A complication of arterial hypertension, which is characterized by high blood pressure, is a hypertensive crisis. In this pathological condition, a sharp rise in pressure is observed, and other symptoms worsen. Certain psychological symptoms may indicate the approach of a hypertensive crisis: internal anxiety, causeless irritability, depression, worsening headache.
Reasons for development
Hypertensive crisis most often occurs with hypertension. It often develops against the background of other pathologies, in particular, patients who are diagnosed with:
- Kidney diseases: pyelonephritis, polycystic kidney disease, diabetic nephropathy, etc.
- Diseases of the endocrine system: pheochromocytoma, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, thyrotoxicosis, etc.
- Atherosclerotic lesion of the aorta and narrowing of its lumen.
The risk group includes people with hereditary complications and women during menopause. The development of a hypertensive crisis can be triggered by smoking, alcohol abuse, unbalanced diet, obesity, lack of physical activity, stress, and sudden refusal of antihypertensive drugs.
Algorithm of actions
As you already understand, a crisis can be called a complication of hypertension. Help is provided in this case as quickly as possible. First of all, you should call an ambulance. If a person is nervous or afraid, the person must be calmed down so that the pressure does not rise even higher. It is important to ensure air flow into the room, it is necessary to unbutton clothes, it is important that breathing is controlled and as smooth as possible. An emergency medicine for blood pressure should be placed under the tongue; Captopril or Nifedipine, as well as Copoten or Corinfar, help well.
If the ambulance does not arrive, and the person has become worse, you can take the medicine again. If pain or compression appears behind the sternum, you need to take Nitroglycerin. In case of chills, it helps to surround the person with bottles, into which warm water is first poured, and wrap them up. Often, upon arrival of the medical team, it becomes clear that hospitalization is not necessary. All measures are taken on site.
Symptoms
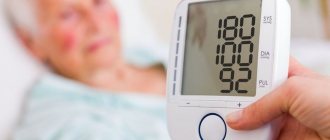
The main symptom of the development of a hypertensive crisis is a sharp jump in blood pressure. As a rule, the upper limit is fixed at 150 mmHg. Art. But in certain cases, depending on the characteristics of the body, the “upper” pressure of 130 mm Hg may become critical. Art.
In addition, the following symptoms are noted during a hypertensive crisis:
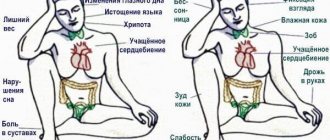
- Headache in the back of the head.
- Dizziness.
- Increased body temperature.
- Problems with vision function, up to the development of temporary blindness.
- Nausea, which in a complicated condition turns into vomiting.
- Oscillations of the eyeball in different directions
- Redness of the skin of the face and neck;
During a hypertensive crisis, patients develop a panic state. Panic state. It causes trembling throughout the body, rapid heartbeat, and increased sweating. Due to emotional stress, coordination of movements may be impaired, which leads to uncertain movements and a shaky gait.
Hypertensive crisis: diagnosis
Diagnosis of a hypertensive crisis begins with examination and questioning of the patient. The doctor measures the patient’s blood pressure, sends him for a fundus examination, clinical urine and blood tests, an ECG, and if a stroke is suspected, the patient is sent for a CT scan. Computed tomography helps determine pathologies of brain tissue in layer-by-layer images of a three-dimensional model of the brain created by a tomograph. Examination of the fundus can reveal the presence of edema and hemorrhage.
At the Yusupov Hospital, treatment of hypertension and hypertensive crisis is carried out in the therapy department. Doctors use an integrated approach; in addition to drug therapy, the patient is prescribed a diet and selects an individual physical therapy program.
Peculiarities
The pathological condition is classified according to the presence of complications. A complicated hypertensive crisis is life-threatening. Against this background, patients develop damage to internal organs: heart, kidneys, brain, eyes. Without emergency medical care in the intensive care unit, there is a risk of death.
An uncomplicated hypertensive crisis manifests itself against a background of high blood pressure with minimal symptoms. In this case, damage to internal organs does not occur. Emergency hospitalization for such a pathological process is not required. You need to buy special medications and take them according to the regimen recommended by the doctor.
There are also options for the development of a hypertensive crisis based on pressure indicators:
- Hyperkinetic. In this case, an increase in upper (systolic) pressure is recorded. The difference with the diastolic indicator increases, which leads to tachycardia.
- Hypokinetic. In this case, an increase in lower (diastolic) pressure is noted. The difference with the systolic indicator increases, which leads to bradycardia.
- Eukinetic. In this case, the upper and lower pressure levels increase. This can lead to both tachycardia and bradycardia.
Hypertensive crisis type 1 (adrenal) develops suddenly and very quickly. There are no warning signs of an attack. A characteristic feature is a severe headache and a feeling of heat, the appearance of pulsation and trembling of the body, redness of the skin surface and increased sweating, sweating. The duration of the attack is often several minutes, but the condition can persist for several hours. This type of hypertensive crisis corresponds to the hyperkinetic variant of development.
Hypertensive crisis type 2 (norepinephrine) develops gradually and is characterized by a severe course. The condition may persist for several days. In addition to severe headaches, problems with hearing and vision often occur, impaired motor ability is noted, confusion and squeezing pain in the heart area are recorded. This type of hypertensive crisis corresponds to the hypokinic variant of development.
Prevention
- Every hypertensive patient should be informed about what causes can lead to a hypertensive crisis.
- Strictly follow all necessary medications prescribed by your doctor. Negligence in taking vital medications often causes a crisis.
- Follow a diet. Excessive consumption of salty foods leads to fluid retention in the body and, consequently, increased blood pressure. Fatty, fried foods cause the formation of cholesterol plaques. The latter, in turn, clog blood vessels and contribute to increased blood pressure.
- Hypertensive patients are strictly not recommended to drink alcoholic beverages, which excite the nervous system and cause vasoconstriction.
- Take medications regularly to normalize blood pressure.
- Eliminate caffeine-containing drinks from your diet.
- Completely get rid of bad habits.
- From time to time, take a course of therapeutic massage.
- Take sedative medications regularly.
Patients suffering from hypertension are advised to regularly monitor their blood pressure, promptly replenish their own first aid kit with the necessary medications, and if the above-described symptoms occur, immediately seek medical help.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, proper, rational nutrition and sports are the reasons for a person’s external and internal health. Any disease can be prevented if you take timely care of your own condition. Following these simple recommendations allows hypertensive patients to keep their blood pressure under control and enjoy a full life.
First aid
Understanding what a hypertensive crisis is, you need to know how to properly provide first aid to a person with the development of a severe, life-threatening condition. First of all, if there is a sharp jump in blood pressure, you need to urgently call an ambulance team. But before the arrival of specialists, it is necessary to try to stabilize the patient’s condition in order to minimize the risks of dangerous consequences.
It is necessary to reduce blood pressure using medications. It should be remembered that it is necessary to lower blood pressure gradually when a hypertensive crisis develops. You should also take a sedative (valerian or corvalol) to relieve anxiety.
It is important that the patient is in a sitting position that is as comfortable as possible. It is imperative to ensure the supply of fresh air. A cold compress should be applied to the patient's forehead. Additionally, you can make hot foot baths with a water temperature of 40°C or apply mustard plasters to your calves.
With the development of a complicated hypertensive crisis, treatment is possible only in intensive care conditions. Patients are kept in the intensive care ward until their condition is completely stabilized. After this treatment, a certain period of time continues in the hospital therapeutic department.
Prevalence
In Russia, about 40% of the population has high blood pressure. Among these people, approximately 1-5% experience a hypertensive crisis each year. Most of the cases are mild, that is, without complications. However, in 25% of cases, patients suffer a crisis with the development of complications such as myocardial infarction, acute heart failure, pulmonary edema, hypertensive encephalopathy, stroke or cerebral infarction, aortic dissection, eclampsia (a condition of pregnant women with the threat of miscarriage) - a complicated hypertensive crisis.
It is almost impossible to determine at what age hypertensive crises occur more often. They occur in both young people at 30 and older people at 80. Concomitant diseases and body conditions, such as pregnancy and stress, are of greater importance here as risk factors.
What to do if you are alone at home?
When a person is at home himself, it is not surprising that he is at a loss. It is important to take your medicine and open the front door. After this you call an ambulance. If you lose consciousness, doctors will be able to get into the house. The arriving team usually administers Dibazol, they use diuretics, and in case of significant tachycardia, beta blockers help. This is Inderal, or Rausedil and Obzidan.
You should definitely put Nifedipine or an analogue of Corinfar under your tongue. If the GC turns out to be complicated, then further measures are taken in the hospital. Sometimes ventricular failure occurs. If coronary insufficiency develops, the patient is placed in intensive care, where they try to relieve the pain. One of the most serious complications can be called a heart attack. This pathological condition requires resuscitation. It is necessary that the person is taken to the hospital as quickly as possible. This gives a chance to save the patient and minimize complications and their risks.
Forecast
If first aid for an uncomplicated crisis was provided in a timely manner and a treatment regimen was prescribed in a hospital or at home, taking into account all the features of the disorder, the prognosis in most cases is favorable.
The statistics are as follows:
- In 70% of patients, after taking antihypertensive drugs, the pressure decreases and the symptoms of the attack decrease. This allows you to avoid hospitalization. The patient is selected for treatment on an outpatient basis, stabilizing the state of health, and recommendations for rehabilitation are given.
- 15% of patients experience an increase in symptoms. At the same time, complications arise that require immediate hospitalization.
- Another 10–15% of people experience iatrogenic complications associated with excessive or too rapid drop in blood pressure. Against this background, arterial hypotension, collapse, and bradycardia can be diagnosed. The patient is admitted to the hospital for further monitoring of the condition and correction of the treatment regimen.
- Some patients experience a complete lack of effect from drug treatment. In this case, doctors change the therapeutic regimen, following the standards, and recommend hospitalization.
A complicated crisis affects target organs, so the prognosis depends on the severity of the complications. A crisis that is never treated at home may include a transient ischemic attack, as well as stroke, heart attack, pulmonary edema, aortic aneurysm dissection, left ventricular failure, arrhythmia, and cerebral edema. High probability of death.
No ads 2