Sometimes problems with the cardiovascular system become so serious that conservative treatment methods no longer have the desired effect. If the patient is diagnosed with atherosclerosis, which has seriously affected one or more vessels, surgical intervention is indicated. In the problem area, certain manipulations are carried out aimed at restoring normal vascular patency and the correct functioning of the entire cardiovascular system.
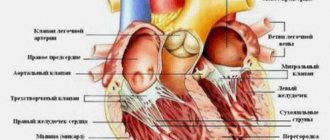
If blood vessels are blocked by atherosclerotic deposits, the heart tissue experiences oxygen starvation. This leads to the occurrence of coronary disease. This condition is extremely dangerous for the patient’s life, especially in the case of complete blockage of the vessel, which entails myocardial infarction. However, today there are effective methods for treating coronary heart disease - stenting and bypass surgery.
What is cardiac bypass surgery?
Bypass surgery is an operation to replace the affected area of a vessel. In the vast majority of cases, this is the coronary artery. Radical surgical intervention significantly increases the patient's life expectancy, reduces the risk of developing acute coronary syndrome, angina pectoris, and heart attack.
The operation lasts from 4 to 6 hours. The patient is put into medicated sleep. Access to the heart is made through an incision in the sternum or intercostal space. The essence of the operation is to create a bypass for blood flow. To do this, a section of the radial, internal mammary artery or femoral vein is taken (at the discretion of the doctor). The vessel is replaced, after which the chest wall is sutured.
How does a shunt work?
So, we have a simple shunt. By the way, in the diagrams it is designated as a resistor. And this is not surprising, because this is a low-resistance resistor.
Let's agree to assume that our current is constant and flows from point A to point B. On its way it meets a shunt and flows through it almost unhindered, since the resistance of the shunt is very small. Do not forget that electric current is characterized by such parameters as Current Strength and Voltage. Electric current flows through the shunt with some force (I), depending on the load of the circuit.
Remember Ohm's Law for a section of an electrical circuit? Here it is:
Where
U - voltage
I - current strength
R - resistance
Our shunt resistance is always constant and does not change, simply put, “constant”. We can find out the voltage drop across the shunt by measuring it with a voltmeter as in the figure:
So, based on the formula
we get the formula:
and we draw a terribly simple conclusion: the readings on the voltmeter will be greater, the greater the current flowing through the shunt.
So what does this mean? This means that we can easily calculate the current flowing through the AB wire ;-). Everything ingenious is simple! And the most wonderful thing is, you know what? We don't even need to use an ammeter ;-).
This is the principle of operation of the shunt. And most often this principle is used precisely to expand the measurement limits of measuring instruments.
What is cardiac stenting?
Stenting is a more modern, low-traumatic operation to restore the affected area of the vessel. The main direction of the intervention is restoration of the lumen of the vessel.
The essence of stenting is the introduction of a special balloon into the affected vessel, which opens under high pressure, destroys the atherosclerotic plaque and ensures patency of the vascular bed. The balloon is located in a stent - a special supporting structure made of a special alloy. When the balloon is deployed, the stent opens and remains in the vessel forever, fixing its walls and preventing the re-formation of atherosclerotic deposits. The balloon is removed from the artery.
Types of shunts
Industrial ammeters look like this:
In fact, no matter how strange it may sound, these are voltmeters. It’s just that their scale is drawn (graduated) with calculations according to Ohm’s law. In short, it shows the voltage, and the count is in Amperes ;-).
On one of them you can see the measurement limit even up to 100 Amperes. What do you think, if you put such a device in an open circuit and pass a current of, say, 90 Amps, will the thin wire of the measuring coil inside the ammeter withstand it? I think there will be white thick smoke). Therefore, such measurements are carried out only through shunts.
And here, in fact, are industrial shunts:
Those on the bottom right can pass through themselves a current of up to a kiloampere or more.
Each industrial ammeter comes with its own shunt. To start using an ammeter, it is enough to assemble a shunt with an ammeter according to this diagram:
In some ammeters, this shunt is built directly into the body of the device itself.
What is the difference between stenting and bypass surgery?
Principles of bypass surgery:
- Abdominal surgery, with access through the chest, is performed under general anesthesia;
- intervention involves the formation of an artificial blood path, excluding the affected one from the circulatory system;
- a fragment of a vein or artery from another area of the body acts as a shunt (if it cannot be removed, artificial materials can be used);
- in most cases, the patient is provided with artificial circulation, operating on a non-functioning heart.
An important point is the rehabilitation period. If bypass surgery is performed, the patient will have a long recovery. Also, after the intervention, it is necessary to observe a number of strict restrictions throughout life in order to prevent the recurrence of atherosclerotic plaques.
The difference between stenting and bypass surgery:
- the operation does not require general anesthesia;
- the intervention practically does not injure the skin - access is carried out through a small puncture in the area of one of the large arteries, most often the femoral;
- stenting is carried out under the control of a radiographer;
no bypass paths for blood flow are formed - the blocked artery is expanded with the help of a stent, and blood circulation is restored naturally.
After the operation, the patient remains in the hospital for 1-3 days. The rehabilitation period is minimal - within a few hours after the intervention, a person can sit down, stand up and even move carefully. The likelihood of complications after stenting is minimal. The most common postoperative problems are damage to the vessel wall, bleeding, and hematoma formation. However, all of them can be quickly resolved in a hospital setting under the supervision of the attending physician.
Shunt operation using a practical example
Our guest is the most ordinary industrial shunt for an ammeter:
On the back you can read its markings:
How to read the characteristics of such markings? Everything is simple here! This means that if the current flowing through the shunt is 20 Amps, then the voltage drop across the shunt will be 75 millivolts.
0.5 is an accuracy class. That is, how much we measured - this value will have an error of 0.5% of the measured value. That is, let's say we measured a voltage drop of 50 millivolts. The measurement error will be 50 plus or minus 0.25. Such accuracy is quite enough for industrial and radio-electronic needs ;-).
So, we have a simple 12-volt car light bulb:
We set the voltage on the Power Supply to 12 Volts, and connect our light bulb. The light bulb lights up and we immediately see how much current it consumes, thanks to the built-in ammeter in the power supply. Our lamp is 1.7 Ampere.
Let's assume we don't have a built-in ammeter in the power supply, but we need to know how much current passes through the light bulb. To do this, we put together a simple diagram:
And we measure the voltage drop on the shunt itself. The result was 6.3 millivolts.
Since we know that at 20 Amps the voltage across the shunt will be 75 millivolts, how much current will flow through the shunt if the voltage drop across it is 6.3 millivolts? We remember the mathematics teacher Maryivanna and solve a simple proportion for the 5th grade 
Do we remember what our power supply showed?
Error of 0.02 Ampere! I think this can be attributed to instrument error).
Since radio amateurs mostly use low voltage and current in their electronic gadgets, you can apply this principle to your designs. To do this, it will be enough to take a low-resistance resistor and use it as a current sensor). As they say, “the need for invention is cunning” 
What is a shunt in electronics and a video about it:
When is bypass surgery performed?
Shunting is performed in the following cases:
- it is impossible to install a stent without surgery;
- the affected vessel has a miniature diameter;
- large extent of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels;
- two or more vessels are affected, which is accompanied by multiple blockages of the lumens.
The operation has a number of contraindications. Bypass surgery should not be performed on elderly patients with severe concomitant diseases. Sometimes doctors are forced to urgently perform an operation even if there are contraindications, but then the risk of death increases significantly, of which the patient’s relatives must be notified.
When is stenting performed?
Stenting is done when the lumen of the arteries is narrowed by more than half. This is an effective operation that is performed even in the presence of concomitant chronic diseases and infectious processes in the body. Initially, when deciding on surgical intervention, the question of stenting is almost always raised. If it cannot be done, then bypass surgery is performed.
General recommendations after surgery
Patients after bypass surgery and stenting are advised to have a proper, varied diet. It is necessary to avoid eating fatty, fried and salty foods. Products with high cholesterol content are strictly prohibited. At the request of the patient, you can receive a referral to a nutritionist who will write out the optimal individual diet.
The rehabilitation period after surgery involves taking medications. In addition to the standard set of medications, you must take anticoagulants prescribed by your doctor. Many people refuse them due to the high cost. However, ignoring the cardiologist’s instructions can lead to the formation of a blood clot in the installed stent/replaced area of the vessel.
What is a shunt
In electronics and electrical engineering you can often hear the words “shunt”, “shunting”, “bypass”.
The word “shunt” came to us from the bourgeois language: shunt - literally translated as “branch”, “transfer to a siding”. Therefore, a shunt in electronics is something that “adjacent” to an electrical circuit and “transmits” the electrical current in a different direction. Well, now it’s easier). In essence, a shunt is a simple resistor that has a low resistance, in other words, a low-resistance resistor. And no matter how strange it may sound: a shunt is the simplest current-to-voltage converter. But how is this possible? Yes, it turns out everything is simple!