoting your free time to your favorite activities, listening to relaxing music and learning to “let go” of the situation. Pregnant women need support and understanding from relatives, and the expectant mother should avoid stressful situations if possible.
Prevention of high blood pressure involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and diet. The diet should be varied, with the obligatory presence of fish, vegetables and fruits, cereals and dairy products. On the recommendation of a doctor, develop a course of taking vitamins and, if necessary, blood pressure medications. During pregnancy, you should not self-prescribe or discontinue medications prescribed by your doctor.
- To avoid pressure, follow these rules:
- avoid noisy places, rooms with a lot of people;
- Avoid interaction with computers;
- Watching TV should not exceed 2 hours a day;
- Ventilate the room regularly;
avoid stress.
How to deal with high blood pressure
Special medications help lower blood pressure, but only a doctor can prescribe them for a pregnant woman. Self-medication in this matter can be very dangerous. Medicines are prescribed based on the results of a comprehensive examination. It is also better not to experiment with dietary supplements, despite their “naturalness” and “naturalness,” they can cause allergies and lead to other complications that are especially dangerous during pregnancy.
But you shouldn’t rely only on medications, while forgetting the simple rules of a healthy lifestyle. Controlling your own weight, regular exercise (if not contraindicated by a doctor), proper nutrition and giving up bad habits helps normalize blood pressure.