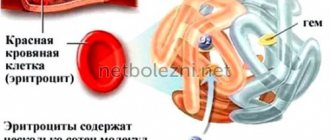
This disease is characterized by an abnormally low concentration of red blood cells. The red blood cells themselves contain hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to various parts of the body. With a reduced content of red blood cells, oxygen deficiency occurs and various parts of the body cease to function normally. Anemia (actually a drop in hemoglobin concentration) is detected in 58.7% of patients. Oncoanemia is calculated by the level of oxygen saturation of the blood, which drops to 12 g/dL and below. This condition is present in some cancer patients who have undergone chemotherapy. Oxygen deficiency in the circulatory system has a detrimental effect on a person’s general condition, worsening the prognosis.
Reasons for appearance
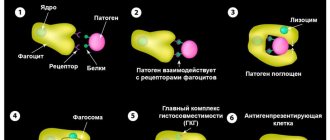
Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow. A hormone called erythropoietin, produced by the kidneys, tells the body to increase the concentration of red blood cells. Oncology and its treatment can cause a drop in hemoglobin concentration in various ways: • certain chemotherapy drugs can damage the bone marrow, which has a detrimental effect on the production of red blood cells; • certain types of cancers that directly affect the bone marrow, or those types of cancer that metastasize into the bones are able to displace normal cellular components of the bone marrow; • chemotherapy drugs containing platinum compounds (for example, cisplatin) can damage the kidneys, reducing the production of erythropoietin; • radiation treatment of large areas of the body or the pelvic bones, legs, sternum and abdominal area can severely damage the bone marrow; • nausea, accompanying vomiting, loss of appetite can provoke a deficiency of nutritional components necessary for the production of red blood cells (in particular, there is a lack of folic acid and vitamin B12); • the immune response to the progression of cancer cells can also lead to a drop in hemoglobin.
Requirements for blood for transfusion
Whole blood transfusion for oncology has negative consequences in the form of increased metastasis. Therefore, for blood transfusion, its drugs are used, which are selected depending on the tasks being solved:
- red blood cell mass - it consists of 80% red blood cells. Used for anemia. During storage, the properties of red blood cells gradually deteriorate;
- cryopreserved red blood cells - freezing with liquid nitrogen preserves their functional properties during long-term storage. Used for anemia;
- cryoprecipitate - obtained from plasma, contains components necessary to enhance coagulation. Used in late stages of cancer, when tumor decay causes coagulation failure;
- platelet concentrate – consists of concentrated platelets isolated by separation. Used to increase clotting;
- fresh frozen plasma – used to treat aplastic anemia and leukemia.
Diagnosis of the pathology in question
Treatment of anemia begins with a general blood test; Also, a biochemical blood test is done. With normal hemoglobin levels, the absence of the disease is diagnosed. When levels are less than 70 g/l, hospitalization and subsequent red blood cell transfusion are required. If hemoglobin drops too much, even people with stage 3-4 cancer are hospitalized. Sometimes doctors refuse to carry out hospitalization. In such situations, you need to be persistent, because transfusion must be carried out without fail. If the hemoglobin level is above 70 g/l, but below normal, you should look at the MCV indicators in the results of a biochemical blood test. This way it will be possible to determine the type of anemic pathology. Based on the average volume of red blood cells, you can understand whether this is due to iron deficiency. • MCV less than 80ft is a microcytic type of anemia caused by iron deficiency. • MCV is in the range of 80-100ft - it is normocytic (here we can talk about its aplastic, hemolytic or hemoglobinopathic type). • MCV above 100ft is macrocytic, caused by a lack of folic acid, vitamin B12, and nutritional deficiency.
What else is worth checking?
Ferritin. This is a protein complex that shows the level of iron reserves in the body; it is responsible for both the storage and release of iron.
- The optimal ferritin range is 50-80 nanograms per milliliter. The figure usually roughly corresponds to our weight,” says Dobretsova. — If the indicator fluctuates between 30-40, then this is a reason for concern, even with a normal hemoglobin level. This indicator is especially recommended for those who take anti-inflammatory or painkillers for persistent headaches, back pain and others. The fact is that these medications can cause erosion of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines and, accordingly, bleeding. Taking antacids (Maalox, for example) can affect the absorption of iron, so such patients should also undergo such testing regularly. Vegetarians, people with frequent bleeding, and those taking blood-thinning medications are also at risk. All of them need to donate blood for this indicator, even in the absence of symptoms of anemia.
Excess ferritin is also dangerous - especially with liver diseases, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. When there is a lot of ferritin, the vessels harden and become fragile. This means that the aging of the body accelerates.
Article on the topic
Iron in the blood. 10 foods that will increase hemoglobin in winter
The first symptoms of oncoanemia
The primary indicators of the defect in question are sudden paleness of the skin and impaired functionality of the digestive system. Most patients lose their appetite; they suffer from constant nausea. The development of cancer is accompanied by a gradual deterioration of the condition. There is systematic malaise, muscle weakness, accelerated fatigue, and loss of former ability to work. Quantitative examination of the circulatory system must be carried out a certain number of times during the treatment of anemia. Thus, the dynamics of cancer progression is assessed.
Treatment of anemia in cancer patients
The main advantage of the intravenous administration of erythrocyte drugs is the rapid restoration of the optimal hemoglobin concentration. However, this approach provides a short-term effect. If the pathology in question begins to show symptoms, a blood transfusion containing a sufficient number of red blood cells may be required. Some people with low hemoglobin caused by chemotherapy can be treated with epoetin alfa or darbepoetin alfa. These medications are forms of erythropoietin produced in the laboratory. They send a signal to the bone marrow to increase the production of red blood cells. In order to eliminate iron deficiency, these medications must be combined with intravenous injections of products containing iron. According to statistics, in 45% of cases a good result is achieved through a combination of erythropoietin and iron. Sometimes you can even get by with just the use of iron supplements.
How are donors' blood tested?
For oncology, you can do a blood transfusion that has undergone a thorough examination for infections, group membership, and Rh factor. If necessary, additional testing is carried out for other group antigens. To completely protect patients from infections, the following measures are taken:
- Before donating blood, the donor answers a questionnaire. He is obliged to talk about possible cases of infection recently. If there is the slightest suspicion of infection in a donor, he is not allowed to donate;
- the donor is examined by doctors and undergoes tests. People who have abnormal test results (abnormal bilirubin, increased white blood cells, high liver enzymes, etc.) are excluded from taking the test;
- After collection, the blood is examined for parenteral infections. If they are absent, she is divided into factions and sent to a six-month quarantine to check the donor again. He could have had infections that were not detected by laboratory methods because they were at an early stage of development.
Erythropoietin in palliative care
In the first stages of anemia treatment, the full dosage of the medication is prescribed. If during a month of such treatment the hemoglobin concentration increases by 10 g/l, the dosage is reduced by a quarter. If over the same period of time the hemoglobin concentration increases by 20 g/l (or more), the dosage is reduced by half. If the hemoglobin concentration exceeds 130 g/l, the course of taking erythropoietin is temporarily stopped (until the level drops to 120 g/l). After this, the course is resumed, but the initial dosage is already reduced by a quarter.
If monthly use of such a remedy is unsuccessful, the dosage is increased (however, it must be within the maximum permissible limits). If a drop in hemoglobin is caused by a lack of nutritional components, iron tablets may be prescribed. Vitamin B12 and folic acid tablets may also be prescribed. Eating foods containing a substantial dose of iron (red meat, certain fruits, almonds) can be of great help in treating anemia.
Blood transfusion procedure for a cancer patient
Transfusion is a serious procedure that requires a number of preparatory measures:
- checking the group, Kell antigen, Rh factor;
- determining the compatibility of the blood of the donor and the patient;
- examination of the patient's condition;
- administration of a test portion followed by observation of the body’s reaction.
After this, the transfusion begins. The patient is in a specialized chair, blood slowly flows through a needle with a catheter into a vein. In one session, no more than 400 ml is infused.
The duration of the blood transfusion procedure for oncology varies depending on the type of drug being transfused. When transfusion of red blood cells takes from 2 to 4 hours, platelet transfusion takes no more than an hour.
The patient is monitored by medical personnel during blood transfusion. If side effects occur, the procedure is interrupted. The patient is monitored after completion of the procedure. There are no universal blood transfusion schemes; their number is determined by the doctor, taking into account the disease and condition of the patient. So, for blood cancer, multiple transfusions of red blood cells are given.
Danger and consequences
Doctors believe that a drop in hemoglobin concentration accompanies all cancer pathologies. A deficiency of red blood cells is dangerous because oxygen starvation of all tissue components can develop. In addition, the presence of such a defect complicates the course of chemo-radiation therapy.
The consequences of the pathology depend on the stage of initial diagnosis of the oncological process. Red blood cell deficiency detected in the early stages usually has a positive prognosis. The favorable outcome is due to the high chances of 100% cure of anemia. Oncoanemia with poor prognosis is usually present in people with stage 3-4 cancer, which causes intoxication, metastasis and death.
Consequences after chemotherapy in women
Chemical drugs, affecting the ovaries, inhibit the growth and development of follicles, damage the hereditary material of germ cells and cause hormonal disorders.
The most common side effect of chemotherapy drugs is menstrual irregularities and cessation of menstruation. Menopause can be temporary, caused by hormonal imbalances, or permanent, caused by ovarian depletion.
Women have a limited number of eggs. During her entire life, she experiences about four hundred menstrual cycles, which means that four hundred follicles go through the development cycle. Chemotherapy reduces the number of follicles, causing ovarian failure.
Here the consequences depend on age: in girls under twenty years of age, with a sufficient supply of follicles, menstruation is restored in seventy percent of cases. In women over thirty, whose ovaries are already depleted, only in their twenties.
However, pregnancy after chemotherapy is quite possible. By taking care of cryopreservation of eggs, embryos or ovarian tissue in advance, you can avoid infertility. This should be done before starting treatment, since even one course of chemotherapy deteriorates the quality of cells and changes the structure of the hereditary material. But even if the patient begins to think about possible infertility after starting treatment, it is not too late to contact a fertility specialist, although it is necessary to freeze the eggs as early as possible.
You can use the stored eggs at any time. The shelf life of the material is unlimited, and children born using preserved eggs will be no different from those conceived naturally.
It is very important to use contraception or avoid sexual contact during the course of treatment to avoid unwanted pregnancy. A woman should definitely consult her doctor about this, since chemotherapy drugs cause deformities in children.
The side effects of chemotherapy on the developing fetus are so strong that if a woman is diagnosed with cancer during pregnancy, the course of treatment is postponed until after birth.