Causes of cardiosclerosis
1. Functional disorders:
- Damage to the heart muscle as a result of inflammatory diseases.
- Hypoxia due to insufficient blood supply to the heart muscles due to narrowing of large cardiac vessels.
- Stretching of the walls of the heart, which leads to an increase in its volume.
2. Lifestyle and bad habits of the patient:
- Alcohol abuse and smoking.
- No, minimal or excessive physical activity.
- Repetitive stress.
- The habit of overeating and, accordingly, excess body weight.
Hereditary factors play an important role in the occurrence of the disease.
Preventive measures
To prevent the development of diffuse atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis, you must follow these recommendations:
- Healthy food;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- avoid stressful situations;
- visit a doctor in a timely manner if the slightest symptoms of this disease appear;
- get rid of bad habits.
Diffuse small-focal cardiosclerosis can not only significantly reduce the patient’s quality of life. In advanced forms, it can cause serious complications, ultimately leading to death. Therefore, if signs of the disease appear, it is necessary to seek medical help, which will prevent the pathological process from starting.
It is much easier to treat this disease in the initial stages; you can get by with taking certain medications. In advanced cases, surgical intervention will be required. If you ignore the symptoms of the disease, death from atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis is possible.
Classification of cardiosclerosis
According to the morphological principle, focal (most often occurs as a complication after myocardial infarction and myocarditis) and diffuse cardiosclerosis, in which the connective tissue spreads to the entire myocardium, are distinguished.
For etiological reasons, the following types are distinguished:
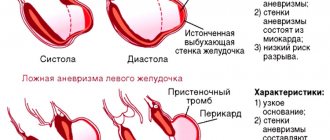
- Post-infarction. As a result of myocardial infarction, scars form at the site of necrotic damage, which reduces the contractility of the heart muscle. The more cases of myocardial infarction a patient has suffered, the more scar tissue is formed. The threat of chronic aneurysm increases due to protrusion of the walls of the heart muscle, which is stretched and weakened by connective tissue. Aneurysm rupture is associated with high mortality.
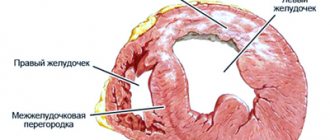
- Myocardial. Myocardial inflammation develops mainly in young patients with chronic allergic and infectious diseases. With this form, the right ventricle of the heart increases in volume and is insufficiently supplied with blood.
- Atherosclerotic. As a rule, it is the result of atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels and coronary heart disease. This form of the disease develops over a long period of time, because due to damage to blood vessels, heart cells do not receive enough oxygen, hypoxia develops, the course of coronary heart disease is complicated, and cholesterol levels increase. This leads to diffuse cardiosclerosis, which is accompanied by arrhythmia.
Alternative medicine
Non-traditional methods of treatment for this pathology can only be auxiliary. Doctors include home recipes in a set of measures aimed at maintaining myocardial function. Any adjustments in treatment should be discussed with your doctor. It is unacceptable to self-prescribe a course of therapy. In myocardial cardiosclerosis, the course of the disease is improved:
- ginger - used as an additive to tea or as a tincture to prevent the formation of blood clots and eliminate atherosclerotic plaques;
- garlic - helps reduce cholesterol concentrations, normalize blood pressure, and is a powerful tool for strengthening vascular walls;
- hawthorn - has a positive effect on blood flow, normalizes cholesterol and blood pressure, restores heart rhythm (tea or alcohol tincture);
- parsley - strengthens the heart muscle, the walls of blood vessels (all components of the plant are used);
- artichoke - consumed in tinctures or in tablet form to strengthen blood vessels and reduce bad cholesterol;
The approach to eliminating the problem and alleviating symptoms should be comprehensive. A competent specialist combines conservative therapy with unconventional methods, recommends the patient to walk more, swim, and dance. It is important to correctly assess your capabilities and not overwork.
Symptoms of cardiosclerosis
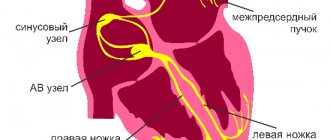
Very often the initial stages of the disease are asymptomatic. In the clinic of the onset of sclerosis, the first symptom may be arrhythmia. Typical manifestations of the diffuse form should be considered heart failure and disturbances in the rhythm of the heartbeat.
Symptoms regardless of the form (post-infarction or atherosclerotic):
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- dyspnea;
- the appearance of fluid in the abdominal and pleural cavities;
- pain in the heart area;
- increased heart rate;
- pulmonary edema;
- increase in liver size.
As the area of affected heart tissue increases, the severity of symptoms increases.
Very often the course of cardiosclerosis is accompanied by arterial hypertension. In this case, high blood pressure alternates with long periods of normal blood pressure.
Power Requirements
If you are diagnosed with myocardial cardiosclerosis, you should reconsider your gastronomic habits. The following are completely excluded from the food basket:
- coffee, caffeinated drinks;
- alcohol containing drinks;
- fast food, street food;
- scrambled eggs;
- rich meat broths;
- sauces, butter.
The diet should mainly consist of vegetables, herbs, fermented milk products, and sea fish. You will have to give up bad habits.
At-risk groups
The risk of cardiosclerosis is highest in patients with pathologies in the development of the heart and cardiovascular diseases, as well as in people with various types of allergies.
Pregnant women can be identified as a separate group. Pregnancy causes hormonal, autonomic, metabolic and hemodynamic changes in the body of women and can act as a proarrhythmogenic factor. Complex heart rhythm disturbances are diagnosed both in pregnant women with cardiovascular pathology and in patients without changes in metabolism and the condition of internal organs.
Cardiosclerosis in children is possible against the background of myocardial pathologies, for example, inflammatory and dystrophic processes, in particular diseases of the heart muscle caused by metabolic disorders in heart cells. These biochemical disorders significantly weaken the contractile, conductive, excitatory and automatic functions of the myocardium.
Treatment
In order to choose the most effective method of treating cardiac cardiosclerosis, the doctor prescribes various diagnostic procedures. This is necessary to identify the degree of damage to the heart by scars, the number of lesions, the type of disease, as well as determine the cause.
In the treatment of cardiosclerosis, the following measures are prescribed:
- echocardiogram;
- dynamic electrocardiogram;
- MRI;
- study of coronary vessels.
In addition, the cardiologist examines the patient’s medical history and determines the disease that triggered the development of cardiosclerosis.
There is no single method for treating cardiac cardiosclerosis. The complex of therapeutic measures is aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease - atherosclerosis in ischemic heart disease, inflammation of the heart muscle, and the consequences of myocardial infarction.
In the post-myocardial form, the entire emphasis will be on treating the infection or allergic reaction that caused cardiosclerosis.
With a diffuse atherosclerotic form, it is necessary to reduce cholesterol in the patient’s blood and take measures to help restore blood circulation in the coronary arteries and correct blood pressure. To do this, they resort to drug therapy using vasodilators and anticoagulants. The choice of therapy to reduce signs of heart failure is imperative. At this stage, treatment of cardiac cardiosclerosis is carried out with the help of cardiac glycosides, diuretics, beta blockers, etc. To correct impaired patency of the coronary arteries, it is permissible to use such surgical methods as stenting and coronary artery bypass grafting.
When treating cardiosclerosis, the patient's diet, physical activity and lifestyle are adjusted. It is imperative to lead a healthy lifestyle. The cardiologist may recommend physical activity - walks in the fresh air, as well as a complex of therapeutic exercises.
When treating cardiosclerosis, the following dietary restrictions apply:
- refusal to use table salt;
- control of the amount of liquid you drink (per day);
- avoidance of foods that stimulate the nervous and cardiovascular systems (alcohol, tea, cocoa, coffee);
- avoiding eating fried meat and fish (baked or stewed only), as well as foods high in cholesterol - offal, eggs.
Part of complex therapy is sanatorium-resort treatment.
Cardiosclerosis medications
The European Society of Cardiology recommends the following medications for the treatment of cardiosclerosis, eliminating the symptoms of the disease, as well as its root cause:
- Antihypertensive drugs. To maintain vascular tone and normalize blood pressure, ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Enalapril, Ramipril) are prescribed; calcium antagonists (Amlodipine, Semlopin, Phenigidine), beta blockers (Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Metoprolol), antiplatelet drugs (Aspirin), lipid-lowering drugs (Simvastatin, Atorvastatin, Allesta).
- Cardioprotectors (antianginal agents). Their task is to maintain the functional activity of the heart and counteract the influence of negative exo- and endogenous factors on it. These include organic nitrates (Nitroglycerin, Isosorbide Mono- and Dinitrate); sydnonimines (Mosikor, Sidocard); metabolic agents (Trimetazidine).
- To normalize heart rate and conduction: amiodarone (Amiodarone), dronedarone (Multak).
- To normalize metabolic processes - potassium and magnesium preparations: Panangin, Asparkam, Magnerot.
- Antibiotics and corticosteroids: for myocarditis and other inflammatory processes.
List of used literature
- Stryuk R.I., Shoikiemova D.U., Borisov I.V.; State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after. A.I. Evdokimov" Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russia / Pregnancy as a risk factor for heart rhythm disturbances
- POKROVSKAYA E.M., 2, Ph.D., N.A. VOLOV 2, Ph.D., I.S. VASILYEVA 2, GORDEEV I.G. 1, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, PAVLIKOVA E.P., 2, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor 1 State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “Russian National Research Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogov" of the Ministry of Health of Russia, Department of Hospital Therapy No. 1, Faculty of Medicine 2, State Budgetary Institution "City Clinical Hospital No. 15 named after. O.M. Filatova "DZ Moscow / NEW OPPORTUNITIES FOR TREATING PATIENTS WITH HEART FAILURE DUE TO POST-INFARCTION CARDIOSCLEROSIS
- Berezin A. E., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Internal Medicine No. 2 of the 1st Medical Faculty of Zaporozhye State Medical University / Combined potassium and magnesium preparations in the treatment of patients with high cardiovascular risk.
Frequently asked questions about cardiosclerosis
Which doctor treats cardiosclerosis?
If you suspect cardiosclerosis, you should contact a cardiologist.
What signs should you see a doctor for?
High blood pressure; arrhythmia; increased fatigue and swelling of the limbs.
Can cardiosclerosis develop in children?
Cardiosclerosis in children can develop against the background of inflammatory and dystrophic processes in the myocardium - in particular, diseases of the heart muscle caused by metabolic disorders in heart cells.
Diagnostics
Cardiological examination of a patient with cardiosclerosis should include:
- collecting anamnesis (complaints, previous diseases, living conditions);
- listening to the heart;
- biochemical blood tests;
- ECG;
- Echo-CG;
- MRI of the heart.
After analyzing the data obtained during the examination, the cardiologist can prescribe complex treatment for diffuse cardiosclerosis to the patient.