The color of the hematoma can be different - from bright red to purple, most often it is heterogeneous - its edges are darker, bluish in color, and the inside of the hematoma is red. Below in the article you will find the causes of the disease; the doctors who treat him; necessary medical procedures for treatment; as well as general information about the disease, its localization, features of diagnosis of diseases and their treatment. However, we advise you to consult a doctor, because self-medication in 90% of cases is fraught with the disease progressing to the chronic stage with extremely unpleasant complications
Make an appointment and consultation
Hematoma. general information
Hematoma is a condition characterized by the accumulation of liquid or coagulated blood inside the body, which occurs as a result of rupture of blood vessels and is localized in soft tissues. Hematomas can be small in size, or they can compress soft tissues and nearby organs. Hematomas form under the skin, mucous membranes, deep within the muscles, in the walls of internal organs, and in the brain.
When treating Hematoma, doctors at the BIOSS clinic use both time-tested and the latest developments and proprietary techniques.
Our clinic employs the best doctors in Moscow who have extensive experience in treating Hematoma
There are several classifications of hematomas:
Prevention
In order to avoid the formation of a bruise or bump after an injection into a vein or taking tests, you must:
| Preventive actions | Description |
| Relaxation of arm muscles | During the procedure, you need to relax your hand as much as possible, since when the muscles are tense, the likelihood of tissue damage increases significantly |
| Choosing the right needle size | To administer the medicine, you must use a syringe with the appropriate needle diameter. If a large volume of fluid is injected with a thin needle, the likelihood of bruising at the injection site increases. |
| Rate of drug administration | The medicine must be injected smoothly and slowly to avoid leakage of the solution into the tissue surrounding the vein |
| Measures after the end of the procedure | After the injection, cotton wool soaked in alcohol is pressed firmly against the vein puncture site for 5–7 minutes. |
If the hematoma at the injection site reaches a large size and quite severe pain or cramps occur, you should consult a doctor.
This may mean that the vein is seriously damaged and may require the help of a surgeon.
WHEN YOU SHOULD SOUND THE ALARM, THE FIRST SYMPTOMS OF HEMATOMA
A hematoma gives its symptoms and signs almost immediately after injury.
- Firstly, the skin at the site of the hematoma is sharply painful.
- After a short period of time, the site of injury begins to swell, the tumor can spread significantly and interfere with movement (for example, with a hematoma on the ankle, the swelling may be such that it is impossible to move independently or step on the affected leg).
- After swelling, the site of hemorrhage quickly turns red. Patients feel internal tension in the area of the hematoma; it is hard to the touch.
The color of the hematoma can be different - from bright red to purple, most often it is heterogeneous - its edges are darker, bluish in color, and the inside of the hematoma is red.
Where can I get a general blood test?
The blood test can be done at a medical laboratory, hospital, or clinic. If your situation requires it, this can also be done right at home.
Results of the same blood test
May vary slightly from lab to lab. This is due to the use of different dosing techniques. The results of the examination will be more or less the same in any case, but it is recommended to have all blood tests done in one laboratory when it comes to regular check-ups to monitor your health. The KDL Clinic has everything you need to take a test.
TYPES OF HEMATOMA AND THEIR TREATMENT
There are several approaches to the classification of hematomas.
Hematomas are distinguished depending on:
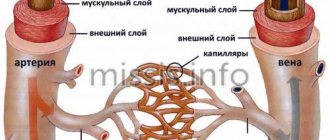
- the nature of bleeding - they can be arterial, venous and mixed;
- localizations – subcutaneous, intramuscular, intracranial, etc.;
- clinical signs - encysted, pulsating, simple.
In addition, situational hematomas are distinguished in the treatment, which require a special approach, for example, hematomas during childbirth, hematomas during pregnancy, etc.
An arterial hematoma is a hematoma that contains arterial blood in the cavity. As a rule, such hematomas are bright red, they are often diffuse - with a wide distribution on the surface. Venous hematoma occurs when there is compression and disruption of the integrity of the vein. These hematomas are bluish-violet in color, they are inactive and hard to the touch. The most common hematomas are mixed, when both arterial and venous blood enters the cavity.
A subcutaneous hematoma forms under the layer of skin and looks more like a bruise. They can form both due to injuries and due to various diseases - tuberculosis, syphilis, scarlet fever, lupus erythematosus. Often such hematomas form in people suffering from hemophilia. At the slightest damage to the vessel, spots appear on the skin. Subcutaneous hematomas can be of three degrees.
With a mild hematoma, its symptoms appear prolonged - approximately a day after the injury, while it absolutely does not interfere with the functioning of the organ on which it appeared. Painful sensations are weak and sometimes do not occur at all. If the hematoma is not complicated by anything, then it goes away on its own without any treatment. A moderate hematoma forms within three to four hours. In this case, the hematoma can partially disrupt the functioning of the organ on which it originated. A slight swelling and swelling of the soft tissues forms around such a hematoma. Apply ice and a pressure bandage to the site of the hematoma and contact a medical facility. A severe hematoma can occur with serious injury. In this case, the presence of a hematoma disrupts the functioning of organs. Hemorrhage forms quickly - literally within an hour you can notice a blue spot at the site of damage. Most often this is a subcutaneous hematoma, which is visible to the naked eye. Over time, the hematoma intensifies and can become intramuscular. In this case, the patient will feel numbness and soreness in the muscles. Such a hematoma requires a mandatory examination by a doctor and further treatment. If a hematoma is not treated, it can cause serious harm to the human body.
Intramuscular hematoma is characterized by the accumulation of blood in the muscles. In this case, the patient feels significant pain in the area of damage. Muscle function is impaired. In order to cure such a hematoma, it is necessary to consult a doctor. You may need to surgically open the hematoma and drain the cavity.
of intracranial hematomas - epidural, intracerebral, subdural, intraventricular.
Epidural hematomas are a collection of blood between the meninges and the skull bone. Most often, such hematomas occur near the temple; their development is associated with a traumatic moment (a blow to a stone, a blow to the head with a blunt object). With an epidural hematoma, the artery most often suffers, so such a hematoma is also arterial. At the site of the rupture, up to one hundred and fifty milliliters of blood quickly accumulates. The appearance of such a hematoma leads to compression of the brain. In this case, the patient loses consciousness for a short time, and then regains consciousness, but feels a headache, weakness, and vomiting. After several hours of improvement, a sharp deterioration occurs. Depending on the size of the hematoma, a state of coma can quickly occur. Heart contractions slow down, blood pressure drops, and the eyes stop responding to stimuli (except for the pupils). When such a hematoma is diagnosed, emergency surgery is prescribed to eliminate it.
Subdural hematomas are hemorrhages between the arachnoid and dura mater of the brain.
Venous blood collects in such hematomas, so they are also venous. Quite often, such hematomas are bilateral - the first occurs at the site of the impact, and the second - at the counter-impact. These hematomas have a larger area than epidural ones and can sometimes contain up to three hundred milliliters of blood. In the presence of such a hematoma, crisis phenomena in the patient may increase over the course of two days - hemiparesis, breathing problems, epilepsy, and bradycardia occur. The surgical treatment of such a hematoma consists of excision of the hematoma itself, restoration of the integrity of the bone and revision of the brain. In some cases, drainage is applied.
Intracerebral hematoma is very difficult to diagnose. Hemorrhage may occur slowly, increasing in volume day by day. Symptoms of intracerebral hematoma gradually appear. In some cases, immediate bruising may appear some time after the injury. The symptoms of such a hemorrhage depend on where it occurred - there may be hearing, speech, vision impairment, loss of consciousness, memory impairment, loss of sensitivity, or vice versa, hypersensitivity. Most often, such a hematoma is treated with special drugs that help it resolve. They are used if the volume of spilled blood is less than thirty milliliters. Otherwise, surgery may be necessary.
Intraventricular hematoma occurs when hemorrhage occurs in the ventricles of the brain. Treatment of such a hematoma depends on its size. If it is impossible to treat such a hematoma conservatively, then they resort to surgical intervention.
How to treat the ailment that has arisen
If a bruise appears on a vein after donating blood, the following measures can be taken to eliminate it.
- Alcohol compresses help a lot. They help the bruise on the vein resolve.
- You can apply an iodine mesh or brilliant green to the vein. Although this option is not the most suitable, since the hand in this place is very sensitive, and these products have a drying effect.
- There are special ointments for bruises that can be purchased at the pharmacy. Their action is based on relieving inflammation of the skin and improving blood circulation in the damaged area. Almost all of them are heparin-based. They can be applied up to 3 times a day.
- Venotonic gels. These are decongestants that are used for venous circulation disorders. They reduce the fragility of capillaries, increase the strength of vessel walls, and improve microcirculation in the vein.
- Taking ascorbic acid helps resolve bruises and improves immunity.
- A simple and effective remedy for a bruise is an ice compress wrapped in a cloth. You need to apply it for 20 minutes and then the bruise will go away faster.
All these methods are very simple and accessible. They have no contraindications. On the other hand, they are not required to be used, since the bruise that appears will go away on its own in a few days.
Preventive actions
A popular proverb says: “It is better to prevent a disease than to treat it later.” To avoid serious problems with veins, people at risk are advised to adhere to the following basic rules:
- Eliminate bad habits from your usual lifestyle (quit smoking, drink excessive alcohol).
- Include vitamin D, F, fish and seafood in your diet.
- Eat vegetable oil from corn, flaxseed, soy, nuts, and sunflower.
- After a long stay on your feet or training in the gym, use a contrast douche on the lower extremities.
- If you are overweight, it is recommended, under the supervision of a specialist, to formulate a competent diet for weight loss.
- Include light physical activity in your daily routine: aerobics, jogging, muscle stretching exercises.
- After physical activity, it is recommended to raise your legs above head level by thirty centimeters for three minutes.
If a person has the first signs of circulatory problems in the lower extremities, it is recommended to wear special underwear or wrap their legs with elastic bandages before going outside.
What are the main reasons for taking a biochemical blood test?
Blood chemistry
is the most commonly prescribed test by doctors and is used to monitor certain chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypothyroidism.
During the consultation, the doctor will determine whether a blood test
and what tests will be requested.
Here are some examples:
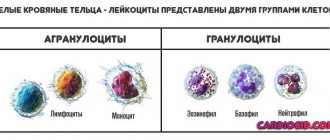
- Complete blood count (blood cell test);
- Determination of ferritin;
- Inflammatory assessment;
- Blood sugar test;
- Lipid balance;
- Kidney assessment;
- Liver test.